Aasish Pappu
Mixture-of-Supernets: Improving Weight-Sharing Supernet Training with Architecture-Routed Mixture-of-Experts
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:Weight-sharing supernet has become a vital component for performance estimation in the state-of-the-art (SOTA) neural architecture search (NAS) frameworks. Although supernet can directly generate different subnetworks without retraining, there is no guarantee for the quality of these subnetworks because of weight sharing. In NLP tasks such as machine translation and pre-trained language modeling, we observe that given the same model architecture, there is a large performance gap between supernet and training from scratch. Hence, supernet cannot be directly used and retraining is necessary after finding the optimal architectures. In this work, we propose mixture-of-supernets, a generalized supernet formulation where mixture-of-experts (MoE) is adopted to enhance the expressive power of the supernet model, with negligible training overhead. In this way, different subnetworks do not share the model weights directly, but through an architecture-based routing mechanism. As a result, model weights of different subnetworks are customized towards their specific architectures and the weight generation is learned by gradient descent. Compared to existing weight-sharing supernet for NLP, our method can minimize the retraining time, greatly improving training efficiency. In addition, the proposed method achieves the SOTA performance in NAS for building fast machine translation models, yielding better latency-BLEU tradeoff compared to HAT, state-of-the-art NAS for MT. We also achieve the SOTA performance in NAS for building memory-efficient task-agnostic BERT models, outperforming NAS-BERT and AutoDistil in various model sizes.
Binary and Ternary Natural Language Generation
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Ternary and binary neural networks enable multiplication-free computation and promise multiple orders of magnitude efficiency gains over full-precision networks if implemented on specialized hardware. However, since both the parameter and the output space are highly discretized, such networks have proven very difficult to optimize. The difficulties are compounded for the class of transformer text generation models due to the sensitivity of the attention operation to quantization and the noise-compounding effects of autoregressive decoding in the high-cardinality output space. We approach the problem with a mix of statistics-based quantization for the weights and elastic quantization of the activations and demonstrate the first ternary and binary transformer models on the downstream tasks of summarization and machine translation. Our ternary BART base achieves an R1 score of 41 on the CNN/DailyMail benchmark, which is merely 3.9 points behind the full model while being 16x more efficient. Our binary model, while less accurate, achieves a highly non-trivial score of 35.6. For machine translation, we achieved BLEU scores of 21.7 and 17.6 on the WMT16 En-Ro benchmark, compared with a full precision mBART model score of 26.8. We also compare our approach in the 8-bit activation setting, where our ternary and even binary weight models can match or outperform the best existing 8-bit weight models in the literature. Our code and models are available at: https://github.com/facebookresearch/Ternary_Binary_Transformer
BiT: Robustly Binarized Multi-distilled Transformer
May 25, 2022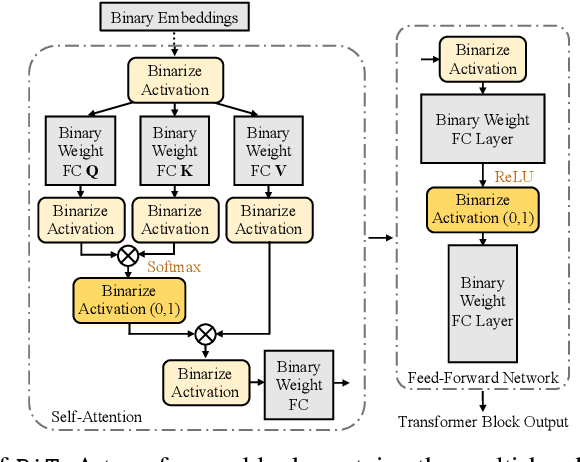
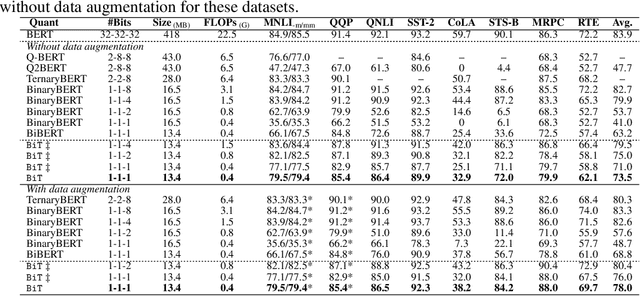
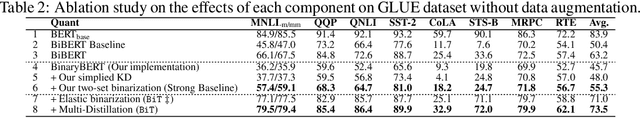
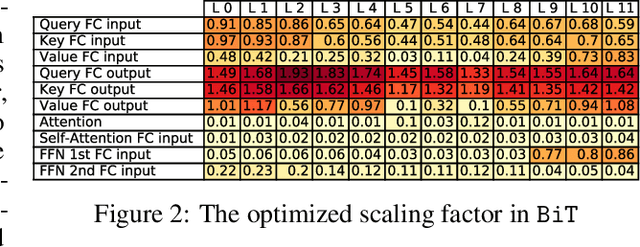
Abstract:Modern pre-trained transformers have rapidly advanced the state-of-the-art in machine learning, but have also grown in parameters and computational complexity, making them increasingly difficult to deploy in resource-constrained environments. Binarization of the weights and activations of the network can significantly alleviate these issues, however is technically challenging from an optimization perspective. In this work, we identify a series of improvements which enables binary transformers at a much higher accuracy than what was possible previously. These include a two-set binarization scheme, a novel elastic binary activation function with learned parameters, and a method to quantize a network to its limit by successively distilling higher precision models into lower precision students. These approaches allow for the first time, fully binarized transformer models that are at a practical level of accuracy, approaching a full-precision BERT baseline on the GLUE language understanding benchmark within as little as 5.9%.
Current Challenges and Future Directions in Podcast Information Access
Jun 17, 2021
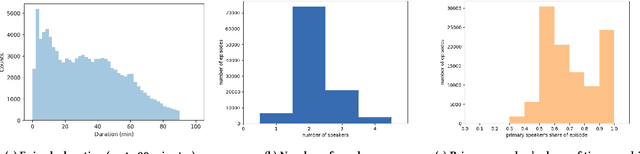
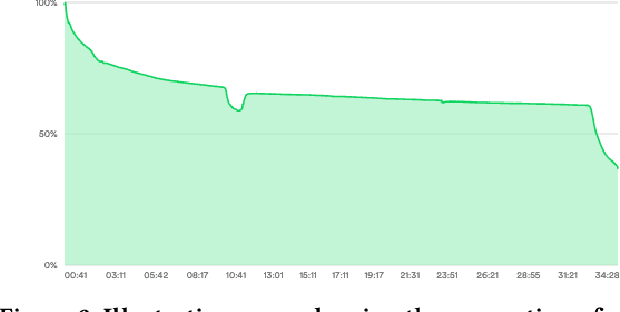
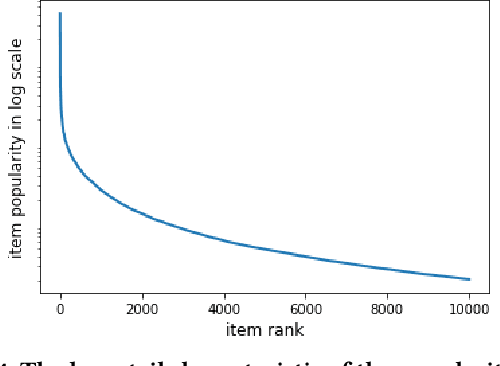
Abstract:Podcasts are spoken documents across a wide-range of genres and styles, with growing listenership across the world, and a rapidly lowering barrier to entry for both listeners and creators. The great strides in search and recommendation in research and industry have yet to see impact in the podcast space, where recommendations are still largely driven by word of mouth. In this perspective paper, we highlight the many differences between podcasts and other media, and discuss our perspective on challenges and future research directions in the domain of podcast information access.
TREC 2020 Podcasts Track Overview
Mar 29, 2021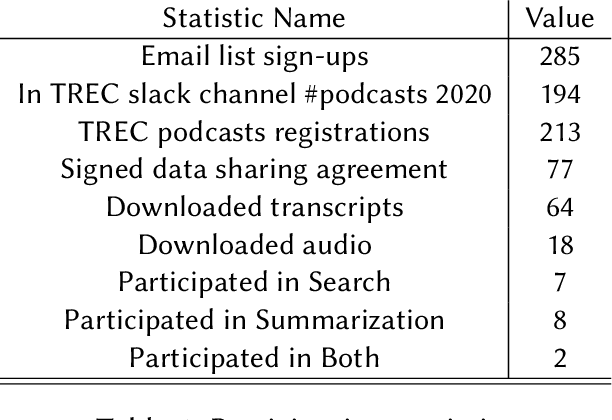
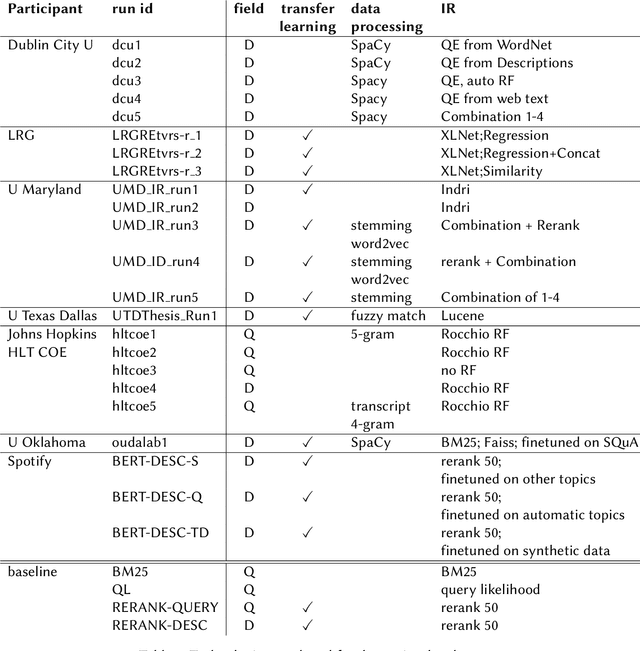
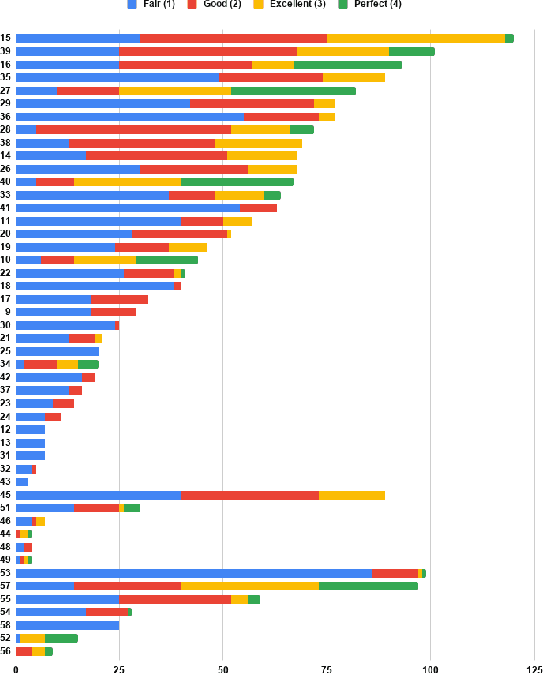
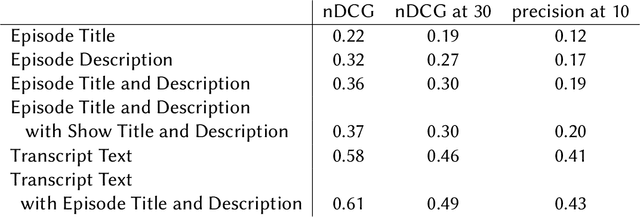
Abstract:The Podcast Track is new at the Text Retrieval Conference (TREC) in 2020. The podcast track was designed to encourage research into podcasts in the information retrieval and NLP research communities. The track consisted of two shared tasks: segment retrieval and summarization, both based on a dataset of over 100,000 podcast episodes (metadata, audio, and automatic transcripts) which was released concurrently with the track. The track generated considerable interest, attracted hundreds of new registrations to TREC and fifteen teams, mostly disjoint between search and summarization, made final submissions for assessment. Deep learning was the dominant experimental approach for both search experiments and summarization. This paper gives an overview of the tasks and the results of the participants' experiments. The track will return to TREC 2021 with the same two tasks, incorporating slight modifications in response to participant feedback.
Detecting Extraneous Content in Podcasts
Mar 03, 2021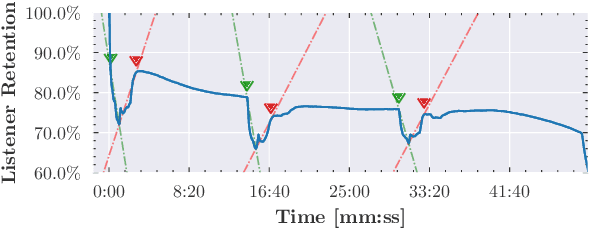
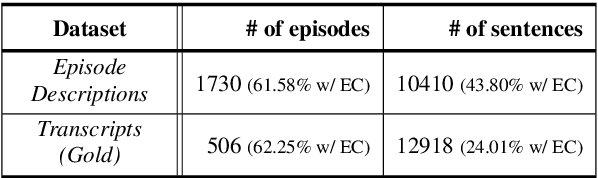
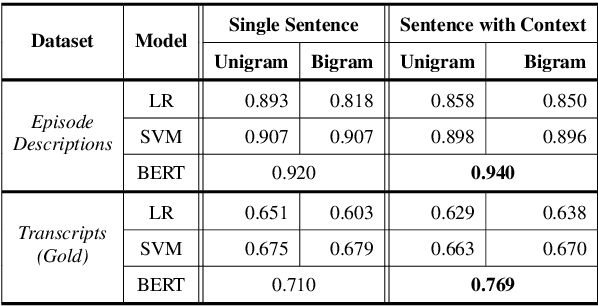
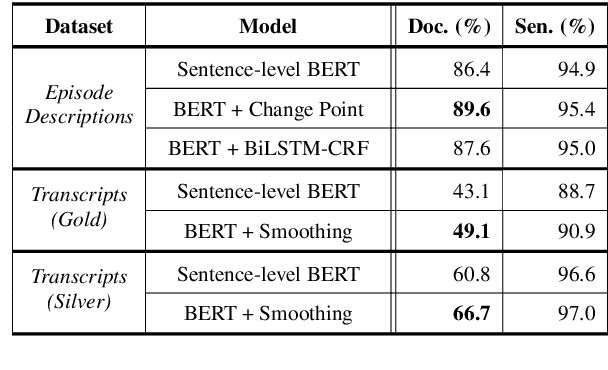
Abstract:Podcast episodes often contain material extraneous to the main content, such as advertisements, interleaved within the audio and the written descriptions. We present classifiers that leverage both textual and listening patterns in order to detect such content in podcast descriptions and audio transcripts. We demonstrate that our models are effective by evaluating them on the downstream task of podcast summarization and show that we can substantively improve ROUGE scores and reduce the extraneous content generated in the summaries.
The Spotify Podcasts Dataset
Apr 08, 2020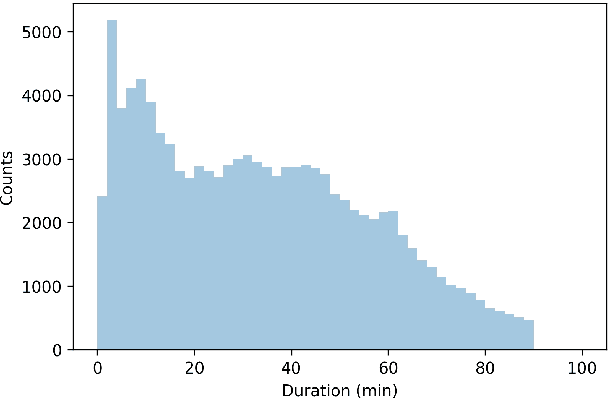
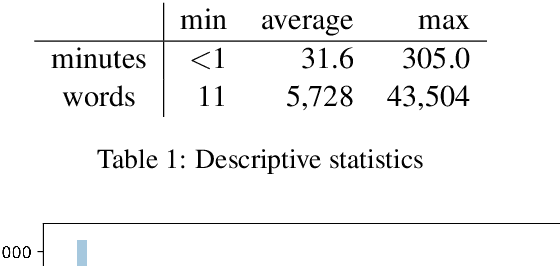

Abstract:Podcasts are a relatively new form of audio media. Episodes appear on a regular cadence, and come in many different formats and levels of formality. They can be formal news journalism or conversational chat; fiction or non-fiction. They are rapidly growing in popularity and yet have been relatively little studied. As an audio format, podcasts are more varied in style and production types than, say, broadcast news, and contain many more genres than typically studied in video research. The medium is therefore a rich domain with many research avenues for the IR and NLP communities. We present the Spotify Podcasts Dataset, a set of approximately 100K podcast episodes comprised of raw audio files along with accompanying ASR transcripts. This represents over 47,000 hours of transcribed audio, and is an order of magnitude larger than previous speech-to-text corpora.
On the Complexity of Opinions and Online Discussions
Feb 19, 2018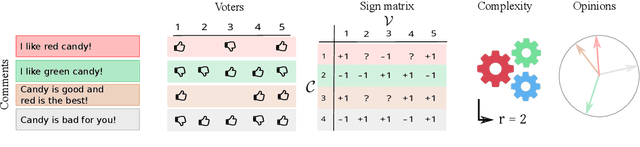
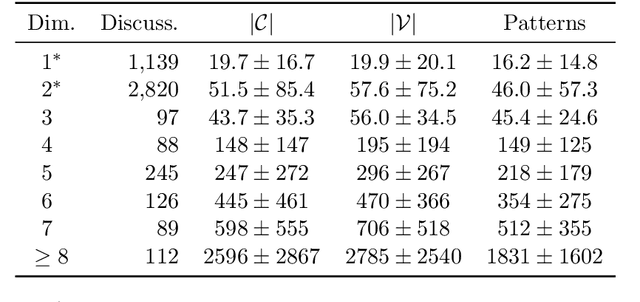
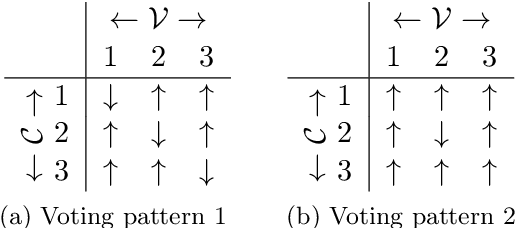
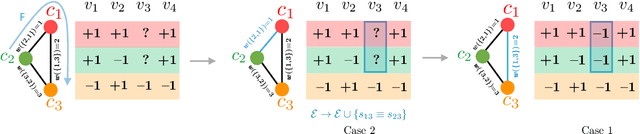
Abstract:In an increasingly polarized world, demagogues who reduce complexity down to simple arguments based on emotion are gaining in popularity. Are opinions and online discussions falling into demagoguery? In this work, we aim to provide computational tools to investigate this question and, by doing so, explore the nature and complexity of online discussions and their space of opinions, uncovering where each participant lies. More specifically, we present a modeling framework to construct latent representations of opinions in online discussions which are consistent with human judgements, as measured by online voting. If two opinions are close in the resulting latent space of opinions, it is because humans think they are similar. Our modeling framework is theoretically grounded and establishes a surprising connection between opinion and voting models and the sign-rank of a matrix. Moreover, it also provides a set of practical algorithms to both estimate the dimension of the latent space of opinions and infer where opinions expressed by the participants of an online discussion lie in this space. Experiments on a large dataset from Yahoo! News, Yahoo! Finance, Yahoo! Sports, and the Newsroom app suggest that unidimensional opinion models may be often unable to accurately represent online discussions, provide insights into human judgements and opinions, and show that our framework is able to circumvent language nuances such as sarcasm or humor by relying on human judgements instead of textual analysis.
DocTag2Vec: An Embedding Based Multi-label Learning Approach for Document Tagging
Jul 14, 2017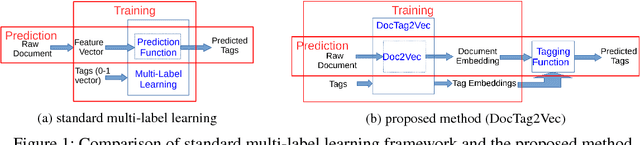
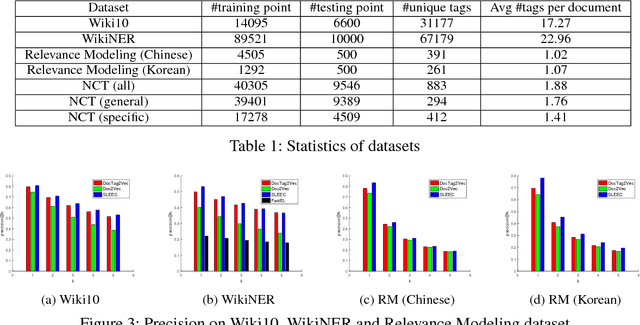
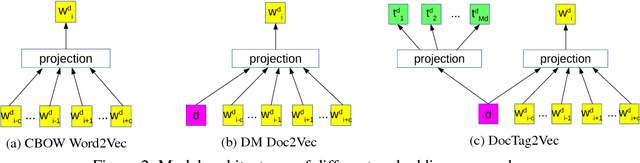
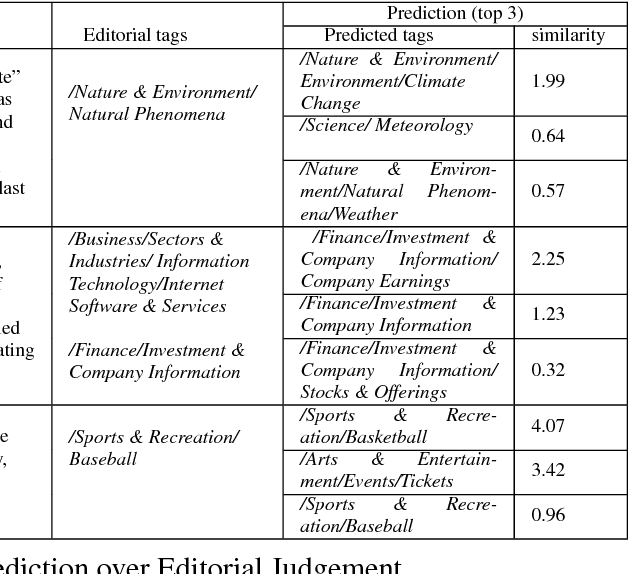
Abstract:Tagging news articles or blog posts with relevant tags from a collection of predefined ones is coined as document tagging in this work. Accurate tagging of articles can benefit several downstream applications such as recommendation and search. In this work, we propose a novel yet simple approach called DocTag2Vec to accomplish this task. We substantially extend Word2Vec and Doc2Vec---two popular models for learning distributed representation of words and documents. In DocTag2Vec, we simultaneously learn the representation of words, documents, and tags in a joint vector space during training, and employ the simple $k$-nearest neighbor search to predict tags for unseen documents. In contrast to previous multi-label learning methods, DocTag2Vec directly deals with raw text instead of provided feature vector, and in addition, enjoys advantages like the learning of tag representation, and the ability of handling newly created tags. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we conduct experiments on several datasets and show promising results against state-of-the-art methods.
Humor in Collective Discourse: Unsupervised Funniness Detection in the New Yorker Cartoon Caption Contest
Jun 26, 2015
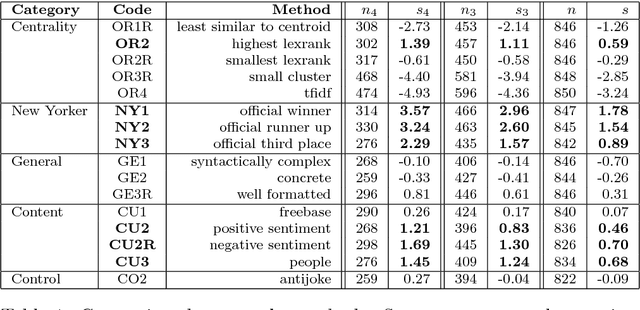


Abstract:The New Yorker publishes a weekly captionless cartoon. More than 5,000 readers submit captions for it. The editors select three of them and ask the readers to pick the funniest one. We describe an experiment that compares a dozen automatic methods for selecting the funniest caption. We show that negative sentiment, human-centeredness, and lexical centrality most strongly match the funniest captions, followed by positive sentiment. These results are useful for understanding humor and also in the design of more engaging conversational agents in text and multimodal (vision+text) systems. As part of this work, a large set of cartoons and captions is being made available to the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge