Renhe Jiang
See2Refine: Vision-Language Feedback Improves LLM-Based eHMI Action Designers
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Automated vehicles lack natural communication channels with other road users, making external Human-Machine Interfaces (eHMIs) essential for conveying intent and maintaining trust in shared environments. However, most eHMI studies rely on developer-crafted message-action pairs, which are difficult to adapt to diverse and dynamic traffic contexts. A promising alternative is to use Large Language Models (LLMs) as action designers that generate context-conditioned eHMI actions, yet such designers lack perceptual verification and typically depend on fixed prompts or costly human-annotated feedback for improvement. We present See2Refine, a human-free, closed-loop framework that uses vision-language model (VLM) perceptual evaluation as automated visual feedback to improve an LLM-based eHMI action designer. Given a driving context and a candidate eHMI action, the VLM evaluates the perceived appropriateness of the action, and this feedback is used to iteratively revise the designer's outputs, enabling systematic refinement without human supervision. We evaluate our framework across three eHMI modalities (lightbar, eyes, and arm) and multiple LLM model sizes. Across settings, our framework consistently outperforms prompt-only LLM designers and manually specified baselines in both VLM-based metrics and human-subject evaluations. Results further indicate that the improvements generalize across modalities and that VLM evaluations are well aligned with human preferences, supporting the robustness and effectiveness of See2Refine for scalable action design.
Towards Resilient Transportation: A Conditional Transformer for Accident-Informed Traffic Forecasting
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Traffic prediction remains a key challenge in spatio-temporal data mining, despite progress in deep learning. Accurate forecasting is hindered by the complex influence of external factors such as traffic accidents and regulations, often overlooked by existing models due to limited data integration. To address these limitations, we present two enriched traffic datasets from Tokyo and California, incorporating traffic accident and regulation data. Leveraging these datasets, we propose ConFormer (Conditional Transformer), a novel framework that integrates graph propagation with guided normalization layer. This design dynamically adjusts spatial and temporal node relationships based on historical patterns, enhancing predictive accuracy. Our model surpasses the state-of-the-art STAEFormer in both predictive performance and efficiency, achieving lower computational costs and reduced parameter demands. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that ConFormer consistently outperforms mainstream spatio-temporal baselines across multiple metrics, underscoring its potential to advance traffic prediction research.
How Different from the Past? Spatio-Temporal Time Series Forecasting with Self-Supervised Deviation Learning
Oct 06, 2025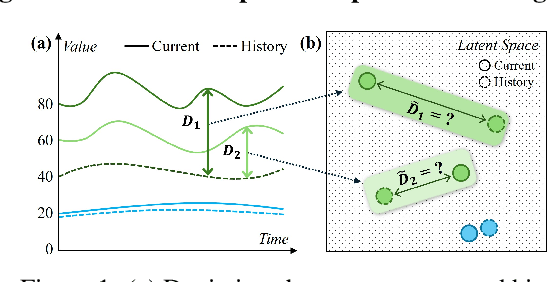
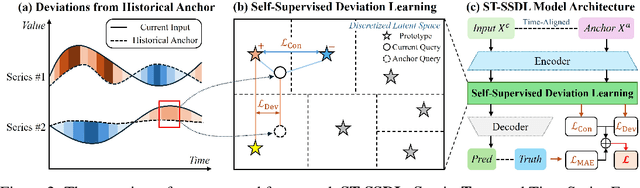
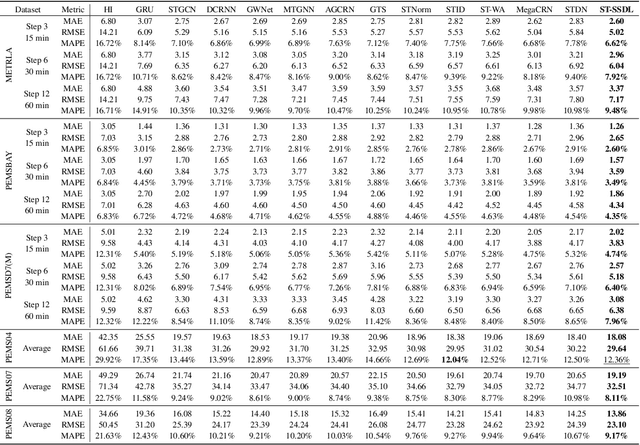
Abstract:Spatio-temporal forecasting is essential for real-world applications such as traffic management and urban computing. Although recent methods have shown improved accuracy, they often fail to account for dynamic deviations between current inputs and historical patterns. These deviations contain critical signals that can significantly affect model performance. To fill this gap, we propose ST-SSDL, a Spatio-Temporal time series forecasting framework that incorporates a Self-Supervised Deviation Learning scheme to capture and utilize such deviations. ST-SSDL anchors each input to its historical average and discretizes the latent space using learnable prototypes that represent typical spatio-temporal patterns. Two auxiliary objectives are proposed to refine this structure: a contrastive loss that enhances inter-prototype discriminability and a deviation loss that regularizes the distance consistency between input representations and corresponding prototypes to quantify deviation. Optimized jointly with the forecasting objective, these components guide the model to organize its hidden space and improve generalization across diverse input conditions. Experiments on six benchmark datasets show that ST-SSDL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across multiple metrics. Visualizations further demonstrate its ability to adaptively respond to varying levels of deviation in complex spatio-temporal scenarios. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/Jimmy-7664/ST-SSDL.
A Call for Collaborative Intelligence: Why Human-Agent Systems Should Precede AI Autonomy
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Recent improvements in large language models (LLMs) have led many researchers to focus on building fully autonomous AI agents. This position paper questions whether this approach is the right path forward, as these autonomous systems still have problems with reliability, transparency, and understanding the actual requirements of human. We suggest a different approach: LLM-based Human-Agent Systems (LLM-HAS), where AI works with humans rather than replacing them. By keeping human involved to provide guidance, answer questions, and maintain control, these systems can be more trustworthy and adaptable. Looking at examples from healthcare, finance, and software development, we show how human-AI teamwork can handle complex tasks better than AI working alone. We also discuss the challenges of building these collaborative systems and offer practical solutions. This paper argues that progress in AI should not be measured by how independent systems become, but by how well they can work with humans. The most promising future for AI is not in systems that take over human roles, but in those that enhance human capabilities through meaningful partnership.
Taming Recommendation Bias with Causal Intervention on Evolving Personal Popularity
May 20, 2025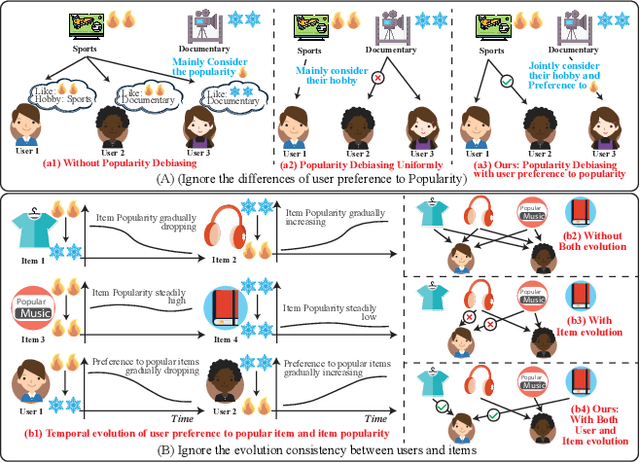
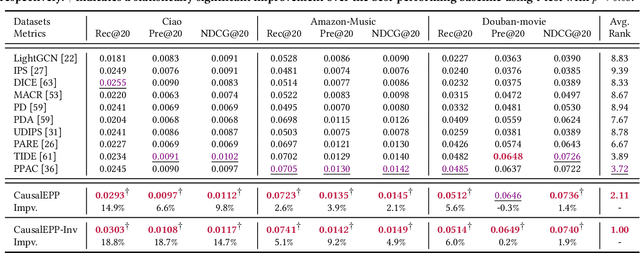
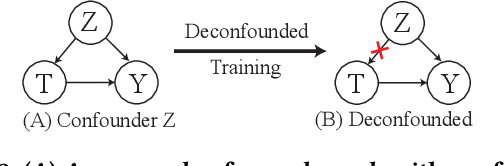
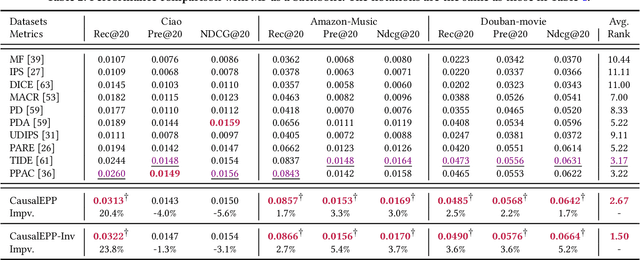
Abstract:Popularity bias occurs when popular items are recommended far more frequently than they should be, negatively impacting both user experience and recommendation accuracy. Existing debiasing methods mitigate popularity bias often uniformly across all users and only partially consider the time evolution of users or items. However, users have different levels of preference for item popularity, and this preference is evolving over time. To address these issues, we propose a novel method called CausalEPP (Causal Intervention on Evolving Personal Popularity) for taming recommendation bias, which accounts for the evolving personal popularity of users. Specifically, we first introduce a metric called {Evolving Personal Popularity} to quantify each user's preference for popular items. Then, we design a causal graph that integrates evolving personal popularity into the conformity effect, and apply deconfounded training to mitigate the popularity bias of the causal graph. During inference, we consider the evolution consistency between users and items to achieve a better recommendation. Empirical studies demonstrate that CausalEPP outperforms baseline methods in reducing popularity bias while improving recommendation accuracy.
A Survey on Large Language Model based Human-Agent Systems
May 01, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in building fully autonomous agents. However, fully autonomous LLM-based agents still face significant challenges, including limited reliability due to hallucinations, difficulty in handling complex tasks, and substantial safety and ethical risks, all of which limit their feasibility and trustworthiness in real-world applications. To overcome these limitations, LLM-based human-agent systems (LLM-HAS) incorporate human-provided information, feedback, or control into the agent system to enhance system performance, reliability and safety. This paper provides the first comprehensive and structured survey of LLM-HAS. It clarifies fundamental concepts, systematically presents core components shaping these systems, including environment & profiling, human feedback, interaction types, orchestration and communication, explores emerging applications, and discusses unique challenges and opportunities. By consolidating current knowledge and offering a structured overview, we aim to foster further research and innovation in this rapidly evolving interdisciplinary field. Paper lists and resources are available at https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-System-Papers.
A Unified Retrieval Framework with Document Ranking and EDU Filtering for Multi-document Summarization
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:In the field of multi-document summarization (MDS), transformer-based models have demonstrated remarkable success, yet they suffer an input length limitation. Current methods apply truncation after the retrieval process to fit the context length; however, they heavily depend on manually well-crafted queries, which are impractical to create for each document set for MDS. Additionally, these methods retrieve information at a coarse granularity, leading to the inclusion of irrelevant content. To address these issues, we propose a novel retrieval-based framework that integrates query selection and document ranking and shortening into a unified process. Our approach identifies the most salient elementary discourse units (EDUs) from input documents and utilizes them as latent queries. These queries guide the document ranking by calculating relevance scores. Instead of traditional truncation, our approach filters out irrelevant EDUs to fit the context length, ensuring that only critical information is preserved for summarization. We evaluate our framework on multiple MDS datasets, demonstrating consistent improvements in ROUGE metrics while confirming its scalability and flexibility across diverse model architectures. Additionally, we validate its effectiveness through an in-depth analysis, emphasizing its ability to dynamically select appropriate queries and accurately rank documents based on their relevance scores. These results demonstrate that our framework effectively addresses context-length constraints, establishing it as a robust and reliable solution for MDS.
LAG: LLM agents for Leaderboard Auto Generation on Demanding
Feb 25, 2025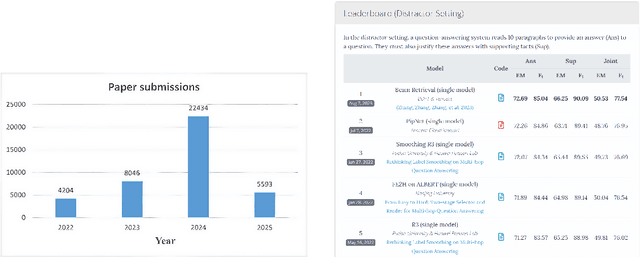
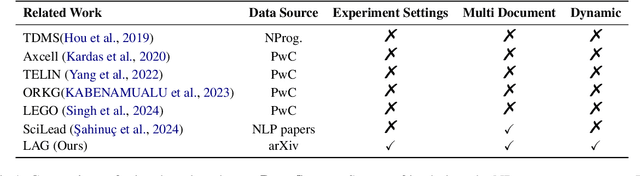
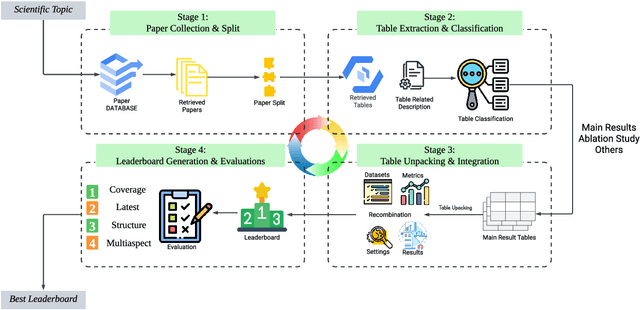

Abstract:This paper introduces Leaderboard Auto Generation (LAG), a novel and well-organized framework for automatic generation of leaderboards on a given research topic in rapidly evolving fields like Artificial Intelligence (AI). Faced with a large number of AI papers updated daily, it becomes difficult for researchers to track every paper's proposed methods, experimental results, and settings, prompting the need for efficient automatic leaderboard construction. While large language models (LLMs) offer promise in automating this process, challenges such as multi-document summarization, leaderboard generation, and experiment fair comparison still remain under exploration. LAG solves these challenges through a systematic approach that involves the paper collection, experiment results extraction and integration, leaderboard generation, and quality evaluation. Our contributions include a comprehensive solution to the leaderboard construction problem, a reliable evaluation method, and experimental results showing the high quality of leaderboards.
Multi-Agent Autonomous Driving Systems with Large Language Models: A Survey of Recent Advances
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Driving Systems (ADSs) are revolutionizing transportation by reducing human intervention, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing safety. Large Language Models (LLMs), known for their exceptional planning and reasoning capabilities, have been integrated into ADSs to assist with driving decision-making. However, LLM-based single-agent ADSs face three major challenges: limited perception, insufficient collaboration, and high computational demands. To address these issues, recent advancements in LLM-based multi-agent ADSs have focused on improving inter-agent communication and cooperation. This paper provides a frontier survey of LLM-based multi-agent ADSs. We begin with a background introduction to related concepts, followed by a categorization of existing LLM-based approaches based on different agent interaction modes. We then discuss agent-human interactions in scenarios where LLM-based agents engage with humans. Finally, we summarize key applications, datasets, and challenges in this field to support future research (https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LLM-based_Multi-agent_ADS-3A5C/README.md).
Revisiting Dynamic Graph Clustering via Matrix Factorization
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Dynamic graph clustering aims to detect and track time-varying clusters in dynamic graphs, revealing the evolutionary mechanisms of complex real-world dynamic systems. Matrix factorization-based methods are promising approaches for this task; however, these methods often struggle with scalability and can be time-consuming when applied to large-scale dynamic graphs. Moreover, they tend to lack robustness and are vulnerable to real-world noisy data. To address these issues, we make three key contributions. First, to improve scalability, we propose temporal separated matrix factorization, where a single matrix is divided into multiple smaller matrices for independent factorization, resulting in faster computation. Second, to improve robustness, we introduce bi-clustering regularization, which jointly optimizes graph embedding and clustering, thereby filtering out noisy features from the graph embeddings. Third, to further enhance effectiveness and efficiency, we propose selective embedding updating, where we update only the embeddings of dynamic nodes while the embeddings of static nodes are fixed among different timestamps. Experimental results on six synthetic and five real-world benchmarks demonstrate the scalability, robustness and effectiveness of our proposed method. Source code is available at https://github.com/Clearloveyuan/DyG-MF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge