Himanshu Maheshwari
Enhancing Presentation Slide Generation by LLMs with a Multi-Staged End-to-End Approach
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:Generating presentation slides from a long document with multimodal elements such as text and images is an important task. This is time consuming and needs domain expertise if done manually. Existing approaches for generating a rich presentation from a document are often semi-automatic or only put a flat summary into the slides ignoring the importance of a good narrative. In this paper, we address this research gap by proposing a multi-staged end-to-end model which uses a combination of LLM and VLM. We have experimentally shown that compared to applying LLMs directly with state-of-the-art prompting, our proposed multi-staged solution is better in terms of automated metrics and human evaluation.
Presentations are not always linear! GNN meets LLM for Document-to-Presentation Transformation with Attribution
May 21, 2024Abstract:Automatically generating a presentation from the text of a long document is a challenging and useful problem. In contrast to a flat summary, a presentation needs to have a better and non-linear narrative, i.e., the content of a slide can come from different and non-contiguous parts of the given document. However, it is difficult to incorporate such non-linear mapping of content to slides and ensure that the content is faithful to the document. LLMs are prone to hallucination and their performance degrades with the length of the input document. Towards this, we propose a novel graph based solution where we learn a graph from the input document and use a combination of graph neural network and LLM to generate a presentation with attribution of content for each slide. We conduct thorough experiments to show the merit of our approach compared to directly using LLMs for this task.
Social Media Ready Caption Generation for Brands
Jan 03, 2024
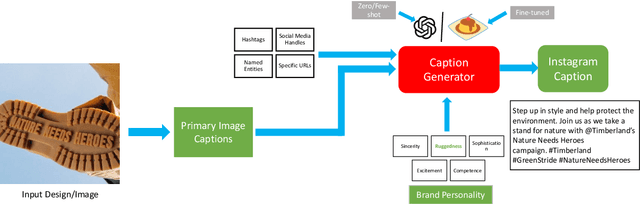
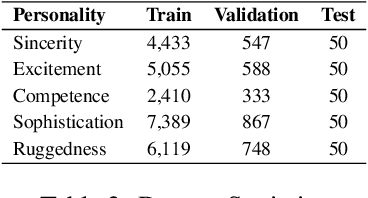
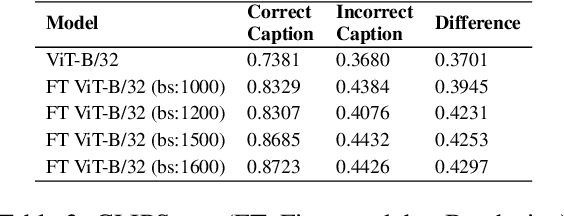
Abstract:Social media advertisements are key for brand marketing, aiming to attract consumers with captivating captions and pictures or logos. While previous research has focused on generating captions for general images, incorporating brand personalities into social media captioning remains unexplored. Brand personalities are shown to be affecting consumers' behaviours and social interactions and thus are proven to be a key aspect of marketing strategies. Current open-source multimodal LLMs are not directly suited for this task. Hence, we propose a pipeline solution to assist brands in creating engaging social media captions that align with the image and the brand personalities. Our architecture is based on two parts: a the first part contains an image captioning model that takes in an image that the brand wants to post online and gives a plain English caption; b the second part takes in the generated caption along with the target brand personality and outputs a catchy personality-aligned social media caption. Along with brand personality, our system also gives users the flexibility to provide hashtags, Instagram handles, URLs, and named entities they want the caption to contain, making the captions more semantically related to the social media handles. Comparative evaluations against various baselines demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Using Selective Masking as a Bridge between Pre-training and Fine-tuning
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Pre-training a language model and then fine-tuning it for downstream tasks has demonstrated state-of-the-art results for various NLP tasks. Pre-training is usually independent of the downstream task, and previous works have shown that this pre-training alone might not be sufficient to capture the task-specific nuances. We propose a way to tailor a pre-trained BERT model for the downstream task via task-specific masking before the standard supervised fine-tuning. For this, a word list is first collected specific to the task. For example, if the task is sentiment classification, we collect a small sample of words representing both positive and negative sentiments. Next, a word's importance for the task, called the word's task score, is measured using the word list. Each word is then assigned a probability of masking based on its task score. We experiment with different masking functions that assign the probability of masking based on the word's task score. The BERT model is further trained on MLM objective, where masking is done using the above strategy. Following this standard supervised fine-tuning is done for different downstream tasks. Results on these tasks show that the selective masking strategy outperforms random masking, indicating its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge