Yi Dai
MISE: Meta-knowledge Inheritance for Social Media-Based Stressor Estimation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Stress haunts people in modern society, which may cause severe health issues if left unattended. With social media becoming an integral part of daily life, leveraging social media to detect stress has gained increasing attention. While the majority of the work focuses on classifying stress states and stress categories, this study introduce a new task aimed at estimating more specific stressors (like exam, writing paper, etc.) through users' posts on social media. Unfortunately, the diversity of stressors with many different classes but a few examples per class, combined with the consistent arising of new stressors over time, hinders the machine understanding of stressors. To this end, we cast the stressor estimation problem within a practical scenario few-shot learning setting, and propose a novel meta-learning based stressor estimation framework that is enhanced by a meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism. This model can not only learn generic stressor context through meta-learning, but also has a good generalization ability to estimate new stressors with little labeled data. A fundamental breakthrough in our approach lies in the inclusion of the meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism, which equips our model with the ability to prevent catastrophic forgetting when adapting to new stressors. The experimental results show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with the baselines. Additionally, we construct a social media-based stressor estimation dataset that can help train artificial intelligence models to facilitate human well-being. The dataset is now public at \href{https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/xinwangcs/stressor-cause-of-mental-health-problem-dataset}{\underline{Kaggle}} and \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/XinWangcs/Stressor}{\underline{Hugging Face}}.
Cognition Chain for Explainable Psychological Stress Detection on Social Media
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Stress is a pervasive global health issue that can lead to severe mental health problems. Early detection offers timely intervention and prevention of stress-related disorders. The current early detection models perform "black box" inference suffering from limited explainability and trust which blocks the real-world clinical application. Thanks to the generative properties introduced by the Large Language Models (LLMs), the decision and the prediction from such models are semi-interpretable through the corresponding description. However, the existing LLMs are mostly trained for general purposes without the guidance of psychological cognitive theory. To this end, we first highlight the importance of prior theory with the observation of performance boosted by the chain-of-thoughts tailored for stress detection. This method termed Cognition Chain explicates the generation of stress through a step-by-step cognitive perspective based on cognitive appraisal theory with a progress pipeline: Stimulus $\rightarrow$ Evaluation $\rightarrow$ Reaction $\rightarrow$ Stress State, guiding LLMs to provide comprehensive reasoning explanations. We further study the benefits brought by the proposed Cognition Chain format by utilising it as a synthetic dataset generation template for LLMs instruction-tuning and introduce CogInstruct, an instruction-tuning dataset for stress detection. This dataset is developed using a three-stage self-reflective annotation pipeline that enables LLMs to autonomously generate and refine instructional data. By instruction-tuning Llama3 with CogInstruct, we develop CogLLM, an explainable stress detection model. Evaluations demonstrate that CogLLM achieves outstanding performance while enhancing explainability. Our work contributes a novel approach by integrating cognitive theories into LLM reasoning processes, offering a promising direction for future explainable AI research.
SciPIP: An LLM-based Scientific Paper Idea Proposer
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:The exponential growth of knowledge and the increasing complexity of interdisciplinary research pose significant challenges for researchers, including information overload and difficulties in exploring novel ideas. The advancements in large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, have shown great potential in enhancing idea proposals, but how to effectively utilize large models for reasonable idea proposal has not been thoroughly explored. This paper proposes a scientific paper idea proposer (SciPIP). Based on a user-provided research background, SciPIP retrieves helpful papers from a literature database while leveraging the capabilities of LLMs to generate more novel and feasible ideas. To this end, 1) we construct a literature retrieval database, extracting lots of papers' multi-dimension information for fast access. Then, a literature retrieval method based on semantics, entity, and citation co-occurrences is proposed to search relevant literature from multiple aspects based on the user-provided background. 2) After literature retrieval, we introduce dual-path idea proposal strategies, where one path infers solutions from the retrieved literature and the other path generates original ideas through model brainstorming. We then combine the two to achieve a good balance between feasibility and originality. Through extensive experiments on the natural language processing (NLP) field, we demonstrate that SciPIP can retrieve citations similar to those of existing top conference papers and generate many ideas consistent with them. Additionally, we evaluate the originality of other ideas generated by SciPIP using large language models, further validating the effectiveness of our proposed method. The code and the database are released at https://github.com/cheerss/SciPIP.
Interpretable Video based Stress Detection with Self-Refine Chain-of-thought Reasoning
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Stress detection is a critical area of research with significant implications for health monitoring and intervention systems. In this paper, we propose a novel interpretable approach for video-based stress detection, leveraging self-refine chain-of-thought reasoning to enhance both accuracy and transparency in decision-making processes. Our method focuses on extracting subtle behavioral and physiological cues from video sequences that indicate stress levels. By incorporating a chain-of-thought reasoning mechanism, the system refines its predictions iteratively, ensuring that the decision-making process can be traced and explained. The model also learns to self-refine through feedback loops, improving its reasoning capabilities over time. We evaluate our approach on several public and private datasets, demonstrating its superior performance in comparison to traditional video-based stress detection methods. Additionally, we provide comprehensive insights into the interpretability of the model's predictions, making the system highly valuable for applications in both healthcare and human-computer interaction domains.
Cocobo: Exploring Large Language Models as the Engine for End-User Robot Programming
Jul 30, 2024Abstract:End-user development allows everyday users to tailor service robots or applications to their needs. One user-friendly approach is natural language programming. However, it encounters challenges such as an expansive user expression space and limited support for debugging and editing, which restrict its application in end-user programming. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) offers promising avenues for the translation and interpretation between human language instructions and the code executed by robots, but their application in end-user programming systems requires further study. We introduce Cocobo, a natural language programming system with interactive diagrams powered by LLMs. Cocobo employs LLMs to understand users' authoring intentions, generate and explain robot programs, and facilitate the conversion between executable code and flowchart representations. Our user study shows that Cocobo has a low learning curve, enabling even users with zero coding experience to customize robot programs successfully.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate significant capabilities but face challenges such as hallucination, outdated knowledge, and non-transparent, untraceable reasoning processes. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a promising solution by incorporating knowledge from external databases. This enhances the accuracy and credibility of the models, particularly for knowledge-intensive tasks, and allows for continuous knowledge updates and integration of domain-specific information. RAG synergistically merges LLMs' intrinsic knowledge with the vast, dynamic repositories of external databases. This comprehensive review paper offers a detailed examination of the progression of RAG paradigms, encompassing the Naive RAG, the Advanced RAG, and the Modular RAG. It meticulously scrutinizes the tripartite foundation of RAG frameworks, which includes the retrieval , the generation and the augmentation techniques. The paper highlights the state-of-the-art technologies embedded in each of these critical components, providing a profound understanding of the advancements in RAG systems. Furthermore, this paper introduces the metrics and benchmarks for assessing RAG models, along with the most up-to-date evaluation framework. In conclusion, the paper delineates prospective avenues for research, including the identification of challenges, the expansion of multi-modalities, and the progression of the RAG infrastructure and its ecosystem.
Exploring Large Language Models for Multi-Modal Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential for reliable and trustworthy machine learning. Recent multi-modal OOD detection leverages textual information from in-distribution (ID) class names for visual OOD detection, yet it currently neglects the rich contextual information of ID classes. Large language models (LLMs) encode a wealth of world knowledge and can be prompted to generate descriptive features for each class. Indiscriminately using such knowledge causes catastrophic damage to OOD detection due to LLMs' hallucinations, as is observed by our analysis. In this paper, we propose to apply world knowledge to enhance OOD detection performance through selective generation from LLMs. Specifically, we introduce a consistency-based uncertainty calibration method to estimate the confidence score of each generation. We further extract visual objects from each image to fully capitalize on the aforementioned world knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art.
Domain Incremental Lifelong Learning in an Open World
May 11, 2023Abstract:Lifelong learning (LL) is an important ability for NLP models to learn new tasks continuously. Architecture-based approaches are reported to be effective implementations for LL models. However, it is non-trivial to extend previous approaches to domain incremental LL scenarios since they either require access to task identities in the testing phase or cannot handle samples from unseen tasks. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Diana}: a \underline{d}ynam\underline{i}c \underline{a}rchitecture-based lifelo\underline{n}g le\underline{a}rning model that tries to learn a sequence of tasks with a prompt-enhanced language model. Four types of hierarchically organized prompts are used in Diana to capture knowledge from different granularities. Specifically, we dedicate task-level prompts to capture task-specific knowledge to retain high LL performances and maintain instance-level prompts to learn knowledge shared across input samples to improve the model's generalization performance. Moreover, we dedicate separate prompts to explicitly model unseen tasks and introduce a set of prompt key vectors to facilitate knowledge sharing between tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Diana outperforms state-of-the-art LL models, especially in handling unseen tasks. We release the code and data at \url{https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/DAMO-ConvAI/tree/main/diana}.
Long-Tailed Question Answering in an Open World
May 11, 2023Abstract:Real-world data often have an open long-tailed distribution, and building a unified QA model supporting various tasks is vital for practical QA applications. However, it is non-trivial to extend previous QA approaches since they either require access to seen tasks of adequate samples or do not explicitly model samples from unseen tasks. In this paper, we define Open Long-Tailed QA (OLTQA) as learning from long-tailed distributed data and optimizing performance over seen and unseen QA tasks. We propose an OLTQA model that encourages knowledge sharing between head, tail and unseen tasks, and explicitly mines knowledge from a large pre-trained language model (LM). Specifically, we organize our model through a pool of fine-grained components and dynamically combine these components for an input to facilitate knowledge sharing. A retrieve-then-rerank frame is further introduced to select in-context examples, which guild the LM to generate text that express knowledge for QA tasks. Moreover, a two-stage training approach is introduced to pre-train the framework by knowledge distillation (KD) from the LM and then jointly train the frame and a QA model through an adaptive mutual KD method. On a large-scale OLTQA dataset we curate from 43 existing QA datasets, our model consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art. We release the code and data at \url{https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/DAMO-ConvAI/tree/main/oltqa}.
VideoPipe 2022 Challenge: Real-World Video Understanding for Urban Pipe Inspection
Oct 20, 2022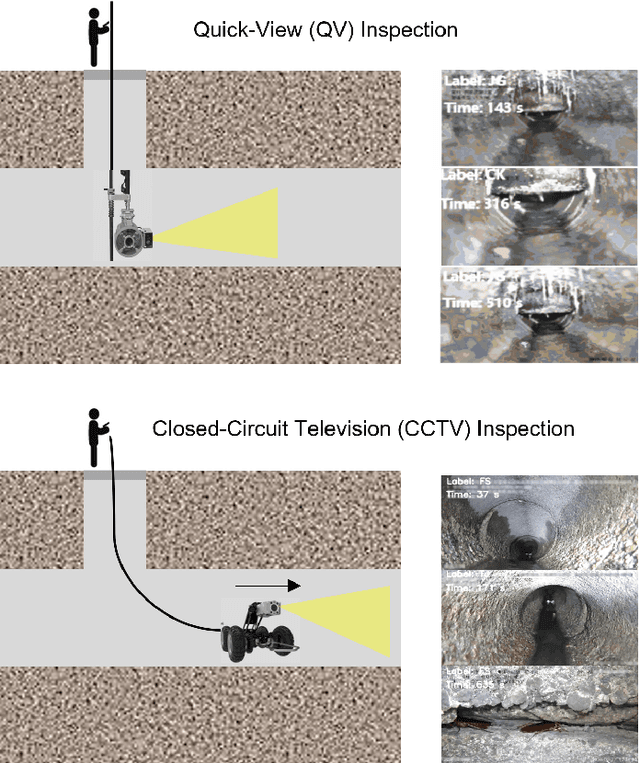

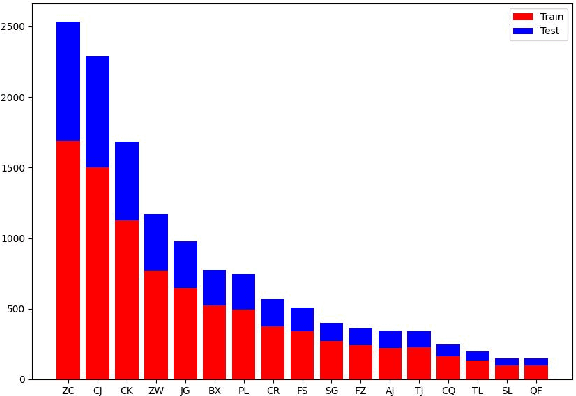
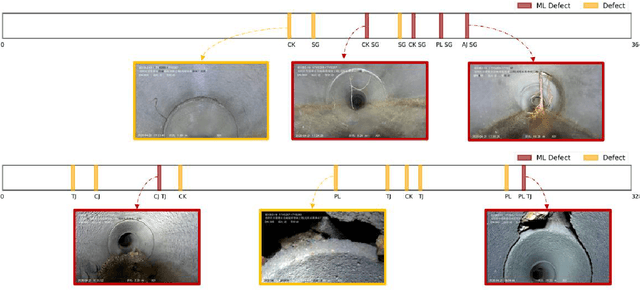
Abstract:Video understanding is an important problem in computer vision. Currently, the well-studied task in this research is human action recognition, where the clips are manually trimmed from the long videos, and a single class of human action is assumed for each clip. However, we may face more complicated scenarios in the industrial applications. For example, in the real-world urban pipe system, anomaly defects are fine-grained, multi-labeled, domain-relevant. To recognize them correctly, we need to understand the detailed video content. For this reason, we propose to advance research areas of video understanding, with a shift from traditional action recognition to industrial anomaly analysis. In particular, we introduce two high-quality video benchmarks, namely QV-Pipe and CCTV-Pipe, for anomaly inspection in the real-world urban pipe systems. Based on these new datasets, we will host two competitions including (1) Video Defect Classification on QV-Pipe and (2) Temporal Defect Localization on CCTV-Pipe. In this report, we describe the details of these benchmarks, the problem definitions of competition tracks, the evaluation metric, and the result summary. We expect that, this competition would bring new opportunities and challenges for video understanding in smart city and beyond. The details of our VideoPipe challenge can be found in https://videopipe.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge