Xiangyu Peng
Strefer: Empowering Video LLMs with Space-Time Referring and Reasoning via Synthetic Instruction Data
Sep 03, 2025



Abstract:Next-generation AI companions must go beyond general video understanding to resolve spatial and temporal references in dynamic, real-world environments. Existing Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs), while capable of coarse-level comprehension, struggle with fine-grained, spatiotemporal reasoning, especially when user queries rely on time-based event references for temporal anchoring, or gestural cues for spatial anchoring to clarify object references and positions. To bridge this critical gap, we introduce Strefer, a synthetic instruction data generation framework designed to equip Video LLMs with spatiotemporal referring and reasoning capabilities. Strefer produces diverse instruction-tuning data using a data engine that pseudo-annotates temporally dense, fine-grained video metadata, capturing rich spatial and temporal information in a structured manner, including subjects, objects, their locations as masklets, and their action descriptions and timelines. Our approach enhances the ability of Video LLMs to interpret spatial and temporal references, fostering more versatile, space-time-aware reasoning essential for real-world AI companions. Without using proprietary models, costly human annotation, or the need to annotate large volumes of new videos, experimental evaluations show that models trained with data produced by Strefer outperform baselines on tasks requiring spatial and temporal disambiguation. Additionally, these models exhibit enhanced space-time-aware reasoning, establishing a new foundation for perceptually grounded, instruction-tuned Video LLMs.
Open-Sora 2.0: Training a Commercial-Level Video Generation Model in $200k
Mar 12, 2025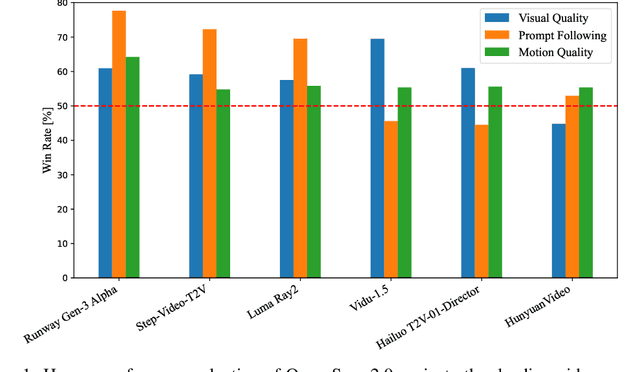
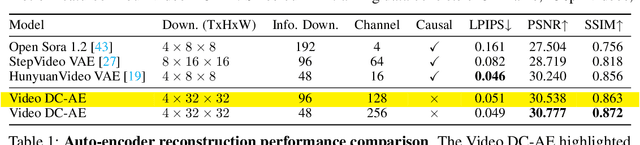
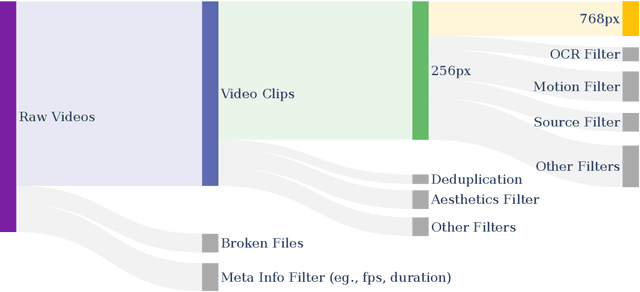
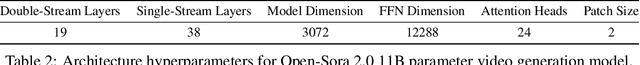
Abstract:Video generation models have achieved remarkable progress in the past year. The quality of AI video continues to improve, but at the cost of larger model size, increased data quantity, and greater demand for training compute. In this report, we present Open-Sora 2.0, a commercial-level video generation model trained for only $200k. With this model, we demonstrate that the cost of training a top-performing video generation model is highly controllable. We detail all techniques that contribute to this efficiency breakthrough, including data curation, model architecture, training strategy, and system optimization. According to human evaluation results and VBench scores, Open-Sora 2.0 is comparable to global leading video generation models including the open-source HunyuanVideo and the closed-source Runway Gen-3 Alpha. By making Open-Sora 2.0 fully open-source, we aim to democratize access to advanced video generation technology, fostering broader innovation and creativity in content creation. All resources are publicly available at: https://github.com/hpcaitech/Open-Sora.
BingoGuard: LLM Content Moderation Tools with Risk Levels
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Malicious content generated by large language models (LLMs) can pose varying degrees of harm. Although existing LLM-based moderators can detect harmful content, they struggle to assess risk levels and may miss lower-risk outputs. Accurate risk assessment allows platforms with different safety thresholds to tailor content filtering and rejection. In this paper, we introduce per-topic severity rubrics for 11 harmful topics and build BingoGuard, an LLM-based moderation system designed to predict both binary safety labels and severity levels. To address the lack of annotations on levels of severity, we propose a scalable generate-then-filter framework that first generates responses across different severity levels and then filters out low-quality responses. Using this framework, we create BingoGuardTrain, a training dataset with 54,897 examples covering a variety of topics, response severity, styles, and BingoGuardTest, a test set with 988 examples explicitly labeled based on our severity rubrics that enables fine-grained analysis on model behaviors on different severity levels. Our BingoGuard-8B, trained on BingoGuardTrain, achieves the state-of-the-art performance on several moderation benchmarks, including WildGuardTest and HarmBench, as well as BingoGuardTest, outperforming best public models, WildGuard, by 4.3\%. Our analysis demonstrates that incorporating severity levels into training significantly enhances detection performance and enables the model to effectively gauge the severity of harmful responses.
Turning Conversations into Workflows: A Framework to Extract and Evaluate Dialog Workflows for Service AI Agents
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Automated service agents require well-structured workflows to provide consistent and accurate responses to customer queries. However, these workflows are often undocumented, and their automatic extraction from conversations remains unexplored. In this work, we present a novel framework for extracting and evaluating dialog workflows from historical interactions. Our extraction process consists of two key stages: (1) a retrieval step to select relevant conversations based on key procedural elements, and (2) a structured workflow generation process using a question-answer-based chain-of-thought (QA-CoT) prompting. To comprehensively assess the quality of extracted workflows, we introduce an automated agent and customer bots simulation framework that measures their effectiveness in resolving customer issues. Extensive experiments on the ABCD and SynthABCD datasets demonstrate that our QA-CoT technique improves workflow extraction by 12.16\% in average macro accuracy over the baseline. Moreover, our evaluation method closely aligns with human assessments, providing a reliable and scalable framework for future research.
Open-Sora: Democratizing Efficient Video Production for All
Dec 29, 2024
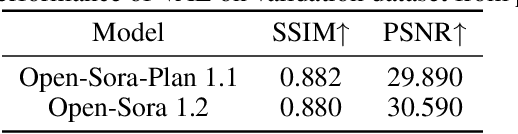
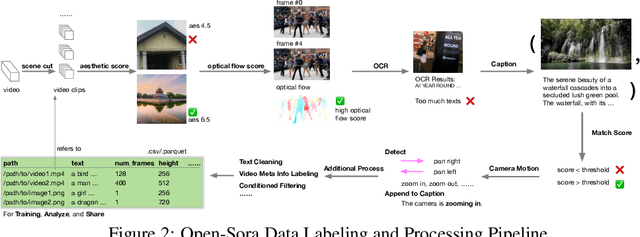
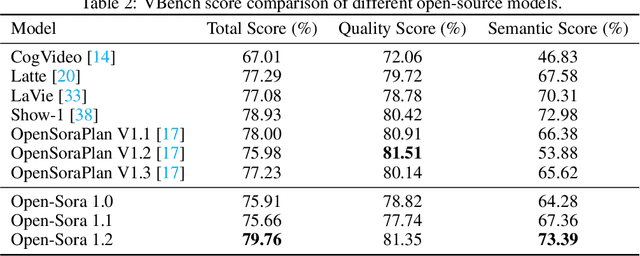
Abstract:Vision and language are the two foundational senses for humans, and they build up our cognitive ability and intelligence. While significant breakthroughs have been made in AI language ability, artificial visual intelligence, especially the ability to generate and simulate the world we see, is far lagging behind. To facilitate the development and accessibility of artificial visual intelligence, we created Open-Sora, an open-source video generation model designed to produce high-fidelity video content. Open-Sora supports a wide spectrum of visual generation tasks, including text-to-image generation, text-to-video generation, and image-to-video generation. The model leverages advanced deep learning architectures and training/inference techniques to enable flexible video synthesis, which could generate video content of up to 15 seconds, up to 720p resolution, and arbitrary aspect ratios. Specifically, we introduce Spatial-Temporal Diffusion Transformer (STDiT), an efficient diffusion framework for videos that decouples spatial and temporal attention. We also introduce a highly compressive 3D autoencoder to make representations compact and further accelerate training with an ad hoc training strategy. Through this initiative, we aim to foster innovation, creativity, and inclusivity within the community of AI content creation. By embracing the open-source principle, Open-Sora democratizes full access to all the training/inference/data preparation codes as well as model weights. All resources are publicly available at: https://github.com/hpcaitech/Open-Sora.
Unanswerability Evaluation for Retreival Augmented Generation
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Existing evaluation frameworks for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems focus on answerable queries, but they overlook the importance of appropriately rejecting unanswerable requests. In this paper, we introduce UAEval4RAG, a framework designed to evaluate whether RAG systems can handle unanswerable queries effectively. We define a taxonomy with six unanswerable categories, and UAEval4RAG automatically synthesizes diverse and challenging queries for any given knowledge base with unanswered ratio and acceptable ratio metrics. We conduct experiments with various RAG components, including retrieval models, rewriting methods, rerankers, language models, and prompting strategies, and reveal hidden trade-offs in performance of RAG systems. Our findings highlight the critical role of component selection and prompt design in optimizing RAG systems to balance the accuracy of answerable queries with high rejection rates of unanswerable ones. UAEval4RAG provides valuable insights and tools for developing more robust and reliable RAG systems.
Distill-SynthKG: Distilling Knowledge Graph Synthesis Workflow for Improved Coverage and Efficiency
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) generated by large language models (LLMs) are becoming increasingly valuable for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications that require knowledge-intensive reasoning. However, existing KG extraction methods predominantly rely on prompt-based approaches, which are inefficient for processing large-scale corpora. These approaches often suffer from information loss, particularly with long documents, due to the lack of specialized design for KG construction. Additionally, there is a gap in evaluation datasets and methodologies for ontology-free KG construction. To overcome these limitations, we propose SynthKG, a multi-step, document-level ontology-free KG synthesis workflow based on LLMs. By fine-tuning a smaller LLM on the synthesized document-KG pairs, we streamline the multi-step process into a single-step KG generation approach called Distill-SynthKG, substantially reducing the number of LLM inference calls. Furthermore, we re-purpose existing question-answering datasets to establish KG evaluation datasets and introduce new evaluation metrics. Using KGs produced by Distill-SynthKG, we also design a novel graph-based retrieval framework for RAG. Experimental results demonstrate that Distill-SynthKG not only surpasses all baseline models in KG quality -- including models up to eight times larger -- but also consistently excels in retrieval and question-answering tasks. Our proposed graph retrieval framework also outperforms all KG-retrieval methods across multiple benchmark datasets. We release the SynthKG dataset and Distill-SynthKG model publicly to support further research and development.
ReGenesis: LLMs can Grow into Reasoning Generalists via Self-Improvement
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:Post-training Large Language Models (LLMs) with explicit reasoning trajectories can enhance their reasoning abilities. However, acquiring such high-quality trajectory data typically demands meticulous supervision from humans or superior models, which can be either expensive or license-constrained. In this paper, we explore how far an LLM can improve its reasoning by self-synthesizing reasoning paths as training data without any additional supervision. Existing self-synthesizing methods, such as STaR, suffer from poor generalization to out-of-domain (OOD) reasoning tasks. We hypothesize it is due to that their self-synthesized reasoning paths are too task-specific, lacking general task-agnostic reasoning guidance. To address this, we propose Reasoning Generalist via Self-Improvement (ReGenesis), a method to self-synthesize reasoning paths as post-training data by progressing from abstract to concrete. More specifically, ReGenesis self-synthesizes reasoning paths by converting general reasoning guidelines into task-specific ones, generating reasoning structures, and subsequently transforming these structures into reasoning paths, without the need for human-designed task-specific examples used in existing methods. We show that ReGenesis achieves superior performance on all in-domain and OOD settings tested compared to existing methods. For six OOD tasks specifically, while previous methods exhibited an average performance decrease of approximately 4.6% after post training, ReGenesis delivers around 6.1% performance improvement. We also conduct in-depth analysis of our framework and show ReGenesis is effective across various LLMs and design choices.
More Than Positive and Negative: Communicating Fine Granularity in Medical Diagnosis
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:With the advance of deep learning, much progress has been made in building powerful artificial intelligence (AI) systems for automatic Chest X-ray (CXR) analysis. Most existing AI models are trained to be a binary classifier with the aim of distinguishing positive and negative cases. However, a large gap exists between the simple binary setting and complicated real-world medical scenarios. In this work, we reinvestigate the problem of automatic radiology diagnosis. We first observe that there is considerable diversity among cases within the positive class, which means simply classifying them as positive loses many important details. This motivates us to build AI models that can communicate fine-grained knowledge from medical images like human experts. To this end, we first propose a new benchmark on fine granularity learning from medical images. Specifically, we devise a division rule based on medical knowledge to divide positive cases into two subcategories, namely atypical positive and typical positive. Then, we propose a new metric termed AUC$^\text{FG}$ on the two subcategories for evaluation of the ability to separate them apart. With the proposed benchmark, we encourage the community to develop AI diagnosis systems that could better learn fine granularity from medical images. Last, we propose a simple risk modulation approach to this problem by only using coarse labels in training. Empirical results show that despite its simplicity, the proposed method achieves superior performance and thus serves as a strong baseline.
Measuring Trust for Exoskeleton Systems
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Wearable robotic systems are a class of robots that have a tight coupling between human and robot movements. Similar to non-wearable robots, it is important to measure the trust a person has that the robot can support achieving the desired goals. While some measures of trust may apply to all potential robotic roles, there are key distinctions between wearable and non-wearable robotic systems. In this paper, we considered the dimensions and sub-dimensions of trust, with example attributes defined for exoskeleton applications. As the research community comes together to discuss measures of trust, it will be important to consider how the selected measures support interpreting trust along different dimensions for the variety of robotic systems that are emerging in the field in a way that leads to actionable outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge