Chenhui Shen
Open-Sora 2.0: Training a Commercial-Level Video Generation Model in $200k
Mar 12, 2025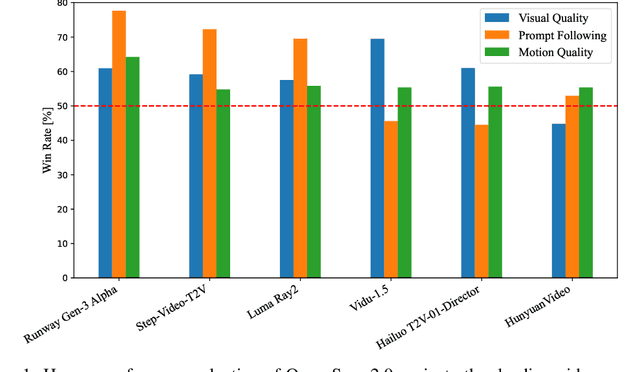
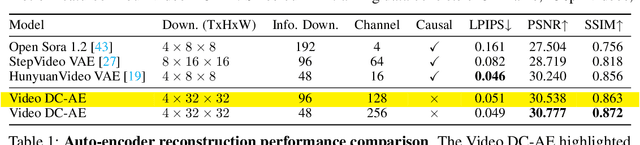
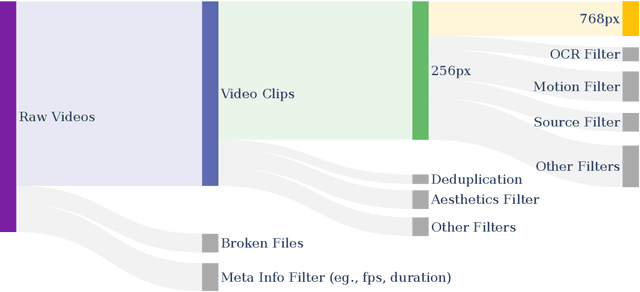
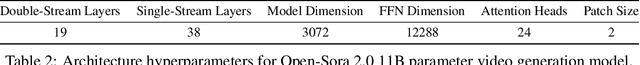
Abstract:Video generation models have achieved remarkable progress in the past year. The quality of AI video continues to improve, but at the cost of larger model size, increased data quantity, and greater demand for training compute. In this report, we present Open-Sora 2.0, a commercial-level video generation model trained for only $200k. With this model, we demonstrate that the cost of training a top-performing video generation model is highly controllable. We detail all techniques that contribute to this efficiency breakthrough, including data curation, model architecture, training strategy, and system optimization. According to human evaluation results and VBench scores, Open-Sora 2.0 is comparable to global leading video generation models including the open-source HunyuanVideo and the closed-source Runway Gen-3 Alpha. By making Open-Sora 2.0 fully open-source, we aim to democratize access to advanced video generation technology, fostering broader innovation and creativity in content creation. All resources are publicly available at: https://github.com/hpcaitech/Open-Sora.
Open-Sora: Democratizing Efficient Video Production for All
Dec 29, 2024
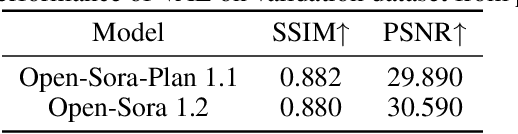
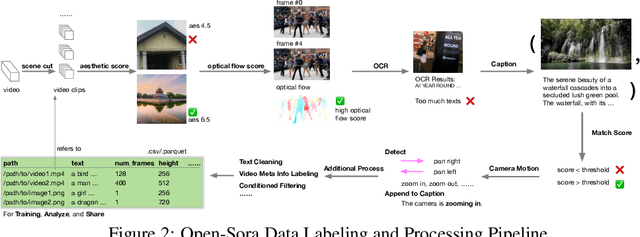
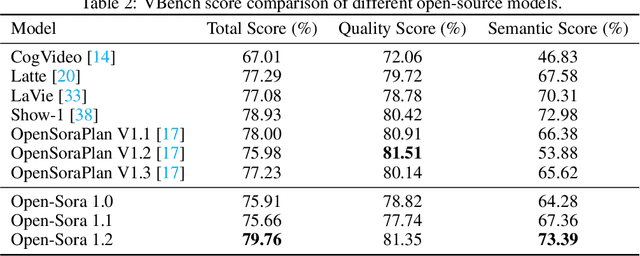
Abstract:Vision and language are the two foundational senses for humans, and they build up our cognitive ability and intelligence. While significant breakthroughs have been made in AI language ability, artificial visual intelligence, especially the ability to generate and simulate the world we see, is far lagging behind. To facilitate the development and accessibility of artificial visual intelligence, we created Open-Sora, an open-source video generation model designed to produce high-fidelity video content. Open-Sora supports a wide spectrum of visual generation tasks, including text-to-image generation, text-to-video generation, and image-to-video generation. The model leverages advanced deep learning architectures and training/inference techniques to enable flexible video synthesis, which could generate video content of up to 15 seconds, up to 720p resolution, and arbitrary aspect ratios. Specifically, we introduce Spatial-Temporal Diffusion Transformer (STDiT), an efficient diffusion framework for videos that decouples spatial and temporal attention. We also introduce a highly compressive 3D autoencoder to make representations compact and further accelerate training with an ad hoc training strategy. Through this initiative, we aim to foster innovation, creativity, and inclusivity within the community of AI content creation. By embracing the open-source principle, Open-Sora democratizes full access to all the training/inference/data preparation codes as well as model weights. All resources are publicly available at: https://github.com/hpcaitech/Open-Sora.
Are Large Language Models Good Evaluators for Abstractive Summarization?
May 22, 2023Abstract:Human evaluations are often required for abstractive summary evaluations to give fairer judgments. However, they are often time-consuming, costly, inconsistent, and non-reproducible. To overcome these challenges, we explore the potential of using an out-of-the-box LLM (i.e. "gpt-3.5-turbo") for summarization evaluation without manually selecting demonstrations or complex prompt tuning. We compare different evaluation methods, including 2 methods for Likert-scale scoring and 1 method for head-to-head comparisons, to investigate the performance of the LLM as a zero-shot evaluator. We further propose a meta-correlation metric to measure the stability of the LLM's evaluation capability. With extensive experiments, we show that certain prompt formats can produce better results than others. We also bring attention to the LLM's deteriorating evaluation capability with the rising qualities of summaries. In addition, we find that the LLM's evaluation capability also depends on the evaluated dimensions. We discuss the pros and cons of each method, make recommendations, and suggest some future directions for improvement.
A Hierarchical Encoding-Decoding Scheme for Abstractive Multi-document Summarization
May 18, 2023Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) have accomplished impressive achievements in abstractive single-document summarization (SDS). However, such benefits may not be readily extended to muti-document summarization (MDS), where the interactions among documents are more complex. Previous works either design new architectures or new pre-training objectives for MDS, or apply PLMs to MDS without considering the complex document interactions. While the former does not make full use of previous pre-training efforts and may not generalize well across multiple domains, the latter cannot fully attend to the intricate relationships unique to MDS tasks. In this paper, we enforce hierarchy on both the encoder and decoder and seek to make better use of a PLM to facilitate multi-document interactions for the MDS task. We test our design on 10 MDS datasets across a wide range of domains. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method can achieve consistent improvements on all these datasets, outperforming the previous best models, and even achieving better or competitive results as compared to some models with additional MDS pre-training or larger model parameters.
SentBS: Sentence-level Beam Search for Controllable Summarization
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:A wide range of control perspectives have been explored in controllable text generation. Structure-controlled summarization is recently proposed as a useful and interesting research direction. However, current structure-controlling methods have limited effectiveness in enforcing the desired structure. To address this limitation, we propose a sentence-level beam search generation method (SentBS), where evaluation is conducted throughout the generation process to select suitable sentences for subsequent generations. We experiment with different combinations of decoding methods to be used as subcomponents by SentBS and evaluate results on the structure-controlled dataset MReD. Experiments show that all explored combinations for SentBS can improve the agreement between the generated text and the desired structure, with the best method significantly reducing the structural discrepancies suffered by the existing model, by approximately 68%.
MReD: A Meta-Review Dataset for Controllable Text Generation
Oct 14, 2021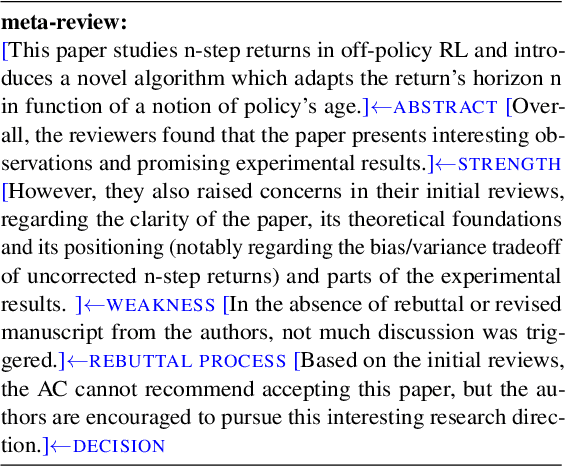
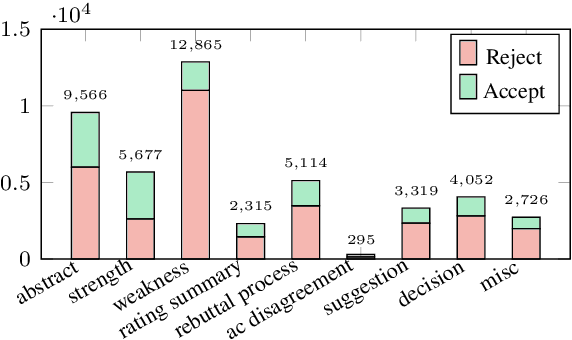
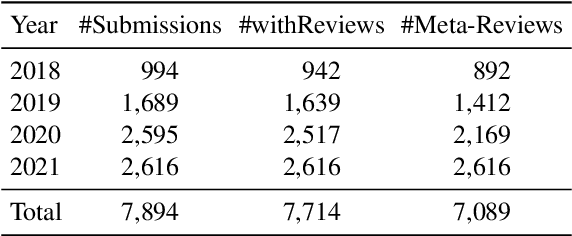
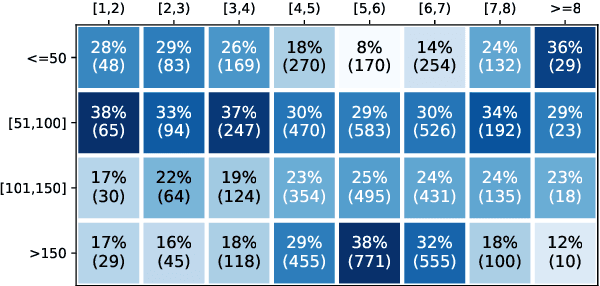
Abstract:When directly using existing text generation datasets for controllable generation, we are facing the problem of not having the domain knowledge and thus the aspects that could be controlled are limited.A typical example is when using CNN/Daily Mail dataset for controllable text summarization, there is no guided information on the emphasis of summary sentences. A more useful text generator should leverage both the input text and control variables to guide the generation, which can only be built with deep understanding of the domain knowledge. Motivated by this vi-sion, our paper introduces a new text generation dataset, named MReD. Our new dataset consists of 7,089 meta-reviews and all its 45k meta-review sentences are manually annotated as one of the carefully defined 9 categories, including abstract, strength, decision, etc. We present experimental results on start-of-the-art summarization models, and propose methods for controlled generation on both extractive and abstractive models using our annotated data. By exploring various settings and analaysing the model behavior with respect to the control inputs, we demonstrate the challenges and values of our dataset. MReD allows us to have a better understanding of the meta-review corpora and enlarge the research room for controllable text generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge