Aldo Pacchiano
Scaling In-Context Online Learning Capability of LLMs via Cross-Episode Meta-RL
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) achieve strong performance when all task-relevant information is available upfront, as in static prediction and instruction-following problems. However, many real-world decision-making tasks are inherently online: crucial information must be acquired through interaction, feedback is delayed, and effective behavior requires balancing information collection and exploitation over time. While in-context learning enables adaptation without weight updates, existing LLMs often struggle to reliably leverage in-context interaction experience in such settings. In this work, we show that this limitation can be addressed through training. We introduce ORBIT, a multi-task, multi-episode meta-reinforcement learning framework that trains LLMs to learn from interaction in context. After meta-training, a relatively small open-source model (Qwen3-14B) demonstrates substantially improved in-context online learning on entirely unseen environments, matching the performance of GPT-5.2 and outperforming standard RL fine-tuning by a large margin. Scaling experiments further reveal consistent gains with model size, suggesting significant headroom for learn-at-inference-time decision-making agents. Code reproducing the results in the paper can be found at https://github.com/XiaofengLin7/ORBIT.
Principled Fine-tuning of LLMs from User-Edits: A Medley of Preference, Supervision, and Reward
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We study how to fine-tune LLMs using user-edit deployment data consisting of a set of context, an agent's response, and user edits. This deployment data is naturally generated by users in applications such as LLMs-based writing assistants and coding agents. The _natural_ origin of user edits makes it a desired source for adapting and personalizing LLMs. In this setup, there emerges a unification of various feedback types namely preferences, supervised labels, and cost that are typically studied separately in the literature. In this paper, we initiate the theoretical investigation of learning from user edits. We first derive bounds for learning algorithms that learn from each of these feedback types. We prove that these algorithms have different trade-offs depending upon the user, data distribution, and model class. We then propose a simple ensembling procedure to jointly learn from these feedback types. On two domains adapted from Gao et al. 2024, we show our ensembling procedure outperforms these methods that learn from individual feedback. Further, we show that our proposed procedure can robustly adapt to different user-edit distributions at test time.
Enhancing Diversity in Large Language Models via Determinantal Point Processes
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning are two popular methods for post-training large language models (LLMs). While improving the model's performance on downstream tasks, they often reduce the model's output diversity, leading to narrow, canonical responses. Existing methods to enhance diversity are limited, either by operating at inference time or by focusing on lexical differences. We propose a novel training method named DQO based on determinantal point processes (DPPs) to jointly optimize LLMs for quality and semantic diversity. Our approach samples and embeds a group of responses for each prompt, then uses the determinant of a kernel-based similarity matrix to measure diversity as the volume spanned by the embeddings of these responses. Experiments across instruction-following, summarization, story generation, and reasoning tasks demonstrate that our method substantially improves semantic diversity without sacrificing model quality.
On the Hardness of Bandit Learning
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:We study the task of bandit learning, also known as best-arm identification, under the assumption that the true reward function f belongs to a known, but arbitrary, function class F. We seek a general theory of bandit learnability, akin to the PAC framework for classification. Our investigation is guided by the following two questions: (1) which classes F are learnable, and (2) how they are learnable. For example, in the case of binary PAC classification, learnability is fully determined by a combinatorial dimension - the VC dimension- and can be attained via a simple algorithmic principle, namely, empirical risk minimization (ERM). In contrast to classical learning-theoretic results, our findings reveal limitations of learning in structured bandits, offering insights into the boundaries of bandit learnability. First, for the question of "which", we show that the paradigm of identifying the learnable classes via a dimension-like quantity fails for bandit learning. We give a simple proof demonstrating that no combinatorial dimension can characterize bandit learnability, even in finite classes, following a standard definition of dimension introduced by Ben-David et al. (2019). For the question of "how", we prove a computational hardness result: we construct a reward function class for which at most two queries are needed to find the optimal action, yet no algorithm can do so in polynomial time unless RP=NP. We also prove that this class admits efficient algorithms for standard algorithmic operations often considered in learning theory, such as an ERM. This implies that computational hardness is in this case inherent to the task of bandit learning. Beyond these results, we investigate additional themes such as learning under noise, trade-offs between noise models, and the relationship between query complexity and regret minimization.
Meet Me at the Arm: The Cooperative Multi-Armed Bandits Problem with Shareable Arms
Jun 11, 2025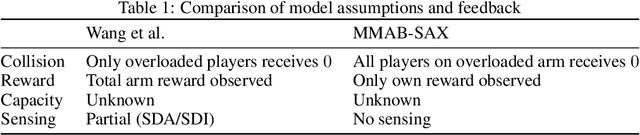
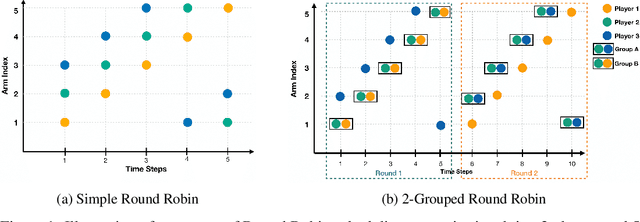
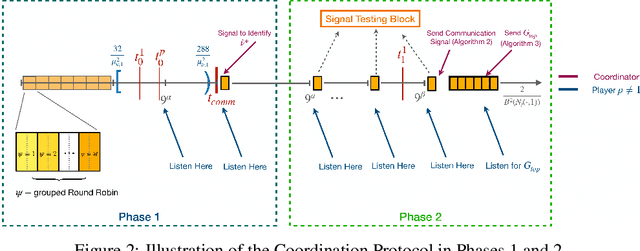
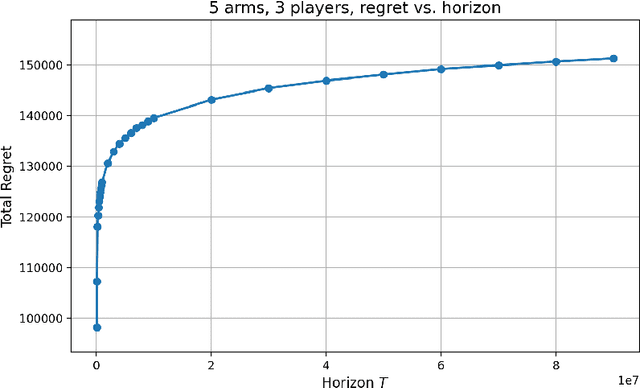
Abstract:We study the decentralized multi-player multi-armed bandits (MMAB) problem under a no-sensing setting, where each player receives only their own reward and obtains no information about collisions. Each arm has an unknown capacity, and if the number of players pulling an arm exceeds its capacity, all players involved receive zero reward. This setting generalizes the classical unit-capacity model and introduces new challenges in coordination and capacity discovery under severe feedback limitations. We propose A-CAPELLA (Algorithm for Capacity-Aware Parallel Elimination for Learning and Allocation), a decentralized algorithm that achieves logarithmic regret in this generalized regime. Our main contribution is a collaborative hypothesis testing protocol that enables synchronized successive elimination and capacity estimation through carefully structured collision patterns. This represents a provably efficient learning result in decentralized no-sensing MMAB with unknown arm capacities.
Pure Exploration with Feedback Graphs
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:We study the sample complexity of pure exploration in an online learning problem with a feedback graph. This graph dictates the feedback available to the learner, covering scenarios between full-information, pure bandit feedback, and settings with no feedback on the chosen action. While variants of this problem have been investigated for regret minimization, no prior work has addressed the pure exploration setting, which is the focus of our study. We derive an instance-specific lower bound on the sample complexity of learning the best action with fixed confidence, even when the feedback graph is unknown and stochastic, and present unidentifiability results for Bernoulli rewards. Additionally, our findings reveal how the sample complexity scales with key graph-dependent quantities. Lastly, we introduce TaS-FG (Track and Stop for Feedback Graphs), an asymptotically optimal algorithm, and demonstrate its efficiency across different graph configurations.
Language Model Personalization via Reward Factorization
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) are optimized for human-aligned responses using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). However, existing RLHF approaches assume a universal preference model and fail to account for individual user preferences, limiting their effectiveness in personalized applications. We introduce a framework that extends RLHF to enable user personalization by leveraging the assumption that user preferences lie in a low-dimensional space. Instead of training a separate model per user, we represent user-specific rewards as a linear combination of base reward functions. Using only ~10 user responses, our method can infer user-specific rewards and align LLM outputs accordingly. We validate our approach through experiments with both synthetic and real users, demonstrating significant personalization achieved by our method. In human evaluations, our method achieves a 67% win rate over default GPT-4o responses.
Adaptive Exploration for Multi-Reward Multi-Policy Evaluation
Feb 04, 2025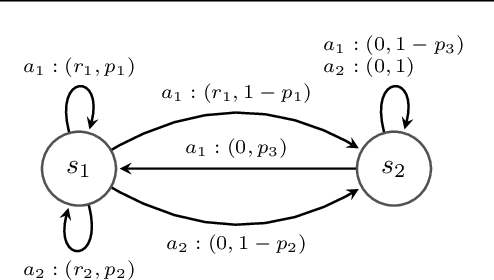
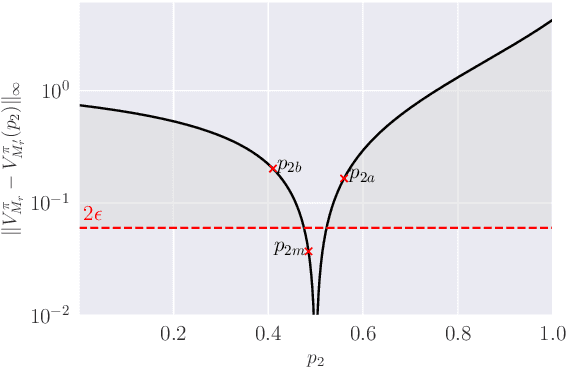
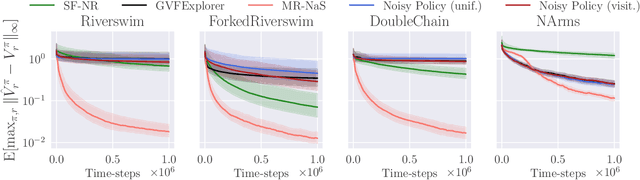
Abstract:We study the policy evaluation problem in an online multi-reward multi-policy discounted setting, where multiple reward functions must be evaluated simultaneously for different policies. We adopt an $(\epsilon,\delta)$-PAC perspective to achieve $\epsilon$-accurate estimates with high confidence across finite or convex sets of rewards, a setting that has not been investigated in the literature. Building on prior work on Multi-Reward Best Policy Identification, we adapt the MR-NaS exploration scheme to jointly minimize sample complexity for evaluating different policies across different reward sets. Our approach leverages an instance-specific lower bound revealing how the sample complexity scales with a measure of value deviation, guiding the design of an efficient exploration policy. Although computing this bound entails a hard non-convex optimization, we propose an efficient convex approximation that holds for both finite and convex reward sets. Experiments in tabular domains demonstrate the effectiveness of this adaptive exploration scheme.
ORSO: Accelerating Reward Design via Online Reward Selection and Policy Optimization
Oct 17, 2024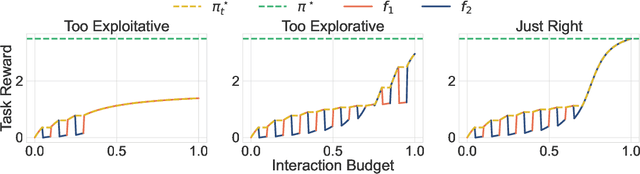
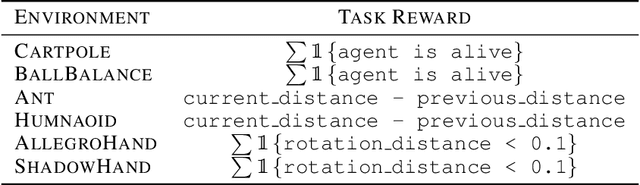
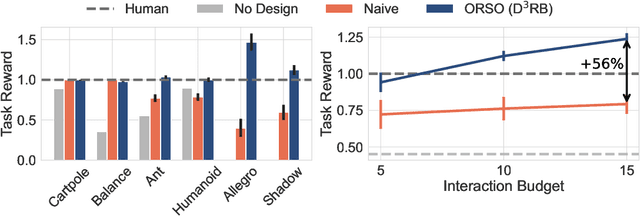
Abstract:Reward shaping is a critical component in reinforcement learning (RL), particularly for complex tasks where sparse rewards can hinder learning. While shaping rewards have been introduced to provide additional guidance, selecting effective shaping functions remains challenging and computationally expensive. This paper introduces Online Reward Selection and Policy Optimization (ORSO), a novel approach that frames shaping reward selection as an online model selection problem. ORSO employs principled exploration strategies to automatically identify promising shaping reward functions without human intervention, balancing exploration and exploitation with provable regret guarantees. We demonstrate ORSO's effectiveness across various continuous control tasks using the Isaac Gym simulator. Compared to traditional methods that fully evaluate each shaping reward function, ORSO significantly improves sample efficiency, reduces computational time, and consistently identifies high-quality reward functions that produce policies comparable to those generated by domain experts through hand-engineered rewards.
State-free Reinforcement Learning
Sep 27, 2024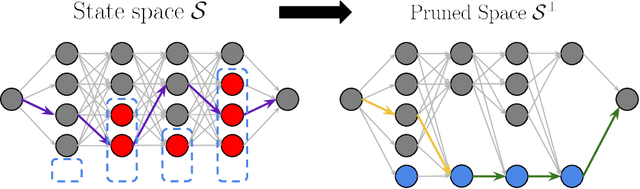
Abstract:In this work, we study the \textit{state-free RL} problem, where the algorithm does not have the states information before interacting with the environment. Specifically, denote the reachable state set by ${S}^\Pi := \{ s|\max_{\pi\in \Pi}q^{P, \pi}(s)>0 \}$, we design an algorithm which requires no information on the state space $S$ while having a regret that is completely independent of ${S}$ and only depend on ${S}^\Pi$. We view this as a concrete first step towards \textit{parameter-free RL}, with the goal of designing RL algorithms that require no hyper-parameter tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge