Ceyao Zhang
Enhancing Zero-Shot Time Series Forecasting in Off-the-Shelf LLMs via Noise Injection
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated effectiveness as zero-shot time series (TS) forecasters. The key challenge lies in tokenizing TS data into textual representations that align with LLMs' pre-trained knowledge. While existing work often relies on fine-tuning specialized modules to bridge this gap, a distinct, yet challenging, paradigm aims to leverage truly off-the-shelf LLMs without any fine-tuning whatsoever, relying solely on strategic tokenization of numerical sequences. The performance of these fully frozen models is acutely sensitive to the textual representation of the input data, as their parameters cannot adapt to distribution shifts. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet highly effective strategy to overcome this brittleness: injecting noise into the raw time series before tokenization. This non-invasive intervention acts as a form of inference-time augmentation, compelling the frozen LLM to extrapolate based on robust underlying temporal patterns rather than superficial numerical artifacts. We theoretically analyze this phenomenon and empirically validate its effectiveness across diverse benchmarks. Notably, to fully eliminate potential biases from data contamination during LLM pre-training, we introduce two novel TS datasets that fall outside all utilized LLMs' pre-training scopes, and consistently observe improved performance. This study provides a further step in directly leveraging off-the-shelf LLMs for time series forecasting.
DexGraspVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Framework Towards General Dexterous Grasping
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Dexterous grasping remains a fundamental yet challenging problem in robotics. A general-purpose robot must be capable of grasping diverse objects in arbitrary scenarios. However, existing research typically relies on specific assumptions, such as single-object settings or limited environments, leading to constrained generalization. Our solution is DexGraspVLA, a hierarchical framework that utilizes a pre-trained Vision-Language model as the high-level task planner and learns a diffusion-based policy as the low-level Action controller. The key insight lies in iteratively transforming diverse language and visual inputs into domain-invariant representations, where imitation learning can be effectively applied due to the alleviation of domain shift. Thus, it enables robust generalization across a wide range of real-world scenarios. Notably, our method achieves a 90+% success rate under thousands of unseen object, lighting, and background combinations in a ``zero-shot'' environment. Empirical analysis further confirms the consistency of internal model behavior across environmental variations, thereby validating our design and explaining its generalization performance. We hope our work can be a step forward in achieving general dexterous grasping. Our demo and code can be found at https://dexgraspvla.github.io/.
SELA: Tree-Search Enhanced LLM Agents for Automated Machine Learning
Oct 22, 2024


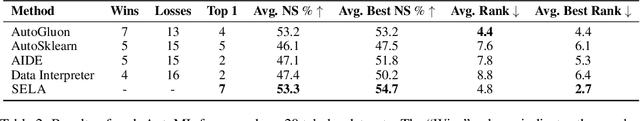
Abstract:Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) approaches encompass traditional methods that optimize fixed pipelines for model selection and ensembling, as well as newer LLM-based frameworks that autonomously build pipelines. While LLM-based agents have shown promise in automating machine learning tasks, they often generate low-diversity and suboptimal code, even after multiple iterations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Tree-Search Enhanced LLM Agents (SELA), an innovative agent-based system that leverages Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to optimize the AutoML process. By representing pipeline configurations as trees, our framework enables agents to conduct experiments intelligently and iteratively refine their strategies, facilitating a more effective exploration of the machine learning solution space. This novel approach allows SELA to discover optimal pathways based on experimental feedback, improving the overall quality of the solutions. In an extensive evaluation across 20 machine learning datasets, we compare the performance of traditional and agent-based AutoML methods, demonstrating that SELA achieves a win rate of 65% to 80% against each baseline across all datasets. These results underscore the significant potential of agent-based strategies in AutoML, offering a fresh perspective on tackling complex machine learning challenges.
OmniJARVIS: Unified Vision-Language-Action Tokenization Enables Open-World Instruction Following Agents
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:We present OmniJARVIS, a novel Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model for open-world instruction-following agents in open-world Minecraft. Compared to prior works that either emit textual goals to separate controllers or produce the control command directly, OmniJARVIS seeks a different path to ensure both strong reasoning and efficient decision-making capabilities via unified tokenization of multimodal interaction data. First, we introduce a self-supervised approach to learn a behavior encoder that produces discretized tokens for behavior trajectories $\tau$ = {$o_0$, $a_0$, $\dots$} and an imitation learning (IL) policy decoder conditioned on these tokens. These additional behavior tokens will be augmented to the vocabulary of pretrained Multimodal Language Models (MLMs). With this encoder, we then pack long-term multimodal interactions involving task instructions, memories, thoughts, observations, textual responses, behavior trajectories, etc. into unified token sequences and model them with autoregressive transformers. Thanks to the semantically meaningful behavior tokens, the resulting VLA model, OmniJARVIS, can reason (by producing chain-of-thoughts), plan, answer questions, and act (by producing behavior tokens for the IL policy decoder). OmniJARVIS demonstrates excellent performances on a comprehensive collection of atomic, programmatic, and open-ended tasks in open-world Minecraft. Our analysis further unveils the crucial design principles in interaction data formation, unified tokenization, and its scaling potentials.
Inverse Design of Photonic Crystal Surface Emitting Lasers is a Sequence Modeling Problem
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:Photonic Crystal Surface Emitting Lasers (PCSEL)'s inverse design demands expert knowledge in physics, materials science, and quantum mechanics which is prohibitively labor-intensive. Advanced AI technologies, especially reinforcement learning (RL), have emerged as a powerful tool to augment and accelerate this inverse design process. By modeling the inverse design of PCSEL as a sequential decision-making problem, RL approaches can construct a satisfactory PCSEL structure from scratch. However, the data inefficiency resulting from online interactions with precise and expensive simulation environments impedes the broader applicability of RL approaches. Recently, sequential models, especially the Transformer architecture, have exhibited compelling performance in sequential decision-making problems due to their simplicity and scalability to large language models. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework named PCSEL Inverse Design Transformer (PiT) that abstracts the inverse design of PCSEL as a sequence modeling problem. The central part of our PiT is a Transformer-based structure that leverages the past trajectories and current states to predict the current actions. Compared with the traditional RL approaches, PiT can output the optimal actions and achieve target PCSEL designs by leveraging offline data and conditioning on the desired return. Results demonstrate that PiT achieves superior performance and data efficiency compared to baselines.
Exploring Large Language Model based Intelligent Agents: Definitions, Methods, and Prospects
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:Intelligent agents stand out as a potential path toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). Thus, researchers have dedicated significant effort to diverse implementations for them. Benefiting from recent progress in large language models (LLMs), LLM-based agents that use universal natural language as an interface exhibit robust generalization capabilities across various applications -- from serving as autonomous general-purpose task assistants to applications in coding, social, and economic domains, LLM-based agents offer extensive exploration opportunities. This paper surveys current research to provide an in-depth overview of LLM-based intelligent agents within single-agent and multi-agent systems. It covers their definitions, research frameworks, and foundational components such as their composition, cognitive and planning methods, tool utilization, and responses to environmental feedback. We also delve into the mechanisms of deploying LLM-based agents in multi-agent systems, including multi-role collaboration, message passing, and strategies to alleviate communication issues between agents. The discussions also shed light on popular datasets and application scenarios. We conclude by envisioning prospects for LLM-based agents, considering the evolving landscape of AI and natural language processing.
ProAgent: Building Proactive Cooperative AI with Large Language Models
Aug 28, 2023


Abstract:Building AIs with adaptive behaviors in human-AI cooperation stands as a pivotal focus in AGI research. Current methods for developing cooperative agents predominantly rely on learning-based methods, where policy generalization heavily hinges on past interactions with specific teammates. These approaches constrain the agent's capacity to recalibrate its strategy when confronted with novel teammates. We propose \textbf{ProAgent}, a novel framework that harnesses large language models (LLMs) to fashion a \textit{pro}active \textit{agent} empowered with the ability to anticipate teammates' forthcoming decisions and formulate enhanced plans for itself. ProAgent excels at cooperative reasoning with the capacity to dynamically adapt its behavior to enhance collaborative efforts with teammates. Moreover, the ProAgent framework exhibits a high degree of modularity and interpretability, facilitating seamless integration to address a wide array of coordination scenarios. Experimental evaluations conducted within the framework of \textit{Overcook-AI} unveil the remarkable performance superiority of ProAgent, outperforming five methods based on self-play and population-based training in cooperation with AI agents. Further, when cooperating with human proxy models, its performance exhibits an average improvement exceeding 10\% compared to the current state-of-the-art, COLE. The advancement was consistently observed across diverse scenarios involving interactions with both AI agents of varying characteristics and human counterparts. These findings inspire future research for human-robot collaborations. For a hands-on demonstration, please visit \url{https://pku-proagent.github.io}.
MetaGPT: Meta Programming for Multi-Agent Collaborative Framework
Aug 17, 2023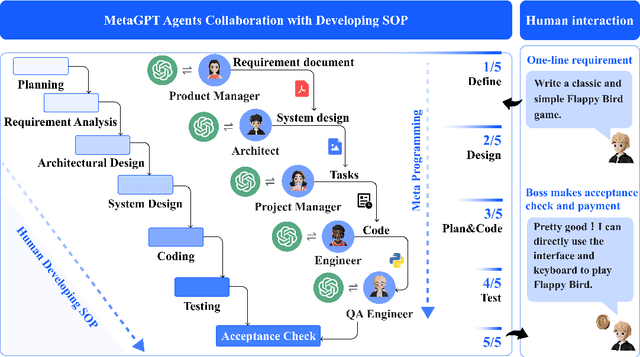
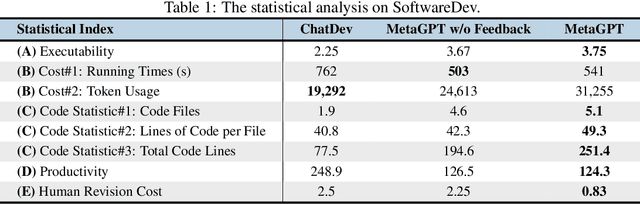
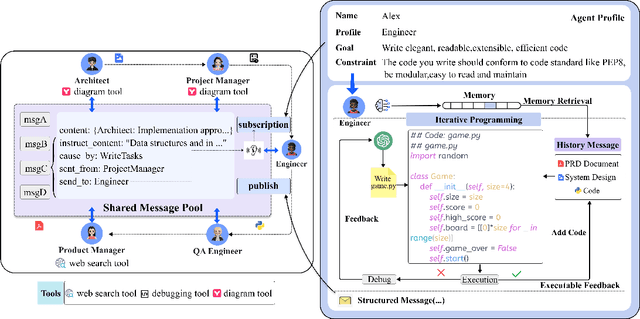
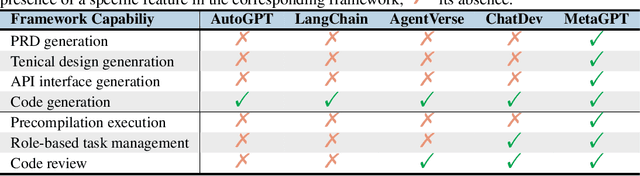
Abstract:Recently, remarkable progress has been made in automated task-solving through the use of multi-agent driven by large language models (LLMs). However, existing LLM-based multi-agent works primarily focus on solving simple dialogue tasks, and complex tasks are rarely studied, mainly due to the LLM hallucination problem. This type of hallucination becomes cascading when naively chaining multiple intelligent agents, resulting in a failure to effectively address complex problems. Therefore, we introduce MetaGPT, an innovative framework that incorporates efficient human workflows as a meta programming approach into LLM-based multi-agent collaboration. Specifically, MetaGPT encodes Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs) into prompts to enhance structured coordination. Subsequently, it mandates modular outputs, empowering agents with domain expertise comparable to human professionals, to validate outputs and minimize compounded errors. In this way, MetaGPT leverages the assembly line paradigm to assign diverse roles to various agents, thereby establishing a framework that can effectively and cohesively deconstruct complex multi-agent collaborative problems. Our experiments on collaborative software engineering benchmarks demonstrate that MetaGPT generates more coherent and correct solutions compared to existing chat-based multi-agent systems. This highlights the potential of integrating human domain knowledge into multi-agent systems, thereby creating new opportunities to tackle complex real-world challenges. The GitHub repository of this project is publicly available on:https://github.com/geekan/MetaGPT.
Heterogeneous Value Evaluation for Large Language Models
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:The emergent capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have made it crucial to align their values with those of humans. Current methodologies typically attempt alignment with a homogeneous human value and requires human verification, yet lack consensus on the desired aspect and depth of alignment and resulting human biases. In this paper, we propose A2EHV, an Automated Alignment Evaluation with a Heterogeneous Value system that (1) is automated to minimize individual human biases, and (2) allows assessments against various target values to foster heterogeneous agents. Our approach pivots on the concept of value rationality, which represents the ability for agents to execute behaviors that satisfy a target value the most. The quantification of value rationality is facilitated by the Social Value Orientation framework from social psychology, which partitions the value space into four categories to assess social preferences from agents' behaviors. We evaluate the value rationality of eight mainstream LLMs and observe that large models are more inclined to align neutral values compared to those with strong personal values. By examining the behavior of these LLMs, we contribute to a deeper understanding of value alignment within a heterogeneous value system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge