Xinyi Ye
FastUMI-100K: Advancing Data-driven Robotic Manipulation with a Large-scale UMI-style Dataset
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Data-driven robotic manipulation learning depends on large-scale, high-quality expert demonstration datasets. However, existing datasets, which primarily rely on human teleoperated robot collection, are limited in terms of scalability, trajectory smoothness, and applicability across different robotic embodiments in real-world environments. In this paper, we present FastUMI-100K, a large-scale UMI-style multimodal demonstration dataset, designed to overcome these limitations and meet the growing complexity of real-world manipulation tasks. Collected by FastUMI, a novel robotic system featuring a modular, hardware-decoupled mechanical design and an integrated lightweight tracking system, FastUMI-100K offers a more scalable, flexible, and adaptable solution to fulfill the diverse requirements of real-world robot demonstration data. Specifically, FastUMI-100K contains over 100K+ demonstration trajectories collected across representative household environments, covering 54 tasks and hundreds of object types. Our dataset integrates multimodal streams, including end-effector states, multi-view wrist-mounted fisheye images and textual annotations. Each trajectory has a length ranging from 120 to 500 frames. Experimental results demonstrate that FastUMI-100K enables high policy success rates across various baseline algorithms, confirming its robustness, adaptability, and real-world applicability for solving complex, dynamic manipulation challenges. The source code and dataset will be released in this link https://github.com/MrKeee/FastUMI-100K.
Trajectory Conditioned Cross-embodiment Skill Transfer
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Learning manipulation skills from human demonstration videos presents a promising yet challenging problem, primarily due to the significant embodiment gap between human body and robot manipulators. Existing methods rely on paired datasets or hand-crafted rewards, which limit scalability and generalization. We propose TrajSkill, a framework for Trajectory Conditioned Cross-embodiment Skill Transfer, enabling robots to acquire manipulation skills directly from human demonstration videos. Our key insight is to represent human motions as sparse optical flow trajectories, which serve as embodiment-agnostic motion cues by removing morphological variations while preserving essential dynamics. Conditioned on these trajectories together with visual and textual inputs, TrajSkill jointly synthesizes temporally consistent robot manipulation videos and translates them into executable actions, thereby achieving cross-embodiment skill transfer. Extensive experiments are conducted, and the results on simulation data (MetaWorld) show that TrajSkill reduces FVD by 39.6\% and KVD by 36.6\% compared with the state-of-the-art, and improves cross-embodiment success rate by up to 16.7\%. Real-robot experiments in kitchen manipulation tasks further validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating practical human-to-robot skill transfer across embodiments.
EmbodiedOneVision: Interleaved Vision-Text-Action Pretraining for General Robot Control
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:The human ability to seamlessly perform multimodal reasoning and physical interaction in the open world is a core goal for general-purpose embodied intelligent systems. Recent vision-language-action (VLA) models, which are co-trained on large-scale robot and visual-text data, have demonstrated notable progress in general robot control. However, they still fail to achieve human-level flexibility in interleaved reasoning and interaction. In this work, introduce EO-Robotics, consists of EO-1 model and EO-Data1.5M dataset. EO-1 is a unified embodied foundation model that achieves superior performance in multimodal embodied reasoning and robot control through interleaved vision-text-action pre-training. The development of EO-1 is based on two key pillars: (i) a unified architecture that processes multimodal inputs indiscriminately (image, text, video, and action), and (ii) a massive, high-quality multimodal embodied reasoning dataset, EO-Data1.5M, which contains over 1.5 million samples with emphasis on interleaved vision-text-action comprehension. EO-1 is trained through synergies between auto-regressive decoding and flow matching denoising on EO-Data1.5M, enabling seamless robot action generation and multimodal embodied reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of interleaved vision-text-action learning for open-world understanding and generalization, validated through a variety of long-horizon, dexterous manipulation tasks across multiple embodiments. This paper details the architecture of EO-1, the data construction strategy of EO-Data1.5M, and the training methodology, offering valuable insights for developing advanced embodied foundation models.
OpenFly: A Versatile Toolchain and Large-scale Benchmark for Aerial Vision-Language Navigation
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) aims to guide agents through an environment by leveraging both language instructions and visual cues, playing a pivotal role in embodied AI. Indoor VLN has been extensively studied, whereas outdoor aerial VLN remains underexplored. The potential reason is that outdoor aerial view encompasses vast areas, making data collection more challenging, which results in a lack of benchmarks. To address this problem, we propose OpenFly, a platform comprising a versatile toolchain and large-scale benchmark for aerial VLN. Firstly, we develop a highly automated toolchain for data collection, enabling automatic point cloud acquisition, scene semantic segmentation, flight trajectory creation, and instruction generation. Secondly, based on the toolchain, we construct a large-scale aerial VLN dataset with 100k trajectories, covering diverse heights and lengths across 18 scenes. The corresponding visual data are generated using various rendering engines and advanced techniques, including Unreal Engine, GTA V, Google Earth, and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D GS). All data exhibit high visual quality. Particularly, 3D GS supports real-to-sim rendering, further enhancing the realism of the dataset. Thirdly, we propose OpenFly-Agent, a keyframe-aware VLN model, which takes language instructions, current observations, and historical keyframes as input, and outputs flight actions directly. Extensive analyses and experiments are conducted, showcasing the superiority of our OpenFly platform and OpenFly-Agent. The toolchain, dataset, and codes will be open-sourced.
SpatialVLA: Exploring Spatial Representations for Visual-Language-Action Model
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we claim that spatial understanding is the keypoint in robot manipulation, and propose SpatialVLA to explore effective spatial representations for the robot foundation model. Specifically, we introduce Ego3D Position Encoding to inject 3D information into the input observations of the visual-language-action model, and propose Adaptive Action Grids to represent spatial robot movement actions with adaptive discretized action grids, facilitating learning generalizable and transferrable spatial action knowledge for cross-robot control. SpatialVLA is first pre-trained on top of a vision-language model with 1.1 Million real-world robot episodes, to learn a generalist manipulation policy across multiple robot environments and tasks. After pre-training, SpatialVLA is directly applied to perform numerous tasks in a zero-shot manner. The superior results in both simulation and real-world robots demonstrate its advantage of inferring complex robot motion trajectories and its strong in-domain multi-task generalization ability. We further show the proposed Adaptive Action Grids offer a new and effective way to fine-tune the pre-trained SpatialVLA model for new simulation and real-world setups, where the pre-learned action grids are re-discretized to capture robot-specific spatial action movements of new setups. The superior results from extensive evaluations demonstrate the exceptional in-distribution generalization and out-of-distribution adaptation capability, highlighting the crucial benefit of the proposed spatial-aware representations for generalist robot policy learning. All the details and codes will be open-sourced.
DreamMover: Leveraging the Prior of Diffusion Models for Image Interpolation with Large Motion
Sep 15, 2024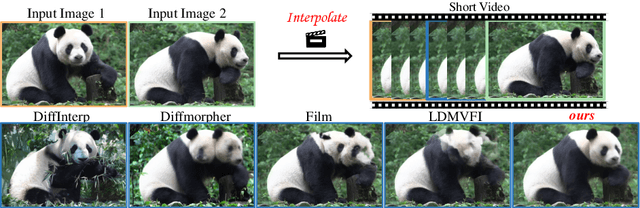
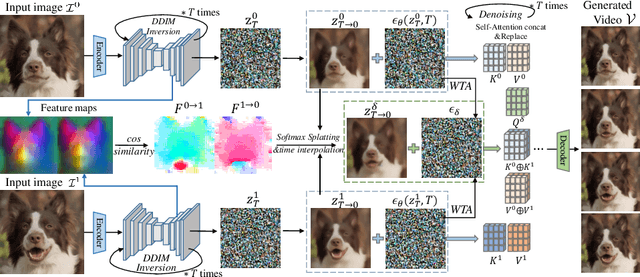
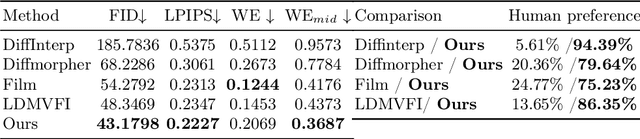

Abstract:We study the problem of generating intermediate images from image pairs with large motion while maintaining semantic consistency. Due to the large motion, the intermediate semantic information may be absent in input images. Existing methods either limit to small motion or focus on topologically similar objects, leading to artifacts and inconsistency in the interpolation results. To overcome this challenge, we delve into pre-trained image diffusion models for their capabilities in semantic cognition and representations, ensuring consistent expression of the absent intermediate semantic representations with the input. To this end, we propose DreamMover, a novel image interpolation framework with three main components: 1) A natural flow estimator based on the diffusion model that can implicitly reason about the semantic correspondence between two images. 2) To avoid the loss of detailed information during fusion, our key insight is to fuse information in two parts, high-level space and low-level space. 3) To enhance the consistency between the generated images and input, we propose the self-attention concatenation and replacement approach. Lastly, we present a challenging benchmark dataset InterpBench to evaluate the semantic consistency of generated results. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our project is available at https://dreamm0ver.github.io .
Lensless fiber endomicroscopic phase imaging with speckle-conditioned diffusion model
Jul 26, 2024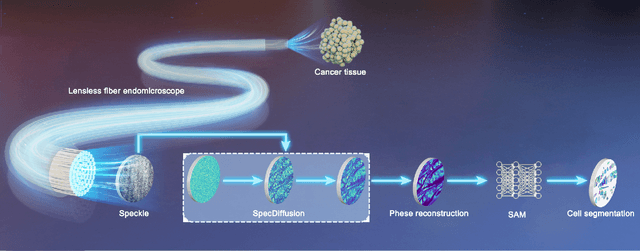
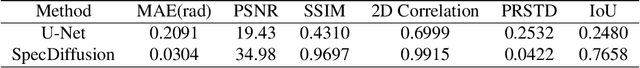
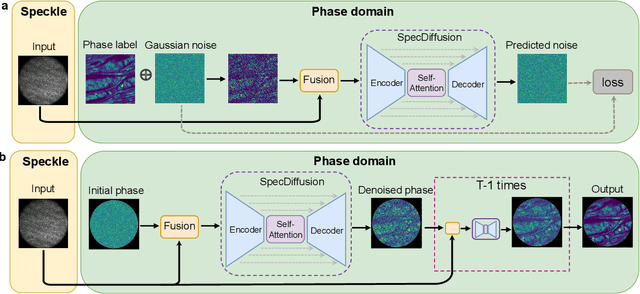
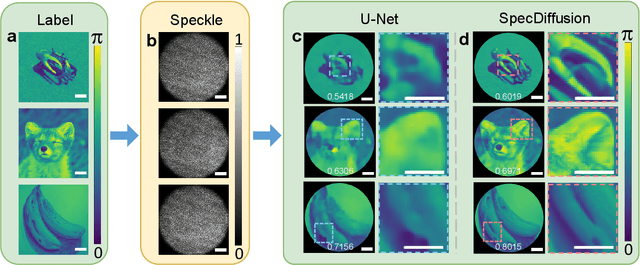
Abstract:Lensless fiber endomicroscope is an emerging tool for in-vivo microscopic imaging, where quantitative phase imaging (QPI) can be utilized as a label-free method to enhance image contrast. However, existing single-shot phase reconstruction methods through lensless fiber endomicroscope typically perform well on simple images but struggle with complex microscopic structures. Here, we propose a speckle-conditioned diffusion model (SpecDiffusion), which reconstructs phase images directly from speckles captured at the detection side of a multi-core fiber (MCF). Unlike conventional neural networks, SpecDiffusion employs iterative phase denoising steps for speckle-driven phase reconstruction. The iteration scheme allows SpecDiffusion to break down the phase reconstruction process into multiple steps, gradually building up to the final phase image. This attribute alleviates the computation challenge at each step and enables the reconstruction of rich details in complex microscopic images. To validate its efficacy, we build an optical system to capture speckles from MCF and construct a dataset consisting of 100,000 paired images. SpecDiffusion provides high-fidelity phase reconstruction results and shows powerful generalization capacity for unseen objects, such as test charts and biological tissues, reducing the average mean absolute error of the reconstructed tissue images by 7 times. Furthermore, the reconstructed tissue images using SpecDiffusion shows higher accuracy in zero-shot cell segmentation tasks compared to the conventional method, demonstrating the potential for further cell morphology analysis through the learning-based lensless fiber endomicroscope. SpecDiffusion offers a precise and generalized method to phase reconstruction through scattering media, including MCFs, opening new perspective in lensless fiber endomicroscopic imaging.
Fast Generalizable Gaussian Splatting Reconstruction from Multi-View Stereo
May 20, 2024



Abstract:We present MVSGaussian, a new generalizable 3D Gaussian representation approach derived from Multi-View Stereo (MVS) that can efficiently reconstruct unseen scenes. Specifically, 1) we leverage MVS to encode geometry-aware Gaussian representations and decode them into Gaussian parameters. 2) To further enhance performance, we propose a hybrid Gaussian rendering that integrates an efficient volume rendering design for novel view synthesis. 3) To support fast fine-tuning for specific scenes, we introduce a multi-view geometric consistent aggregation strategy to effectively aggregate the point clouds generated by the generalizable model, serving as the initialization for per-scene optimization. Compared with previous generalizable NeRF-based methods, which typically require minutes of fine-tuning and seconds of rendering per image, MVSGaussian achieves real-time rendering with better synthesis quality for each scene. Compared with the vanilla 3D-GS, MVSGaussian achieves better view synthesis with less training computational cost. Extensive experiments on DTU, Real Forward-facing, NeRF Synthetic, and Tanks and Temples datasets validate that MVSGaussian attains state-of-the-art performance with convincing generalizability, real-time rendering speed, and fast per-scene optimization.
Geometry-aware Reconstruction and Fusion-refined Rendering for Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields
Apr 26, 2024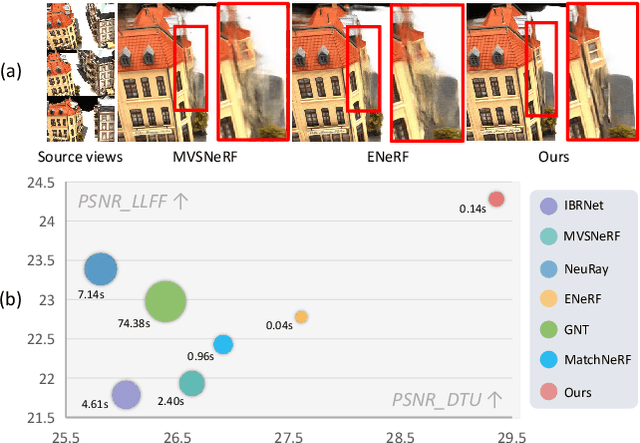
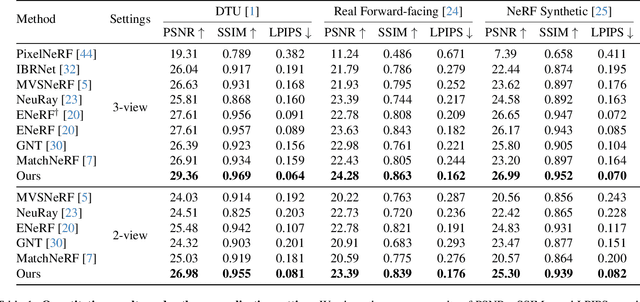
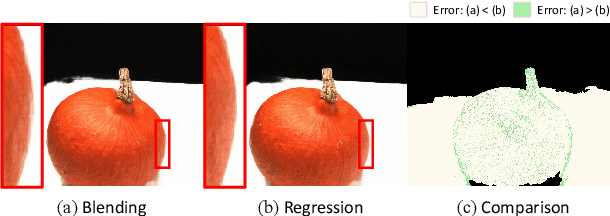
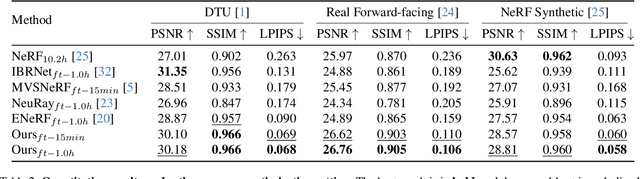
Abstract:Generalizable NeRF aims to synthesize novel views for unseen scenes. Common practices involve constructing variance-based cost volumes for geometry reconstruction and encoding 3D descriptors for decoding novel views. However, existing methods show limited generalization ability in challenging conditions due to inaccurate geometry, sub-optimal descriptors, and decoding strategies. We address these issues point by point. First, we find the variance-based cost volume exhibits failure patterns as the features of pixels corresponding to the same point can be inconsistent across different views due to occlusions or reflections. We introduce an Adaptive Cost Aggregation (ACA) approach to amplify the contribution of consistent pixel pairs and suppress inconsistent ones. Unlike previous methods that solely fuse 2D features into descriptors, our approach introduces a Spatial-View Aggregator (SVA) to incorporate 3D context into descriptors through spatial and inter-view interaction. When decoding the descriptors, we observe the two existing decoding strategies excel in different areas, which are complementary. A Consistency-Aware Fusion (CAF) strategy is proposed to leverage the advantages of both. We incorporate the above ACA, SVA, and CAF into a coarse-to-fine framework, termed Geometry-aware Reconstruction and Fusion-refined Rendering (GeFu). GeFu attains state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/TQTQliu/GeFu .
3D Multi-frame Fusion for Video Stabilization
Apr 19, 2024
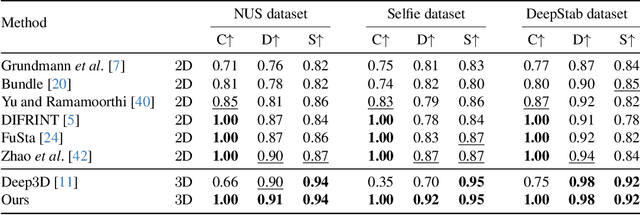
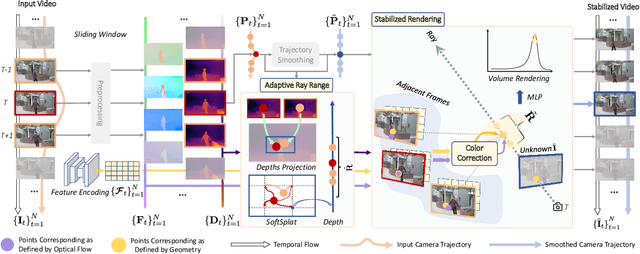

Abstract:In this paper, we present RStab, a novel framework for video stabilization that integrates 3D multi-frame fusion through volume rendering. Departing from conventional methods, we introduce a 3D multi-frame perspective to generate stabilized images, addressing the challenge of full-frame generation while preserving structure. The core of our approach lies in Stabilized Rendering (SR), a volume rendering module, which extends beyond the image fusion by incorporating feature fusion. The core of our RStab framework lies in Stabilized Rendering (SR), a volume rendering module, fusing multi-frame information in 3D space. Specifically, SR involves warping features and colors from multiple frames by projection, fusing them into descriptors to render the stabilized image. However, the precision of warped information depends on the projection accuracy, a factor significantly influenced by dynamic regions. In response, we introduce the Adaptive Ray Range (ARR) module to integrate depth priors, adaptively defining the sampling range for the projection process. Additionally, we propose Color Correction (CC) assisting geometric constraints with optical flow for accurate color aggregation. Thanks to the three modules, our RStab demonstrates superior performance compared with previous stabilizers in the field of view (FOV), image quality, and video stability across various datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge