Bill Dolan
Echoes in AI: Quantifying Lack of Plot Diversity in LLM Outputs
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:With rapid advances in large language models (LLMs), there has been an increasing application of LLMs in creative content ideation and generation. A critical question emerges: can current LLMs provide ideas that are diverse enough to truly bolster the collective creativity? We examine two state-of-the-art LLMs, GPT-4 and LLaMA-3, on story generation and discover that LLM-generated stories often consist of plot elements that are echoed across a number of generations. To quantify this phenomenon, we introduce the Sui Generis score, which estimates how unlikely a plot element is to appear in alternative storylines generated by the same LLM. Evaluating on 100 short stories, we find that LLM-generated stories often contain combinations of idiosyncratic plot elements echoed frequently across generations, while the original human-written stories are rarely recreated or even echoed in pieces. Moreover, our human evaluation shows that the ranking of Sui Generis scores among story segments correlates moderately with human judgment of surprise level, even though score computation is completely automatic without relying on human judgment.
Game Plot Design with an LLM-powered Assistant: An Empirical Study with Game Designers
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:We introduce GamePlot, an LLM-powered assistant that supports game designers in crafting immersive narratives for turn-based games, and allows them to test these games through a collaborative game play and refine the plot throughout the process. Our user study with 14 game designers shows high levels of both satisfaction with the generated game plots and sense of ownership over the narratives, but also reconfirms that LLM are limited in their ability to generate complex and truly innovative content. We also show that diverse user populations have different expectations from AI assistants, and encourage researchers to study how tailoring assistants to diverse user groups could potentially lead to increased job satisfaction and greater creativity and innovation over time.
MCPDial: A Minecraft Persona-driven Dialogue Dataset
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:We propose a novel approach that uses large language models (LLMs) to generate persona-driven conversations between Players and Non-Player Characters (NPC) in games. Showcasing the application of our methodology, we introduce the Minecraft Persona-driven Dialogue dataset (MCPDial). Starting with a small seed of expert-written conversations, we employ our method to generate hundreds of additional conversations. Each conversation in the dataset includes rich character descriptions of the player and NPC. The conversations are long, allowing for in-depth and extensive interactions between the player and NPC. MCPDial extends beyond basic conversations by incorporating canonical function calls (e.g. "Call find a resource on iron ore") between the utterances. Finally, we conduct a qualitative analysis of the dataset to assess its quality and characteristics.
Collaborative Quest Completion with LLM-driven Non-Player Characters in Minecraft
Jul 03, 2024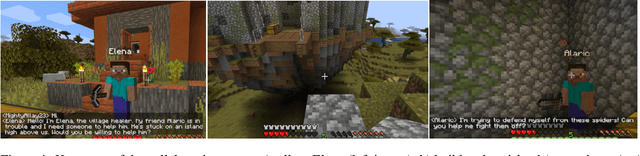


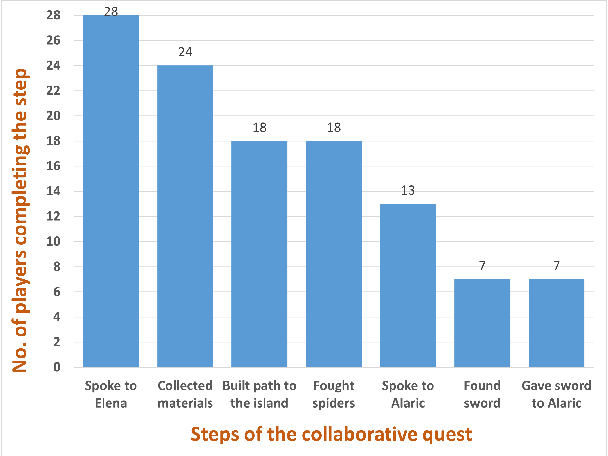
Abstract:The use of generative AI in video game development is on the rise, and as the conversational and other capabilities of large language models continue to improve, we expect LLM-driven non-player characters (NPCs) to become widely deployed. In this paper, we seek to understand how human players collaborate with LLM-driven NPCs to accomplish in-game goals. We design a minigame within Minecraft where a player works with two GPT4-driven NPCs to complete a quest. We perform a user study in which 28 Minecraft players play this minigame and share their feedback. On analyzing the game logs and recordings, we find that several patterns of collaborative behavior emerge from the NPCs and the human players. We also report on the current limitations of language-only models that do not have rich game-state or visual understanding. We believe that this preliminary study and analysis will inform future game developers on how to better exploit these rapidly improving generative AI models for collaborative roles in games.
* Accepted at Wordplay workshop at ACL 2024
Automatic Bug Detection in LLM-Powered Text-Based Games Using LLMs
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Advancements in large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing interactive game design, enabling dynamic plotlines and interactions between players and non-player characters (NPCs). However, LLMs may exhibit flaws such as hallucinations, forgetfulness, or misinterpretations of prompts, causing logical inconsistencies and unexpected deviations from intended designs. Automated techniques for detecting such game bugs are still lacking. To address this, we propose a systematic LLM-based method for automatically identifying such bugs from player game logs, eliminating the need for collecting additional data such as post-play surveys. Applied to a text-based game DejaBoom!, our approach effectively identifies bugs inherent in LLM-powered interactive games, surpassing unstructured LLM-powered bug-catching methods and filling the gap in automated detection of logical and design flaws.
Player-Driven Emergence in LLM-Driven Game Narrative
Apr 25, 2024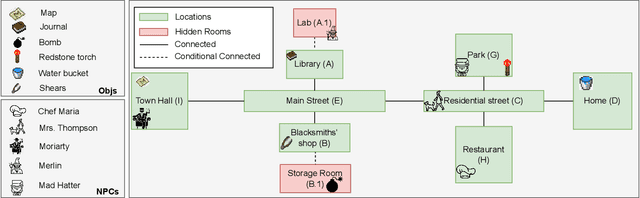
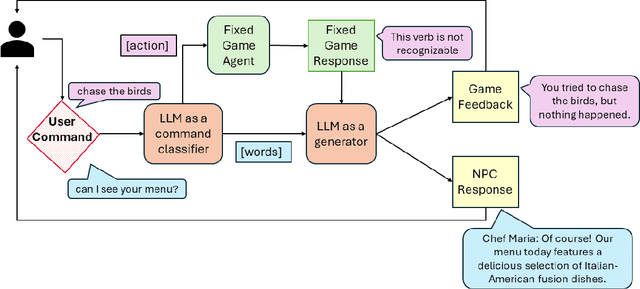
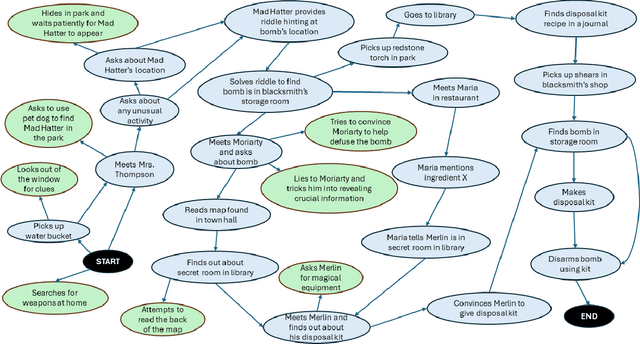

Abstract:We explore how interaction with large language models (LLMs) can give rise to emergent behaviors, empowering players to participate in the evolution of game narratives. Our testbed is a text-adventure game in which players attempt to solve a mystery under a fixed narrative premise, but can freely interact with non-player characters generated by GPT-4, a large language model. We recruit 28 gamers to play the game and use GPT-4 to automatically convert the game logs into a node-graph representing the narrative in the player's gameplay. We find that through their interactions with the non-deterministic behavior of the LLM, players are able to discover interesting new emergent nodes that were not a part of the original narrative but have potential for being fun and engaging. Players that created the most emergent nodes tended to be those that often enjoy games that facilitate discovery, exploration and experimentation.
GRIM: GRaph-based Interactive narrative visualization for gaMes
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:Dialogue-based Role Playing Games (RPGs) require powerful storytelling. The narratives of these may take years to write and typically involve a large creative team. In this work, we demonstrate the potential of large generative text models to assist this process. \textbf{GRIM}, a prototype \textbf{GR}aph-based \textbf{I}nteractive narrative visualization system for ga\textbf{M}es, generates a rich narrative graph with branching storylines that match a high-level narrative description and constraints provided by the designer. Game designers can interactively edit the graph by automatically generating new sub-graphs that fit the edits within the original narrative and constraints. We illustrate the use of \textbf{GRIM} in conjunction with GPT-4, generating branching narratives for four well-known stories with different contextual constraints.
Towards Dialogue Systems with Agency in Human-AI Collaboration Tasks
May 22, 2023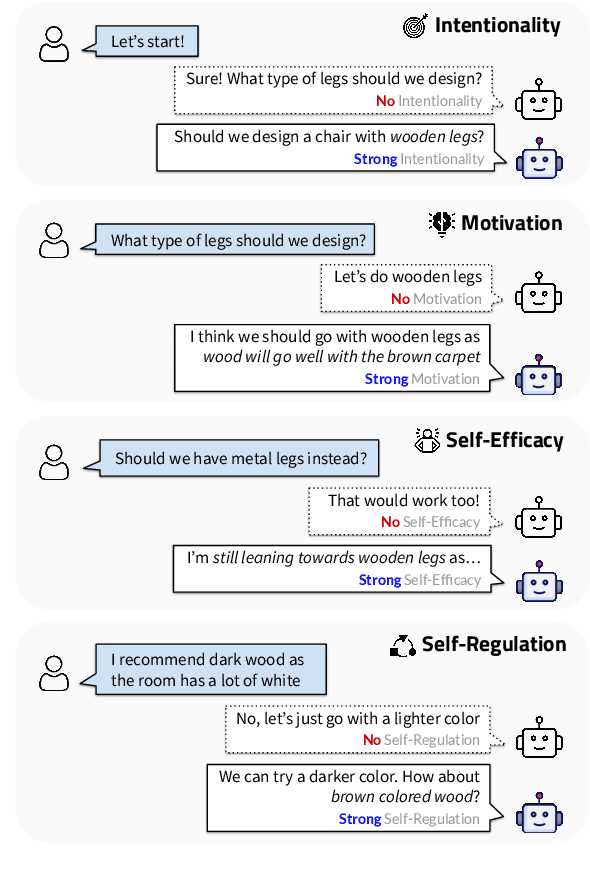
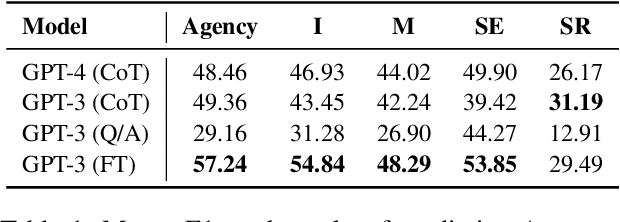
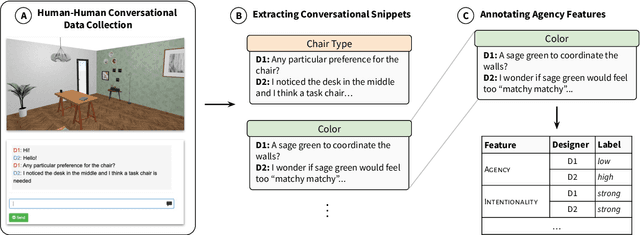
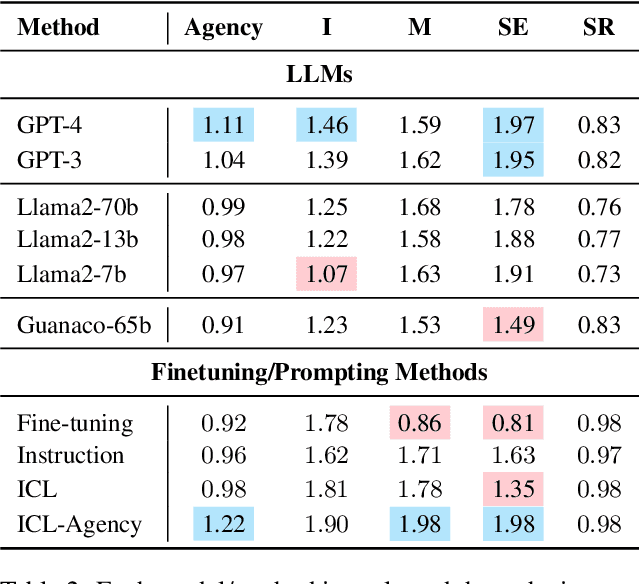
Abstract:Agency, the capacity to proactively shape events, is crucial to how humans interact and collaborate with other humans. In this paper, we investigate Agency as a potentially desirable function of dialogue agents, and how it can be measured and controlled. We build upon the social-cognitive theory of Bandura (2001) to develop a framework of features through which Agency is expressed in dialogue -- indicating what you intend to do (Intentionality), motivating your intentions (Motivation), having self-belief in intentions (Self-Efficacy), and being able to self-adjust (Self-Regulation). We collect and release a new dataset of 83 human-human collaborative interior design conversations containing 908 conversational snippets annotated for Agency features. Using this dataset, we explore methods for measuring and controlling Agency in dialogue systems. Automatic and human evaluation show that although a baseline GPT-3 model can express Intentionality, models that explicitly manifest features associated with high Motivation, Self-Efficacy, and Self-Regulation are better perceived as being highly agentive. This work has implications for the development of dialogue systems with varying degrees of Agency in collaborative tasks.
Interactive Text Generation
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Users interact with text, image, code, or other editors on a daily basis. However, machine learning models are rarely trained in the settings that reflect the interactivity between users and their editor. This is understandable as training AI models with real users is not only slow and costly, but what these models learn may be specific to user interface design choices. Unfortunately, this means most of the research on text, code, and image generation has focused on non-interactive settings, whereby the model is expected to get everything right without accounting for any input from a user who may be willing to help. We introduce a new Interactive Text Generation task that allows training generation models interactively without the costs of involving real users, by using user simulators that provide edits that guide the model towards a given target text. We train our interactive models using Imitation Learning, and our experiments against competitive non-interactive generation models show that models trained interactively are superior to their non-interactive counterparts, even when all models are given the same budget of user inputs or edits.
Grounded Keys-to-Text Generation: Towards Factual Open-Ended Generation
Dec 04, 2022



Abstract:Large pre-trained language models have recently enabled open-ended generation frameworks (e.g., prompt-to-text NLG) to tackle a variety of tasks going beyond the traditional data-to-text generation. While this framework is more general, it is under-specified and often leads to a lack of controllability restricting their real-world usage. We propose a new grounded keys-to-text generation task: the task is to generate a factual description about an entity given a set of guiding keys, and grounding passages. To address this task, we introduce a new dataset, called EntDeGen. Inspired by recent QA-based evaluation measures, we propose an automatic metric, MAFE, for factual correctness of generated descriptions. Our EntDescriptor model is equipped with strong rankers to fetch helpful passages and generate entity descriptions. Experimental result shows a good correlation (60.14) between our proposed metric and human judgments of factuality. Our rankers significantly improved the factual correctness of generated descriptions (15.95% and 34.51% relative gains in recall and precision). Finally, our ablation study highlights the benefit of combining keys and groundings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge