Fengxiang He
Rationality Measurement and Theory for Reinforcement Learning Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes a suite of rationality measures and associated theory for reinforcement learning agents, a property increasingly critical yet rarely explored. We define an action in deployment to be perfectly rational if it maximises the hidden true value function in the steepest direction. The expected value discrepancy of a policy's actions against their rational counterparts, culminating over the trajectory in deployment, is defined to be expected rational risk; an empirical average version in training is also defined. Their difference, termed as rational risk gap, is decomposed into (1) an extrinsic component caused by environment shifts between training and deployment, and (2) an intrinsic one due to the algorithm's generalisability in a dynamic environment. They are upper bounded by, respectively, (1) the $1$-Wasserstein distance between transition kernels and initial state distributions in training and deployment, and (2) the empirical Rademacher complexity of the value function class. Our theory suggests hypotheses on the benefits from regularisers (including layer normalisation, $\ell_2$ regularisation, and weight normalisation) and domain randomisation, as well as the harm from environment shifts. Experiments are in full agreement with these hypotheses. The code is available at https://github.com/EVIEHub/Rationality.
DeXposure-FM: A Time-series, Graph Foundation Model for Credit Exposures and Stability on Decentralized Financial Networks
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Credit exposure in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is often implicit and token-mediated, creating a dense web of inter-protocol dependencies. Thus, a shock to one token may result in significant and uncontrolled contagion effects. As the DeFi ecosystem becomes increasingly linked with traditional financial infrastructure through instruments, such as stablecoins, the risk posed by this dynamic demands more powerful quantification tools. We introduce DeXposure-FM, the first time-series, graph foundation model for measuring and forecasting inter-protocol credit exposure on DeFi networks, to the best of our knowledge. Employing a graph-tabular encoder, with pre-trained weight initialization, and multiple task-specific heads, DeXposure-FM is trained on the DeXposure dataset that has 43.7 million data entries, across 4,300+ protocols on 602 blockchains, covering 24,300+ unique tokens. The training is operationalized for credit-exposure forecasting, predicting the joint dynamics of (1) protocol-level flows, and (2) the topology and weights of credit-exposure links. The DeXposure-FM is empirically validated on two machine learning benchmarks; it consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches, including a graph foundation model and temporal graph neural networks. DeXposure-FM further produces financial economics tools that support macroprudential monitoring and scenario-based DeFi stress testing, by enabling protocol-level systemic-importance scores, sector-level spillover and concentration measures via a forecast-then-measure pipeline. Empirical verification fully supports our financial economics tools. The model and code have been publicly available. Model: https://huggingface.co/EVIEHub/DeXposure-FM. Code: https://github.com/EVIEHub/DeXposure-FM.
Drawback of Enforcing Equivariance and its Compensation via the Lens of Expressive Power
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Equivariant neural networks encode symmetry as an inductive bias and have achieved strong empirical performance in wide domains. However, their expressive power remains not well understood. Focusing on 2-layer ReLU networks, this paper investigates the impact of equivariance constraints on the expressivity of equivariant and layer-wise equivariant networks. By examining the boundary hyperplanes and the channel vectors of ReLU networks, we construct an example showing that equivariance constraints could strictly limit expressive power. However, we demonstrate that this drawback can be compensated via enlarging the model size. Furthermore, we show that despite a larger model size, the resulting architecture could still correspond to a hypothesis space with lower complexity, implying superior generalizability for equivariant networks.
The Current State of AI Bias Bounties: An Overview of Existing Programmes and Research
Oct 02, 2025

Abstract:Current bias evaluation methods rarely engage with communities impacted by AI systems. Inspired by bug bounties, bias bounties have been proposed as a reward-based method that involves communities in AI bias detection by asking users of AI systems to report biases they encounter when interacting with such systems. In the absence of a state-of-the-art review, this survey aimed to identify and analyse existing AI bias bounty programmes and to present academic literature on bias bounties. Google, Google Scholar, PhilPapers, and IEEE Xplore were searched, and five bias bounty programmes, as well as five research publications, were identified. All bias bounties were organised by U.S.-based organisations as time-limited contests, with public participation in four programmes and prize pools ranging from 7,000 to 24,000 USD. The five research publications included a report on the application of bug bounties to algorithmic harms, an article addressing Twitter's bias bounty, a proposal for bias bounties as an institutional mechanism to increase AI scrutiny, a workshop discussing bias bounties from queer perspectives, and an algorithmic framework for bias bounties. We argue that reducing the technical requirements to enter bounty programmes is important to include those without coding experience. Given the limited adoption of bias bounties, future efforts should explore the transferability of the best practices from bug bounties and examine how such programmes can be designed to be sensitive to underrepresented groups while lowering adoption barriers for organisations.
DICE: Data Influence Cascade in Decentralized Learning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Decentralized learning offers a promising approach to crowdsource data consumptions and computational workloads across geographically distributed compute interconnected through peer-to-peer networks, accommodating the exponentially increasing demands. However, proper incentives are still in absence, considerably discouraging participation. Our vision is that a fair incentive mechanism relies on fair attribution of contributions to participating nodes, which faces non-trivial challenges arising from the localized connections making influence ``cascade'' in a decentralized network. To overcome this, we design the first method to estimate \textbf{D}ata \textbf{I}nfluence \textbf{C}ascad\textbf{E} (DICE) in a decentralized environment. Theoretically, the framework derives tractable approximations of influence cascade over arbitrary neighbor hops, suggesting the influence cascade is determined by an interplay of data, communication topology, and the curvature of loss landscape. DICE also lays the foundations for applications including selecting suitable collaborators and identifying malicious behaviors. Project page is available at https://raiden-zhu.github.io/blog/2025/DICE/.
When a Reinforcement Learning Agent Encounters Unknown Unknowns
May 19, 2025Abstract:An AI agent might surprisingly find she has reached an unknown state which she has never been aware of -- an unknown unknown. We mathematically ground this scenario in reinforcement learning: an agent, after taking an action calculated from value functions $Q$ and $V$ defined on the {\it {aware domain}}, reaches a state out of the domain. To enable the agent to handle this scenario, we propose an {\it episodic Markov decision {process} with growing awareness} (EMDP-GA) model, taking a new {\it noninformative value expansion} (NIVE) approach to expand value functions to newly aware areas: when an agent arrives at an unknown unknown, value functions $Q$ and $V$ whereon are initialised by noninformative beliefs -- the averaged values on the aware domain. This design is out of respect for the complete absence of knowledge in the newly discovered state. The upper confidence bound momentum Q-learning is then adapted to the growing awareness for training the EMDP-GA model. We prove that (1) the regret of our approach is asymptotically consistent with the state of the art (SOTA) without exposure to unknown unknowns in an extremely uncertain environment, and (2) our computational complexity and space complexity are comparable with the SOTA -- these collectively suggest that though an unknown unknown is surprising, it will be asymptotically properly discovered with decent speed and an affordable cost.
Ensuring Safety in an Uncertain Environment: Constrained MDPs via Stochastic Thresholds
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:This paper studies constrained Markov decision processes (CMDPs) with constraints against stochastic thresholds, aiming at safety of reinforcement learning in unknown and uncertain environments. We leverage a Growing-Window estimator sampling from interactions with the uncertain and dynamic environment to estimate the thresholds, based on which we design Stochastic Pessimistic-Optimistic Thresholding (SPOT), a novel model-based primal-dual algorithm for multiple constraints against stochastic thresholds. SPOT enables reinforcement learning under both pessimistic and optimistic threshold settings. We prove that our algorithm achieves sublinear regret and constraint violation; i.e., a reward regret of $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(\sqrt{T})$ while allowing an $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(\sqrt{T})$ constraint violation over $T$ episodes. The theoretical guarantees show that our algorithm achieves performance comparable to that of an approach relying on fixed and clear thresholds. To the best of our knowledge, SPOT is the first reinforcement learning algorithm that realises theoretical guaranteed performance in an uncertain environment where even thresholds are unknown.
XAI for In-hospital Mortality Prediction via Multimodal ICU Data
Dec 29, 2023Abstract:Predicting in-hospital mortality for intensive care unit (ICU) patients is key to final clinical outcomes. AI has shown advantaged accuracy but suffers from the lack of explainability. To address this issue, this paper proposes an eXplainable Multimodal Mortality Predictor (X-MMP) approaching an efficient, explainable AI solution for predicting in-hospital mortality via multimodal ICU data. We employ multimodal learning in our framework, which can receive heterogeneous inputs from clinical data and make decisions. Furthermore, we introduce an explainable method, namely Layer-Wise Propagation to Transformer, as a proper extension of the LRP method to Transformers, producing explanations over multimodal inputs and revealing the salient features attributed to prediction. Moreover, the contribution of each modality to clinical outcomes can be visualized, assisting clinicians in understanding the reasoning behind decision-making. We construct a multimodal dataset based on MIMIC-III and MIMIC-III Waveform Database Matched Subset. Comprehensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed framework can achieve reasonable interpretation with competitive prediction accuracy. In particular, our framework can be easily transferred to other clinical tasks, which facilitates the discovery of crucial factors in healthcare research.
Boosting Fair Classifier Generalization through Adaptive Priority Reweighing
Sep 30, 2023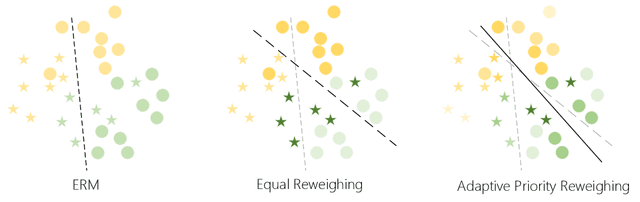
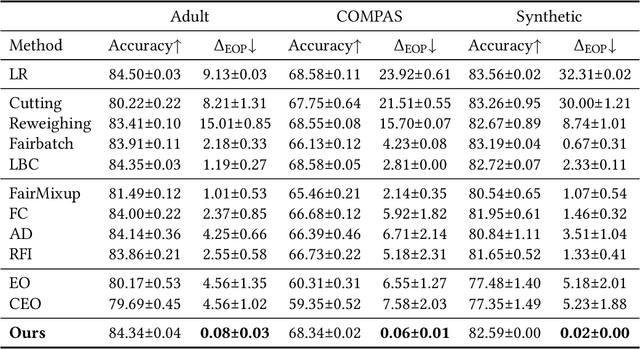
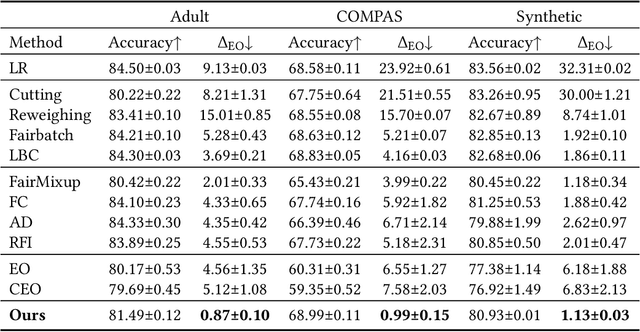
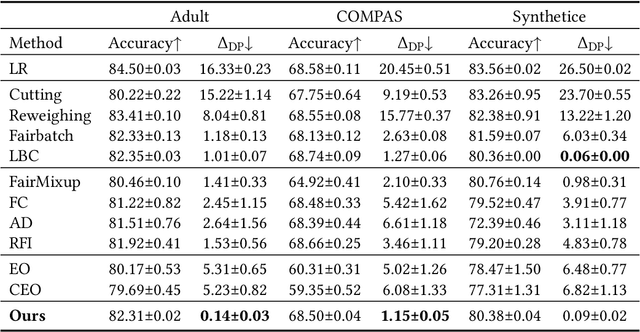
Abstract:With the increasing penetration of machine learning applications in critical decision-making areas, calls for algorithmic fairness are more prominent. Although there have been various modalities to improve algorithmic fairness through learning with fairness constraints, their performance does not generalize well in the test set. A performance-promising fair algorithm with better generalizability is needed. This paper proposes a novel adaptive reweighing method to eliminate the impact of the distribution shifts between training and test data on model generalizability. Most previous reweighing methods propose to assign a unified weight for each (sub)group. Rather, our method granularly models the distance from the sample predictions to the decision boundary. Our adaptive reweighing method prioritizes samples closer to the decision boundary and assigns a higher weight to improve the generalizability of fair classifiers. Extensive experiments are performed to validate the generalizability of our adaptive priority reweighing method for accuracy and fairness measures (i.e., equal opportunity, equalized odds, and demographic parity) in tabular benchmarks. We also highlight the performance of our method in improving the fairness of language and vision models. The code is available at https://github.com/che2198/APW.
Heterogeneous Multi-Task Gaussian Cox Processes
Aug 29, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a novel extension of multi-task Gaussian Cox processes for modeling multiple heterogeneous correlated tasks jointly, e.g., classification and regression, via multi-output Gaussian processes (MOGP). A MOGP prior over the parameters of the dedicated likelihoods for classification, regression and point process tasks can facilitate sharing of information between heterogeneous tasks, while allowing for nonparametric parameter estimation. To circumvent the non-conjugate Bayesian inference in the MOGP modulated heterogeneous multi-task framework, we employ the data augmentation technique and derive a mean-field approximation to realize closed-form iterative updates for estimating model parameters. We demonstrate the performance and inference on both 1D synthetic data as well as 2D urban data of Vancouver.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge