Pulkit Agrawal
Self-Distillation Enables Continual Learning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Continual learning, enabling models to acquire new skills and knowledge without degrading existing capabilities, remains a fundamental challenge for foundation models. While on-policy reinforcement learning can reduce forgetting, it requires explicit reward functions that are often unavailable. Learning from expert demonstrations, the primary alternative, is dominated by supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which is inherently off-policy. We introduce Self-Distillation Fine-Tuning (SDFT), a simple method that enables on-policy learning directly from demonstrations. SDFT leverages in-context learning by using a demonstration-conditioned model as its own teacher, generating on-policy training signals that preserve prior capabilities while acquiring new skills. Across skill learning and knowledge acquisition tasks, SDFT consistently outperforms SFT, achieving higher new-task accuracy while substantially reducing catastrophic forgetting. In sequential learning experiments, SDFT enables a single model to accumulate multiple skills over time without performance regression, establishing on-policy distillation as a practical path to continual learning from demonstrations.
SpecMap: Hierarchical LLM Agent for Datasheet-to-Code Traceability Link Recovery in Systems Engineering
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Establishing precise traceability between embedded systems datasheets and their corresponding code implementations remains a fundamental challenge in systems engineering, particularly for low-level software where manual mapping between specification documents and large code repositories is infeasible. Existing Traceability Link Recovery approaches primarily rely on lexical similarity and information retrieval techniques, which struggle to capture the semantic, structural, and symbol level relationships prevalent in embedded systems software. We present a hierarchical datasheet-to-code mapping methodology that employs large language models for semantic analysis while explicitly structuring the traceability process across multiple abstraction levels. Rather than performing direct specification-to-code matching, the proposed approach progressively narrows the search space through repository-level structure inference, file-level relevance estimation, and fine-grained symbollevel alignment. The method extends beyond function-centric mapping by explicitly covering macros, structs, constants, configuration parameters, and register definitions commonly found in systems-level C/C++ codebases. We evaluate the approach on multiple open-source embedded systems repositories using manually curated datasheet-to-code ground truth. Experimental results show substantial improvements over traditional information-retrieval-based baselines, achieving up to 73.3% file mapping accuracy. We significantly reduce computational overhead, lowering total LLM token consumption by 84% and end-to-end runtime by approximately 80%. This methodology supports automated analysis of large embedded software systems and enables downstream applications such as training data generation for systems-aware machine learning models, standards compliance verification, and large-scale specification coverage analysis.
RL's Razor: Why Online Reinforcement Learning Forgets Less
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Comparison of fine-tuning models with reinforcement learning (RL) and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) reveals that, despite similar performance at a new task, RL preserves prior knowledge and capabilities significantly better. We find that the degree of forgetting is determined by the distributional shift, measured as the KL-divergence between the fine-tuned and base policy evaluated on the new task. Our analysis reveals that on-policy RL is implicitly biased towards KL-minimal solutions among the many that solve the new task, whereas SFT can converge to distributions arbitrarily far from the base model. We validate these findings through experiments with large language models and robotic foundation models and further provide theoretical justification for why on-policy RL updates lead to a smaller KL change. We term this principle $\textit{RL's Razor}$: among all ways to solve a new task, RL prefers those closest in KL to the original model.
DEXOP: A Device for Robotic Transfer of Dexterous Human Manipulation
Sep 04, 2025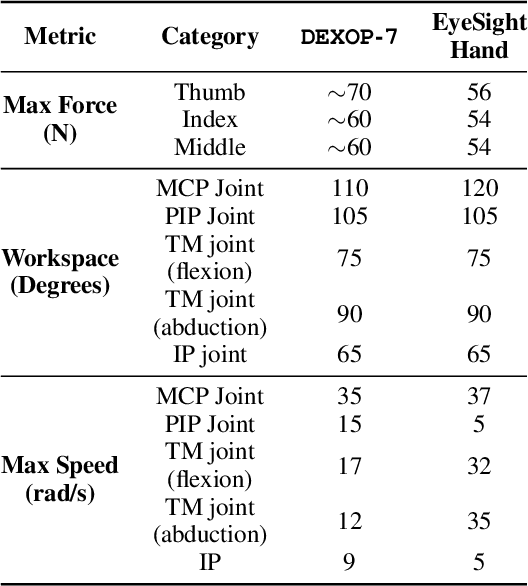
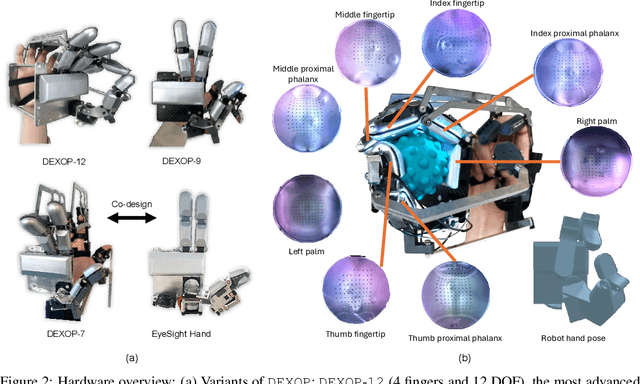
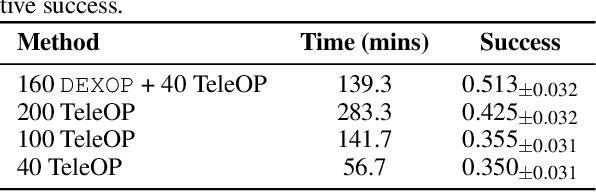
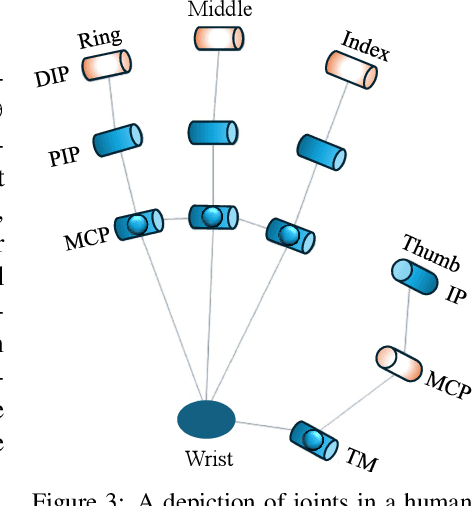
Abstract:We introduce perioperation, a paradigm for robotic data collection that sensorizes and records human manipulation while maximizing the transferability of the data to real robots. We implement this paradigm in DEXOP, a passive hand exoskeleton designed to maximize human ability to collect rich sensory (vision + tactile) data for diverse dexterous manipulation tasks in natural environments. DEXOP mechanically connects human fingers to robot fingers, providing users with direct contact feedback (via proprioception) and mirrors the human hand pose to the passive robot hand to maximize the transfer of demonstrated skills to the robot. The force feedback and pose mirroring make task demonstrations more natural for humans compared to teleoperation, increasing both speed and accuracy. We evaluate DEXOP across a range of dexterous, contact-rich tasks, demonstrating its ability to collect high-quality demonstration data at scale. Policies learned with DEXOP data significantly improve task performance per unit time of data collection compared to teleoperation, making DEXOP a powerful tool for advancing robot dexterity. Our project page is at https://dex-op.github.io.
DexWrist: A Robotic Wrist for Constrained and Dynamic Manipulation
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:We present the DexWrist, a compliant robotic wrist designed to advance robotic manipulation in highly-constrained environments, enable dynamic tasks, and speed up data collection. DexWrist is designed to be close to the functional capabilities of the human wrist and achieves mechanical compliance and a greater workspace as compared to existing robotic wrist designs. The DexWrist can supercharge policy learning by (i) enabling faster teleoperation and therefore making data collection more scalable; (ii) completing tasks in fewer steps which reduces trajectory lengths and therefore can ease policy learning; (iii) DexWrist is designed to be torque transparent with easily simulatable kinematics for simulated data collection; and (iv) most importantly expands the workspace of manipulation for approaching highly cluttered scenes and tasks. More details about the wrist can be found at: dexwrist.csail.mit.edu.
Self-Adapting Language Models
Jun 12, 2025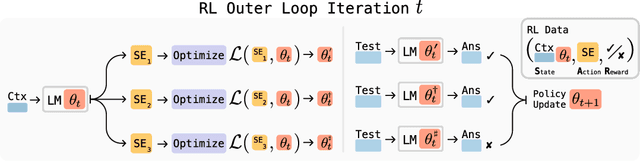
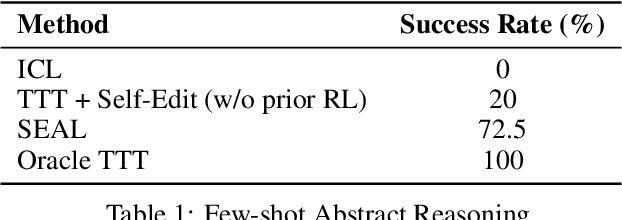
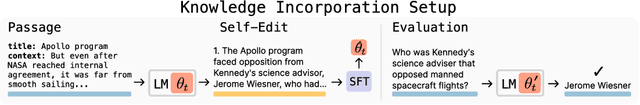
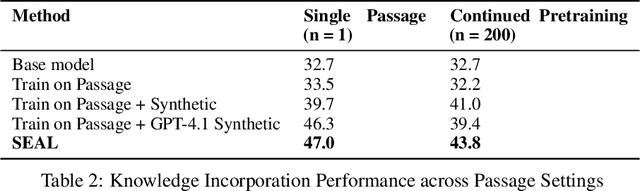
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are powerful but static; they lack mechanisms to adapt their weights in response to new tasks, knowledge, or examples. We introduce Self-Adapting LLMs (SEAL), a framework that enables LLMs to self-adapt by generating their own finetuning data and update directives. Given a new input, the model produces a self-edit-a generation that may restructure the information in different ways, specify optimization hyperparameters, or invoke tools for data augmentation and gradient-based updates. Through supervised finetuning (SFT), these self-edits result in persistent weight updates, enabling lasting adaptation. To train the model to produce effective self-edits, we use a reinforcement learning loop with the downstream performance of the updated model as the reward signal. Unlike prior approaches that rely on separate adaptation modules or auxiliary networks, SEAL directly uses the model's own generation to control its adaptation process. Experiments on knowledge incorporation and few-shot generalization show that SEAL is a promising step toward language models capable of self-directed adaptation. Our website and code is available at https://jyopari.github.io/posts/seal.
FAST-Q: Fast-track Exploration with Adversarially Balanced State Representations for Counterfactual Action Estimation in Offline Reinforcement Learning
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in state-of-the-art (SOTA) offline reinforcement learning (RL) have primarily focused on addressing function approximation errors, which contribute to the overestimation of Q-values for out-of-distribution actions, a challenge that static datasets exacerbate. However, high stakes applications such as recommendation systems in online gaming, introduce further complexities due to player's psychology (intent) driven by gameplay experiences and the inherent volatility on the platform. These factors create highly sparse, partially overlapping state spaces across policies, further influenced by the experiment path selection logic which biases state spaces towards specific policies. Current SOTA methods constrain learning from such offline data by clipping known counterfactual actions as out-of-distribution due to poor generalization across unobserved states. Further aggravating conservative Q-learning and necessitating more online exploration. FAST-Q introduces a novel approach that (1) leverages Gradient Reversal Learning to construct balanced state representations, regularizing the policy-specific bias between the player's state and action thereby enabling counterfactual estimation; (2) supports offline counterfactual exploration in parallel with static data exploitation; and (3) proposes a Q-value decomposition strategy for multi-objective optimization, facilitating explainable recommendations over short and long-term objectives. These innovations demonstrate superiority of FAST-Q over prior SOTA approaches and demonstrates at least 0.15 percent increase in player returns, 2 percent improvement in lifetime value (LTV), 0.4 percent enhancement in the recommendation driven engagement, 2 percent improvement in the player's platform dwell time and an impressive 10 percent reduction in the costs associated with the recommendation, on our volatile gaming platform.
Language Model Personalization via Reward Factorization
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) are optimized for human-aligned responses using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). However, existing RLHF approaches assume a universal preference model and fail to account for individual user preferences, limiting their effectiveness in personalized applications. We introduce a framework that extends RLHF to enable user personalization by leveraging the assumption that user preferences lie in a low-dimensional space. Instead of training a separate model per user, we represent user-specific rewards as a linear combination of base reward functions. Using only ~10 user responses, our method can infer user-specific rewards and align LLM outputs accordingly. We validate our approach through experiments with both synthetic and real users, demonstrating significant personalization achieved by our method. In human evaluations, our method achieves a 67% win rate over default GPT-4o responses.
General Reasoning Requires Learning to Reason from the Get-go
Feb 26, 2025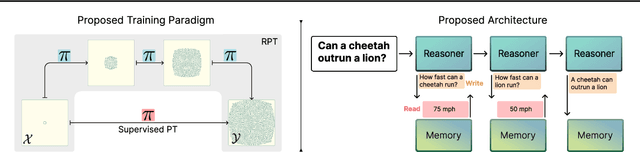
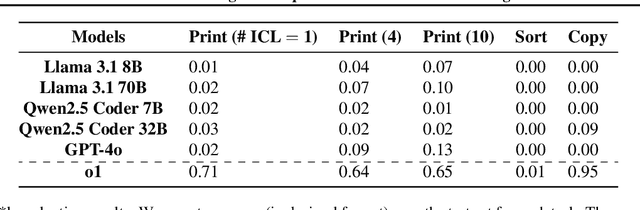
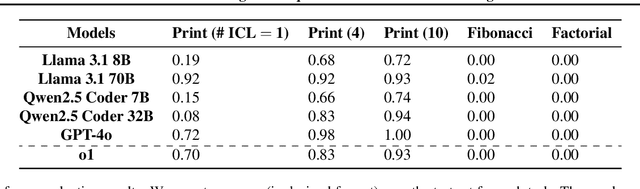
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive real-world utility, exemplifying artificial useful intelligence (AUI). However, their ability to reason adaptively and robustly -- the hallmarks of artificial general intelligence (AGI) -- remains fragile. While LLMs seemingly succeed in commonsense reasoning, programming, and mathematics, they struggle to generalize algorithmic understanding across novel contexts. Our experiments with algorithmic tasks in esoteric programming languages reveal that LLM's reasoning overfits to the training data and is limited in its transferability. We hypothesize that the core issue underlying such limited transferability is the coupling of reasoning and knowledge in LLMs. To transition from AUI to AGI, we propose disentangling knowledge and reasoning through three key directions: (1) pretaining to reason using RL from scratch as an alternative to the widely used next-token prediction pretraining, (2) using a curriculum of synthetic tasks to ease the learning of a \textit{reasoning prior} for RL that can then be transferred to natural language tasks, and (3) learning more generalizable reasoning functions using a small context window to reduce exploiting spurious correlations between tokens. Such a reasoning system coupled with a trained retrieval system and a large external memory bank as a knowledge store can overcome several limitations of existing architectures at learning to reason in novel scenarios.
Hovering Flight of Soft-Actuated Insect-Scale Micro Aerial Vehicles using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Feb 17, 2025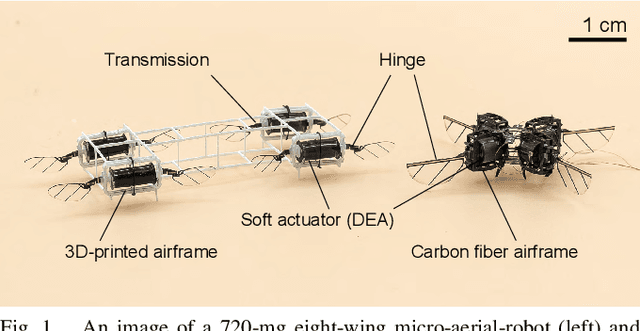
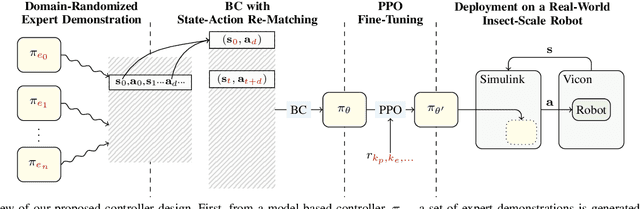
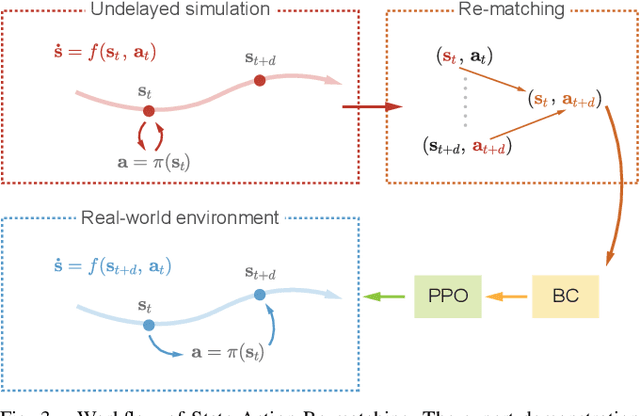
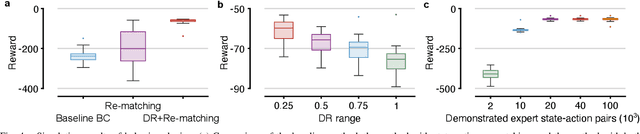
Abstract:Soft-actuated insect-scale micro aerial vehicles (IMAVs) pose unique challenges for designing robust and computationally efficient controllers. At the millimeter scale, fast robot dynamics ($\sim$ms), together with system delay, model uncertainty, and external disturbances significantly affect flight performances. Here, we design a deep reinforcement learning (RL) controller that addresses system delay and uncertainties. To initialize this neural network (NN) controller, we propose a modified behavior cloning (BC) approach with state-action re-matching to account for delay and domain-randomized expert demonstration to tackle uncertainty. Then we apply proximal policy optimization (PPO) to fine-tune the policy during RL, enhancing performance and smoothing commands. In simulations, our modified BC substantially increases the mean reward compared to baseline BC; and RL with PPO improves flight quality and reduces command fluctuations. We deploy this controller on two different insect-scale aerial robots that weigh 720 mg and 850 mg, respectively. The robots demonstrate multiple successful zero-shot hovering flights, with the longest lasting 50 seconds and root-mean-square errors of 1.34 cm in lateral direction and 0.05 cm in altitude, marking the first end-to-end deep RL-based flight on soft-driven IMAVs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge