Felix Faltings
ProxelGen: Generating Proteins as 3D Densities
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:We develop ProxelGen, a protein structure generative model that operates on 3D densities as opposed to the prevailing 3D point cloud representations. Representing proteins as voxelized densities, or proxels, enables new tasks and conditioning capabilities. We generate proteins encoded as proxels via a 3D CNN-based VAE in conjunction with a diffusion model operating on its latent space. Compared to state-of-the-art models, ProxelGen's samples achieve higher novelty, better FID scores, and the same level of designability as the training set. ProxelGen's advantages are demonstrated in a standard motif scaffolding benchmark, and we show how 3D density-based generation allows for more flexible shape conditioning.
Language Model Personalization via Reward Factorization
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) are optimized for human-aligned responses using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). However, existing RLHF approaches assume a universal preference model and fail to account for individual user preferences, limiting their effectiveness in personalized applications. We introduce a framework that extends RLHF to enable user personalization by leveraging the assumption that user preferences lie in a low-dimensional space. Instead of training a separate model per user, we represent user-specific rewards as a linear combination of base reward functions. Using only ~10 user responses, our method can infer user-specific rewards and align LLM outputs accordingly. We validate our approach through experiments with both synthetic and real users, demonstrating significant personalization achieved by our method. In human evaluations, our method achieves a 67% win rate over default GPT-4o responses.
Interactive Text Generation
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Users interact with text, image, code, or other editors on a daily basis. However, machine learning models are rarely trained in the settings that reflect the interactivity between users and their editor. This is understandable as training AI models with real users is not only slow and costly, but what these models learn may be specific to user interface design choices. Unfortunately, this means most of the research on text, code, and image generation has focused on non-interactive settings, whereby the model is expected to get everything right without accounting for any input from a user who may be willing to help. We introduce a new Interactive Text Generation task that allows training generation models interactively without the costs of involving real users, by using user simulators that provide edits that guide the model towards a given target text. We train our interactive models using Imitation Learning, and our experiments against competitive non-interactive generation models show that models trained interactively are superior to their non-interactive counterparts, even when all models are given the same budget of user inputs or edits.
Text Editing by Command
Oct 24, 2020
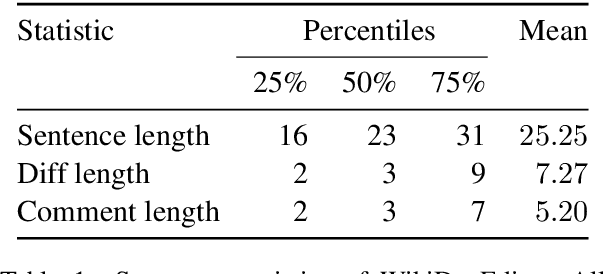
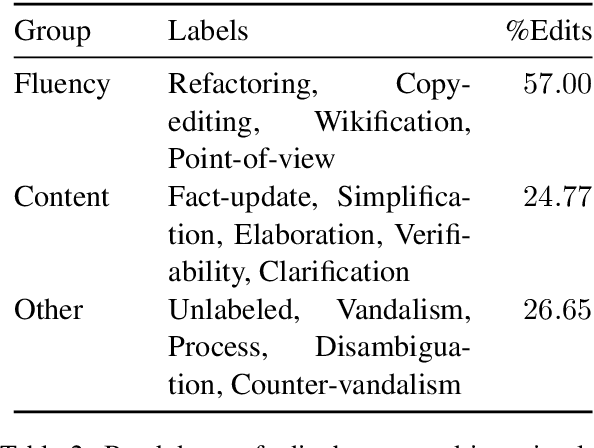
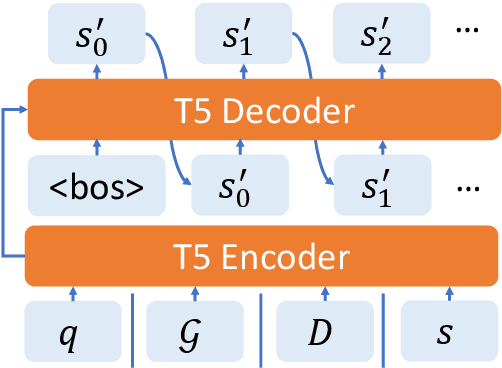
Abstract:A prevailing paradigm in neural text generation is one-shot generation, where text is produced in a single step. The one-shot setting is inadequate, however, when the constraints the user wishes to impose on the generated text are dynamic, especially when authoring longer documents. We address this limitation with an interactive text generation setting in which the user interacts with the system by issuing commands to edit existing text. To this end, we propose a novel text editing task, and introduce WikiDocEdits, a dataset of single-sentence edits crawled from Wikipedia. We show that our Interactive Editor, a transformer-based model trained on this dataset, outperforms baselines and obtains positive results in both automatic and human evaluations. We present empirical and qualitative analyses of this model's performance.
On the impact of publicly available news and information transfer to financial markets
Oct 22, 2020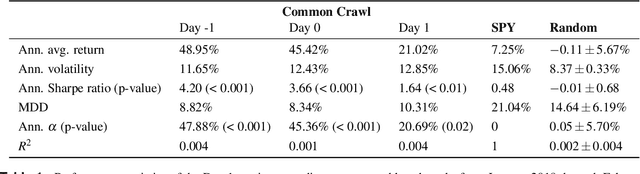
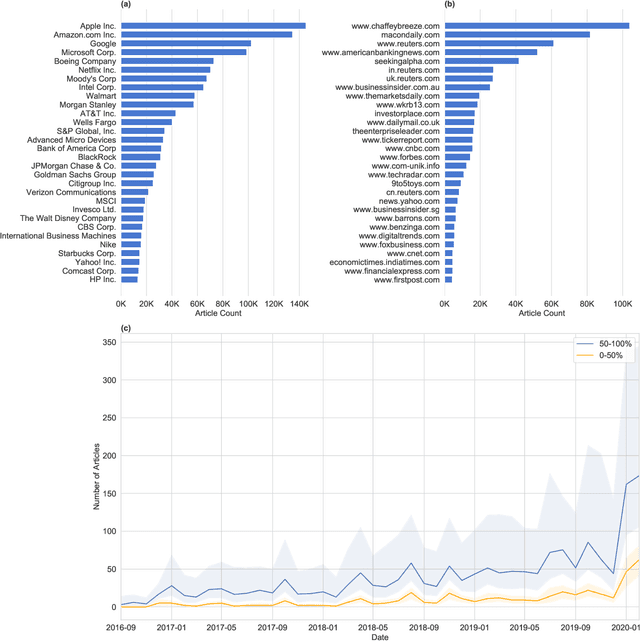
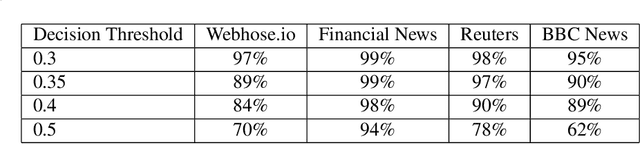
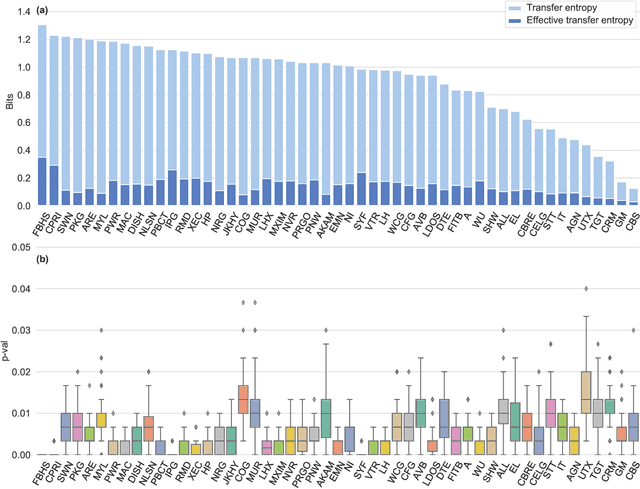
Abstract:We quantify the propagation and absorption of large-scale publicly available news articles from the World Wide Web to financial markets. To extract publicly available information, we use the news archives from the Common Crawl, a nonprofit organization that crawls a large part of the web. We develop a processing pipeline to identify news articles associated with the constituent companies in the S\&P 500 index, an equity market index that measures the stock performance of U.S. companies. Using machine learning techniques, we extract sentiment scores from the Common Crawl News data and employ tools from information theory to quantify the information transfer from public news articles to the U.S. stock market. Furthermore, we analyze and quantify the economic significance of the news-based information with a simple sentiment-based portfolio trading strategy. Our findings provides support for that information in publicly available news on the World Wide Web has a statistically and economically significant impact on events in financial markets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge