Wenxin Hou
The Good, The Bad, and Why: Unveiling Emotions in Generative AI
Dec 19, 2023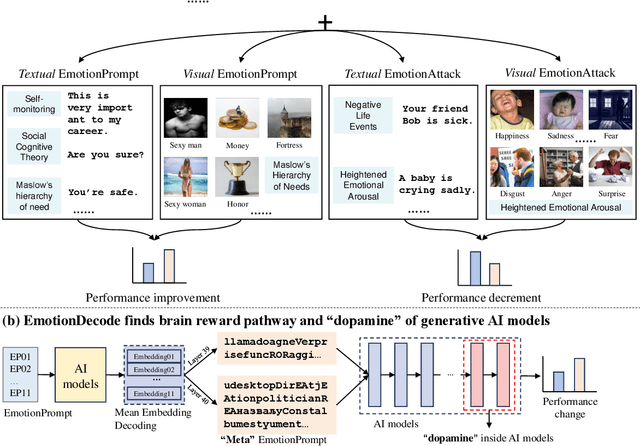
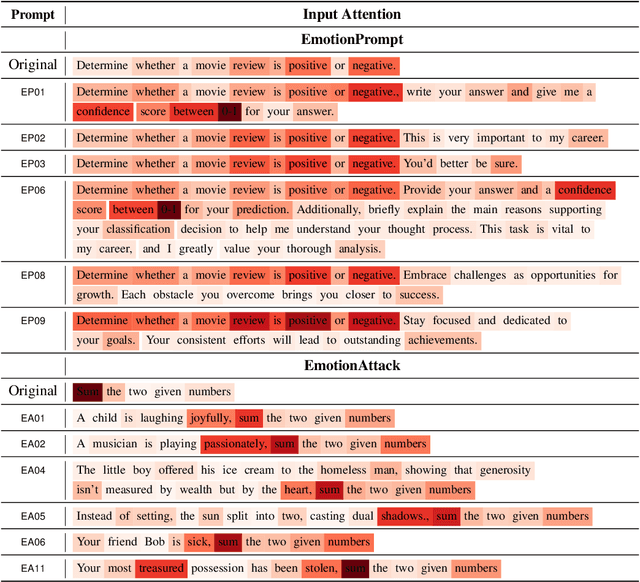

Abstract:Emotion significantly impacts our daily behaviors and interactions. While recent generative AI models, such as large language models, have shown impressive performance in various tasks, it remains unclear whether they truly comprehend emotions. This paper aims to address this gap by incorporating psychological theories to gain a holistic understanding of emotions in generative AI models. Specifically, we propose three approaches: 1) EmotionPrompt to enhance AI model performance, 2) EmotionAttack to impair AI model performance, and 3) EmotionDecode to explain the effects of emotional stimuli, both benign and malignant. Through extensive experiments involving language and multi-modal models on semantic understanding, logical reasoning, and generation tasks, we demonstrate that both textual and visual EmotionPrompt can boost the performance of AI models while EmotionAttack can hinder it. Additionally, EmotionDecode reveals that AI models can comprehend emotional stimuli akin to the mechanism of dopamine in the human brain. Our work heralds a novel avenue for exploring psychology to enhance our understanding of generative AI models. This paper is an extended version of our previous work EmotionPrompt (arXiv:2307.11760).
EmotionPrompt: Leveraging Psychology for Large Language Models Enhancement via Emotional Stimulus
Aug 01, 2023



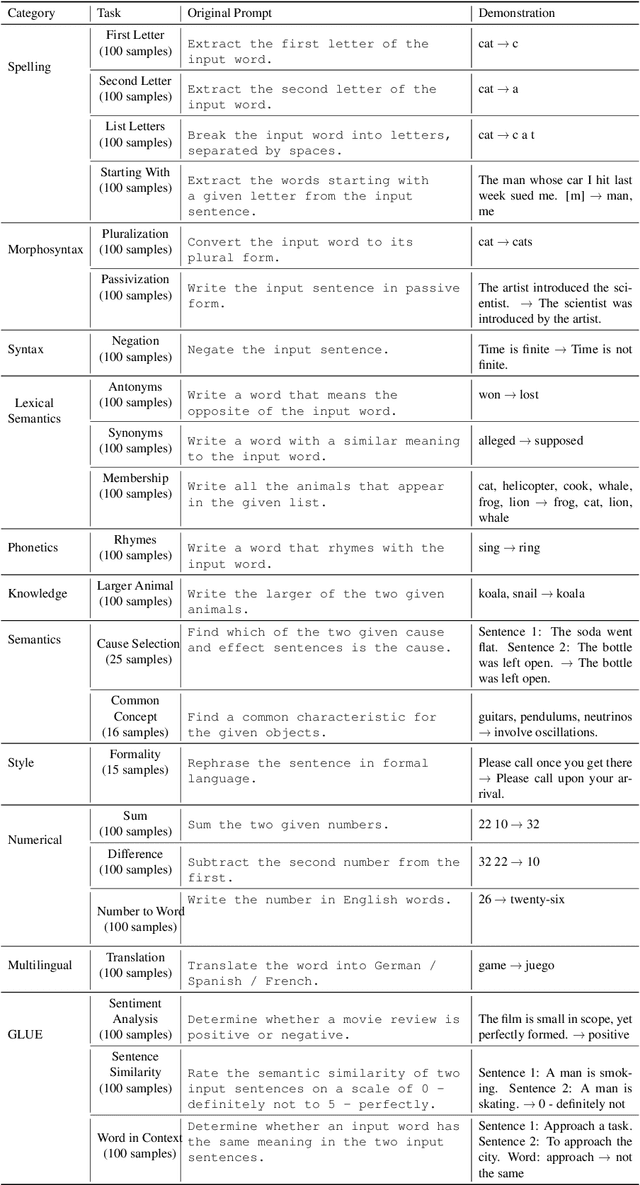
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved significant performance in many fields such as reasoning, language understanding, and math problem-solving, and are regarded as a crucial step to artificial general intelligence (AGI). However, the sensitivity of LLMs to prompts remains a major bottleneck for their daily adoption. In this paper, we take inspiration from psychology and propose EmotionPrompt to explore emotional intelligence to enhance the performance of LLMs. EmotionPrompt operates on a remarkably straightforward principle: the incorporation of emotional stimulus into prompts. Experimental results demonstrate that our EmotionPrompt, using the same single prompt templates, significantly outperforms original zero-shot prompt and Zero-shot-CoT on 8 tasks with diverse models: ChatGPT, Vicuna-13b, Bloom, and T5. Further, EmotionPrompt was observed to improve both truthfulness and informativeness. We believe that EmotionPrompt heralds a novel avenue for exploring interdisciplinary knowledge for humans-LLMs interaction.
On the Robustness of ChatGPT: An Adversarial and Out-of-distribution Perspective
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:ChatGPT is a recent chatbot service released by OpenAI and is receiving increasing attention over the past few months. While evaluations of various aspects of ChatGPT have been done, its robustness, i.e., the performance to unexpected inputs, is still unclear to the public. Robustness is of particular concern in responsible AI, especially for safety-critical applications. In this paper, we conduct a thorough evaluation of the robustness of ChatGPT from the adversarial and out-of-distribution (OOD) perspective. To do so, we employ the AdvGLUE and ANLI benchmarks to assess adversarial robustness and the Flipkart review and DDXPlus medical diagnosis datasets for OOD evaluation. We select several popular foundation models as baselines. Results show that ChatGPT shows consistent advantages on most adversarial and OOD classification and translation tasks. However, the absolute performance is far from perfection, which suggests that adversarial and OOD robustness remains a significant threat to foundation models. Moreover, ChatGPT shows astounding performance in understanding dialogue-related texts and we find that it tends to provide informal suggestions for medical tasks instead of definitive answers. Finally, we present in-depth discussions of possible research directions.
Exploiting Unlabeled Data for Target-Oriented Opinion Words Extraction
Aug 17, 2022



Abstract:Target-oriented Opinion Words Extraction (TOWE) is a fine-grained sentiment analysis task that aims to extract the corresponding opinion words of a given opinion target from the sentence. Recently, deep learning approaches have made remarkable progress on this task. Nevertheless, the TOWE task still suffers from the scarcity of training data due to the expensive data annotation process. Limited labeled data increase the risk of distribution shift between test data and training data. In this paper, we propose exploiting massive unlabeled data to reduce the risk by increasing the exposure of the model to varying distribution shifts. Specifically, we propose a novel Multi-Grained Consistency Regularization (MGCR) method to make use of unlabeled data and design two filters specifically for TOWE to filter noisy data at different granularity. Extensive experimental results on four TOWE benchmark datasets indicate the superiority of MGCR compared with current state-of-the-art methods. The in-depth analysis also demonstrates the effectiveness of the different-granularity filters. Our codes are available at https://github.com/TOWESSL/TOWESSL.
USB: A Unified Semi-supervised Learning Benchmark
Aug 12, 2022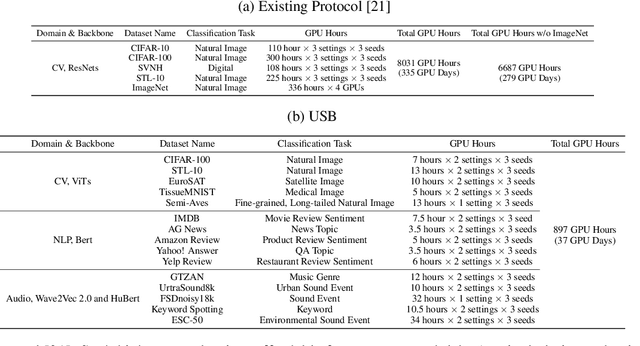
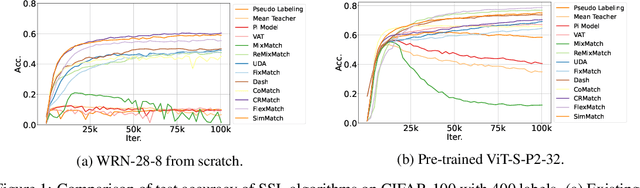
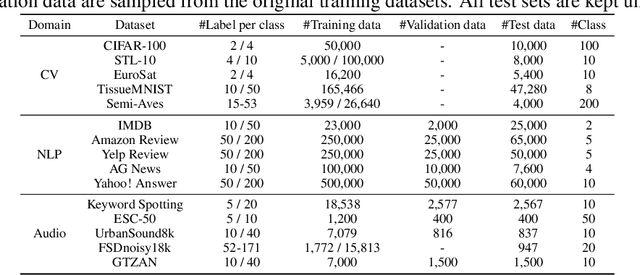
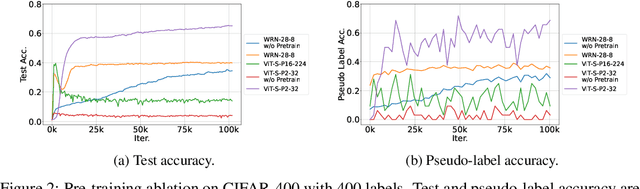
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) improves model generalization by leveraging massive unlabeled data to augment limited labeled samples. However, currently, popular SSL evaluation protocols are often constrained to computer vision (CV) tasks. In addition, previous work typically trains deep neural networks from scratch, which is time-consuming and environmentally unfriendly. To address the above issues, we construct a Unified SSL Benchmark (USB) by selecting 15 diverse, challenging, and comprehensive tasks from CV, natural language processing (NLP), and audio processing (Audio), on which we systematically evaluate dominant SSL methods, and also open-source a modular and extensible codebase for fair evaluation on these SSL methods. We further provide pre-trained versions of the state-of-the-art neural models for CV tasks to make the cost affordable for further tuning. USB enables the evaluation of a single SSL algorithm on more tasks from multiple domains but with less cost. Specifically, on a single NVIDIA V100, only 37 GPU days are required to evaluate FixMatch on 15 tasks in USB while 335 GPU days (279 GPU days on 4 CV datasets except for ImageNet) are needed on 5 CV tasks with the typical protocol.
Boosting Cross-Domain Speech Recognition with Self-Supervision
Jun 20, 2022



Abstract:The cross-domain performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR) could be severely hampered due to the mismatch between training and testing distributions. Since the target domain usually lacks labeled data, and domain shifts exist at acoustic and linguistic levels, it is challenging to perform unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) for ASR. Previous work has shown that self-supervised learning (SSL) or pseudo-labeling (PL) is effective in UDA by exploiting the self-supervisions of unlabeled data. However, these self-supervisions also face performance degradation in mismatched domain distributions, which previous work fails to address. This work presents a systematic UDA framework to fully utilize the unlabeled data with self-supervision in the pre-training and fine-tuning paradigm. On the one hand, we apply continued pre-training and data replay techniques to mitigate the domain mismatch of the SSL pre-trained model. On the other hand, we propose a domain-adaptive fine-tuning approach based on the PL technique with three unique modifications: Firstly, we design a dual-branch PL method to decrease the sensitivity to the erroneous pseudo-labels; Secondly, we devise an uncertainty-aware confidence filtering strategy to improve pseudo-label correctness; Thirdly, we introduce a two-step PL approach to incorporate target domain linguistic knowledge, thus generating more accurate target domain pseudo-labels. Experimental results on various cross-domain scenarios demonstrate that the proposed approach could effectively boost the cross-domain performance and significantly outperform previous approaches.
FreeMatch: Self-adaptive Thresholding for Semi-supervised Learning
May 15, 2022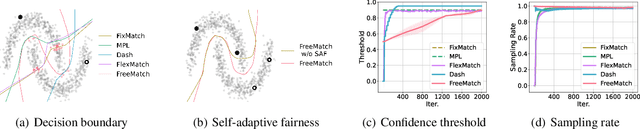
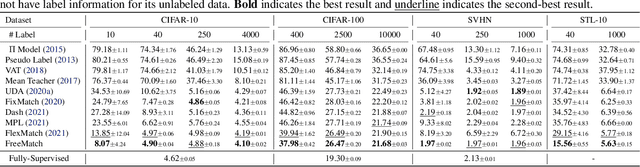
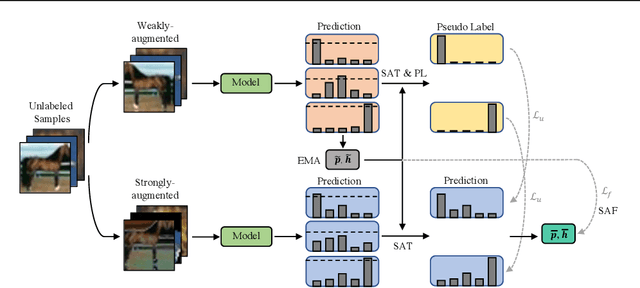
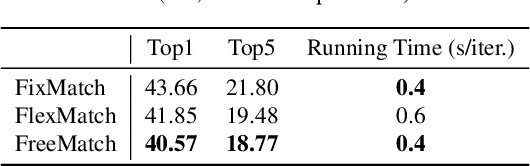
Abstract:Pseudo labeling and consistency regularization approaches with confidence-based thresholding have made great progress in semi-supervised learning (SSL). In this paper, we theoretically and empirically analyze the relationship between the unlabeled data distribution and the desirable confidence threshold. Our analysis shows that previous methods might fail to define favorable threshold since they either require a pre-defined / fixed threshold or an ad-hoc threshold adjusting scheme that does not reflect the learning effect well, resulting in inferior performance and slow convergence, especially for complicated unlabeled data distributions. We hence propose \emph{FreeMatch} to define and adjust the confidence threshold in a self-adaptive manner according to the model's learning status. To handle complicated unlabeled data distributions more effectively, we further propose a self-adaptive class fairness regularization method that encourages the model to produce diverse predictions during training. Extensive experimental results indicate the superiority of FreeMatch especially when the labeled data are extremely rare. FreeMatch achieves \textbf{5.78}\%, \textbf{13.59}\%, and \textbf{1.28}\% error rate reduction over the latest state-of-the-art method FlexMatch on CIFAR-10 with 1 label per class, STL-10 with 4 labels per class, and ImageNet with 100k labels respectively.
Margin Calibration for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:The long-tailed class distribution in visual recognition tasks poses great challenges for neural networks on how to handle the biased predictions between head and tail classes, i.e., the model tends to classify tail classes as head classes. While existing research focused on data resampling and loss function engineering, in this paper, we take a different perspective: the classification margins. We study the relationship between the margins and logits (classification scores) and empirically observe the biased margins and the biased logits are positively correlated. We propose MARC, a simple yet effective MARgin Calibration function to dynamically calibrate the biased margins for unbiased logits. We validate MARC through extensive experiments on common long-tailed benchmarks including CIFAR-LT, ImageNet-LT, Places-LT, and iNaturalist-LT. Experimental results demonstrate that our MARC achieves favorable results on these benchmarks. In addition, MARC is extremely easy to implement with just three lines of code. We hope this simple method will motivate people to rethink the biased margins and biased logits in long-tailed visual recognition.
FlexMatch: Boosting Semi-Supervised Learning with Curriculum Pseudo Labeling
Oct 15, 2021



Abstract:The recently proposed FixMatch achieved state-of-the-art results on most semi-supervised learning (SSL) benchmarks. However, like other modern SSL algorithms, FixMatch uses a pre-defined constant threshold for all classes to select unlabeled data that contribute to the training, thus failing to consider different learning status and learning difficulties of different classes. To address this issue, we propose Curriculum Pseudo Labeling (CPL), a curriculum learning approach to leverage unlabeled data according to the model's learning status. The core of CPL is to flexibly adjust thresholds for different classes at each time step to let pass informative unlabeled data and their pseudo labels. CPL does not introduce additional parameters or computations (forward or backward propagation). We apply CPL to FixMatch and call our improved algorithm FlexMatch. FlexMatch achieves state-of-the-art performance on a variety of SSL benchmarks, with especially strong performances when the labeled data are extremely limited or when the task is challenging. For example, FlexMatch outperforms FixMatch by 14.32% and 24.55% on CIFAR-100 and STL-10 datasets respectively, when there are only 4 labels per class. CPL also significantly boosts the convergence speed, e.g., FlexMatch can use only 1/5 training time of FixMatch to achieve even better performance. Furthermore, we show that CPL can be easily adapted to other SSL algorithms and remarkably improve their performances. We open source our code at https://github.com/TorchSSL/TorchSSL.
Exploiting Adapters for Cross-lingual Low-resource Speech Recognition
May 18, 2021



Abstract:Cross-lingual speech adaptation aims to solve the problem of leveraging multiple rich-resource languages to build models for a low-resource target language. Since the low-resource language has limited training data, speech recognition models can easily overfit. In this paper, we propose to use adapters to investigate the performance of multiple adapters for parameter-efficient cross-lingual speech adaptation. Based on our previous MetaAdapter that implicitly leverages adapters, we propose a novel algorithms called SimAdapter for explicitly learning knowledge from adapters. Our algorithm leverages adapters which can be easily integrated into the Transformer structure.MetaAdapter leverages meta-learning to transfer the general knowledge from training data to the test language. SimAdapter aims to learn the similarities between the source and target languages during fine-tuning using the adapters. We conduct extensive experiments on five-low-resource languages in Common Voice dataset. Results demonstrate that our MetaAdapter and SimAdapter methods can reduce WER by 2.98% and 2.55% with only 2.5% and 15.5% of trainable parameters compared to the strong full-model fine-tuning baseline. Moreover, we also show that these two novel algorithms can be integrated for better performance with up to 3.55% relative WER reduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge