Manabu Okumura
Who Laughs with Whom? Disentangling Influential Factors in Humor Preferences across User Clusters and LLMs
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Humor preferences vary widely across individuals and cultures, complicating the evaluation of humor using large language models (LLMs). In this study, we model heterogeneity in humor preferences in Oogiri, a Japanese creative response game, by clustering users with voting logs and estimating cluster-specific weights over interpretable preference factors using Bradley-Terry-Luce models. We elicit preference judgments from LLMs by prompting them to select the funnier response and found that user clusters exhibit distinct preference patterns and that the LLM results can resemble those of particular clusters. Finally, we demonstrate that, by persona prompting, LLM preferences can be directed toward a specific cluster. The scripts for data collection and analysis will be released to support reproducibility.
Oogiri-Master: Benchmarking Humor Understanding via Oogiri
Dec 25, 2025
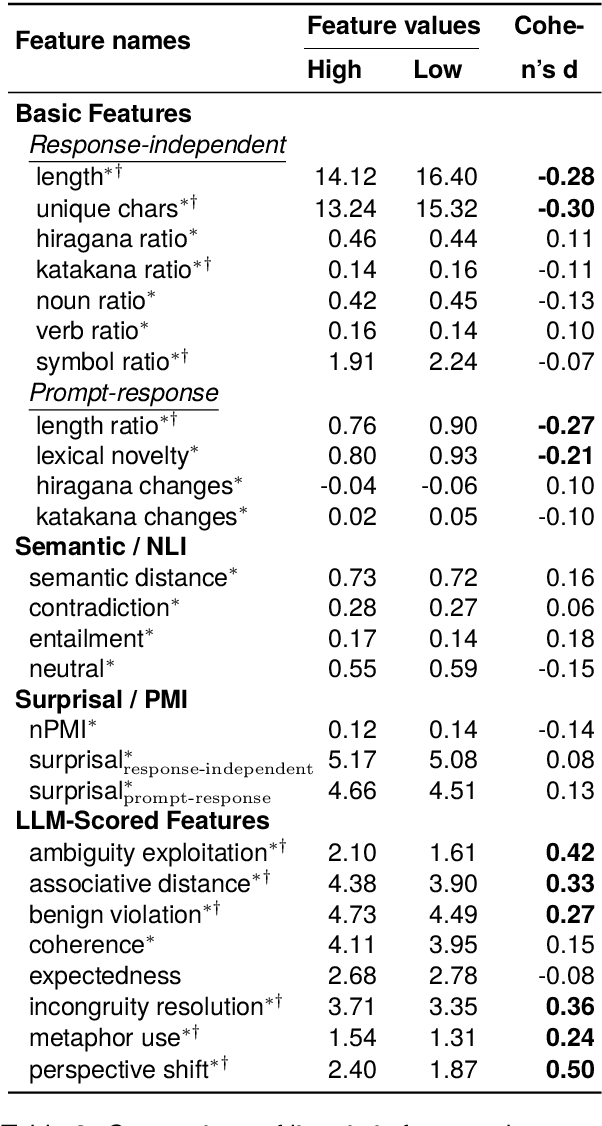

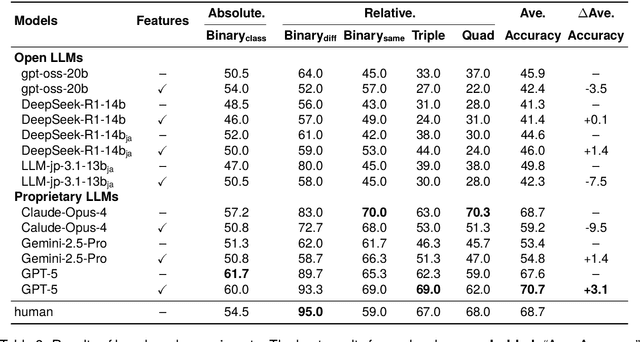
Abstract:Humor is a salient testbed for human-like creative thinking in large language models (LLMs). We study humor using the Japanese creative response game Oogiri, in which participants produce witty responses to a given prompt, and ask the following research question: What makes such responses funny to humans? Previous work has offered only limited reliable means to answer this question. Existing datasets contain few candidate responses per prompt, expose popularity signals during ratings, and lack objective and comparable metrics for funniness. Thus, we introduce Oogiri-Master and Oogiri-Corpus, which are a benchmark and dataset designed to enable rigorous evaluation of humor understanding in LLMs. Each prompt is paired with approximately 100 diverse candidate responses, and funniness is rated independently by approximately 100 human judges without access to others' ratings, reducing popularity bias and enabling robust aggregation. Using Oogiri-Corpus, we conduct a quantitative analysis of the linguistic factors associated with funniness, such as text length, ambiguity, and incongruity resolution, and derive objective metrics for predicting human judgments. Subsequently, we benchmark a range of LLMs and human baselines in Oogiri-Master, demonstrating that state-of-the-art models approach human performance and that insight-augmented prompting improves the model performance. Our results provide a principled basis for evaluating and advancing humor understanding in LLMs.
Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding for Error Span Detection in Reference-Free Automatic Machine Translation Evaluation
Dec 19, 2025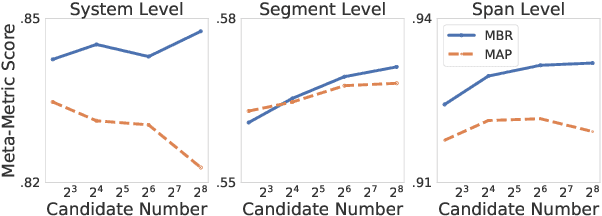

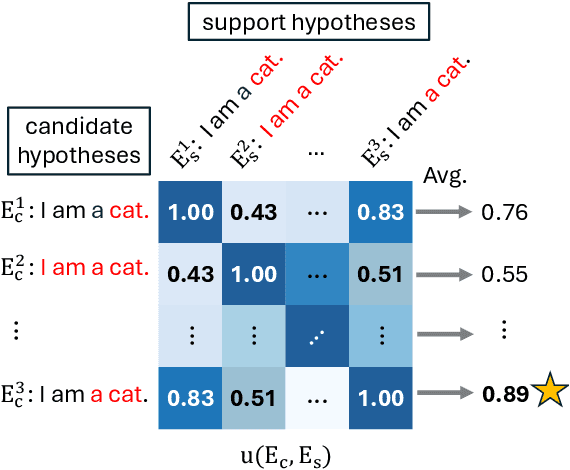
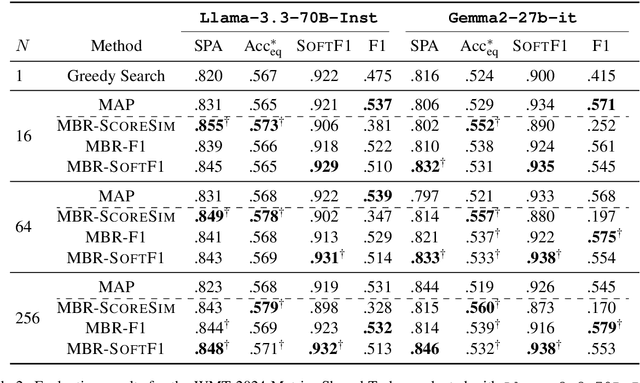
Abstract:Error Span Detection (ESD) extends automatic machine translation (MT) evaluation by localizing translation errors and labeling their severity. Current generative ESD methods typically use Maximum a Posteriori (MAP) decoding, assuming that the model-estimated probabilities are perfectly correlated with similarity to the human annotation, but we often observe higher likelihood assigned to an incorrect annotation than to the human one. We instead apply Minimum Bayes Risk (MBR) decoding to generative ESD. We use a sentence- or span-level similarity function for MBR decoding, which selects candidate hypotheses based on their approximate similarity to the human annotation. Experimental results on the WMT24 Metrics Shared Task show that MBR decoding significantly improves span-level performance and generally matches or outperforms MAP at the system and sentence levels. To reduce the computational cost of MBR decoding, we further distill its decisions into a model decoded via greedy search, removing the inference-time latency bottleneck.
MMCIG: Multimodal Cover Image Generation for Text-only Documents and Its Dataset Construction via Pseudo-labeling
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:In this study, we introduce a novel cover image generation task that produces both a concise summary and a visually corresponding image from a given text-only document. Because no existing datasets are available for this task, we propose a multimodal pseudo-labeling method to construct high-quality datasets at low cost. We first collect documents that contain multiple images with their captions, and their summaries by excluding factually inconsistent instances. Our approach selects one image from the multiple images accompanying the documents. Using the gold summary, we independently rank both the images and their captions. Then, we annotate a pseudo-label for an image when both the image and its corresponding caption are ranked first in their respective rankings. Finally, we remove documents that contain direct image references within texts. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed multimodal pseudo-labeling method constructs more precise datasets and generates higher quality images than text- and image-only pseudo-labeling methods, which consider captions and images separately. We release our code at: https://github.com/HyeyeeonKim/MMCIG
CodeNER: Code Prompting for Named Entity Recognition
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have explored various approaches for treating candidate named entity spans as both source and target sequences in named entity recognition (NER) by leveraging large language models (LLMs). Although previous approaches have successfully generated candidate named entity spans with suitable labels, they rely solely on input context information when using LLMs, particularly, ChatGPT. However, NER inherently requires capturing detailed labeling requirements with input context information. To address this issue, we propose a novel method that leverages code-based prompting to improve the capabilities of LLMs in understanding and performing NER. By embedding code within prompts, we provide detailed BIO schema instructions for labeling, thereby exploiting the ability of LLMs to comprehend long-range scopes in programming languages. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed code-based prompting method outperforms conventional text-based prompting on ten benchmarks across English, Arabic, Finnish, Danish, and German datasets, indicating the effectiveness of explicitly structuring NER instructions. We also verify that combining the proposed code-based prompting method with the chain-of-thought prompting further improves performance.
Length Representations in Large Language Models
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across various tasks, that are learned from massive amounts of text-based data. Although LLMs can control output sequence length, particularly in instruction-based settings, the internal mechanisms behind this control have been unexplored yet. In this study, we provide empirical evidence on how output sequence length information is encoded within the internal representations in LLMs. In particular, our findings show that multi-head attention mechanisms are critical in determining output sequence length, which can be adjusted in a disentangled manner. By scaling specific hidden units within the model, we can control the output sequence length without losing the informativeness of the generated text, thereby indicating that length information is partially disentangled from semantic information. Moreover, some hidden units become increasingly active as prompts become more length-specific, thus reflecting the model's internal awareness of this attribute. Our findings suggest that LLMs have learned robust and adaptable internal mechanisms for controlling output length without any external control.
Diversity of Transformer Layers: One Aspect of Parameter Scaling Laws
May 29, 2025
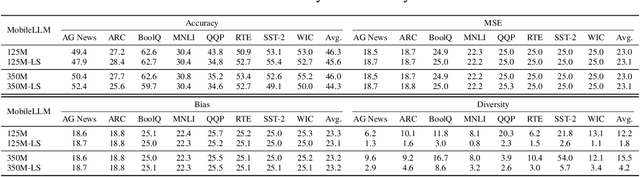
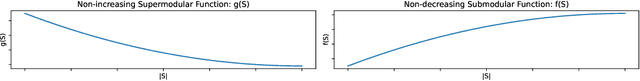
Abstract:Transformers deliver outstanding performance across a wide range of tasks and are now a dominant backbone architecture for large language models (LLMs). Their task-solving performance is improved by increasing parameter size, as shown in the recent studies on parameter scaling laws. Although recent mechanistic-interpretability studies have deepened our understanding of the internal behavior of Transformers by analyzing their residual stream, the relationship between these internal mechanisms and the parameter scaling laws remains unclear. To bridge this gap, we focus on layers and their size, which mainly decide the parameter size of Transformers. For this purpose, we first theoretically investigate the layers within the residual stream through a bias-diversity decomposition. The decomposition separates (i) bias, the error of each layer's output from the ground truth, and (ii) diversity, which indicates how much the outputs of each layer differ from each other. Analyzing Transformers under this theory reveals that performance improves when individual layers make predictions close to the correct answer and remain mutually diverse. We show that diversity becomes especially critical when individual layers' outputs are far from the ground truth. Finally, we introduce an information-theoretic diversity and show our main findings that adding layers enhances performance only when those layers behave differently, i.e., are diverse. We also reveal the performance gains from increasing the number of layers exhibit submodularity: marginal improvements diminish as additional layers increase, mirroring the logarithmic convergence predicted by the parameter scaling laws. Experiments on multiple semantic-understanding tasks with various LLMs empirically confirm the theoretical properties derived in this study.
AdParaphrase v2.0: Generating Attractive Ad Texts Using a Preference-Annotated Paraphrase Dataset
May 27, 2025Abstract:Identifying factors that make ad text attractive is essential for advertising success. This study proposes AdParaphrase v2.0, a dataset for ad text paraphrasing, containing human preference data, to enable the analysis of the linguistic factors and to support the development of methods for generating attractive ad texts. Compared with v1.0, this dataset is 20 times larger, comprising 16,460 ad text paraphrase pairs, each annotated with preference data from ten evaluators, thereby enabling a more comprehensive and reliable analysis. Through the experiments, we identified multiple linguistic features of engaging ad texts that were not observed in v1.0 and explored various methods for generating attractive ad texts. Furthermore, our analysis demonstrated the relationships between human preference and ad performance, and highlighted the potential of reference-free metrics based on large language models for evaluating ad text attractiveness. The dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/CyberAgentAILab/AdParaphrase-v2.0.
Taming Recommendation Bias with Causal Intervention on Evolving Personal Popularity
May 20, 2025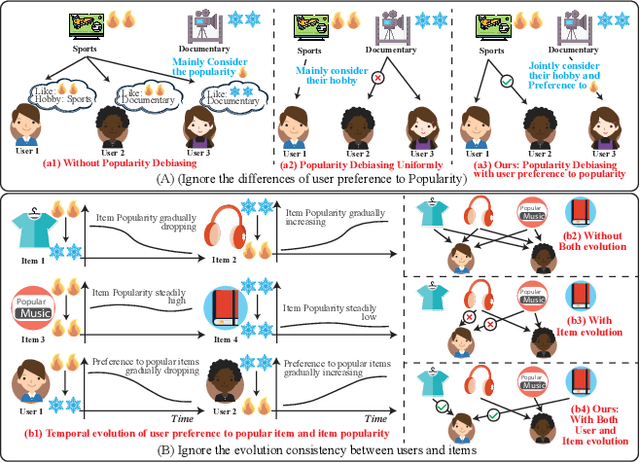
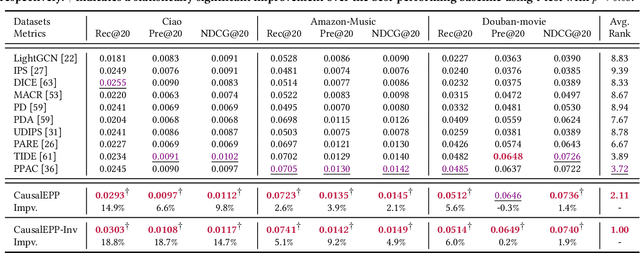
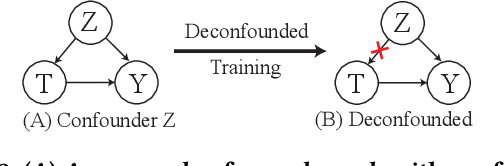
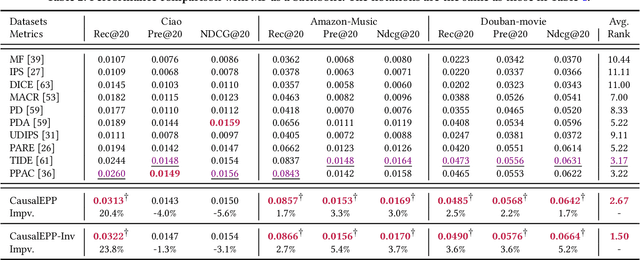
Abstract:Popularity bias occurs when popular items are recommended far more frequently than they should be, negatively impacting both user experience and recommendation accuracy. Existing debiasing methods mitigate popularity bias often uniformly across all users and only partially consider the time evolution of users or items. However, users have different levels of preference for item popularity, and this preference is evolving over time. To address these issues, we propose a novel method called CausalEPP (Causal Intervention on Evolving Personal Popularity) for taming recommendation bias, which accounts for the evolving personal popularity of users. Specifically, we first introduce a metric called {Evolving Personal Popularity} to quantify each user's preference for popular items. Then, we design a causal graph that integrates evolving personal popularity into the conformity effect, and apply deconfounded training to mitigate the popularity bias of the causal graph. During inference, we consider the evolution consistency between users and items to achieve a better recommendation. Empirical studies demonstrate that CausalEPP outperforms baseline methods in reducing popularity bias while improving recommendation accuracy.
TextTIGER: Text-based Intelligent Generation with Entity Prompt Refinement for Text-to-Image Generation
Apr 25, 2025



Abstract:Generating images from prompts containing specific entities requires models to retain as much entity-specific knowledge as possible. However, fully memorizing such knowledge is impractical due to the vast number of entities and their continuous emergence. To address this, we propose Text-based Intelligent Generation with Entity prompt Refinement (TextTIGER), which augments knowledge on entities included in the prompts and then summarizes the augmented descriptions using Large Language Models (LLMs) to mitigate performance degradation from longer inputs. To evaluate our method, we introduce WiT-Cub (WiT with Captions and Uncomplicated Background-explanations), a dataset comprising captions, images, and an entity list. Experiments on four image generation models and five LLMs show that TextTIGER improves image generation performance in standard metrics (IS, FID, and CLIPScore) compared to caption-only prompts. Additionally, multiple annotators' evaluation confirms that the summarized descriptions are more informative, validating LLMs' ability to generate concise yet rich descriptions. These findings demonstrate that refining prompts with augmented and summarized entity-related descriptions enhances image generation capabilities. The code and dataset will be available upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge