Noboru Koshizuka
Place with Intention: An Empirical Attendance Predictive Study of Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Accurate forecasting of daily attendance is vital for managing transportation, crowd flows, and services at large-scale international events such as Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan. However, existing approaches often rely on multi-source external data (such as weather, traffic, and social media) to improve accuracy, which can lead to unreliable results when historical data are insufficient. To address these challenges, we propose a Transformer-based framework that leverages reservation dynamics, i.e., ticket bookings and subsequent updates within a time window, as a proxy for visitors' attendance intentions, under the assumption that such intentions are eventually reflected in reservation patterns. This design avoids the complexity of multi-source integration while still capturing external influences like weather and promotions implicitly embedded in reservation dynamics. We construct a dataset combining entrance records and reservation dynamics and evaluate the model under both single-channel (total attendance) and two-channel (separated by East and West gates) settings. Results show that separately modeling East and West gates consistently improves accuracy, particularly for short- and medium-term horizons. Ablation studies further confirm the importance of the encoder-decoder structure, inverse-style embedding, and adaptive fusion module. Overall, our findings indicate that reservation dynamics offer a practical and informative foundation for attendance forecasting in large-scale international events.
Time-Probability Dependent Knowledge Extraction in IoT-enabled Smart Building
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Smart buildings incorporate various emerging Internet of Things (IoT) applications for comprehensive management of energy efficiency, human comfort, automation, and security. However, the development of a knowledge extraction framework is fundamental. Currently, there is a lack of a unified and practical framework for modeling heterogeneous sensor data within buildings. In this paper, we propose a practical inference framework for extracting status-to-event knowledge within smart building. Our proposal includes IoT-based API integration, ontology model design, and time probability dependent knowledge extraction methods. The Building Topology Ontology (BOT) was leveraged to construct spatial relations among sensors and spaces within the building. We utilized Apache Jena Fuseki's SPARQL server for storing and querying the RDF triple data. Two types of knowledge could be extracted: timestamp-based probability for abnormal event detection and time interval-based probability for conjunction of multiple events. We conducted experiments (over a 78-day period) in a real smart building environment. The data of light and elevator states has been collected for evaluation. The evaluation revealed several inferred events, such as room occupancy, elevator trajectory tracking, and the conjunction of both events. The numerical values of detected event counts and probability demonstrate the potential for automatic control in the smart building.
FRTP: Federating Route Search Records to Enhance Long-term Traffic Prediction
Dec 23, 2024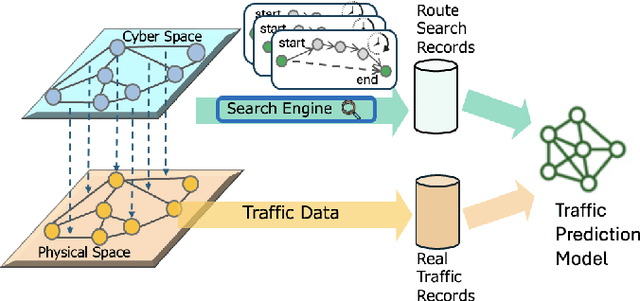
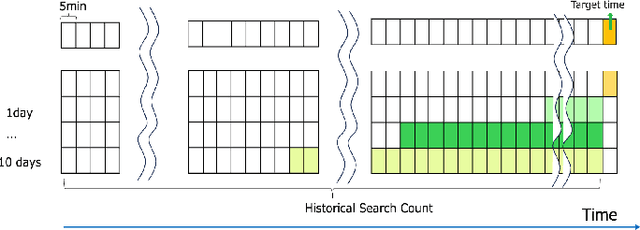
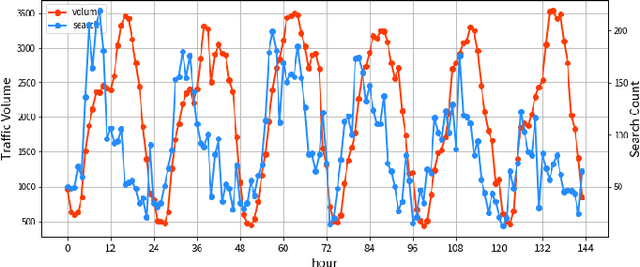
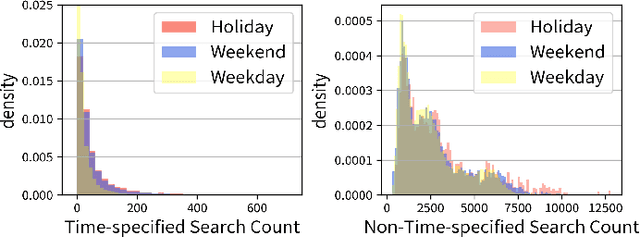
Abstract:Accurate traffic prediction, especially predicting traffic conditions several days in advance is essential for intelligent transportation systems (ITS). Such predictions enable mid- and long-term traffic optimization, which is crucial for efficient transportation planning. However, the inclusion of diverse external features, alongside the complexities of spatial relationships and temporal uncertainties, significantly increases the complexity of forecasting models. Additionally, traditional approaches have handled data preprocessing separately from the learning model, leading to inefficiencies caused by repeated trials of preprocessing and training. In this study, we propose a federated architecture capable of learning directly from raw data with varying features and time granularities or lengths. The model adopts a unified design that accommodates different feature types, time scales, and temporal periods. Our experiments focus on federating route search records and begin by processing raw data within the model framework. Unlike traditional models, this approach integrates the data federation phase into the learning process, enabling compatibility with various time frequencies and input/output configurations. The accuracy of the proposed model is demonstrated through evaluations using diverse learning patterns and parameter settings. The results show that online search log data is useful for forecasting long-term traffic, highlighting the model's adaptability and efficiency.
CausalMob: Causal Human Mobility Prediction with LLMs-derived Human Intentions toward Public Events
Dec 03, 2024
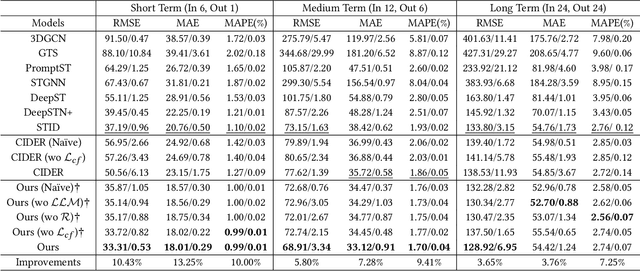
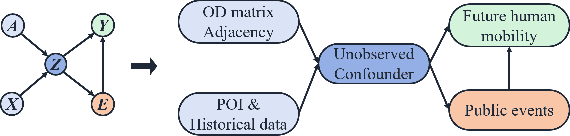
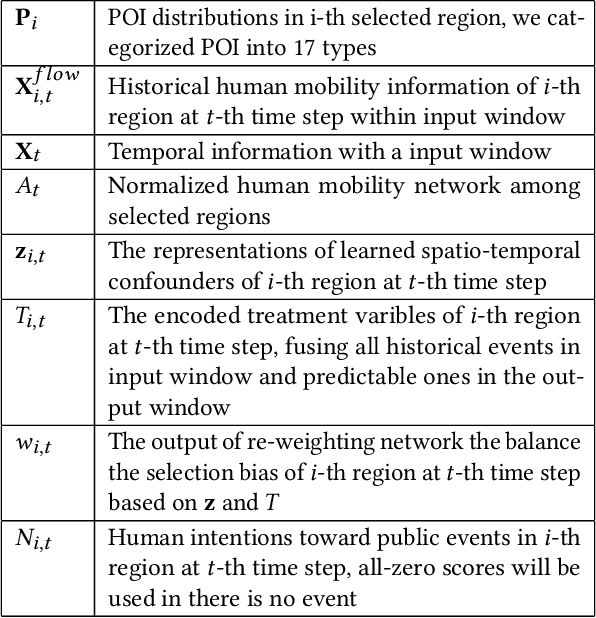
Abstract:Large-scale human mobility exhibits spatial and temporal patterns that can assist policymakers in decision making. Although traditional prediction models attempt to capture these patterns, they often interfered by non-periodic public events, such as disasters and occasional celebrations. Since regular human mobility patterns are heavily affected by these events, estimating their causal effects is critical to accurate mobility predictions. Although news articles provide unique perspectives on these events in an unstructured format, processing is a challenge. In this study, we propose a causality-augmented prediction model, called \textbf{CausalMob}, to analyze the causal effects of public events. We first utilize large language models (LLMs) to extract human intentions from news articles and transform them into features that act as causal treatments. Next, the model learns representations of spatio-temporal regional covariates from multiple data sources to serve as confounders for causal inference. Finally, we present a causal effect estimation framework to ensure event features remain independent of confounders during prediction. Based on large-scale real-world data, the experimental results show that the proposed model excels in human mobility prediction, outperforming state-of-the-art models.
Efficient Compressed Ratio Estimation using Online Sequential Learning for Edge Computing
Nov 08, 2022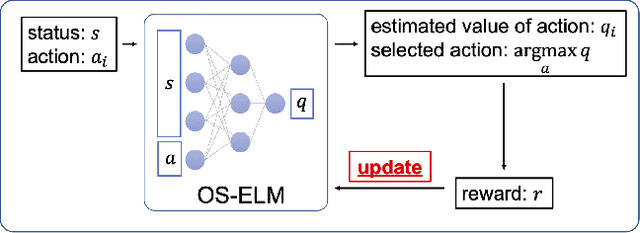
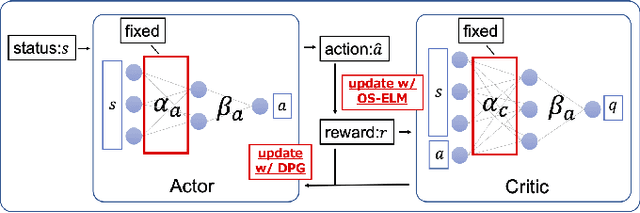
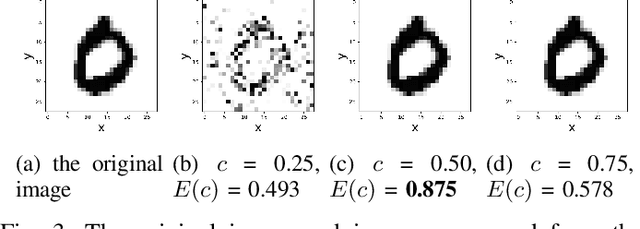
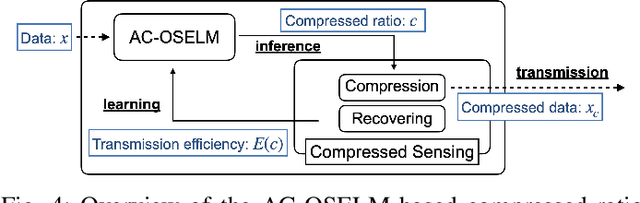
Abstract:Owing to the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things, a vast amount of sensor information is being acquired in real time. Accordingly, the communication cost of data from edge devices is increasing. Compressed sensing (CS), a data compression method that can be used on edge devices, has been attracting attention as a method to reduce communication costs. In CS, estimating the appropriate compression ratio is important. There is a method to adaptively estimate the compression ratio for the acquired data using reinforcement learning. However, the computational costs associated with existing reinforcement learning methods that can be utilized on edges are expensive. In this study, we developed an efficient reinforcement learning method for edge devices, referred to as the actor--critic online sequential extreme learning machine (AC-OSELM), and a system to compress data by estimating an appropriate compression ratio on the edge using AC-OSELM. The performance of the proposed method in estimating the compression ratio is evaluated by comparing it with other reinforcement learning methods for edge devices. The experimental results show that AC-OSELM achieved the same or better compression performance and faster compression ratio estimation than the existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge