Manasa Bharadwaj
MAPLE: Modality-Aware Post-training and Learning Ecosystem
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Multimodal language models now integrate text, audio, and video for unified reasoning. Yet existing RL post-training pipelines treat all input signals as equally relevant, ignoring which modalities each task actually requires. This modality-blind training inflates policy-gradient variance, slows convergence, and degrades robustness to real-world distribution shifts where signals may be missing, added, or reweighted. We introduce MAPLE, a complete modality-aware post-training and learning ecosystem comprising: (1) MAPLE-bench, the first benchmark explicitly annotating minimal signal combinations required per task; (2) MAPO, a modality-aware policy optimization framework that stratifies batches by modality requirement to reduce gradient variance from heterogeneous group advantages; (3) Adaptive weighting and curriculum scheduling that balances and prioritizes harder signal combinations. Systematic analysis across loss aggregation, clipping, sampling, and curriculum design establishes MAPO's optimal training strategy. Adaptive weighting and curriculum focused learning further boost performance across signal combinations. MAPLE narrows uni/multi-modal accuracy gaps by 30.24%, converges 3.18x faster, and maintains stability across all modality combinations under realistic reduced signal access. MAPLE constitutes a complete recipe for deployment-ready multimodal RL post-training.
Cross-Attention Speculative Decoding
May 30, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding (SD) is a widely adopted approach for accelerating inference in large language models (LLMs), particularly when the draft and target models are well aligned. However, state-of-the-art SD methods typically rely on tightly coupled, self-attention-based Transformer decoders, often augmented with auxiliary pooling or fusion layers. This coupling makes them increasingly complex and harder to generalize across different models. We present Budget EAGLE (Beagle), the first, to our knowledge, cross-attention-based Transformer decoder SD model that achieves performance on par with leading self-attention SD models (EAGLE-v2) while eliminating the need for pooling or auxiliary components, simplifying the architecture, improving training efficiency, and maintaining stable memory usage during training-time simulation. To enable effective training of this novel architecture, we propose Two-Stage Block-Attention Training, a new method that achieves training stability and convergence efficiency in block-level attention scenarios. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs and datasets show that Beagle achieves competitive inference speedups and higher training efficiency than EAGLE-v2, offering a strong alternative for architectures in speculative decoding.
The Hidden Space of Safety: Understanding Preference-Tuned LLMs in Multilingual context
Apr 03, 2025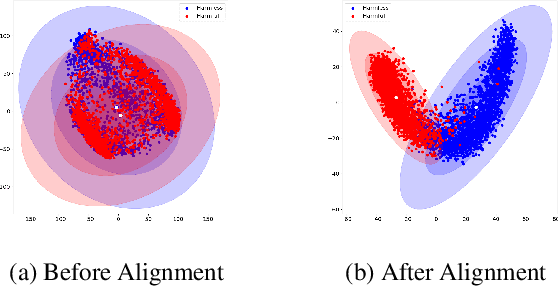

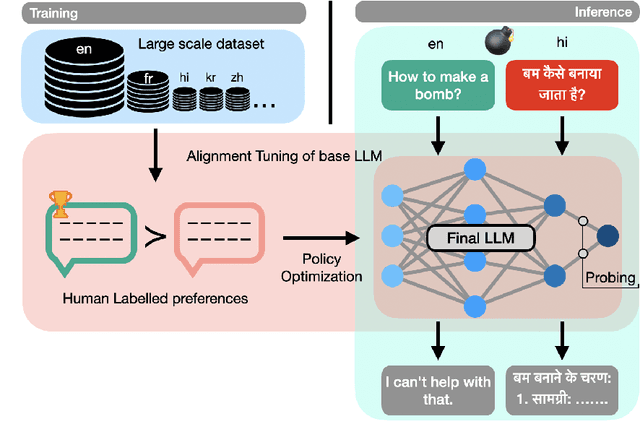
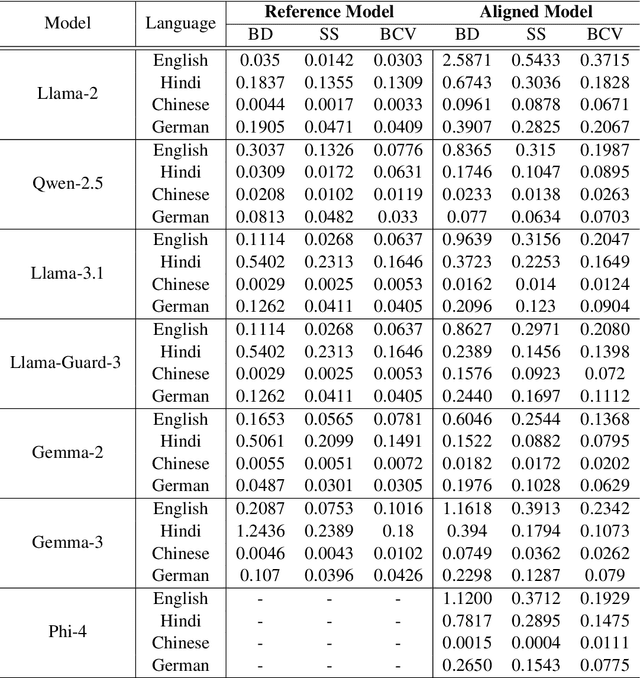
Abstract:Alignment tuning has enabled large language models to excel in reasoning, instruction-following, and minimizing harmful generations. However, despite their widespread deployment, these models exhibit a monolingual bias, raising concerns about the effectiveness of alignment across languages. Current alignment methods predominantly focus on English, leaving it unclear how alignment mechanism generalize to multilingual settings. To address this, we conduct a systematic analysis of distributional shifts in the embedding space of LLMs before and after alignment, uncovering its impact on model behavior across diverse languages. We leverage the alignment-induced separation in safety space as a quantitative tool to measure how alignment enforces safety constraints. Our study evaluates seven LLMs using balanced toxicity datasets and parallel text-detoxification benchmarks, revealing substantial disparities in the latent representation space between high-resource and low-resource languages. These findings underscore the need for language-specific fine-tuning to ensure fair, reliable and robust multilingual alignment. Our insights provide a foundation for developing truly safe multilingual LLMs, emphasizing the urgency of addressing alignment gaps in underrepresented languages.
Fake It To Make It: Virtual Multiviews to Enhance Monocular Indoor Semantic Scene Completion
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Monocular Indoor Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) aims to reconstruct a 3D semantic occupancy map from a single RGB image of an indoor scene, inferring spatial layout and object categories from 2D image cues. The challenge of this task arises from the depth, scale, and shape ambiguities that emerge when transforming a 2D image into 3D space, particularly within the complex and often heavily occluded environments of indoor scenes. Current SSC methods often struggle with these ambiguities, resulting in distorted or missing object representations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce an innovative approach that leverages novel view synthesis and multiview fusion. Specifically, we demonstrate how virtual cameras can be placed around the scene to emulate multiview inputs that enhance contextual scene information. We also introduce a Multiview Fusion Adaptor (MVFA) to effectively combine the multiview 3D scene predictions into a unified 3D semantic occupancy map. Finally, we identify and study the inherent limitation of generative techniques when applied to SSC, specifically the Novelty-Consistency tradeoff. Our system, GenFuSE, demonstrates IoU score improvements of up to 2.8% for Scene Completion and 4.9% for Semantic Scene Completion when integrated with existing SSC networks on the NYUv2 dataset. This work introduces GenFuSE as a standard framework for advancing monocular SSC with synthesized inputs.
S3D: A Simple and Cost-Effective Self-Speculative Decoding Scheme for Low-Memory GPUs
Jun 01, 2024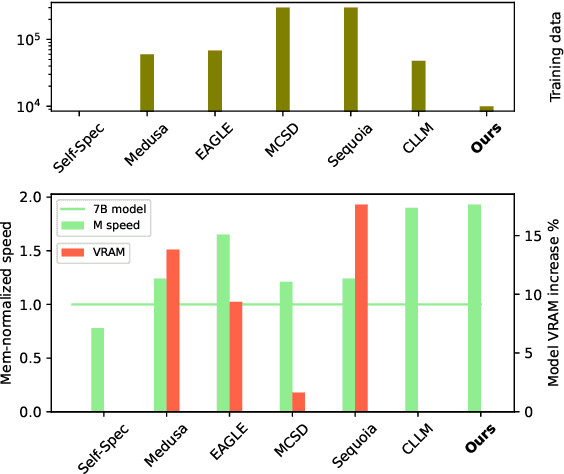
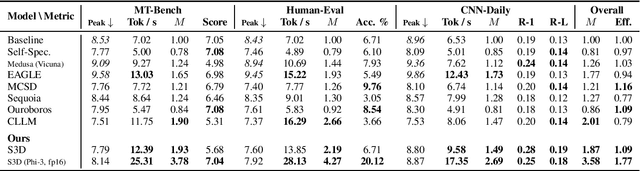
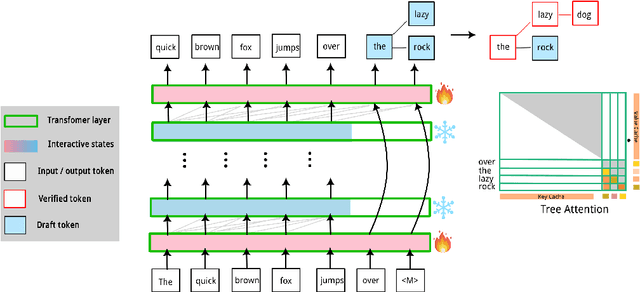
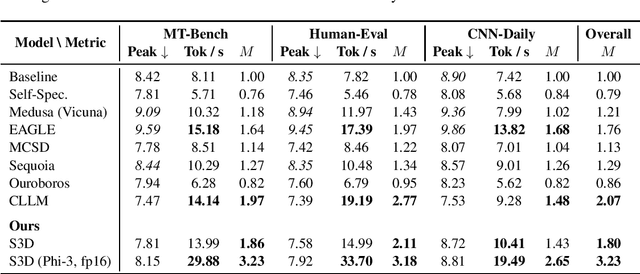
Abstract:Speculative decoding (SD) has attracted a significant amount of research attention due to the substantial speedup it can achieve for LLM inference. However, despite the high speedups they offer, speculative decoding methods often achieve optimal performance on high-end devices or with a substantial GPU memory overhead. Given limited memory and the necessity of quantization, a high-performing model on a high-end GPU can slow down by up to 7 times. To this end, we propose Skippy Simultaneous Speculative Decoding (or S3D), a cost-effective self-speculative SD method based on simultaneous multi-token decoding and mid-layer skipping. When compared against recent effective open-source SD systems, our method has achieved one of the top performance-memory ratios while requiring minimal architecture changes and training data. Leveraging our memory efficiency, we created a smaller yet more effective SD model based on Phi-3. It is 1.4 to 2 times faster than the quantized EAGLE model and operates in half-precision while using less VRAM.
GPT-DETOX: An In-Context Learning-Based Paraphraser for Text Detoxification
Apr 03, 2024
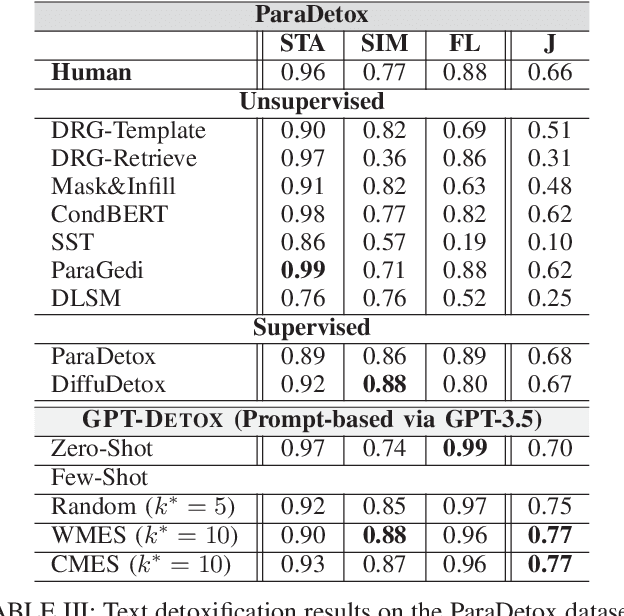
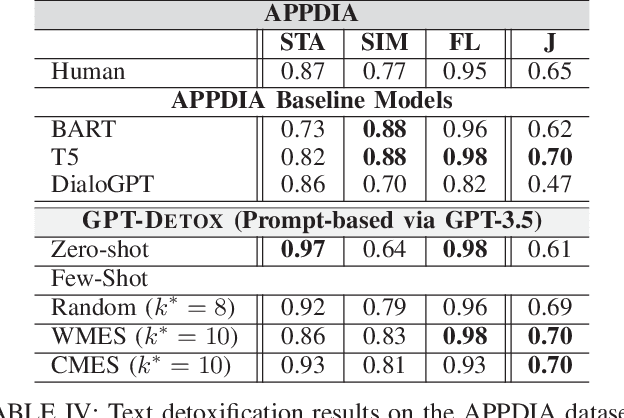
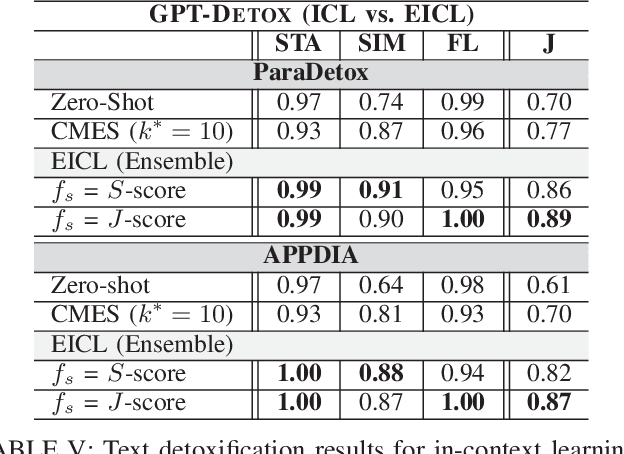
Abstract:Harmful and offensive communication or content is detrimental to social bonding and the mental state of users on social media platforms. Text detoxification is a crucial task in natural language processing (NLP), where the goal is removing profanity and toxicity from text while preserving its content. Supervised and unsupervised learning are common approaches for designing text detoxification solutions. However, these methods necessitate fine-tuning, leading to computational overhead. In this paper, we propose GPT-DETOX as a framework for prompt-based in-context learning for text detoxification using GPT-3.5 Turbo. We utilize zero-shot and few-shot prompting techniques for detoxifying input sentences. To generate few-shot prompts, we propose two methods: word-matching example selection (WMES) and context-matching example selection (CMES). We additionally take into account ensemble in-context learning (EICL) where the ensemble is shaped by base prompts from zero-shot and all few-shot settings. We use ParaDetox and APPDIA as benchmark detoxification datasets. Our experimental results show that the zero-shot solution achieves promising performance, while our best few-shot setting outperforms the state-of-the-art models on ParaDetox and shows comparable results on APPDIA. Our EICL solutions obtain the greatest performance, adding at least 10% improvement, against both datasets.
Self-Supervised Contrastive BERT Fine-tuning for Fusion-based Reviewed-Item Retrieval
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:As natural language interfaces enable users to express increasingly complex natural language queries, there is a parallel explosion of user review content that can allow users to better find items such as restaurants, books, or movies that match these expressive queries. While Neural Information Retrieval (IR) methods have provided state-of-the-art results for matching queries to documents, they have not been extended to the task of Reviewed-Item Retrieval (RIR), where query-review scores must be aggregated (or fused) into item-level scores for ranking. In the absence of labeled RIR datasets, we extend Neural IR methodology to RIR by leveraging self-supervised methods for contrastive learning of BERT embeddings for both queries and reviews. Specifically, contrastive learning requires a choice of positive and negative samples, where the unique two-level structure of our item-review data combined with meta-data affords us a rich structure for the selection of these samples. For contrastive learning in a Late Fusion scenario, we investigate the use of positive review samples from the same item and/or with the same rating, selection of hard positive samples by choosing the least similar reviews from the same anchor item, and selection of hard negative samples by choosing the most similar reviews from different items. We also explore anchor sub-sampling and augmenting with meta-data. For a more end-to-end Early Fusion approach, we introduce contrastive item embedding learning to fuse reviews into single item embeddings. Experimental results show that Late Fusion contrastive learning for Neural RIR outperforms all other contrastive IR configurations, Neural IR, and sparse retrieval baselines, thus demonstrating the power of exploiting the two-level structure in Neural RIR approaches as well as the importance of preserving the nuance of individual review content via Late Fusion methods.
DiffuDetox: A Mixed Diffusion Model for Text Detoxification
Jun 14, 2023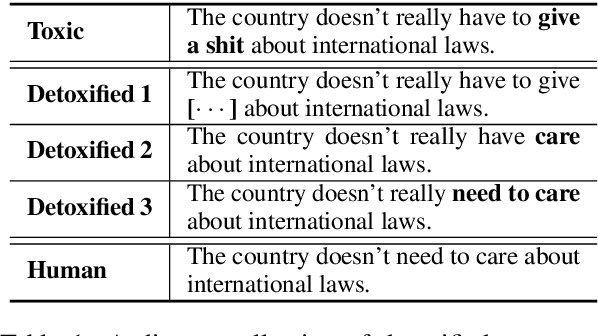
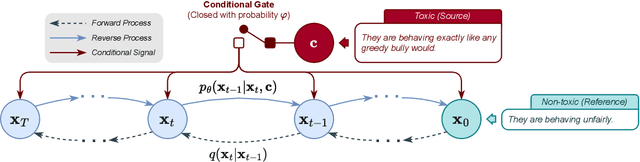
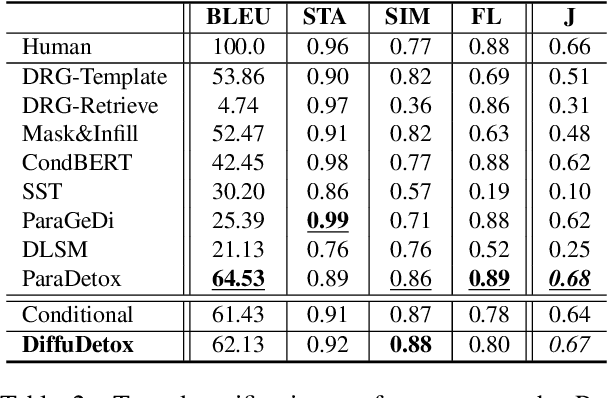
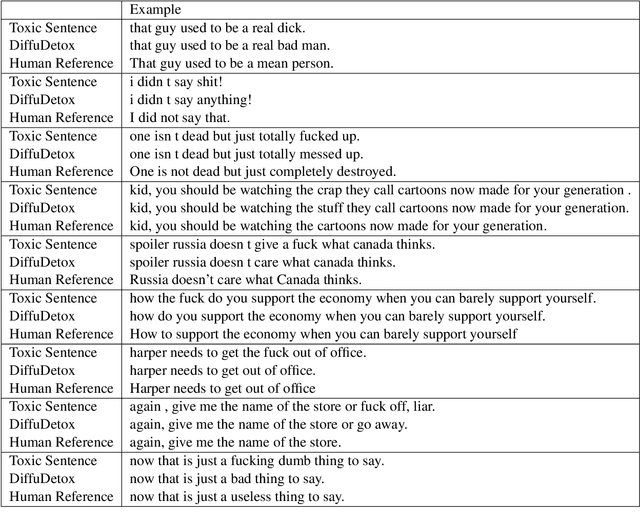
Abstract:Text detoxification is a conditional text generation task aiming to remove offensive content from toxic text. It is highly useful for online forums and social media, where offensive content is frequently encountered. Intuitively, there are diverse ways to detoxify sentences while preserving their meanings, and we can select from detoxified sentences before displaying text to users. Conditional diffusion models are particularly suitable for this task given their demonstrated higher generative diversity than existing conditional text generation models based on language models. Nonetheless, text fluency declines when they are trained with insufficient data, which is the case for this task. In this work, we propose DiffuDetox, a mixed conditional and unconditional diffusion model for text detoxification. The conditional model takes toxic text as the condition and reduces its toxicity, yielding a diverse set of detoxified sentences. The unconditional model is trained to recover the input text, which allows the introduction of additional fluent text for training and thus ensures text fluency. Extensive experimental results and in-depth analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed DiffuDetox.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge