Haoming Song
Information Filtering via Variational Regularization for Robot Manipulation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Diffusion-based visuomotor policies built on 3D visual representations have achieved strong performance in learning complex robotic skills. However, most existing methods employ an oversized denoising decoder. While increasing model capacity can improve denoising, empirical evidence suggests that it also introduces redundancy and noise in intermediate feature blocks. Crucially, we find that randomly masking backbone features at inference time (without changing training) can improve performance, confirming the presence of task-irrelevant noise in intermediate features. To this end, we propose Variational Regularization (VR), a lightweight module that imposes a timestep-conditioned Gaussian over backbone features and applies a KL-divergence regularizer, forming an adaptive information bottleneck. Extensive experiments on three simulation benchmarks (RoboTwin2.0, Adroit, and MetaWorld) show that, compared to the baseline DP3, our approach improves the success rate by 6.1% on RoboTwin2.0 and by 4.1% on Adroit and MetaWorld, achieving new state-of-the-art results. Real-world experiments further demonstrate that our method performs well in practical deployments. Code will released.
PocketDP3: Efficient Pocket-Scale 3D Visuomotor Policy
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recently, 3D vision-based diffusion policies have shown strong capability in learning complex robotic manipulation skills. However, a common architectural mismatch exists in these models: a tiny yet efficient point-cloud encoder is often paired with a massive decoder. Given a compact scene representation, we argue that this may lead to substantial parameter waste in the decoder. Motivated by this observation, we propose PocketDP3, a pocket-scale 3D diffusion policy that replaces the heavy conditional U-Net decoder used in prior methods with a lightweight Diffusion Mixer (DiM) built on MLP-Mixer blocks. This architecture enables efficient fusion across temporal and channel dimensions, significantly reducing model size. Notably, without any additional consistency distillation techniques, our method supports two-step inference without sacrificing performance, improving practicality for real-time deployment. Across three simulation benchmarks--RoboTwin2.0, Adroit, and MetaWorld--PocketDP3 achieves state-of-the-art performance with fewer than 1% of the parameters of prior methods, while also accelerating inference. Real-world experiments further demonstrate the practicality and transferability of our method in real-world settings. Code will be released.
Advances and Innovations in the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models and vision-languageaction models have significantly driven progress in Embodied AI. As the field transitions toward more complex task scenarios, multi-agent system frameworks are becoming essential for achieving scalable, efficient, and collaborative solutions. This shift is fueled by three primary factors: increasing agent capabilities, enhancing system efficiency through task delegation, and enabling advanced human-agent interactions. To address the challenges posed by multi-agent collaboration, we propose the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge, held at the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on SpaVLE. The competition focuses on two critical areas: planning and control, where participants explore multi-agent embodied planning using vision-language models (VLMs) to coordinate tasks and policy execution to perform robotic manipulation in dynamic environments. By evaluating solutions submitted by participants, the challenge provides valuable insights into the design and coordination of embodied multi-agent systems, contributing to the future development of advanced collaborative AI systems.
Are We Ready for RL in Text-to-3D Generation? A Progressive Investigation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL), earlier proven to be effective in large language and multi-modal models, has been successfully extended to enhance 2D image generation recently. However, applying RL to 3D generation remains largely unexplored due to the higher spatial complexity of 3D objects, which require globally consistent geometry and fine-grained local textures. This makes 3D generation significantly sensitive to reward designs and RL algorithms. To address these challenges, we conduct the first systematic study of RL for text-to-3D autoregressive generation across several dimensions. (1) Reward designs: We evaluate reward dimensions and model choices, showing that alignment with human preference is crucial, and that general multi-modal models provide robust signal for 3D attributes. (2) RL algorithms: We study GRPO variants, highlighting the effectiveness of token-level optimization, and further investigate the scaling of training data and iterations. (3) Text-to-3D Benchmarks: Since existing benchmarks fail to measure implicit reasoning abilities in 3D generation models, we introduce MME-3DR. (4) Advanced RL paradigms: Motivated by the natural hierarchy of 3D generation, we propose Hi-GRPO, which optimizes the global-to-local hierarchical 3D generation through dedicated reward ensembles. Based on these insights, we develop AR3D-R1, the first RL-enhanced text-to-3D model, expert from coarse shape to texture refinement. We hope this study provides insights into RL-driven reasoning for 3D generation. Code is released at https://github.com/Ivan-Tang-3D/3DGen-R1.
FastUMI-100K: Advancing Data-driven Robotic Manipulation with a Large-scale UMI-style Dataset
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Data-driven robotic manipulation learning depends on large-scale, high-quality expert demonstration datasets. However, existing datasets, which primarily rely on human teleoperated robot collection, are limited in terms of scalability, trajectory smoothness, and applicability across different robotic embodiments in real-world environments. In this paper, we present FastUMI-100K, a large-scale UMI-style multimodal demonstration dataset, designed to overcome these limitations and meet the growing complexity of real-world manipulation tasks. Collected by FastUMI, a novel robotic system featuring a modular, hardware-decoupled mechanical design and an integrated lightweight tracking system, FastUMI-100K offers a more scalable, flexible, and adaptable solution to fulfill the diverse requirements of real-world robot demonstration data. Specifically, FastUMI-100K contains over 100K+ demonstration trajectories collected across representative household environments, covering 54 tasks and hundreds of object types. Our dataset integrates multimodal streams, including end-effector states, multi-view wrist-mounted fisheye images and textual annotations. Each trajectory has a length ranging from 120 to 500 frames. Experimental results demonstrate that FastUMI-100K enables high policy success rates across various baseline algorithms, confirming its robustness, adaptability, and real-world applicability for solving complex, dynamic manipulation challenges. The source code and dataset will be released in this link https://github.com/MrKeee/FastUMI-100K.
Trajectory Conditioned Cross-embodiment Skill Transfer
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Learning manipulation skills from human demonstration videos presents a promising yet challenging problem, primarily due to the significant embodiment gap between human body and robot manipulators. Existing methods rely on paired datasets or hand-crafted rewards, which limit scalability and generalization. We propose TrajSkill, a framework for Trajectory Conditioned Cross-embodiment Skill Transfer, enabling robots to acquire manipulation skills directly from human demonstration videos. Our key insight is to represent human motions as sparse optical flow trajectories, which serve as embodiment-agnostic motion cues by removing morphological variations while preserving essential dynamics. Conditioned on these trajectories together with visual and textual inputs, TrajSkill jointly synthesizes temporally consistent robot manipulation videos and translates them into executable actions, thereby achieving cross-embodiment skill transfer. Extensive experiments are conducted, and the results on simulation data (MetaWorld) show that TrajSkill reduces FVD by 39.6\% and KVD by 36.6\% compared with the state-of-the-art, and improves cross-embodiment success rate by up to 16.7\%. Real-robot experiments in kitchen manipulation tasks further validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating practical human-to-robot skill transfer across embodiments.
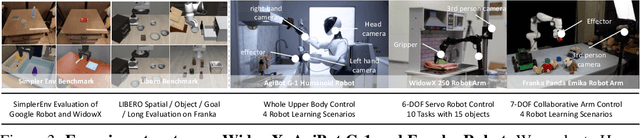
F1: A Vision-Language-Action Model Bridging Understanding and Generation to Actions
Sep 09, 2025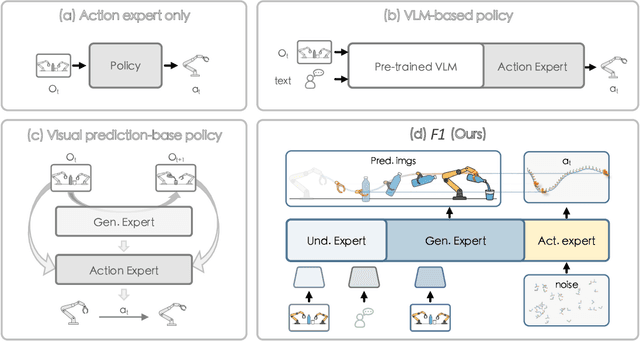

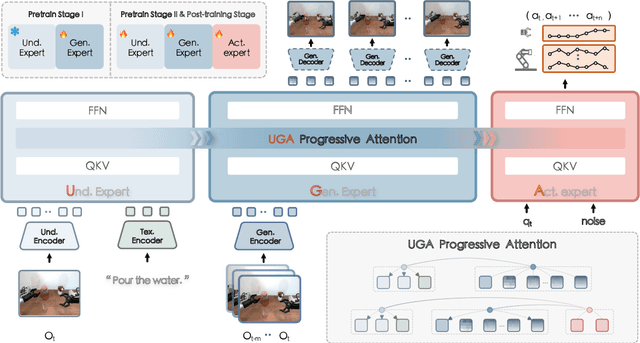

Abstract:Executing language-conditioned tasks in dynamic visual environments remains a central challenge in embodied AI. Existing Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models predominantly adopt reactive state-to-action mappings, often leading to short-sighted behaviors and poor robustness in dynamic scenes. In this paper, we introduce F1, a pretrained VLA framework which integrates the visual foresight generation into decision-making pipeline. F1 adopts a Mixture-of-Transformer architecture with dedicated modules for perception, foresight generation, and control, thereby bridging understanding, generation, and actions. At its core, F1 employs a next-scale prediction mechanism to synthesize goal-conditioned visual foresight as explicit planning targets. By forecasting plausible future visual states, F1 reformulates action generation as a foresight-guided inverse dynamics problem, enabling actions that implicitly achieve visual goals. To endow F1 with robust and generalizable capabilities, we propose a three-stage training recipe on an extensive dataset comprising over 330k trajectories across 136 diverse tasks. This training scheme enhances modular reasoning and equips the model with transferable visual foresight, which is critical for complex and dynamic environments. Extensive evaluations on real-world tasks and simulation benchmarks demonstrate F1 consistently outperforms existing approaches, achieving substantial gains in both task success rate and generalization ability.
EmbodiedOneVision: Interleaved Vision-Text-Action Pretraining for General Robot Control
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:The human ability to seamlessly perform multimodal reasoning and physical interaction in the open world is a core goal for general-purpose embodied intelligent systems. Recent vision-language-action (VLA) models, which are co-trained on large-scale robot and visual-text data, have demonstrated notable progress in general robot control. However, they still fail to achieve human-level flexibility in interleaved reasoning and interaction. In this work, introduce EO-Robotics, consists of EO-1 model and EO-Data1.5M dataset. EO-1 is a unified embodied foundation model that achieves superior performance in multimodal embodied reasoning and robot control through interleaved vision-text-action pre-training. The development of EO-1 is based on two key pillars: (i) a unified architecture that processes multimodal inputs indiscriminately (image, text, video, and action), and (ii) a massive, high-quality multimodal embodied reasoning dataset, EO-Data1.5M, which contains over 1.5 million samples with emphasis on interleaved vision-text-action comprehension. EO-1 is trained through synergies between auto-regressive decoding and flow matching denoising on EO-Data1.5M, enabling seamless robot action generation and multimodal embodied reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of interleaved vision-text-action learning for open-world understanding and generalization, validated through a variety of long-horizon, dexterous manipulation tasks across multiple embodiments. This paper details the architecture of EO-1, the data construction strategy of EO-Data1.5M, and the training methodology, offering valuable insights for developing advanced embodied foundation models.
Hume: Introducing System-2 Thinking in Visual-Language-Action Model
May 29, 2025


Abstract:Humans practice slow thinking before performing actual actions when handling complex tasks in the physical world. This thinking paradigm, recently, has achieved remarkable advancement in boosting Large Language Models (LLMs) to solve complex tasks in digital domains. However, the potential of slow thinking remains largely unexplored for robotic foundation models interacting with the physical world. In this work, we propose Hume: a dual-system Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model with value-guided System-2 thinking and cascaded action denoising, exploring human-like thinking capabilities of Vision-Language-Action models for dexterous robot control. System 2 of Hume implements value-Guided thinking by extending a Vision-Language-Action Model backbone with a novel value-query head to estimate the state-action value of predicted actions. The value-guided thinking is conducted by repeat sampling multiple action candidates and selecting one according to state-action value. System 1 of Hume is a lightweight reactive visuomotor policy that takes System 2 selected action and performs cascaded action denoising for dexterous robot control. At deployment time, System 2 performs value-guided thinking at a low frequency while System 1 asynchronously receives the System 2 selected action candidate and predicts fluid actions in real time. We show that Hume outperforms the existing state-of-the-art Vision-Language-Action models across multiple simulation benchmark and real-robot deployments.
Think Small, Act Big: Primitive Prompt Learning for Lifelong Robot Manipulation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Building a lifelong robot that can effectively leverage prior knowledge for continuous skill acquisition remains significantly challenging. Despite the success of experience replay and parameter-efficient methods in alleviating catastrophic forgetting problem, naively applying these methods causes a failure to leverage the shared primitives between skills. To tackle these issues, we propose Primitive Prompt Learning (PPL), to achieve lifelong robot manipulation via reusable and extensible primitives. Within our two stage learning scheme, we first learn a set of primitive prompts to represent shared primitives through multi-skills pre-training stage, where motion-aware prompts are learned to capture semantic and motion shared primitives across different skills. Secondly, when acquiring new skills in lifelong span, new prompts are appended and optimized with frozen pretrained prompts, boosting the learning via knowledge transfer from old skills to new ones. For evaluation, we construct a large-scale skill dataset and conduct extensive experiments in both simulation and real-world tasks, demonstrating PPL's superior performance over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge