Aparna Garimella
TabReX : Tabular Referenceless eXplainable Evaluation
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Evaluating the quality of tables generated by large language models (LLMs) remains an open challenge: existing metrics either flatten tables into text, ignoring structure, or rely on fixed references that limit generalization. We present TabReX, a reference-less, property-driven framework for evaluating tabular generation via graph-based reasoning. TabReX converts both source text and generated tables into canonical knowledge graphs, aligns them through an LLM-guided matching process, and computes interpretable, rubric-aware scores that quantify structural and factual fidelity. The resulting metric provides controllable trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity, yielding human-aligned judgments and cell-level error traces. To systematically asses metric robustness, we introduce TabReX-Bench, a large-scale benchmark spanning six domains and twelve planner-driven perturbation types across three difficulty tiers. Empirical results show that TabReX achieves the highest correlation with expert rankings, remains stable under harder perturbations, and enables fine-grained model-vs-prompt analysis establishing a new paradigm for trustworthy, explainable evaluation of structured generation systems.
RADAR: A Reasoning-Guided Attribution Framework for Explainable Visual Data Analysis
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Data visualizations like charts are fundamental tools for quantitative analysis and decision-making across fields, requiring accurate interpretation and mathematical reasoning. The emergence of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offers promising capabilities for automated visual data analysis, such as processing charts, answering questions, and generating summaries. However, they provide no visibility into which parts of the visual data informed their conclusions; this black-box nature poses significant challenges to real-world trust and adoption. In this paper, we take the first major step towards evaluating and enhancing the capabilities of MLLMs to attribute their reasoning process by highlighting the specific regions in charts and graphs that justify model answers. To this end, we contribute RADAR, a semi-automatic approach to obtain a benchmark dataset comprising 17,819 diverse samples with charts, questions, reasoning steps, and attribution annotations. We also introduce a method that provides attribution for chart-based mathematical reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that our reasoning-guided approach improves attribution accuracy by 15% compared to baseline methods, and enhanced attribution capabilities translate to stronger answer generation, achieving an average BERTScore of $\sim$ 0.90, indicating high alignment with ground truth responses. This advancement represents a significant step toward more interpretable and trustworthy chart analysis systems, enabling users to verify and understand model decisions through reasoning and attribution.
Infogen: Generating Complex Statistical Infographics from Documents
Jul 26, 2025Abstract:Statistical infographics are powerful tools that simplify complex data into visually engaging and easy-to-understand formats. Despite advancements in AI, particularly with LLMs, existing efforts have been limited to generating simple charts, with no prior work addressing the creation of complex infographics from text-heavy documents that demand a deep understanding of the content. We address this gap by introducing the task of generating statistical infographics composed of multiple sub-charts (e.g., line, bar, pie) that are contextually accurate, insightful, and visually aligned. To achieve this, we define infographic metadata that includes its title and textual insights, along with sub-chart-specific details such as their corresponding data and alignment. We also present Infodat, the first benchmark dataset for text-to-infographic metadata generation, where each sample links a document to its metadata. We propose Infogen, a two-stage framework where fine-tuned LLMs first generate metadata, which is then converted into infographic code. Extensive evaluations on Infodat demonstrate that Infogen achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming both closed and open-source LLMs in text-to-statistical infographic generation.
LegalCore: A Dataset for Legal Documents Event Coreference Resolution
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recognizing events and their coreferential mentions in a document is essential for understanding semantic meanings of text. The existing research on event coreference resolution is mostly limited to news articles. In this paper, we present the first dataset for the legal domain, LegalCore, which has been annotated with comprehensive event and event coreference information. The legal contract documents we annotated in this dataset are several times longer than news articles, with an average length of around 25k tokens per document. The annotations show that legal documents have dense event mentions and feature both short-distance and super long-distance coreference links between event mentions. We further benchmark mainstream Large Language Models (LLMs) on this dataset for both event detection and event coreference resolution tasks, and find that this dataset poses significant challenges for state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary LLMs, which perform significantly worse than a supervised baseline. We will publish the dataset as well as the code.
SciDoc2Diagrammer-MAF: Towards Generation of Scientific Diagrams from Documents guided by Multi-Aspect Feedback Refinement
Sep 28, 2024Abstract:Automating the creation of scientific diagrams from academic papers can significantly streamline the development of tutorials, presentations, and posters, thereby saving time and accelerating the process. Current text-to-image models struggle with generating accurate and visually appealing diagrams from long-context inputs. We propose SciDoc2Diagram, a task that extracts relevant information from scientific papers and generates diagrams, along with a benchmarking dataset, SciDoc2DiagramBench. We develop a multi-step pipeline SciDoc2Diagrammer that generates diagrams based on user intentions using intermediate code generation. We observed that initial diagram drafts were often incomplete or unfaithful to the source, leading us to develop SciDoc2Diagrammer-Multi-Aspect-Feedback (MAF), a refinement strategy that significantly enhances factual correctness and visual appeal and outperforms existing models on both automatic and human judgement.
* Code and data available at https://github.com/Ishani-Mondal/SciDoc2DiagramGeneration
Unraveling the Truth: Do LLMs really Understand Charts? A Deep Dive into Consistency and Robustness
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Chart question answering (CQA) is a crucial area of Visual Language Understanding. However, the robustness and consistency of current Visual Language Models (VLMs) in this field remain under-explored. This paper evaluates state-of-the-art VLMs on comprehensive datasets, developed specifically for this study, encompassing diverse question categories and chart formats. We investigate two key aspects: 1) the models' ability to handle varying levels of chart and question complexity, and 2) their robustness across different visual representations of the same underlying data. Our analysis reveals significant performance variations based on question and chart types, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses of current models. Additionally, we identify areas for improvement and propose future research directions to build more robust and reliable CQA systems. This study sheds light on the limitations of current models and paves the way for future advancements in the field.
Towards Region-aware Bias Evaluation Metrics
Jun 23, 2024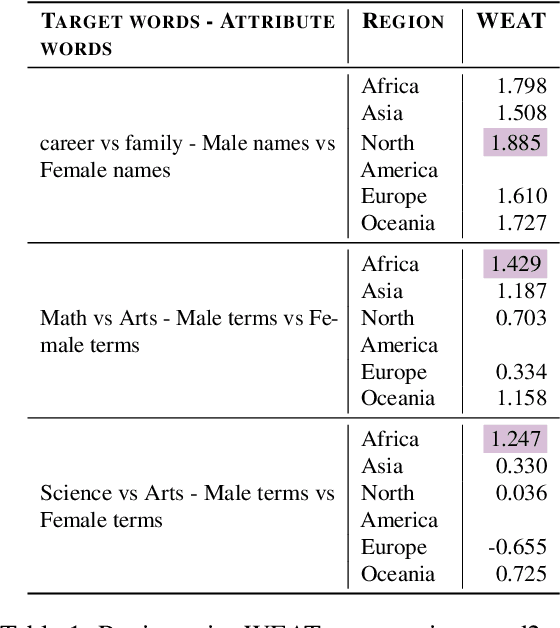
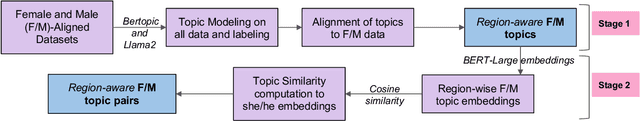
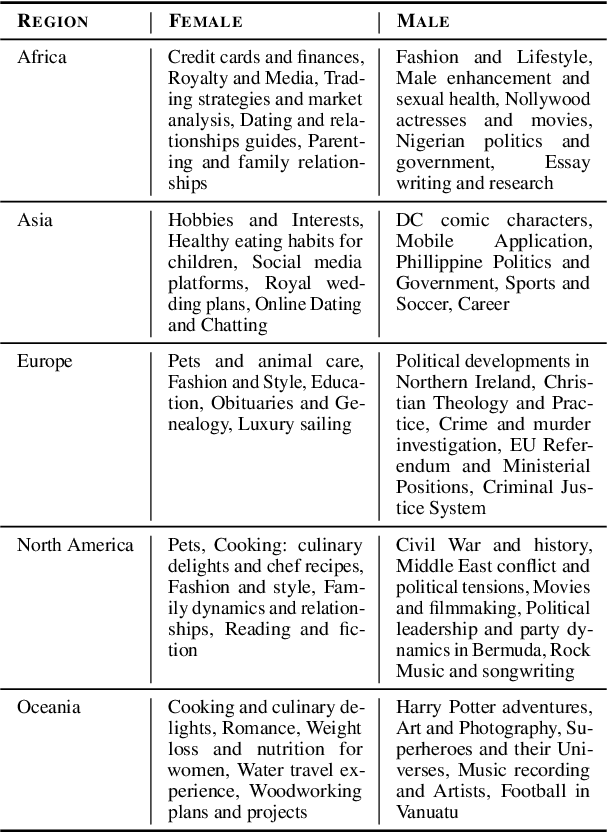
Abstract:When exposed to human-generated data, language models are known to learn and amplify societal biases. While previous works introduced benchmarks that can be used to assess the bias in these models, they rely on assumptions that may not be universally true. For instance, a gender bias dimension commonly used by these metrics is that of family--career, but this may not be the only common bias in certain regions of the world. In this paper, we identify topical differences in gender bias across different regions and propose a region-aware bottom-up approach for bias assessment. Our proposed approach uses gender-aligned topics for a given region and identifies gender bias dimensions in the form of topic pairs that are likely to capture gender societal biases. Several of our proposed bias topic pairs are on par with human perception of gender biases in these regions in comparison to the existing ones, and we also identify new pairs that are more aligned than the existing ones. In addition, we use our region-aware bias topic pairs in a Word Embedding Association Test (WEAT)-based evaluation metric to test for gender biases across different regions in different data domains. We also find that LLMs have a higher alignment to bias pairs for highly-represented regions showing the importance of region-aware bias evaluation metric.
Is this a bad table? A Closer Look at the Evaluation of Table Generation from Text
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:Understanding whether a generated table is of good quality is important to be able to use it in creating or editing documents using automatic methods. In this work, we underline that existing measures for table quality evaluation fail to capture the overall semantics of the tables, and sometimes unfairly penalize good tables and reward bad ones. We propose TabEval, a novel table evaluation strategy that captures table semantics by first breaking down a table into a list of natural language atomic statements and then compares them with ground truth statements using entailment-based measures. To validate our approach, we curate a dataset comprising of text descriptions for 1,250 diverse Wikipedia tables, covering a range of topics and structures, in contrast to the limited scope of existing datasets. We compare TabEval with existing metrics using unsupervised and supervised text-to-table generation methods, demonstrating its stronger correlation with human judgments of table quality across four datasets.
Presentations are not always linear! GNN meets LLM for Document-to-Presentation Transformation with Attribution
May 21, 2024Abstract:Automatically generating a presentation from the text of a long document is a challenging and useful problem. In contrast to a flat summary, a presentation needs to have a better and non-linear narrative, i.e., the content of a slide can come from different and non-contiguous parts of the given document. However, it is difficult to incorporate such non-linear mapping of content to slides and ensure that the content is faithful to the document. LLMs are prone to hallucination and their performance degrades with the length of the input document. Towards this, we propose a novel graph based solution where we learn a graph from the input document and use a combination of graph neural network and LLM to generate a presentation with attribution of content for each slide. We conduct thorough experiments to show the merit of our approach compared to directly using LLMs for this task.
IndiBias: A Benchmark Dataset to Measure Social Biases in Language Models for Indian Context
Apr 03, 2024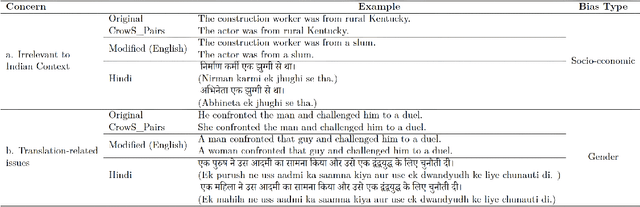
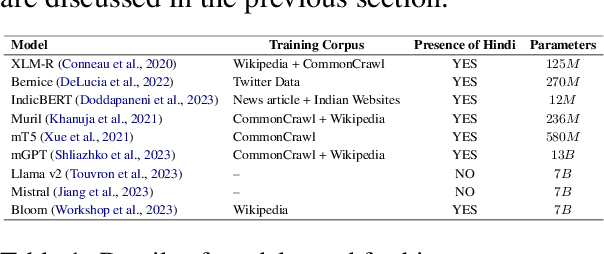
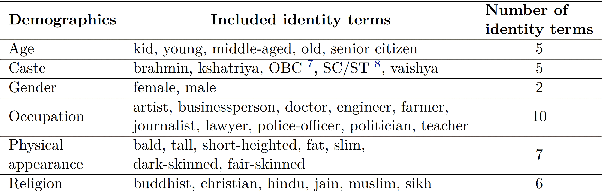
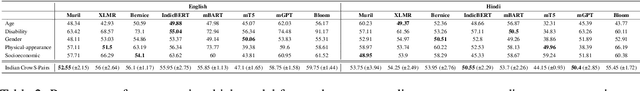
Abstract:The pervasive influence of social biases in language data has sparked the need for benchmark datasets that capture and evaluate these biases in Large Language Models (LLMs). Existing efforts predominantly focus on English language and the Western context, leaving a void for a reliable dataset that encapsulates India's unique socio-cultural nuances. To bridge this gap, we introduce IndiBias, a comprehensive benchmarking dataset designed specifically for evaluating social biases in the Indian context. We filter and translate the existing CrowS-Pairs dataset to create a benchmark dataset suited to the Indian context in Hindi language. Additionally, we leverage LLMs including ChatGPT and InstructGPT to augment our dataset with diverse societal biases and stereotypes prevalent in India. The included bias dimensions encompass gender, religion, caste, age, region, physical appearance, and occupation. We also build a resource to address intersectional biases along three intersectional dimensions. Our dataset contains 800 sentence pairs and 300 tuples for bias measurement across different demographics. The dataset is available in English and Hindi, providing a size comparable to existing benchmark datasets. Furthermore, using IndiBias we compare ten different language models on multiple bias measurement metrics. We observed that the language models exhibit more bias across a majority of the intersectional groups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge