Kaisheng Zeng
MISE: Meta-knowledge Inheritance for Social Media-Based Stressor Estimation
May 03, 2025Abstract:Stress haunts people in modern society, which may cause severe health issues if left unattended. With social media becoming an integral part of daily life, leveraging social media to detect stress has gained increasing attention. While the majority of the work focuses on classifying stress states and stress categories, this study introduce a new task aimed at estimating more specific stressors (like exam, writing paper, etc.) through users' posts on social media. Unfortunately, the diversity of stressors with many different classes but a few examples per class, combined with the consistent arising of new stressors over time, hinders the machine understanding of stressors. To this end, we cast the stressor estimation problem within a practical scenario few-shot learning setting, and propose a novel meta-learning based stressor estimation framework that is enhanced by a meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism. This model can not only learn generic stressor context through meta-learning, but also has a good generalization ability to estimate new stressors with little labeled data. A fundamental breakthrough in our approach lies in the inclusion of the meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism, which equips our model with the ability to prevent catastrophic forgetting when adapting to new stressors. The experimental results show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with the baselines. Additionally, we construct a social media-based stressor estimation dataset that can help train artificial intelligence models to facilitate human well-being. The dataset is now public at \href{https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/xinwangcs/stressor-cause-of-mental-health-problem-dataset}{\underline{Kaggle}} and \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/XinWangcs/Stressor}{\underline{Hugging Face}}.
EventSum: A Large-Scale Event-Centric Summarization Dataset for Chinese Multi-News Documents
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:In real life, many dynamic events, such as major disasters and large-scale sports events, evolve continuously over time. Obtaining an overview of these events can help people quickly understand the situation and respond more effectively. This is challenging because the key information of the event is often scattered across multiple documents, involving complex event knowledge understanding and reasoning, which is under-explored in previous work. Therefore, we proposed the Event-Centric Multi-Document Summarization (ECS) task, which aims to generate concise and comprehensive summaries of a given event based on multiple related news documents. Based on this, we constructed the EventSum dataset, which was constructed using Baidu Baike entries and underwent extensive human annotation, to facilitate relevant research. It is the first large scale Chinese multi-document summarization dataset, containing 5,100 events and a total of 57,984 news documents, with an average of 11.4 input news documents and 13,471 characters per event. To ensure data quality and mitigate potential data leakage, we adopted a multi-stage annotation approach for manually labeling the test set. Given the complexity of event-related information, existing metrics struggle to comprehensively assess the quality of generated summaries. We designed specific metrics including Event Recall, Argument Recall, Causal Recall, and Temporal Recall along with corresponding calculation methods for evaluation. We conducted comprehensive experiments on EventSum to evaluate the performance of advanced long-context Large Language Models (LLMs) on this task. Our experimental results indicate that: 1) The event-centric multi-document summarization task remains challenging for existing long-context LLMs; 2) The recall metrics we designed are crucial for evaluating the comprehensiveness of the summary information.
LLMAEL: Large Language Models are Good Context Augmenters for Entity Linking
Jul 04, 2024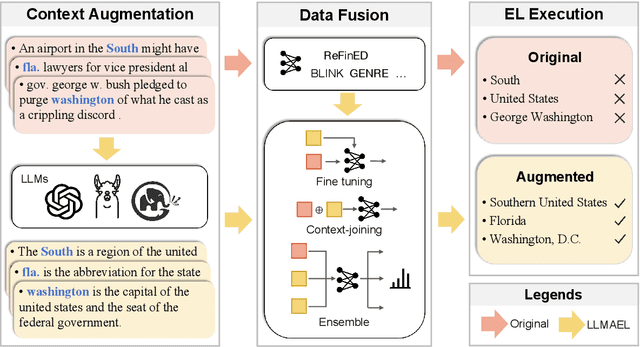
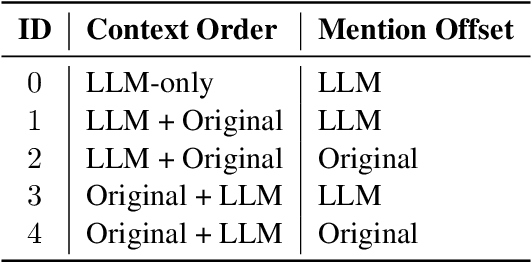
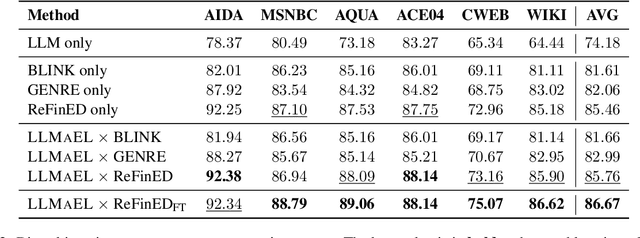
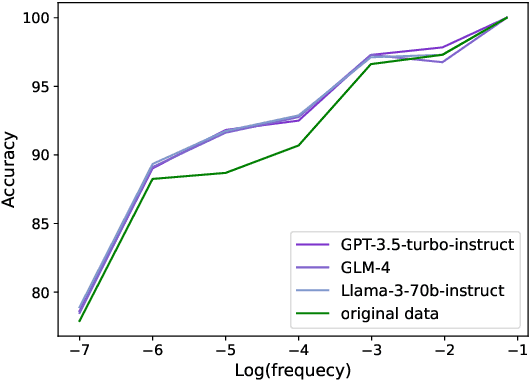
Abstract:Entity Linking (EL) models are well-trained at mapping mentions to their corresponding entities according to a given context. However, EL models struggle to disambiguate long-tail entities due to their limited training data. Meanwhile, large language models (LLMs) are more robust at interpreting uncommon mentions. Yet, due to a lack of specialized training, LLMs suffer at generating correct entity IDs. Furthermore, training an LLM to perform EL is cost-intensive. Building upon these insights, we introduce LLM-Augmented Entity Linking LLMAEL, a plug-and-play approach to enhance entity linking through LLM data augmentation. We leverage LLMs as knowledgeable context augmenters, generating mention-centered descriptions as additional input, while preserving traditional EL models for task specific processing. Experiments on 6 standard datasets show that the vanilla LLMAEL outperforms baseline EL models in most cases, while the fine-tuned LLMAEL set the new state-of-the-art results across all 6 benchmarks.
CMNEE: A Large-Scale Document-Level Event Extraction Dataset based on Open-Source Chinese Military News
Apr 18, 2024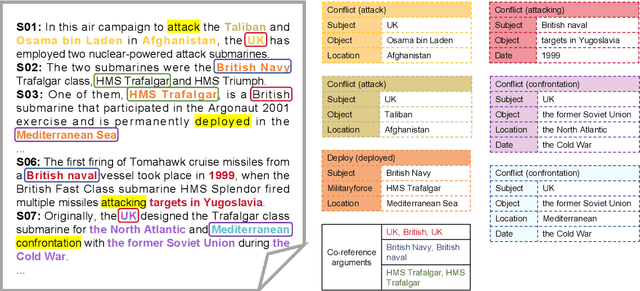
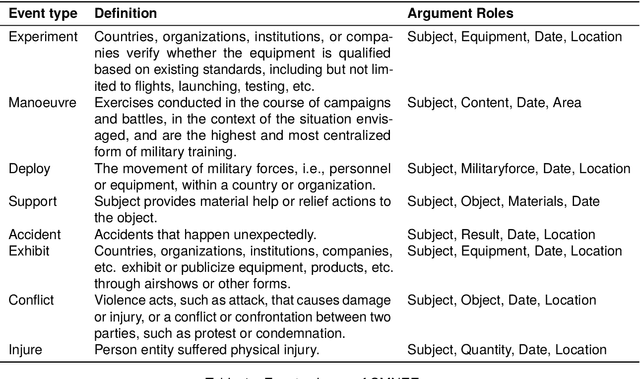
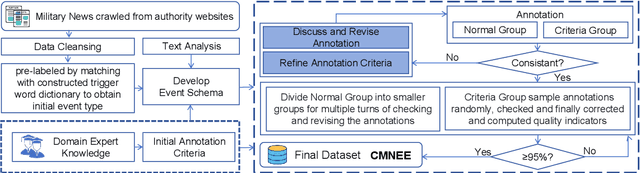

Abstract:Extracting structured event knowledge, including event triggers and corresponding arguments, from military texts is fundamental to many applications, such as intelligence analysis and decision assistance. However, event extraction in the military field faces the data scarcity problem, which impedes the research of event extraction models in this domain. To alleviate this problem, we propose CMNEE, a large-scale, document-level open-source Chinese Military News Event Extraction dataset. It contains 17,000 documents and 29,223 events, which are all manually annotated based on a pre-defined schema for the military domain including 8 event types and 11 argument role types. We designed a two-stage, multi-turns annotation strategy to ensure the quality of CMNEE and reproduced several state-of-the-art event extraction models with a systematic evaluation. The experimental results on CMNEE fall shorter than those on other domain datasets obviously, which demonstrates that event extraction for military domain poses unique challenges and requires further research efforts. Our code and data can be obtained from https://github.com/Mzzzhu/CMNEE.
Event-level Knowledge Editing
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:Knowledge editing aims at updating knowledge of large language models (LLMs) to prevent them from becoming outdated. Existing work edits LLMs at the level of factual knowledge triplets. However, natural knowledge updates in the real world come from the occurrences of new events rather than direct changes in factual triplets. In this paper, we propose a new task setting: event-level knowledge editing, which directly edits new events into LLMs and improves over conventional triplet-level editing on (1) Efficiency. A single event edit leads to updates in multiple entailed knowledge triplets. (2) Completeness. Beyond updating factual knowledge, event-level editing also requires considering the event influences and updating LLMs' knowledge about future trends. We construct a high-quality event-level editing benchmark ELKEN, consisting of 1,515 event edits, 6,449 questions about factual knowledge, and 10,150 questions about future tendencies. We systematically evaluate the performance of various knowledge editing methods and LLMs on this benchmark. We find that ELKEN poses significant challenges to existing knowledge editing approaches. Our codes and dataset are publicly released to facilitate further research.
When does In-context Learning Fall Short and Why? A Study on Specification-Heavy Tasks
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) has become the default method for using large language models (LLMs), making the exploration of its limitations and understanding the underlying causes crucial. In this paper, we find that ICL falls short of handling specification-heavy tasks, which are tasks with complicated and extensive task specifications, requiring several hours for ordinary humans to master, such as traditional information extraction tasks. The performance of ICL on these tasks mostly cannot reach half of the state-of-the-art results. To explore the reasons behind this failure, we conduct comprehensive experiments on 18 specification-heavy tasks with various LLMs and identify three primary reasons: inability to specifically understand context, misalignment in task schema comprehension with humans, and inadequate long-text understanding ability. Furthermore, we demonstrate that through fine-tuning, LLMs can achieve decent performance on these tasks, indicating that the failure of ICL is not an inherent flaw of LLMs, but rather a drawback of existing alignment methods that renders LLMs incapable of handling complicated specification-heavy tasks via ICL. To substantiate this, we perform dedicated instruction tuning on LLMs for these tasks and observe a notable improvement. We hope the analyses in this paper could facilitate advancements in alignment methods enabling LLMs to meet more sophisticated human demands.
MAVEN-Arg: Completing the Puzzle of All-in-One Event Understanding Dataset with Event Argument Annotation
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Understanding events in texts is a core objective of natural language understanding, which requires detecting event occurrences, extracting event arguments, and analyzing inter-event relationships. However, due to the annotation challenges brought by task complexity, a large-scale dataset covering the full process of event understanding has long been absent. In this paper, we introduce MAVEN-Arg, which augments MAVEN datasets with event argument annotations, making the first all-in-one dataset supporting event detection, event argument extraction (EAE), and event relation extraction. As an EAE benchmark, MAVEN-Arg offers three main advantages: (1) a comprehensive schema covering 162 event types and 612 argument roles, all with expert-written definitions and examples; (2) a large data scale, containing 98,591 events and 290,613 arguments obtained with laborious human annotation; (3) the exhaustive annotation supporting all task variants of EAE, which annotates both entity and non-entity event arguments in document level. Experiments indicate that MAVEN-Arg is quite challenging for both fine-tuned EAE models and proprietary large language models (LLMs). Furthermore, to demonstrate the benefits of an all-in-one dataset, we preliminarily explore a potential application, future event prediction, with LLMs. MAVEN-Arg and our code can be obtained from https://github.com/THU-KEG/MAVEN-Argument.
Mastering the Task of Open Information Extraction with Large Language Models and Consistent Reasoning Environment
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Open Information Extraction (OIE) aims to extract objective structured knowledge from natural texts, which has attracted growing attention to build dedicated models with human experience. As the large language models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable in-context learning capabilities, a question arises as to whether the task of OIE can be effectively tackled with this paradigm? In this paper, we explore solving the OIE problem by constructing an appropriate reasoning environment for LLMs. Specifically, we first propose a method to effectively estimate the discrepancy of syntactic distribution between a LLM and test samples, which can serve as correlation evidence for preparing positive demonstrations. Upon the evidence, we introduce a simple yet effective mechanism to establish the reasoning environment for LLMs on specific tasks. Without bells and whistles, experimental results on the standard CaRB benchmark demonstrate that our $6$-shot approach outperforms state-of-the-art supervised method, achieving an $55.3$ $F_1$ score. Further experiments on TACRED and ACE05 show that our method can naturally generalize to other information extraction tasks, resulting in improvements of $5.7$ and $6.8$ $F_1$ scores, respectively.
Exploring Large Language Models for Multi-Modal Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential for reliable and trustworthy machine learning. Recent multi-modal OOD detection leverages textual information from in-distribution (ID) class names for visual OOD detection, yet it currently neglects the rich contextual information of ID classes. Large language models (LLMs) encode a wealth of world knowledge and can be prompted to generate descriptive features for each class. Indiscriminately using such knowledge causes catastrophic damage to OOD detection due to LLMs' hallucinations, as is observed by our analysis. In this paper, we propose to apply world knowledge to enhance OOD detection performance through selective generation from LLMs. Specifically, we introduce a consistency-based uncertainty calibration method to estimate the confidence score of each generation. We further extract visual objects from each image to fully capitalize on the aforementioned world knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art.
OmniEvent: A Comprehensive, Fair, and Easy-to-Use Toolkit for Event Understanding
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:Event understanding aims at understanding the content and relationship of events within texts, which covers multiple complicated information extraction tasks: event detection, event argument extraction, and event relation extraction. To facilitate related research and application, we present an event understanding toolkit OmniEvent, which features three desiderata: (1) Comprehensive. OmniEvent supports mainstream modeling paradigms of all the event understanding tasks and the processing of 15 widely-used English and Chinese datasets. (2) Fair. OmniEvent carefully handles the inconspicuous evaluation pitfalls reported in Peng et al. (2023), which ensures fair comparisons between different models. (3) Easy-to-use. OmniEvent is designed to be easily used by users with varying needs. We provide off-the-shelf models that can be directly deployed as web services. The modular framework also enables users to easily implement and evaluate new event understanding models with OmniEvent. The toolkit (https://github.com/THU-KEG/OmniEvent) is publicly released along with the demonstration website and video (https://omnievent.xlore.cn/).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge