Apoorv Saxena
FlowCast: Trajectory Forecasting for Scalable Zero-Cost Speculative Flow Matching
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Flow Matching (FM) has recently emerged as a powerful approach for high-quality visual generation. However, their prohibitively slow inference due to a large number of denoising steps limits their potential use in real-time or interactive applications. Existing acceleration methods, like distillation, truncation, or consistency training, either degrade quality, incur costly retraining, or lack generalization. We propose FlowCast, a training-free speculative generation framework that accelerates inference by exploiting the fact that FM models are trained to preserve constant velocity. FlowCast speculates future velocity by extrapolating current velocity without incurring additional time cost, and accepts it if it is within a mean-squared error threshold. This constant-velocity forecasting allows redundant steps in stable regions to be aggressively skipped while retaining precision in complex ones. FlowCast is a plug-and-play framework that integrates seamlessly with any FM model and requires no auxiliary networks. We also present a theoretical analysis and bound the worst-case deviation between speculative and full FM trajectories. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that FlowCast achieves $>2.5\times$ speedup in image generation, video generation, and editing tasks, outperforming existing baselines with no quality loss as compared to standard full generation.
ContextFocus: Activation Steering for Contextual Faithfulness in Large Language Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) encode vast amounts of parametric knowledge during pre-training. As world knowledge evolves, effective deployment increasingly depends on their ability to faithfully follow externally retrieved context. When such evidence conflicts with the model's internal knowledge, LLMs often default to memorized facts, producing unfaithful outputs. In this work, we introduce ContextFocus, a lightweight activation steering approach that improves context faithfulness in such knowledge-conflict settings while preserving fluency and efficiency. Unlike prior approaches, our solution requires no model finetuning and incurs minimal inference-time overhead, making it highly efficient. We evaluate ContextFocus on the ConFiQA benchmark, comparing it against strong baselines including ContextDPO, COIECD, and prompting-based methods. Furthermore, we show that our method is complementary to prompting strategies and remains effective on larger models. Extensive experiments show that ContextFocus significantly improves contextual-faithfulness. Our results highlight the effectiveness, robustness, and efficiency of ContextFocus in improving contextual-faithfulness of LLM outputs.
RADAR: A Reasoning-Guided Attribution Framework for Explainable Visual Data Analysis
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Data visualizations like charts are fundamental tools for quantitative analysis and decision-making across fields, requiring accurate interpretation and mathematical reasoning. The emergence of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offers promising capabilities for automated visual data analysis, such as processing charts, answering questions, and generating summaries. However, they provide no visibility into which parts of the visual data informed their conclusions; this black-box nature poses significant challenges to real-world trust and adoption. In this paper, we take the first major step towards evaluating and enhancing the capabilities of MLLMs to attribute their reasoning process by highlighting the specific regions in charts and graphs that justify model answers. To this end, we contribute RADAR, a semi-automatic approach to obtain a benchmark dataset comprising 17,819 diverse samples with charts, questions, reasoning steps, and attribution annotations. We also introduce a method that provides attribution for chart-based mathematical reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that our reasoning-guided approach improves attribution accuracy by 15% compared to baseline methods, and enhanced attribution capabilities translate to stronger answer generation, achieving an average BERTScore of $\sim$ 0.90, indicating high alignment with ground truth responses. This advancement represents a significant step toward more interpretable and trustworthy chart analysis systems, enabling users to verify and understand model decisions through reasoning and attribution.
RCStat: A Statistical Framework for using Relative Contextualization in Transformers
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Prior work on input-token importance in auto-regressive transformers has relied on Softmax-normalized attention weights, which obscure the richer structure of pre-Softmax query-key logits. We introduce RCStat, a statistical framework that harnesses raw attention logits via Relative Contextualization (RC), a random variable measuring contextual alignment between token segments, and derive an efficient upper bound for RC. We demonstrate two applications: (i) Key-Value compression, where RC-based thresholds drive adaptive key-value eviction for substantial cache reduction with minimal quality loss; and (ii) Attribution, where RC yields higher-fidelity token-, sentence-, and chunk-level explanations than post-Softmax methods. Across question answering, summarization, and attribution benchmarks, RCStat achieves significant empirical gains, delivering state-of-the-art compression and attribution performance without any model retraining.
PLD+: Accelerating LLM inference by leveraging Language Model Artifacts
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:To reduce the latency associated with autoretrogressive LLM inference, speculative decoding has emerged as a novel decoding paradigm, where future tokens are drafted and verified in parallel. However, the practical deployment of speculative decoding is hindered by its requirements for additional computational resources and fine-tuning, which limits its out-of-the-box usability. To address these challenges, we present PLD+, a suite of novel algorithms developed to accelerate the inference process of LLMs, particularly for input-guided tasks. These tasks, which include code editing, text editing, summarization, etc., often feature outputs with substantial overlap with their inputs-an attribute PLD+ is designed to exploit. PLD+ also leverages the artifacts (attention and hidden states) generated during inference to accelerate inference speed. We test our approach on five input-guided tasks and through extensive experiments we find that PLD+ outperforms all tuning-free approaches. In the greedy setting, it even outperforms the state-of-the-art tuning-dependent approach EAGLE on four of the tasks. (by a margin of upto 2.31 in terms of avg. speedup). Our approach is tuning free, does not require any additional compute and can easily be used for accelerating inference of any LLM.
Beyond Logit Lens: Contextual Embeddings for Robust Hallucination Detection & Grounding in VLMs
Nov 28, 2024Abstract:The rapid development of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) has significantly advanced multimodal understanding by harnessing the language abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and integrating modality-specific encoders. However, LMMs are plagued by hallucinations that limit their reliability and adoption. While traditional methods to detect and mitigate these hallucinations often involve costly training or rely heavily on external models, recent approaches utilizing internal model features present a promising alternative. In this paper, we critically assess the limitations of the state-of-the-art training-free technique, the logit lens, in handling generalized visual hallucinations. We introduce a refined method that leverages contextual token embeddings from middle layers of LMMs. This approach significantly improves hallucination detection and grounding across diverse categories, including actions and OCR, while also excelling in tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as spatial relations and attribute comparison. Our novel grounding technique yields highly precise bounding boxes, facilitating a transition from Zero-Shot Object Segmentation to Grounded Visual Question Answering. Our contributions pave the way for more reliable and interpretable multimodal models.
Enhancing Post-Hoc Attributions in Long Document Comprehension via Coarse Grained Answer Decomposition
Sep 25, 2024
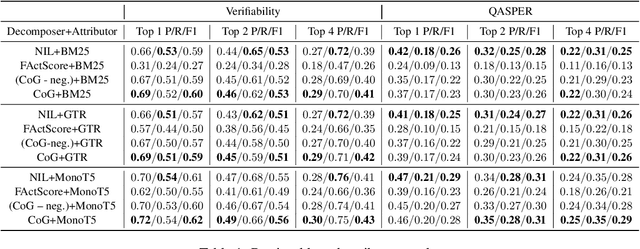
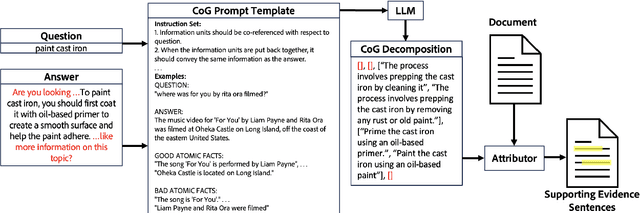
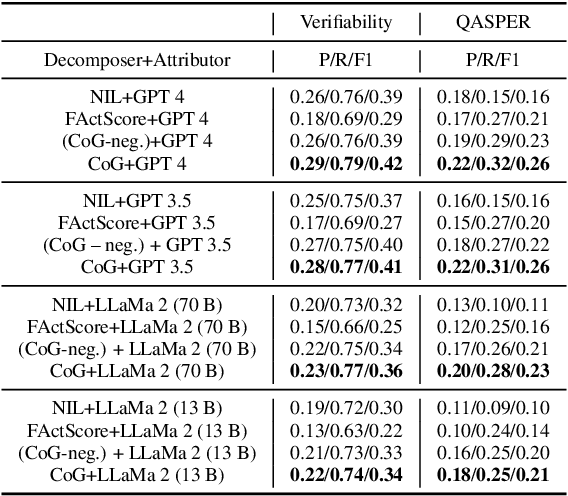
Abstract:Accurately attributing answer text to its source document is crucial for developing a reliable question-answering system. However, attribution for long documents remains largely unexplored. Post-hoc attribution systems are designed to map answer text back to the source document, yet the granularity of this mapping has not been addressed. Furthermore, a critical question arises: What precisely should be attributed, with an emphasis on identifying the information units within an answer that necessitate grounding? In this paper, we propose and investigate a novel approach to the factual decomposition of generated answers for attribution, employing template-based in-context learning. To accomplish this, we utilize the question and integrate negative sampling during few-shot in-context learning for decomposition. This approach enhances the semantic understanding of both abstractive and extractive answers. We examine the impact of answer decomposition by providing a thorough examination of various attribution approaches, ranging from retrieval-based techniques to LLM-based attributors.
Enhancing Presentation Slide Generation by LLMs with a Multi-Staged End-to-End Approach
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:Generating presentation slides from a long document with multimodal elements such as text and images is an important task. This is time consuming and needs domain expertise if done manually. Existing approaches for generating a rich presentation from a document are often semi-automatic or only put a flat summary into the slides ignoring the importance of a good narrative. In this paper, we address this research gap by proposing a multi-staged end-to-end model which uses a combination of LLM and VLM. We have experimentally shown that compared to applying LLMs directly with state-of-the-art prompting, our proposed multi-staged solution is better in terms of automated metrics and human evaluation.
Peering into the Mind of Language Models: An Approach for Attribution in Contextual Question Answering
May 28, 2024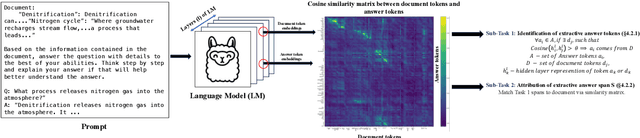
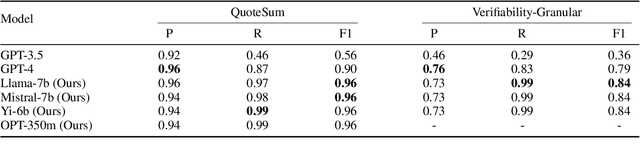
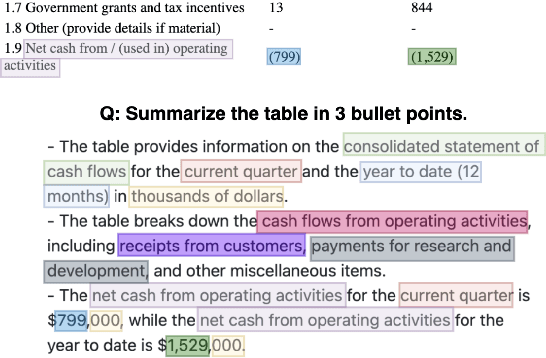
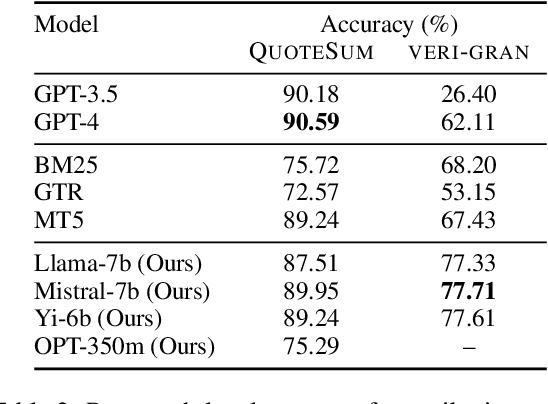
Abstract:With the enhancement in the field of generative artificial intelligence (AI), contextual question answering has become extremely relevant. Attributing model generations to the input source document is essential to ensure trustworthiness and reliability. We observe that when large language models (LLMs) are used for contextual question answering, the output answer often consists of text copied verbatim from the input prompt which is linked together with "glue text" generated by the LLM. Motivated by this, we propose that LLMs have an inherent awareness from where the text was copied, likely captured in the hidden states of the LLM. We introduce a novel method for attribution in contextual question answering, leveraging the hidden state representations of LLMs. Our approach bypasses the need for extensive model retraining and retrieval model overhead, offering granular attributions and preserving the quality of generated answers. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method performs on par or better than GPT-4 at identifying verbatim copied segments in LLM generations and in attributing these segments to their source. Importantly, our method shows robust performance across various LLM architectures, highlighting its broad applicability. Additionally, we present Verifiability-granular, an attribution dataset which has token level annotations for LLM generations in the contextual question answering setup.
Towards Optimizing the Costs of LLM Usage
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Generative AI and LLMs in particular are heavily used nowadays for various document processing tasks such as question answering and summarization. However, different LLMs come with different capabilities for different tasks as well as with different costs, tokenization, and latency. In fact, enterprises are already incurring huge costs of operating or using LLMs for their respective use cases. In this work, we propose optimizing the usage costs of LLMs by estimating their output quality (without actually invoking the LLMs), and then solving an optimization routine for the LLM selection to either keep costs under a budget, or minimize the costs, in a quality and latency aware manner. We propose a model to predict the output quality of LLMs on document processing tasks like summarization, followed by an LP rounding algorithm to optimize the selection of LLMs. We study optimization problems trading off the quality and costs, both theoretically and empirically. We further propose a sentence simplification model for reducing the number of tokens in a controlled manner. Additionally, we propose several deterministic heuristics for reducing tokens in a quality aware manner, and study the related optimization problem of applying the heuristics optimizing the quality and cost trade-off. We perform extensive empirical validation of our methods on not only enterprise datasets but also on open-source datasets, annotated by us, and show that we perform much better compared to closest baselines. Our methods reduce costs by 40%- 90% while improving quality by 4%-7%. We will release the annotated open source datasets to the community for further research and exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge