Ann Clifton
Transforming Podcast Preview Generation: From Expert Models to LLM-Based Systems
May 29, 2025Abstract:Discovering and evaluating long-form talk content such as videos and podcasts poses a significant challenge for users, as it requires a considerable time investment. Previews offer a practical solution by providing concise snippets that showcase key moments of the content, enabling users to make more informed and confident choices. We propose an LLM-based approach for generating podcast episode previews and deploy the solution at scale, serving hundreds of thousands of podcast previews in a real-world application. Comprehensive offline evaluations and online A/B testing demonstrate that LLM-generated previews consistently outperform a strong baseline built on top of various ML expert models, showcasing a significant reduction in the need for meticulous feature engineering. The offline results indicate notable enhancements in understandability, contextual clarity, and interest level, and the online A/B test shows a 4.6% increase in user engagement with preview content, along with a 5x boost in processing efficiency, offering a more streamlined and performant solution compared to the strong baseline of feature-engineered expert models.
PODTILE: Facilitating Podcast Episode Browsing with Auto-generated Chapters
Oct 21, 2024
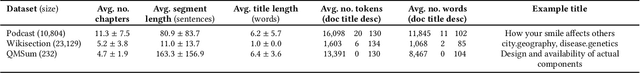

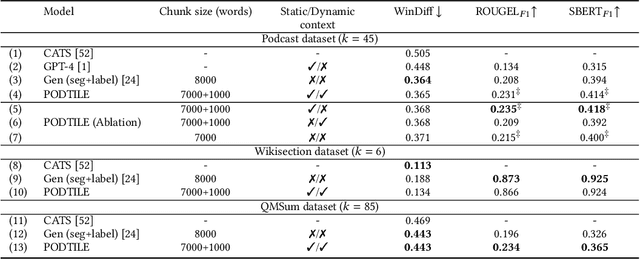
Abstract:Listeners of long-form talk-audio content, such as podcast episodes, often find it challenging to understand the overall structure and locate relevant sections. A practical solution is to divide episodes into chapters--semantically coherent segments labeled with titles and timestamps. Since most episodes on our platform at Spotify currently lack creator-provided chapters, automating the creation of chapters is essential. Scaling the chapterization of podcast episodes presents unique challenges. First, episodes tend to be less structured than written texts, featuring spontaneous discussions with nuanced transitions. Second, the transcripts are usually lengthy, averaging about 16,000 tokens, which necessitates efficient processing that can preserve context. To address these challenges, we introduce PODTILE, a fine-tuned encoder-decoder transformer to segment conversational data. The model simultaneously generates chapter transitions and titles for the input transcript. To preserve context, each input text is augmented with global context, including the episode's title, description, and previous chapter titles. In our intrinsic evaluation, PODTILE achieved an 11% improvement in ROUGE score over the strongest baseline. Additionally, we provide insights into the practical benefits of auto-generated chapters for listeners navigating episode content. Our findings indicate that auto-generated chapters serve as a useful tool for engaging with less popular podcasts. Finally, we present empirical evidence that using chapter titles can enhance effectiveness of sparse retrieval in search tasks.
Cem Mil Podcasts: A Spoken Portuguese Document Corpus
Sep 23, 2022
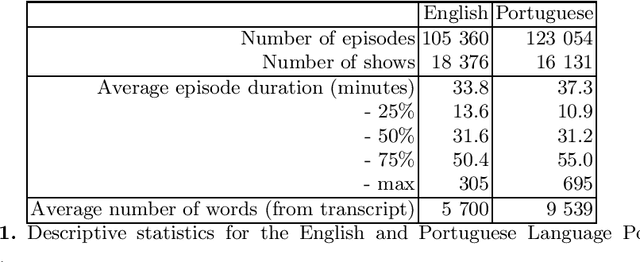
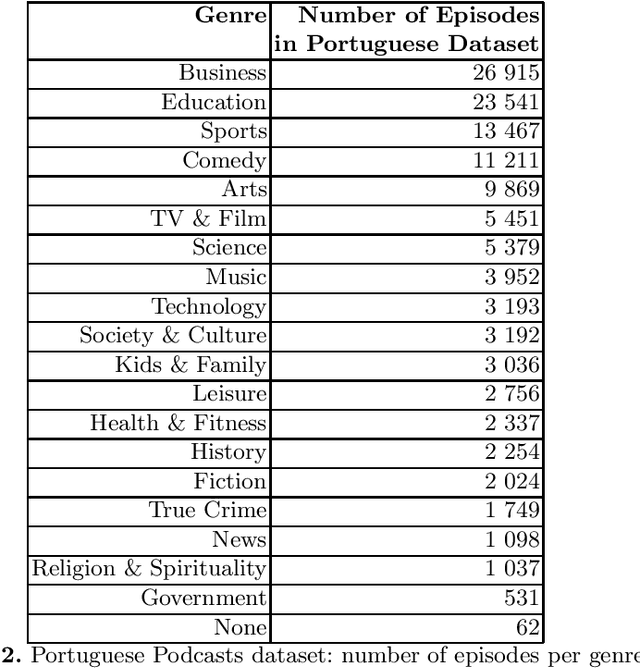
Abstract:This document describes the Portuguese language podcast dataset released by Spotify for academic research purposes. We give an overview of how the data was sampled, some basic statistics over the collection, as well as brief information of distribution over Brazilian and Portuguese dialects.
Podcast Metadata and Content: Episode Relevance andAttractiveness in Ad Hoc Search
Aug 25, 2021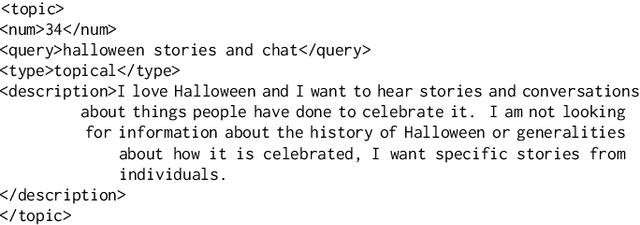
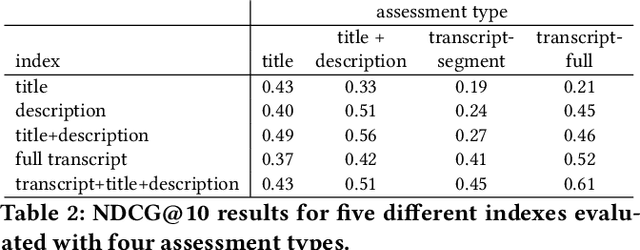
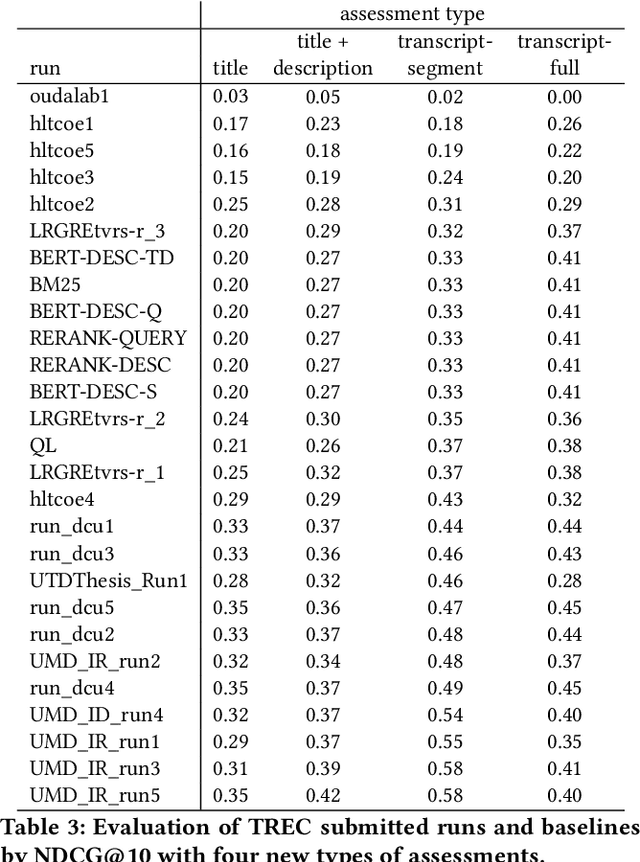
Abstract:Rapidly growing online podcast archives contain diverse content on a wide range of topics. These archives form an important resource for entertainment and professional use, but their value can only be realized if users can rapidly and reliably locate content of interest. Search for relevant content can be based on metadata provided by content creators, but also on transcripts of the spoken content itself. Excavating relevant content from deep within these audio streams for diverse types of information needs requires varying the approach to systems prototyping. We describe a set of diverse podcast information needs and different approaches to assessing retrieved content for relevance. We use these information needs in an investigation of the utility and effectiveness of these information sources. Based on our analysis, we recommend approaches for indexing and retrieving podcast content for ad hoc search.
Current Challenges and Future Directions in Podcast Information Access
Jun 17, 2021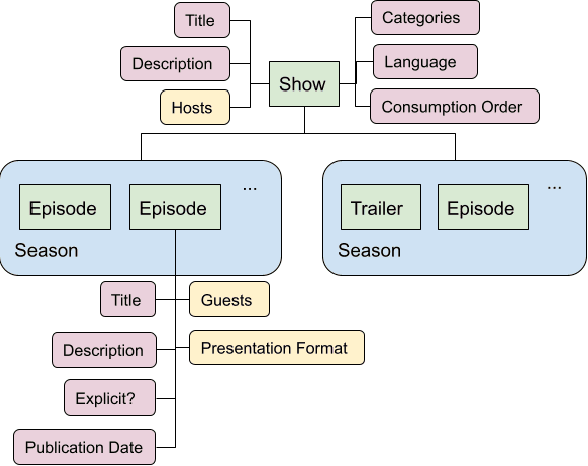
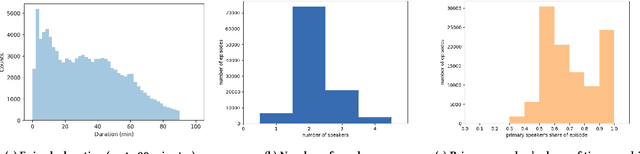
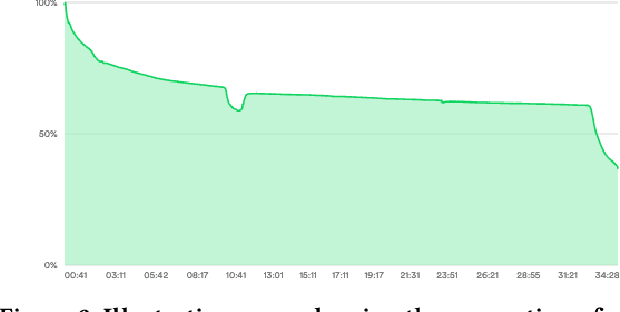
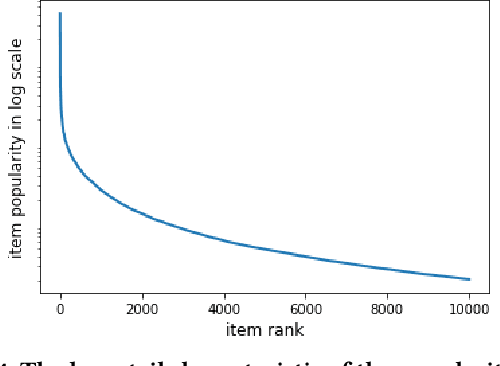
Abstract:Podcasts are spoken documents across a wide-range of genres and styles, with growing listenership across the world, and a rapidly lowering barrier to entry for both listeners and creators. The great strides in search and recommendation in research and industry have yet to see impact in the podcast space, where recommendations are still largely driven by word of mouth. In this perspective paper, we highlight the many differences between podcasts and other media, and discuss our perspective on challenges and future research directions in the domain of podcast information access.
Spotify at TREC 2020: Genre-Aware Abstractive Podcast Summarization
Apr 07, 2021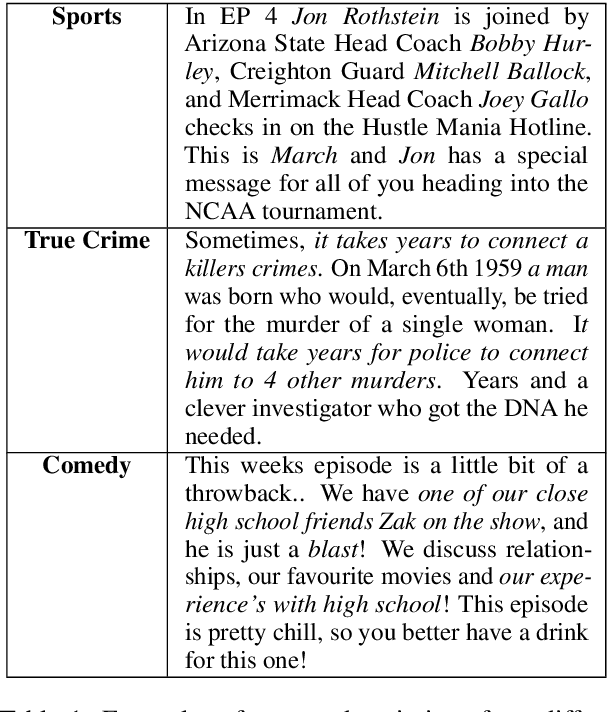
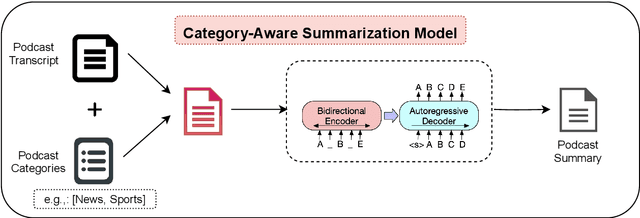
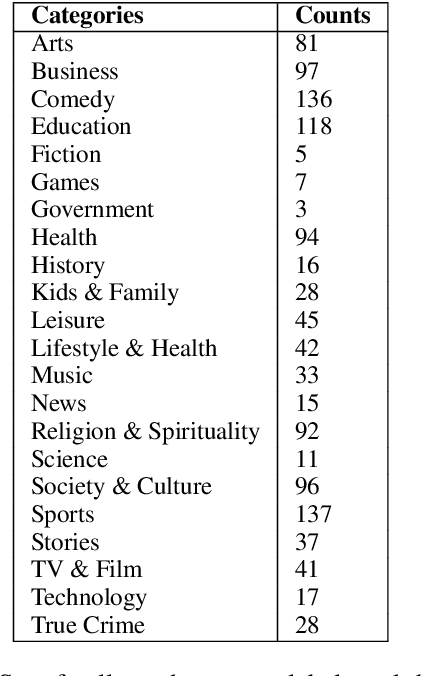
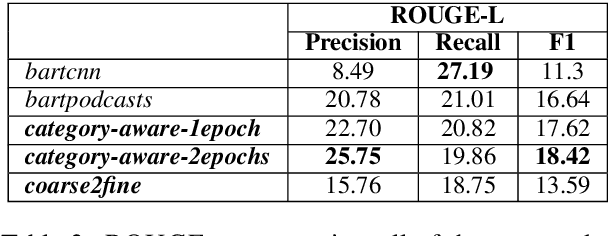
Abstract:This paper contains the description of our submissions to the summarization task of the Podcast Track in TREC (the Text REtrieval Conference) 2020. The goal of this challenge was to generate short, informative summaries that contain the key information present in a podcast episode using automatically generated transcripts of the podcast audio. Since podcasts vary with respect to their genre, topic, and granularity of information, we propose two summarization models that explicitly take genre and named entities into consideration in order to generate summaries appropriate to the style of the podcasts. Our models are abstractive, and supervised using creator-provided descriptions as ground truth summaries. The results of the submitted summaries show that our best model achieves an aggregate quality score of 1.58 in comparison to the creator descriptions and a baseline abstractive system which both score 1.49 (an improvement of 9%) as assessed by human evaluators.
TREC 2020 Podcasts Track Overview
Mar 29, 2021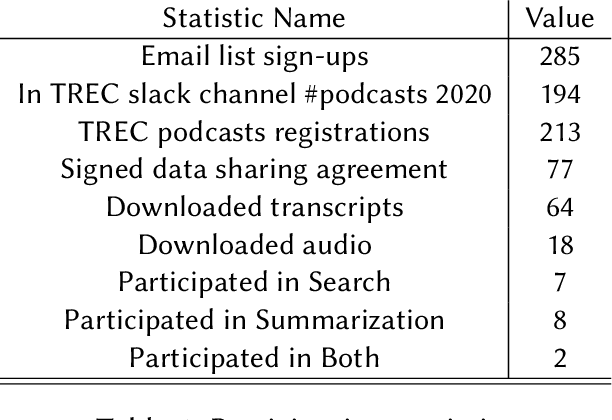
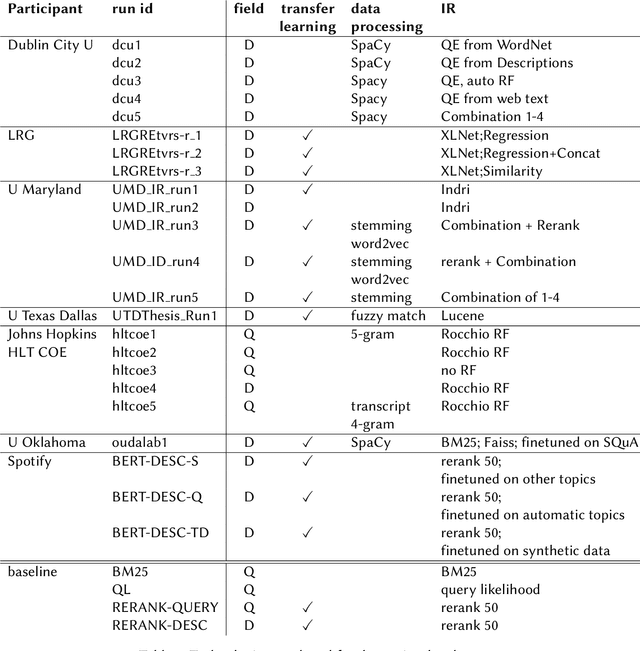
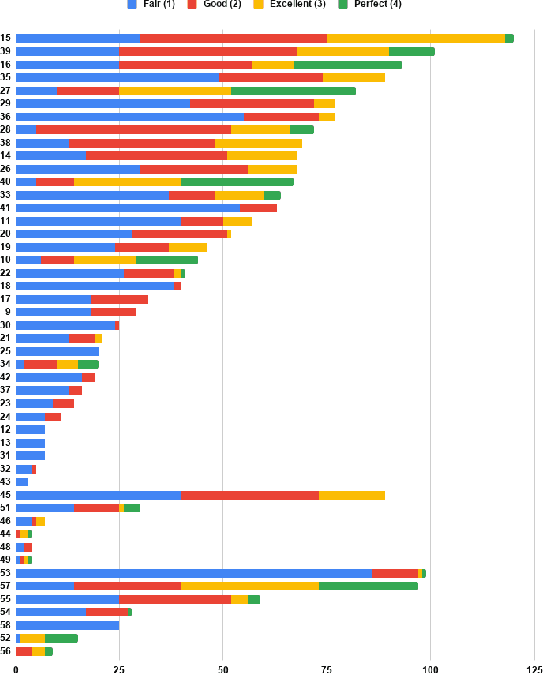
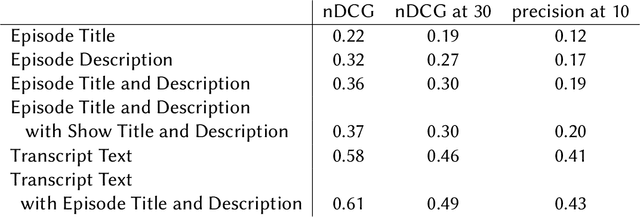
Abstract:The Podcast Track is new at the Text Retrieval Conference (TREC) in 2020. The podcast track was designed to encourage research into podcasts in the information retrieval and NLP research communities. The track consisted of two shared tasks: segment retrieval and summarization, both based on a dataset of over 100,000 podcast episodes (metadata, audio, and automatic transcripts) which was released concurrently with the track. The track generated considerable interest, attracted hundreds of new registrations to TREC and fifteen teams, mostly disjoint between search and summarization, made final submissions for assessment. Deep learning was the dominant experimental approach for both search experiments and summarization. This paper gives an overview of the tasks and the results of the participants' experiments. The track will return to TREC 2021 with the same two tasks, incorporating slight modifications in response to participant feedback.
The Spotify Podcasts Dataset
Apr 08, 2020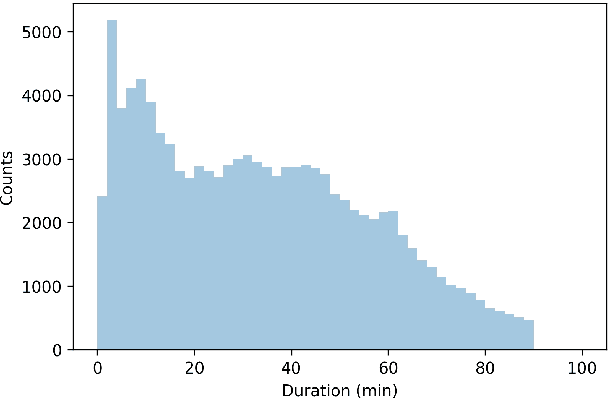
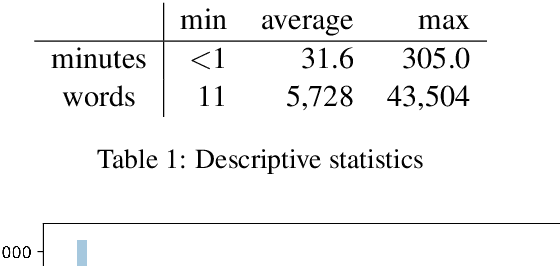

Abstract:Podcasts are a relatively new form of audio media. Episodes appear on a regular cadence, and come in many different formats and levels of formality. They can be formal news journalism or conversational chat; fiction or non-fiction. They are rapidly growing in popularity and yet have been relatively little studied. As an audio format, podcasts are more varied in style and production types than, say, broadcast news, and contain many more genres than typically studied in video research. The medium is therefore a rich domain with many research avenues for the IR and NLP communities. We present the Spotify Podcasts Dataset, a set of approximately 100K podcast episodes comprised of raw audio files along with accompanying ASR transcripts. This represents over 47,000 hours of transcribed audio, and is an order of magnitude larger than previous speech-to-text corpora.
Sockeye: A Toolkit for Neural Machine Translation
Jun 01, 2018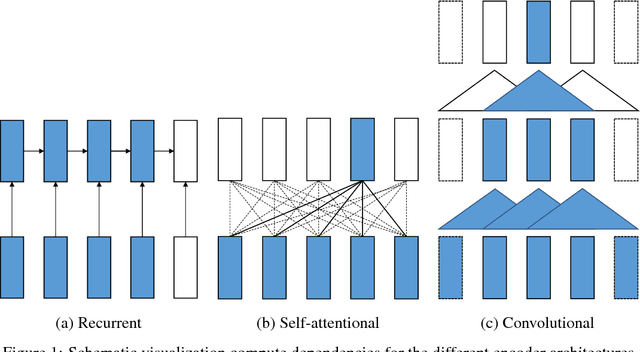
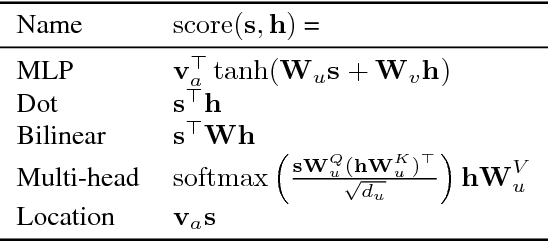

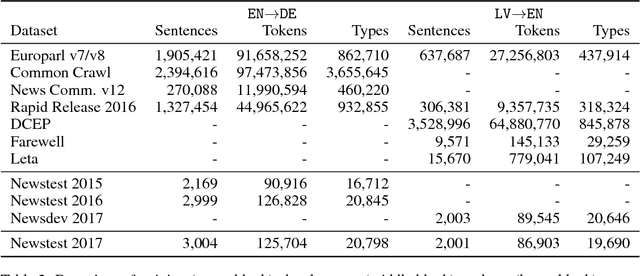
Abstract:We describe Sockeye (version 1.12), an open-source sequence-to-sequence toolkit for Neural Machine Translation (NMT). Sockeye is a production-ready framework for training and applying models as well as an experimental platform for researchers. Written in Python and built on MXNet, the toolkit offers scalable training and inference for the three most prominent encoder-decoder architectures: attentional recurrent neural networks, self-attentional transformers, and fully convolutional networks. Sockeye also supports a wide range of optimizers, normalization and regularization techniques, and inference improvements from current NMT literature. Users can easily run standard training recipes, explore different model settings, and incorporate new ideas. In this paper, we highlight Sockeye's features and benchmark it against other NMT toolkits on two language arcs from the 2017 Conference on Machine Translation (WMT): English-German and Latvian-English. We report competitive BLEU scores across all three architectures, including an overall best score for Sockeye's transformer implementation. To facilitate further comparison, we release all system outputs and training scripts used in our experiments. The Sockeye toolkit is free software released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Non-Uniform Stochastic Average Gradient Method for Training Conditional Random Fields
Apr 16, 2015

Abstract:We apply stochastic average gradient (SAG) algorithms for training conditional random fields (CRFs). We describe a practical implementation that uses structure in the CRF gradient to reduce the memory requirement of this linearly-convergent stochastic gradient method, propose a non-uniform sampling scheme that substantially improves practical performance, and analyze the rate of convergence of the SAGA variant under non-uniform sampling. Our experimental results reveal that our method often significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of the training objective, and performs as well or better than optimally-tuned stochastic gradient methods in terms of test error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge