Zihan Chen
Lean Clients, Full Accuracy: Hybrid Zeroth- and First-Order Split Federated Learning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Split Federated Learning (SFL) enables collaborative training between resource-constrained edge devices and a compute-rich server. Communication overhead is a central issue in SFL and can be mitigated with auxiliary networks. Yet, the fundamental client-side computation challenge remains, as back-propagation requires substantial memory and computation costs, severely limiting the scale of models that edge devices can support. To enable more resource-efficient client computation and reduce the client-server communication, we propose HERON-SFL, a novel hybrid optimization framework that integrates zeroth-order (ZO) optimization for local client training while retaining first-order (FO) optimization on the server. With the assistance of auxiliary networks, ZO updates enable clients to approximate local gradients using perturbed forward-only evaluations per step, eliminating memory-intensive activation caching and avoiding explicit gradient computation in the traditional training process. Leveraging the low effective rank assumption, we theoretically prove that HERON-SFL's convergence rate is independent of model dimensionality, addressing a key scalability concern common to ZO algorithms. Empirically, on ResNet training and language model (LM) fine-tuning tasks, HERON-SFL matches benchmark accuracy while reducing client peak memory by up to 64% and client-side compute cost by up to 33% per step, substantially expanding the range of models that can be trained or adapted on resource-limited devices.
Machine Learning-Driven Creep Law Discovery Across Alloy Compositional Space
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Hihg-temperature creep characterization of structural alloys traditionally relies on serial uniaxial tests, which are highly inefficient for exploring the large search space of alloy compositions and for material discovery. Here, we introduce a machine-learning-assisted, high-throughput framework for creep law identification based on a dimple array bulge instrument (DABI) configuration, which enables parallel creep testing of 25 dimples, each fabricated from a different alloy, in a single experiment. Full-field surface displacements of dimples undergoing time-dependent creep-induced bulging under inert gas pressure are measured by 3D digital image correlation. We train a recurrent neural network (RNN) as a surrogate model, mapping creep parameters and loading conditions to the time-dependent deformation response of DABI. Coupling this surrogate with a particle swarm optimization scheme enables rapid and global inverse identification with sparsity regularization of creep parameters from experiment displacement-time histories. In addition, we propose a phenomenological creep law with a time-dependent stress exponent that captures the sigmoidal primary creep observed in wrought INCONEL 625 and extracts its temperature dependence from DABI test at multiple temperatures. Furthermore, we employ a general creep law combining several conventional forms together with regularized inversion to identify the creep laws for 47 additional Fe-, Ni-, and Co-rich alloys and to automatically select the dominant functional form for each alloy. This workflow combined with DABI experiment provides a quantitative, high-throughput creep characterization platform that is compatible with data mining, composition-property modeling, and nonlinear structural optimization with creep behavior across a large alloy design space.
When Large Language Models Do Not Work: Online Incivility Prediction through Graph Neural Networks
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Online incivility has emerged as a widespread and persistent problem in digital communities, imposing substantial social and psychological burdens on users. Although many platforms attempt to curb incivility through moderation and automated detection, the performance of existing approaches often remains limited in both accuracy and efficiency. To address this challenge, we propose a Graph Neural Network (GNN) framework for detecting three types of uncivil behavior (i.e., toxicity, aggression, and personal attacks) within the English Wikipedia community. Our model represents each user comment as a node, with textual similarity between comments defining the edges, allowing the network to jointly learn from both linguistic content and relational structures among comments. We also introduce a dynamically adjusted attention mechanism that adaptively balances nodal and topological features during information aggregation. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our proposed architecture outperforms 12 state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) across multiple metrics while requiring significantly lower inference cost. These findings highlight the crucial role of structural context in detecting online incivility and address the limitations of text-only LLM paradigms in behavioral prediction. All datasets and comparative outputs will be publicly available in our repository to support further research and reproducibility.
Adaptive Digital Twin of Sheet Metal Forming via Proper Orthogonal Decomposition-Based Koopman Operator with Model Predictive Control
Nov 13, 2025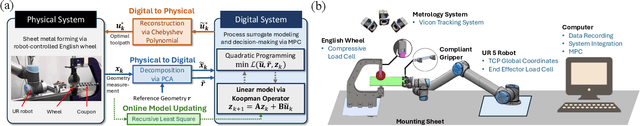

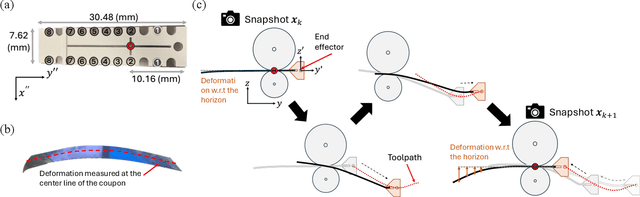
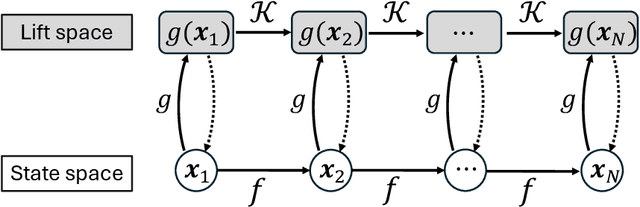
Abstract:Digital Twin (DT) technologies are transforming manufacturing by enabling real-time prediction, monitoring, and control of complex processes. Yet, applying DT to deformation-based metal forming remains challenging because of the strongly coupled spatial-temporal behavior and the nonlinear relationship between toolpath and material response. For instance, sheet-metal forming by the English wheel, a highly flexible but artisan-dependent process, still lacks digital counterparts that can autonomously plan and adapt forming strategies. This study presents an adaptive DT framework that integrates Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) for physics-aware dimensionality reduction with a Koopman operator for representing nonlinear system in a linear lifted space for the real-time decision-making via model predictive control (MPC). To accommodate evolving process conditions or material states, an online Recursive Least Squares (RLS) algorithm is introduced to update the operator coefficients in real time, enabling continuous adaptation of the DT model as new deformation data become available. The proposed framework is experimentally demonstrated on a robotic English Wheel sheet metal forming system, where deformation fields are measured and modeled under varying toolpaths. Results show that the adaptive DT is capable of controlling the forming process to achieve the given target shape by effectively capturing non-stationary process behaviors. Beyond this case study, the proposed framework establishes a generalizable approach for interpretable, adaptive, and computationally-efficient DT of nonlinear manufacturing systems, bridging reduced-order physics representations with data-driven adaptability to support autonomous process control and optimization.
GraphTOP: Graph Topology-Oriented Prompting for Graph Neural Networks
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have revolutionized the field of graph learning by learning expressive graph representations from massive graph data. As a common pattern to train powerful GNNs, the "pre-training, adaptation" scheme first pre-trains GNNs over unlabeled graph data and subsequently adapts them to specific downstream tasks. In the adaptation phase, graph prompting is an effective strategy that modifies input graph data with learnable prompts while keeping pre-trained GNN models frozen. Typically, existing graph prompting studies mainly focus on *feature-oriented* methods that apply graph prompts to node features or hidden representations. However, these studies often achieve suboptimal performance, as they consistently overlook the potential of *topology-oriented* prompting, which adapts pre-trained GNNs by modifying the graph topology. In this study, we conduct a pioneering investigation of graph prompting in terms of graph topology. We propose the first **Graph** **T**opology-**O**riented **P**rompting (GraphTOP) framework to effectively adapt pre-trained GNN models for downstream tasks. More specifically, we reformulate topology-oriented prompting as an edge rewiring problem within multi-hop local subgraphs and relax it into the continuous probability space through reparameterization while ensuring tight relaxation and preserving graph sparsity. Extensive experiments on five graph datasets under four pre-training strategies demonstrate that our proposed GraphTOP outshines six baselines on multiple node classification datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/xbfu/GraphTOP.
ALLabel: Three-stage Active Learning for LLM-based Entity Recognition using Demonstration Retrieval
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Many contemporary data-driven research efforts in the natural sciences, such as chemistry and materials science, require large-scale, high-performance entity recognition from scientific datasets. Large language models (LLMs) have increasingly been adopted to solve the entity recognition task, with the same trend being observed on all-spectrum NLP tasks. The prevailing entity recognition LLMs rely on fine-tuned technology, yet the fine-tuning process often incurs significant cost. To achieve a best performance-cost trade-off, we propose ALLabel, a three-stage framework designed to select the most informative and representative samples in preparing the demonstrations for LLM modeling. The annotated examples are used to construct a ground-truth retrieval corpus for LLM in-context learning. By sequentially employing three distinct active learning strategies, ALLabel consistently outperforms all baselines under the same annotation budget across three specialized domain datasets. Experimental results also demonstrate that selectively annotating only 5\%-10\% of the dataset with ALLabel can achieve performance comparable to the method annotating the entire dataset. Further analyses and ablation studies verify the effectiveness and generalizability of our proposal.
Learning from Diverse Reasoning Paths with Routing and Collaboration
Aug 23, 2025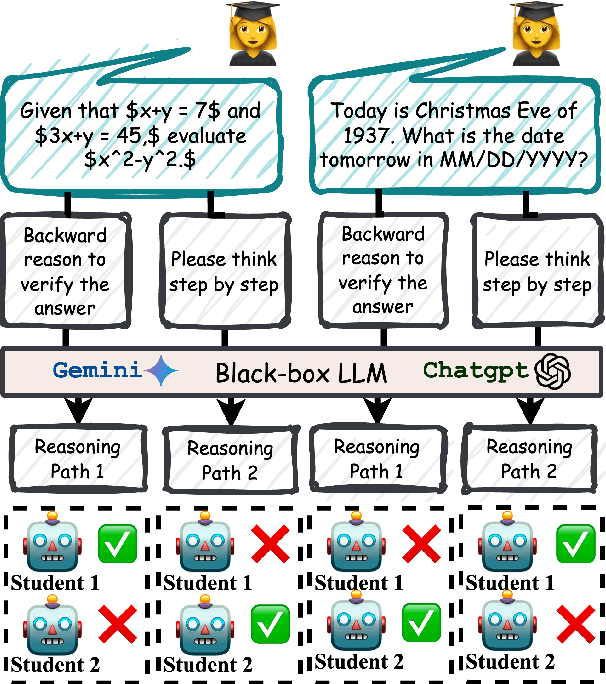
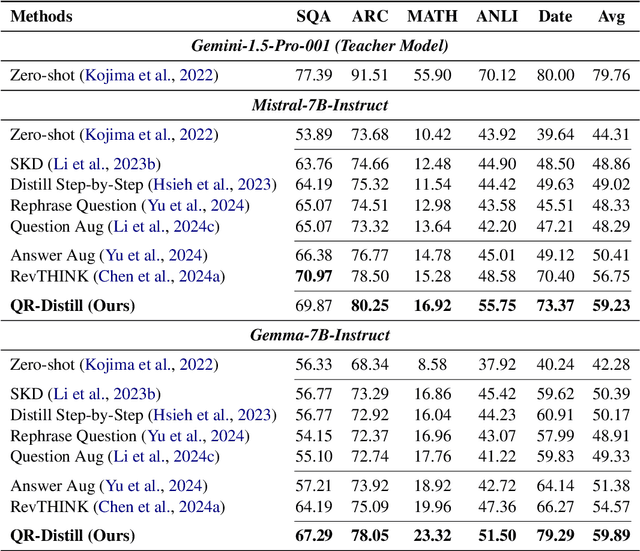
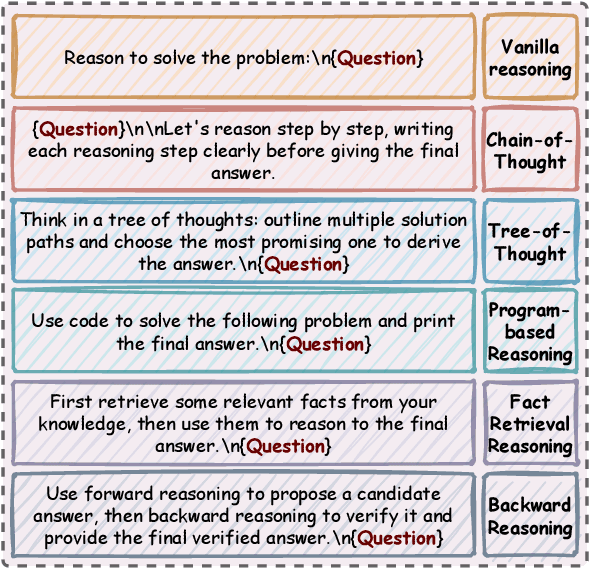
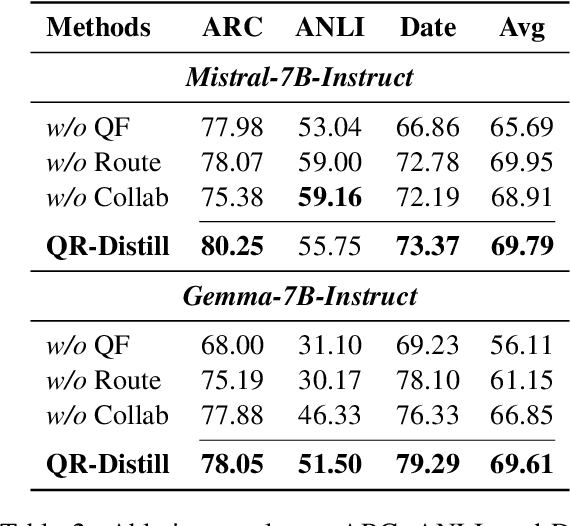
Abstract:Advances in large language models (LLMs) significantly enhance reasoning capabilities but their deployment is restricted in resource-constrained scenarios. Knowledge distillation addresses this by transferring knowledge from powerful teacher models to compact and transparent students. However, effectively capturing the teacher's comprehensive reasoning is challenging due to conventional token-level supervision's limited scope. Using multiple reasoning paths per query alleviates this problem, but treating each path identically is suboptimal as paths vary widely in quality and suitability across tasks and models. We propose Quality-filtered Routing with Cooperative Distillation (QR-Distill), combining path quality filtering, conditional routing, and cooperative peer teaching. First, quality filtering retains only correct reasoning paths scored by an LLM-based evaluation. Second, conditional routing dynamically assigns paths tailored to each student's current learning state. Finally, cooperative peer teaching enables students to mutually distill diverse insights, addressing knowledge gaps and biases toward specific reasoning styles. Experiments demonstrate QR-Distill's superiority over traditional single- and multi-path distillation methods. Ablation studies further highlight the importance of each component including quality filtering, conditional routing, and peer teaching in effective knowledge transfer. Our code is available at https://github.com/LzyFischer/Distill.
Graph Prompting for Graph Learning Models: Recent Advances and Future Directions
Jun 10, 2025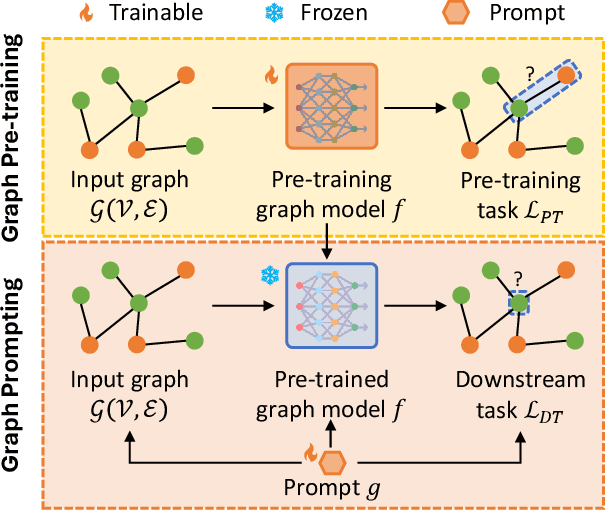
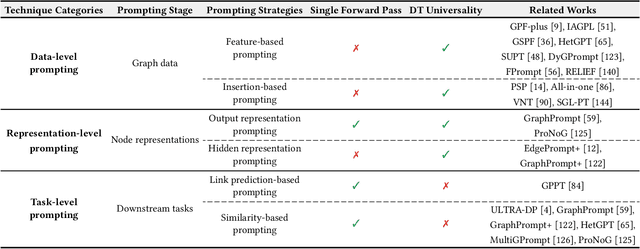
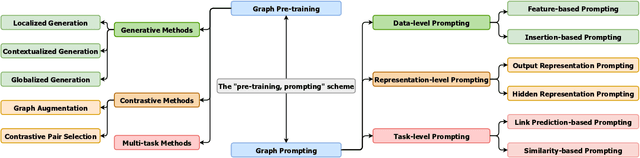
Abstract:Graph learning models have demonstrated great prowess in learning expressive representations from large-scale graph data in a wide variety of real-world scenarios. As a prevalent strategy for training powerful graph learning models, the "pre-training, adaptation" scheme first pre-trains graph learning models on unlabeled graph data in a self-supervised manner and then adapts them to specific downstream tasks. During the adaptation phase, graph prompting emerges as a promising approach that learns trainable prompts while keeping the pre-trained graph learning models unchanged. In this paper, we present a systematic review of recent advancements in graph prompting. First, we introduce representative graph pre-training methods that serve as the foundation step of graph prompting. Next, we review mainstream techniques in graph prompting and elaborate on how they design learnable prompts for graph prompting. Furthermore, we summarize the real-world applications of graph prompting from different domains. Finally, we discuss several open challenges in existing studies with promising future directions in this field.
From Static to Adaptive Defense: Federated Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning-Driven Moving Target Defense Against DoS Attacks in UAV Swarm Networks
Jun 09, 2025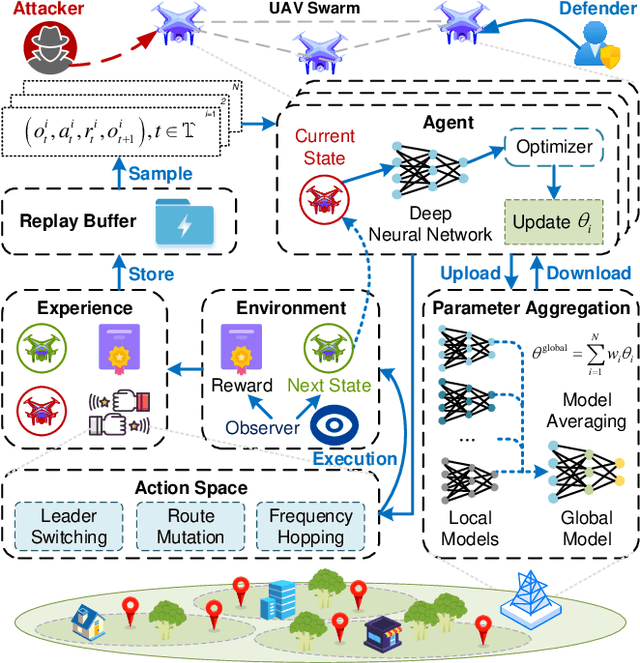
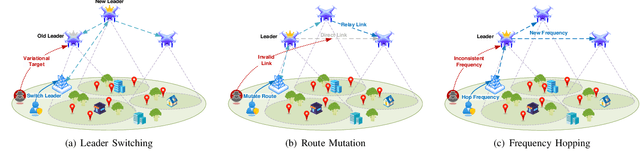
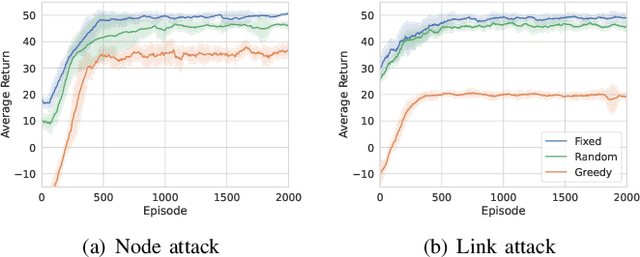
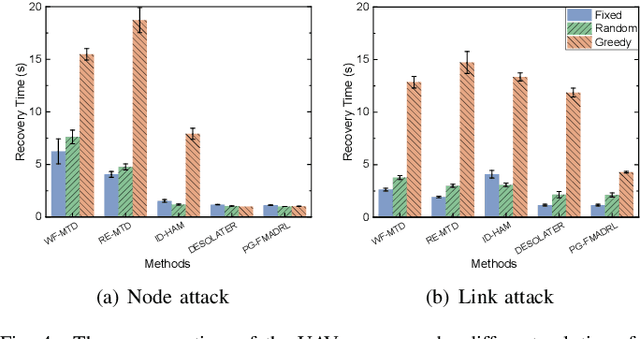
Abstract:The proliferation of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarms has enabled a wide range of mission-critical applications, but also exposes UAV networks to severe Denial-of-Service (DoS) threats due to their open wireless environment, dynamic topology, and resource constraints. Traditional static or centralized defense mechanisms are often inadequate for such dynamic and distributed scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a novel federated multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (FMADRL)-driven moving target defense (MTD) framework for proactive and adaptive DoS mitigation in UAV swarm networks. Specifically, we design three lightweight and coordinated MTD mechanisms, including leader switching, route mutation, and frequency hopping, that leverage the inherent flexibility of UAV swarms to disrupt attacker efforts and enhance network resilience. The defense problem is formulated as a multi-agent partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP), capturing the distributed, resource-constrained, and uncertain nature of UAV swarms under attack. Each UAV is equipped with a local policy agent that autonomously selects MTD actions based on partial observations and local experiences. By employing a policy gradient-based FMADRL algorithm, UAVs collaboratively optimize their defense policies via reward-weighted aggregation, enabling distributed learning without sharing raw data and thus reducing communication overhead. Extensive simulations demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving up to a 34.6% improvement in attack mitigation rate, a reduction in average recovery time of up to 94.6%, and decreases in energy consumption and defense cost by as much as 29.3% and 98.3%, respectively, while maintaining robust mission continuity under various DoS attack strategies.
MAPLE: Many-Shot Adaptive Pseudo-Labeling for In-Context Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) empowers Large Language Models (LLMs) to tackle diverse tasks by incorporating multiple input-output examples, known as demonstrations, into the input of LLMs. More recently, advancements in the expanded context windows of LLMs have led to many-shot ICL, which uses hundreds of demonstrations and outperforms few-shot ICL, which relies on fewer examples. However, this approach is often hindered by the high cost of obtaining large amounts of labeled data. To address this challenge, we propose Many-Shot Adaptive Pseudo-LabEling, namely MAPLE, a novel influence-based many-shot ICL framework that utilizes pseudo-labeled samples to compensate for the lack of label information. We first identify a subset of impactful unlabeled samples and perform pseudo-labeling on them by querying LLMs. These pseudo-labeled samples are then adaptively selected and tailored to each test query as input to improve the performance of many-shot ICL, without significant labeling costs. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework, showcasing its ability to enhance LLM adaptability and performance with limited labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge