Helia Hashemi
LLM-Rubric: A Multidimensional, Calibrated Approach to Automated Evaluation of Natural Language Texts
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a framework for the automated evaluation of natural language texts. A manually constructed rubric describes how to assess multiple dimensions of interest. To evaluate a text, a large language model (LLM) is prompted with each rubric question and produces a distribution over potential responses. The LLM predictions often fail to agree well with human judges -- indeed, the humans do not fully agree with one another. However, the multiple LLM distributions can be $\textit{combined}$ to $\textit{predict}$ each human judge's annotations on all questions, including a summary question that assesses overall quality or relevance. LLM-Rubric accomplishes this by training a small feed-forward neural network that includes both judge-specific and judge-independent parameters. When evaluating dialogue systems in a human-AI information-seeking task, we find that LLM-Rubric with 9 questions (assessing dimensions such as naturalness, conciseness, and citation quality) predicts human judges' assessment of overall user satisfaction, on a scale of 1--4, with RMS error $< 0.5$, a $2\times$ improvement over the uncalibrated baseline.
* Updated version of 17 June 2024
Dense Retrieval Adaptation using Target Domain Description
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:In information retrieval (IR), domain adaptation is the process of adapting a retrieval model to a new domain whose data distribution is different from the source domain. Existing methods in this area focus on unsupervised domain adaptation where they have access to the target document collection or supervised (often few-shot) domain adaptation where they additionally have access to (limited) labeled data in the target domain. There also exists research on improving zero-shot performance of retrieval models with no adaptation. This paper introduces a new category of domain adaptation in IR that is as-yet unexplored. Here, similar to the zero-shot setting, we assume the retrieval model does not have access to the target document collection. In contrast, it does have access to a brief textual description that explains the target domain. We define a taxonomy of domain attributes in retrieval tasks to understand different properties of a source domain that can be adapted to a target domain. We introduce a novel automatic data construction pipeline that produces a synthetic document collection, query set, and pseudo relevance labels, given a textual domain description. Extensive experiments on five diverse target domains show that adapting dense retrieval models using the constructed synthetic data leads to effective retrieval performance on the target domain.
Current Challenges and Future Directions in Podcast Information Access
Jun 17, 2021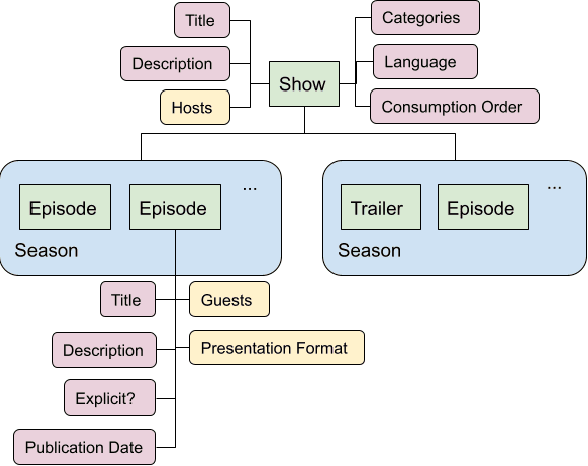
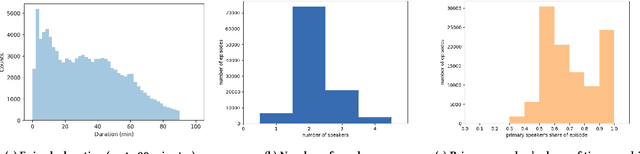
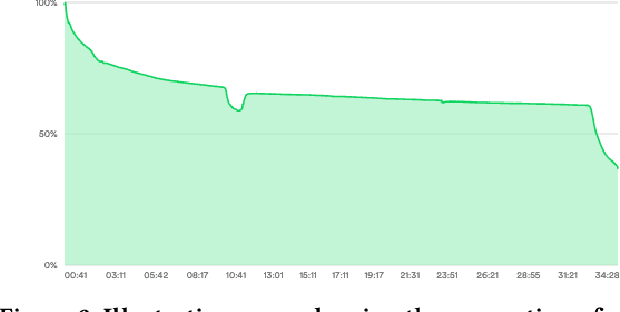
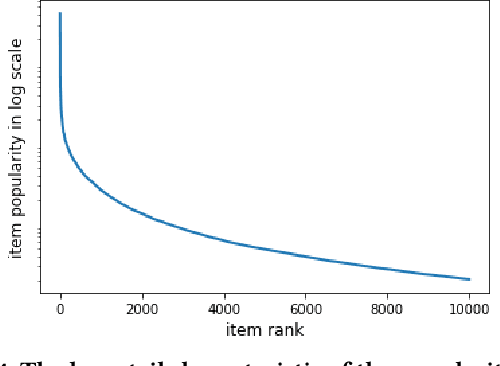
Abstract:Podcasts are spoken documents across a wide-range of genres and styles, with growing listenership across the world, and a rapidly lowering barrier to entry for both listeners and creators. The great strides in search and recommendation in research and industry have yet to see impact in the podcast space, where recommendations are still largely driven by word of mouth. In this perspective paper, we highlight the many differences between podcasts and other media, and discuss our perspective on challenges and future research directions in the domain of podcast information access.
Guided Transformer: Leveraging Multiple External Sources for Representation Learning in Conversational Search
Jun 13, 2020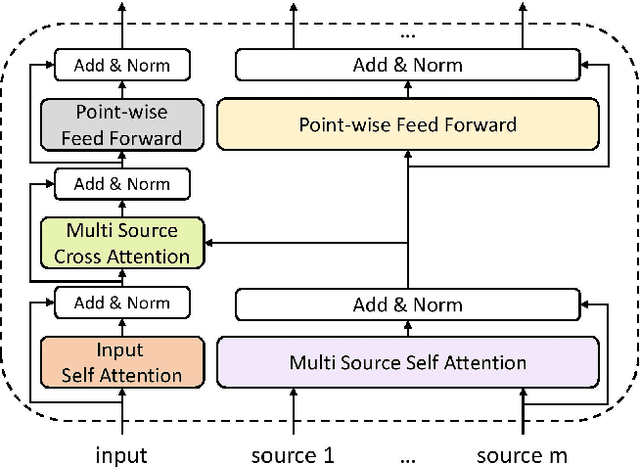
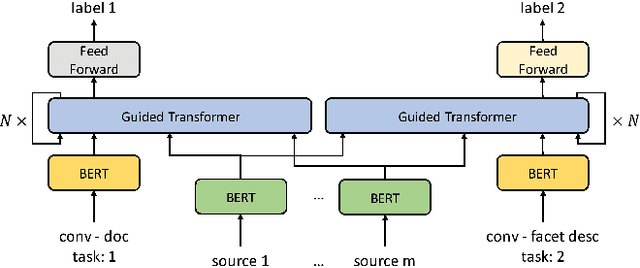

Abstract:Asking clarifying questions in response to ambiguous or faceted queries has been recognized as a useful technique for various information retrieval systems, especially conversational search systems with limited bandwidth interfaces. Analyzing and generating clarifying questions have been studied recently but the accurate utilization of user responses to clarifying questions has been relatively less explored. In this paper, we enrich the representations learned by Transformer networks using a novel attention mechanism from external information sources that weights each term in the conversation. We evaluate this Guided Transformer model in a conversational search scenario that includes clarifying questions. In our experiments, we use two separate external sources, including the top retrieved documents and a set of different possible clarifying questions for the query. We implement the proposed representation learning model for two downstream tasks in conversational search; document retrieval and next clarifying question selection. Our experiments use a public dataset for search clarification and demonstrate significant improvements compared to competitive baselines.
ANTIQUE: A Non-Factoid Question Answering Benchmark
May 22, 2019



Abstract:Considering the widespread use of mobile and voice search, answer passage retrieval for non-factoid questions plays a critical role in modern information retrieval systems. Despite the importance of the task, the community still feels the significant lack of large-scale non-factoid question answering collections with real questions and comprehensive relevance judgments. In this paper, we develop and release a collection of 2,626 open-domain non-factoid questions from a diverse set of categories. The dataset, called ANTIQUE, contains 34,011 manual relevance annotations. The questions were asked by real users in a community question answering service, i.e., Yahoo! Answers. Relevance judgments for all the answers to each question were collected through crowdsourcing. To facilitate further research, we also include a brief analysis of the data as well as baseline results on both classical and recently developed neural IR models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge