Chul Lee
Test-Time Scaling in Diffusion LLMs via Hidden Semi-Autoregressive Experts
Oct 06, 2025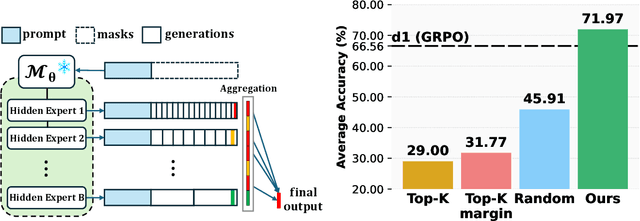
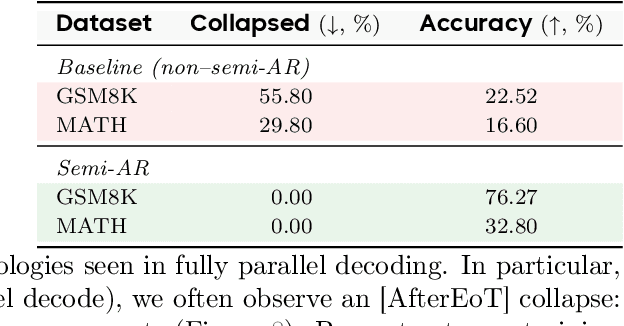
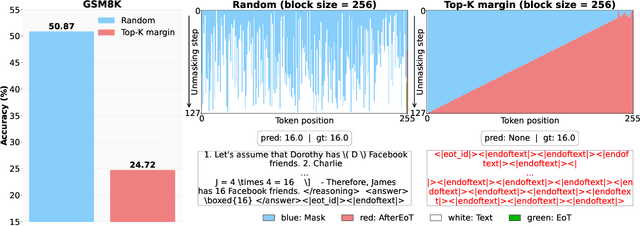
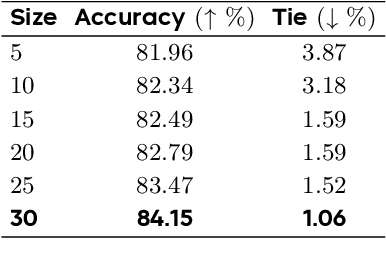
Abstract:Diffusion-based large language models (dLLMs) are trained flexibly to model extreme dependence in the data distribution; however, how to best utilize this information at inference time remains an open problem. In this work, we uncover an interesting property of these models: dLLMs trained on textual data implicitly learn a mixture of semi-autoregressive experts, where different generation orders reveal different specialized behaviors. We show that committing to any single, fixed inference time schedule, a common practice, collapses performance by failing to leverage this latent ensemble. To address this, we introduce HEX (Hidden semiautoregressive EXperts for test-time scaling), a training-free inference method that ensembles across heterogeneous block schedules. By doing a majority vote over diverse block-sized generation paths, HEX robustly avoids failure modes associated with any single fixed schedule. On reasoning benchmarks such as GSM8K, it boosts accuracy by up to 3.56X (from 24.72% to 88.10%), outperforming top-K margin inference and specialized fine-tuned methods like GRPO, without additional training. HEX even yields significant gains on MATH benchmark from 16.40% to 40.00%, scientific reasoning on ARC-C from 54.18% to 87.80%, and TruthfulQA from 28.36% to 57.46%. Our results establish a new paradigm for test-time scaling in diffusion-based LLMs (dLLMs), revealing that the sequence in which masking is performed plays a critical role in determining performance during inference.
Cross-Attention Speculative Decoding
May 30, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding (SD) is a widely adopted approach for accelerating inference in large language models (LLMs), particularly when the draft and target models are well aligned. However, state-of-the-art SD methods typically rely on tightly coupled, self-attention-based Transformer decoders, often augmented with auxiliary pooling or fusion layers. This coupling makes them increasingly complex and harder to generalize across different models. We present Budget EAGLE (Beagle), the first, to our knowledge, cross-attention-based Transformer decoder SD model that achieves performance on par with leading self-attention SD models (EAGLE-v2) while eliminating the need for pooling or auxiliary components, simplifying the architecture, improving training efficiency, and maintaining stable memory usage during training-time simulation. To enable effective training of this novel architecture, we propose Two-Stage Block-Attention Training, a new method that achieves training stability and convergence efficiency in block-level attention scenarios. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and datasets show that Beagle achieves competitive inference speedups and higher training efficiency than EAGLE-v2, offering a strong alternative for architectures in speculative decoding.
3D Face Tracking from 2D Video through Iterative Dense UV to Image Flow
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:When working with 3D facial data, improving fidelity and avoiding the uncanny valley effect is critically dependent on accurate 3D facial performance capture. Because such methods are expensive and due to the widespread availability of 2D videos, recent methods have focused on how to perform monocular 3D face tracking. However, these methods often fall short in capturing precise facial movements due to limitations in their network architecture, training, and evaluation processes. Addressing these challenges, we propose a novel face tracker, FlowFace, that introduces an innovative 2D alignment network for dense per-vertex alignment. Unlike prior work, FlowFace is trained on high-quality 3D scan annotations rather than weak supervision or synthetic data. Our 3D model fitting module jointly fits a 3D face model from one or many observations, integrating existing neutral shape priors for enhanced identity and expression disentanglement and per-vertex deformations for detailed facial feature reconstruction. Additionally, we propose a novel metric and benchmark for assessing tracking accuracy. Our method exhibits superior performance on both custom and publicly available benchmarks. We further validate the effectiveness of our tracker by generating high-quality 3D data from 2D videos, which leads to performance gains on downstream tasks.
H2O-SDF: Two-phase Learning for 3D Indoor Reconstruction using Object Surface Fields
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:Advanced techniques using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), Signed Distance Fields (SDF), and Occupancy Fields have recently emerged as solutions for 3D indoor scene reconstruction. We introduce a novel two-phase learning approach, H2O-SDF, that discriminates between object and non-object regions within indoor environments. This method achieves a nuanced balance, carefully preserving the geometric integrity of room layouts while also capturing intricate surface details of specific objects. A cornerstone of our two-phase learning framework is the introduction of the Object Surface Field (OSF), a novel concept designed to mitigate the persistent vanishing gradient problem that has previously hindered the capture of high-frequency details in other methods. Our proposed approach is validated through several experiments that include ablation studies.
Blending-NeRF: Text-Driven Localized Editing in Neural Radiance Fields
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:Text-driven localized editing of 3D objects is particularly difficult as locally mixing the original 3D object with the intended new object and style effects without distorting the object's form is not a straightforward process. To address this issue, we propose a novel NeRF-based model, Blending-NeRF, which consists of two NeRF networks: pretrained NeRF and editable NeRF. Additionally, we introduce new blending operations that allow Blending-NeRF to properly edit target regions which are localized by text. By using a pretrained vision-language aligned model, CLIP, we guide Blending-NeRF to add new objects with varying colors and densities, modify textures, and remove parts of the original object. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Blending-NeRF produces naturally and locally edited 3D objects from various text prompts. Our project page is available at https://seokhunchoi.github.io/Blending-NeRF/
Harmonic (Quantum) Neural Networks
Dec 14, 2022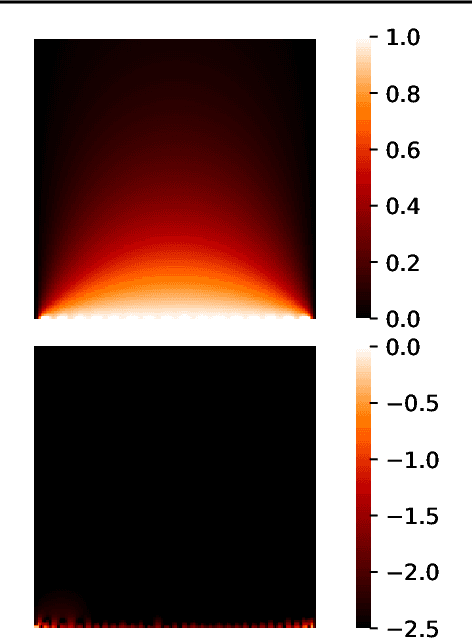
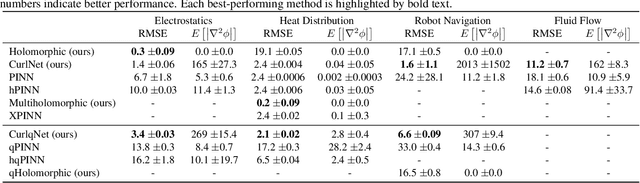
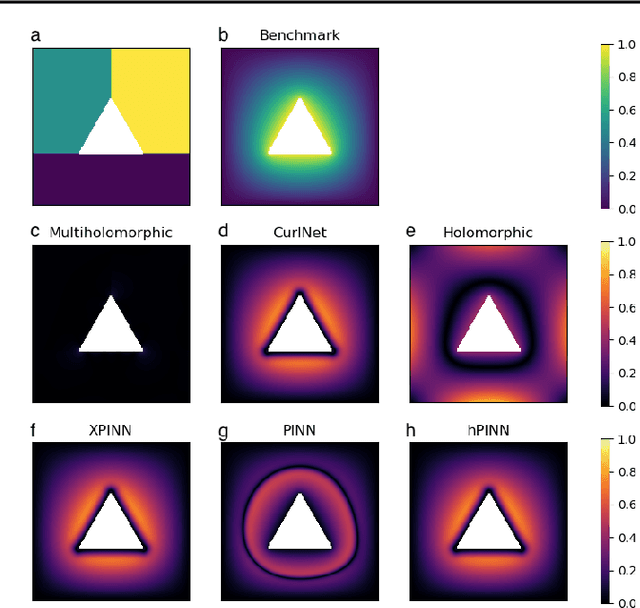
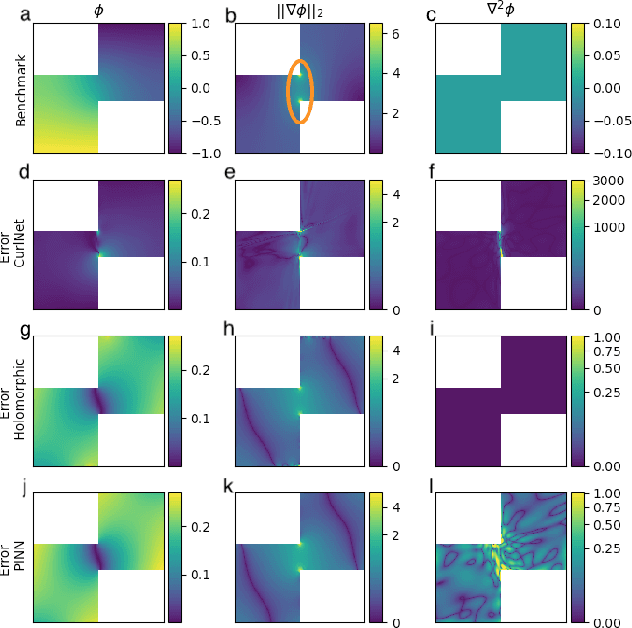
Abstract:Harmonic functions are abundant in nature, appearing in limiting cases of Maxwell's, Navier-Stokes equations, the heat and the wave equation. Consequently, there are many applications of harmonic functions, spanning applications from industrial process optimisation to robotic path planning and the calculation of first exit times of random walks. Despite their ubiquity and relevance, there have been few attempts to develop effective means of representing harmonic functions in the context of machine learning architectures, either in machine learning on classical computers, or in the nascent field of quantum machine learning. Architectures which impose or encourage an inductive bias towards harmonic functions would facilitate data-driven modelling and the solution of inverse problems in a range of applications. For classical neural networks, it has already been established how leveraging inductive biases can in general lead to improved performance of learning algorithms. The introduction of such inductive biases within a quantum machine learning setting is instead still in its nascent stages. In this work, we derive exactly-harmonic (conventional- and quantum-) neural networks in two dimensions for simply-connected domains by leveraging the characteristics of holomorphic complex functions. We then demonstrate how these can be approximately extended to multiply-connected two-dimensional domains using techniques inspired by domain decomposition in physics-informed neural networks. We further provide architectures and training protocols to effectively impose approximately harmonic constraints in three dimensions and higher, and as a corollary we report divergence-free network architectures in arbitrary dimensions. Our approaches are demonstrated with applications to heat transfer, electrostatics and robot navigation, with comparisons to physics-informed neural networks included.
Depth Map Decomposition for Monocular Depth Estimation
Aug 23, 2022
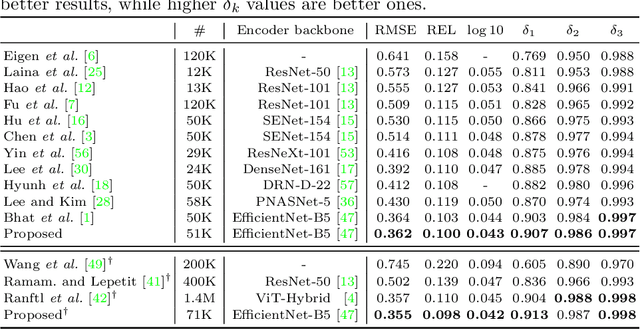
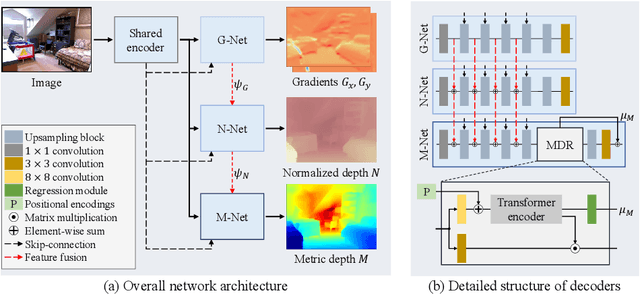
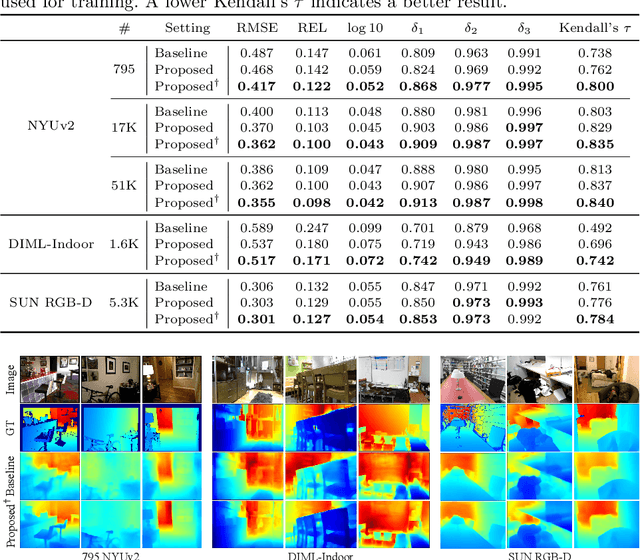
Abstract:We propose a novel algorithm for monocular depth estimation that decomposes a metric depth map into a normalized depth map and scale features. The proposed network is composed of a shared encoder and three decoders, called G-Net, N-Net, and M-Net, which estimate gradient maps, a normalized depth map, and a metric depth map, respectively. M-Net learns to estimate metric depths more accurately using relative depth features extracted by G-Net and N-Net. The proposed algorithm has the advantage that it can use datasets without metric depth labels to improve the performance of metric depth estimation. Experimental results on various datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm not only provides competitive performance to state-of-the-art algorithms but also yields acceptable results even when only a small amount of metric depth data is available for its training.
QbyE-MLPMixer: Query-by-Example Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting using MLPMixer
Jun 23, 2022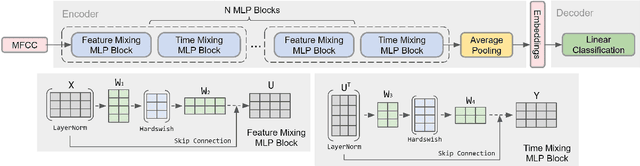
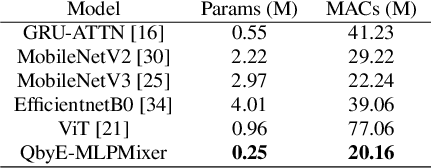
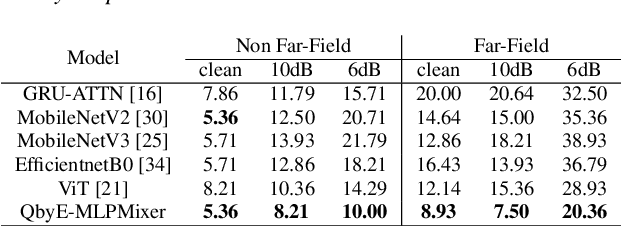
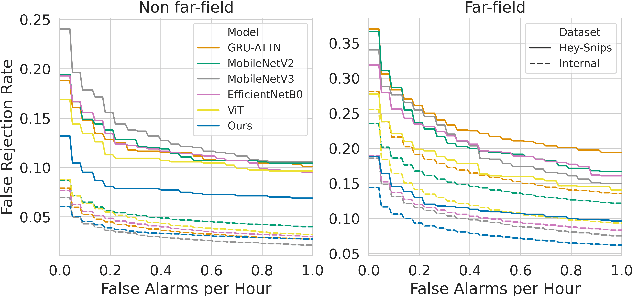
Abstract:Current keyword spotting systems are typically trained with a large amount of pre-defined keywords. Recognizing keywords in an open-vocabulary setting is essential for personalizing smart device interaction. Towards this goal, we propose a pure MLP-based neural network that is based on MLPMixer - an MLP model architecture that effectively replaces the attention mechanism in Vision Transformers. We investigate different ways of adapting the MLPMixer architecture to the QbyE open-vocabulary keyword spotting task. Comparisons with the state-of-the-art RNN and CNN models show that our method achieves better performance in challenging situations (10dB and 6dB environments) on both the publicly available Hey-Snips dataset and a larger scale internal dataset with 400 speakers. Our proposed model also has a smaller number of parameters and MACs compared to the baseline models.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on High Dynamic Range Imaging: Methods and Results
May 25, 2022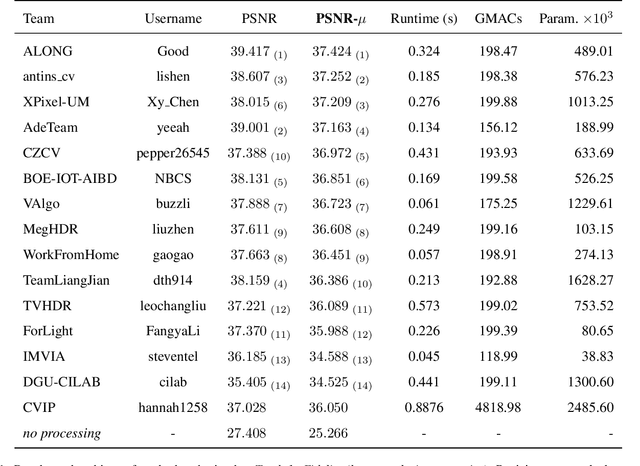
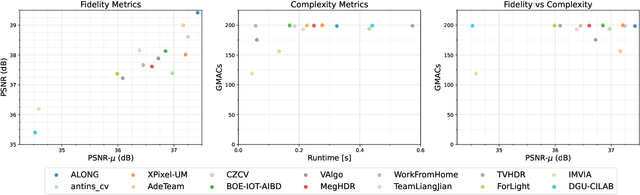
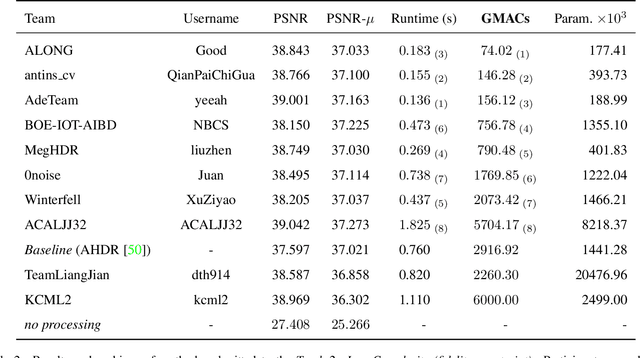
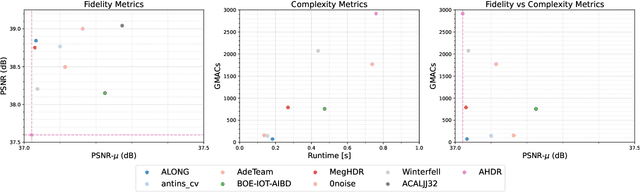
Abstract:This paper reviews the challenge on constrained high dynamic range (HDR) imaging that was part of the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE) workshop, held in conjunction with CVPR 2022. This manuscript focuses on the competition set-up, datasets, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge aims at estimating an HDR image from multiple respective low dynamic range (LDR) observations, which might suffer from under- or over-exposed regions and different sources of noise. The challenge is composed of two tracks with an emphasis on fidelity and complexity constraints: In Track 1, participants are asked to optimize objective fidelity scores while imposing a low-complexity constraint (i.e. solutions can not exceed a given number of operations). In Track 2, participants are asked to minimize the complexity of their solutions while imposing a constraint on fidelity scores (i.e. solutions are required to obtain a higher fidelity score than the prescribed baseline). Both tracks use the same data and metrics: Fidelity is measured by means of PSNR with respect to a ground-truth HDR image (computed both directly and with a canonical tonemapping operation), while complexity metrics include the number of Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations and runtime (in seconds).
* CVPR Workshops 2022. 15 pages, 21 figures, 2 tables
openFEAT: Improving Speaker Identification by Open-set Few-shot Embedding Adaptation with Transformer
Feb 24, 2022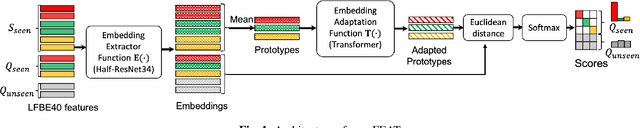
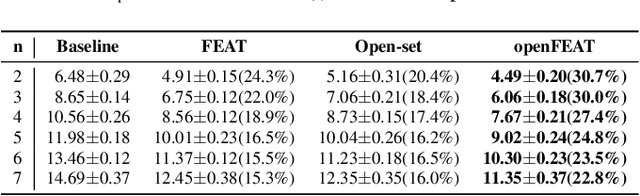
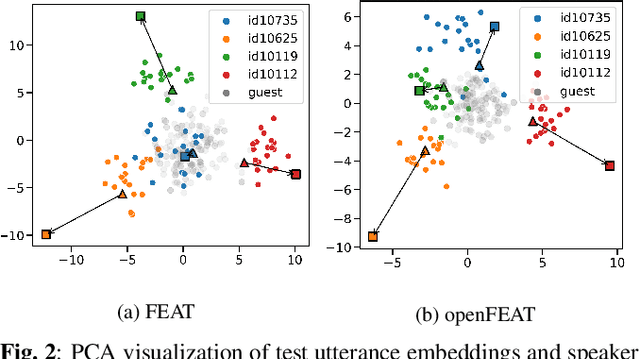
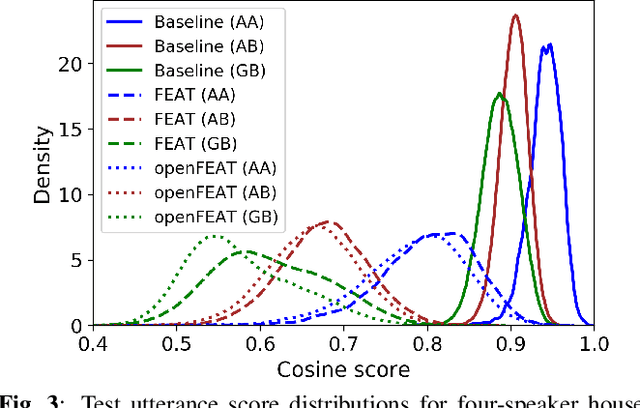
Abstract:Household speaker identification with few enrollment utterances is an important yet challenging problem, especially when household members share similar voice characteristics and room acoustics. A common embedding space learned from a large number of speakers is not universally applicable for the optimal identification of every speaker in a household. In this work, we first formulate household speaker identification as a few-shot open-set recognition task and then propose a novel embedding adaptation framework to adapt speaker representations from the given universal embedding space to a household-specific embedding space using a set-to-set function, yielding better household speaker identification performance. With our algorithm, Open-set Few-shot Embedding Adaptation with Transformer (openFEAT), we observe that the speaker identification equal error rate (IEER) on simulated households with 2 to 7 hard-to-discriminate speakers is reduced by 23% to 31% relative.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge