Wen Zhang
Zhejiang University
Quantile-Physics Hybrid Framework for Safe-Speed Recommendation under Diverse Weather Conditions Leveraging Connected Vehicle and Road Weather Information Systems Data
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Inclement weather conditions can significantly impact driver visibility and tire-road surface friction, requiring adjusted safe driving speeds to reduce crash risk. This study proposes a hybrid predictive framework that recommends real-time safe speed intervals for freeway travel under diverse weather conditions. Leveraging high-resolution Connected Vehicle (CV) data and Road Weather Information System (RWIS) data collected in Buffalo, NY, from 2022 to 2023, we construct a spatiotemporally aligned dataset containing over 6.6 million records across 73 days. The core model employs Quantile Regression Forests (QRF) to estimate vehicle speed distributions in 10-minute windows, using 26 input features that capture meteorological, pavement, and temporal conditions. To enforce safety constraints, a physics-based upper speed limit is computed for each interval based on real-time road grip and visibility, ensuring that vehicles can safely stop within their sight distance. The final recommended interval fuses QRF-predicted quantiles with both posted speed limits and the physics-derived upper bound. Experimental results demonstrate strong predictive performance: the QRF model achieves a mean absolute error of 1.55 mph, with 96.43% of median speed predictions within 5 mph, a PICP (50%) of 48.55%, and robust generalization across weather types. The model's ability to respond to changing weather conditions and generalize across road segments shows promise for real-world deployment, thereby improving traffic safety and reducing weather-related crashes.
NEAT: Neuron-Based Early Exit for Large Reasoning Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) often suffer from \emph{overthinking}, a phenomenon in which redundant reasoning steps are generated after a correct solution has already been reached. Existing early reasoning exit methods primarily rely on output-level heuristics or trained probing models to skip redundant reasoning steps, thereby mitigating overthinking. However, these approaches typically require additional rollout computation or externally labeled datasets. In this paper, we propose \textbf{NEAT}, a \textbf{N}euron-based \textbf{E}arly re\textbf{A}soning exi\textbf{T} framework that monitors neuron-level activation dynamics to enable training-free early exits, without introducing additional test-time computation. NEAT identifies exit-associated neurons and tracks their activation patterns during reasoning to dynamically trigger early exit or suppress reflection, thereby reducing unnecessary reasoning while preserving solution quality. Experiments on four reasoning benchmarks across six models with different scales and architectures show that, for each model, NEAT achieves an average token reduction of 22\% to 28\% when averaged over the four benchmarks, while maintaining accuracy.
Temp-R1: A Unified Autonomous Agent for Complex Temporal KGQA via Reverse Curriculum Reinforcement Learning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Temporal Knowledge Graph Question Answering (TKGQA) is inherently challenging, as it requires sophisticated reasoning over dynamic facts with multi-hop dependencies and complex temporal constraints. Existing methods rely on fixed workflows and expensive closed-source APIs, limiting flexibility and scalability. We propose Temp-R1, the first autonomous end-to-end agent for TKGQA trained through reinforcement learning. To address cognitive overload in single-action reasoning, we expand the action space with specialized internal actions alongside external action. To prevent shortcut learning on simple questions, we introduce reverse curriculum learning that trains on difficult questions first, forcing the development of sophisticated reasoning before transferring to easier cases. Our 8B-parameter Temp-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on MultiTQ and TimelineKGQA, improving 19.8% over strong baselines on complex questions. Our work establishes a new paradigm for autonomous temporal reasoning agents. Our code will be publicly available soon at https://github.com/zjukg/Temp-R1.
CoG: Controllable Graph Reasoning via Relational Blueprints and Failure-Aware Refinement over Knowledge Graphs
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities but often grapple with reliability challenges like hallucinations. While Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offer explicit grounding, existing paradigms of KG-augmented LLMs typically exhibit cognitive rigidity--applying homogeneous search strategies that render them vulnerable to instability under neighborhood noise and structural misalignment leading to reasoning stagnation. To address these challenges, we propose CoG, a training-free framework inspired by Dual-Process Theory that mimics the interplay between intuition and deliberation. First, functioning as the fast, intuitive process, the Relational Blueprint Guidance module leverages relational blueprints as interpretable soft structural constraints to rapidly stabilize the search direction against noise. Second, functioning as the prudent, analytical process, the Failure-Aware Refinement module intervenes upon encountering reasoning impasses. It triggers evidence-conditioned reflection and executes controlled backtracking to overcome reasoning stagnation. Experimental results on three benchmarks demonstrate that CoG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both accuracy and efficiency.
ES4R: Speech Encoding Based on Prepositive Affective Modeling for Empathetic Response Generation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Empathetic speech dialogue requires not only understanding linguistic content but also perceiving rich paralinguistic information such as prosody, tone, and emotional intensity for affective understandings. Existing speech-to-speech large language models either rely on ASR transcription or use encoders to extract latent representations, often weakening affective information and contextual coherence in multi-turn dialogues. To address this, we propose \textbf{ES4R}, a framework for speech-based empathetic response generation. Our core innovation lies in explicitly modeling structured affective context before speech encoding, rather than relying on implicit learning by the encoder or explicit emotion supervision. Specifically, we introduce a dual-level attention mechanism to capture turn-level affective states and dialogue-level affective dynamics. The resulting affective representations are then integrated with textual semantics through speech-guided cross-modal attention to generate empathetic responses. For speech output, we employ energy-based strategy selection and style fusion to achieve empathetic speech synthesis. ES4R consistently outperforms strong baselines in both automatic and human evaluations and remains robust across different LLM backbones.
A Specialized Large Language Model for Clinical Reasoning and Diagnosis in Rare Diseases
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Rare diseases affect hundreds of millions worldwide, yet diagnosis often spans years. Convectional pipelines decouple noisy evidence extraction from downstream inferential diagnosis, and general/medical large language models (LLMs) face scarce real world electronic health records (EHRs), stale domain knowledge, and hallucinations. We assemble a large, domain specialized clinical corpus and a clinician validated reasoning set, and develop RareSeek R1 via staged instruction tuning, chain of thought learning, and graph grounded retrieval. Across multicenter EHR narratives and public benchmarks, RareSeek R1 attains state of the art accuracy, robust generalization, and stability under noisy or overlapping phenotypes. Augmented retrieval yields the largest gains when narratives pair with prioritized variants by resolving ambiguity and aligning candidates to mechanisms. Human studies show performance on par with experienced physicians and consistent gains in assistive use. Notably, transparent reasoning highlights decisive non phenotypic evidence (median 23.1%, such as imaging, interventions, functional tests) underpinning many correct diagnoses. This work advances a narrative first, knowledge integrated reasoning paradigm that shortens the diagnostic odyssey and enables auditable, clinically translatable decision support.
Self-Correction Distillation for Structured Data Question Answering
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Structured data question answering (QA), including table QA, Knowledge Graph (KG) QA, and temporal KG QA, is a pivotal research area. Advances in large language models (LLMs) have driven significant progress in unified structural QA frameworks like TrustUQA. However, these frameworks face challenges when applied to small-scale LLMs since small-scale LLMs are prone to errors in generating structured queries. To improve the structured data QA ability of small-scale LLMs, we propose a self-correction distillation (SCD) method. In SCD, an error prompt mechanism (EPM) is designed to detect errors and provide customized error messages during inference, and a two-stage distillation strategy is designed to transfer large-scale LLMs' query-generation and error-correction capabilities to small-scale LLM. Experiments across 5 benchmarks with 3 structured data types demonstrate that our SCD achieves the best performance and superior generalization on small-scale LLM (8B) compared to other distillation methods, and closely approaches the performance of GPT4 on some datasets. Furthermore, large-scale LLMs equipped with EPM surpass the state-of-the-art results on most datasets.
Last Layer Logits to Logic: Empowering LLMs with Logic-Consistent Structured Knowledge Reasoning
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve excellent performance in natural language reasoning tasks through pre-training on vast unstructured text, enabling them to understand the logic in natural language and generate logic-consistent responses. However, the representational differences between unstructured and structured knowledge make LLMs inherently struggle to maintain logic consistency, leading to \textit{Logic Drift} challenges in structured knowledge reasoning tasks such as Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA). Existing methods address this limitation by designing complex workflows embedded in prompts to guide LLM reasoning. Nevertheless, these approaches only provide input-level guidance and fail to fundamentally address the \textit{Logic Drift} in LLM outputs. Additionally, their inflexible reasoning workflows cannot adapt to different tasks and knowledge graphs. To enhance LLMs' logic consistency in structured knowledge reasoning, we specifically target the logits output from the autoregressive generation process. We propose the \textit{Logits-to-Logic} framework, which incorporates logits strengthening and logits filtering as core modules to correct logical defects in LLM outputs. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly improves LLMs' logic consistency in structured knowledge reasoning and achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple KGQA benchmarks.
SpecAware: A Spectral-Content Aware Foundation Model for Unifying Multi-Sensor Learning in Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Mapping
Oct 31, 2025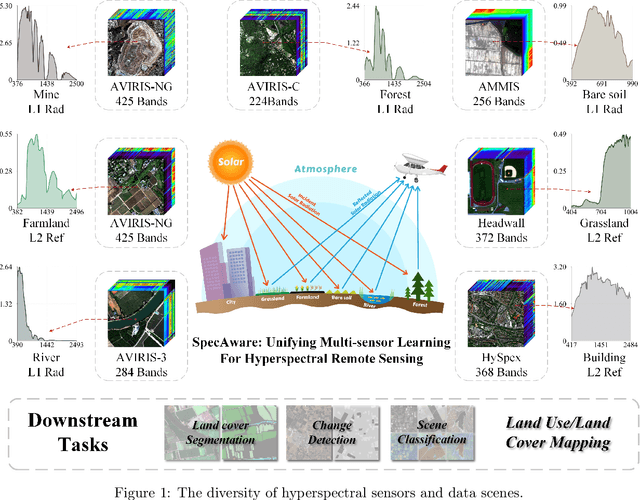
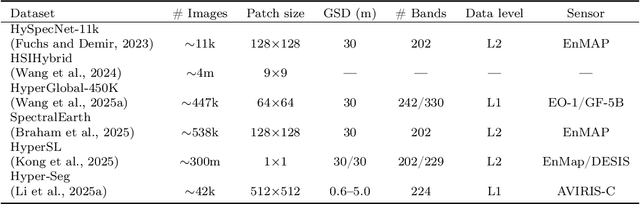
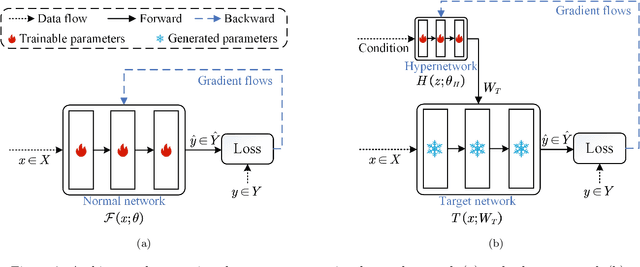
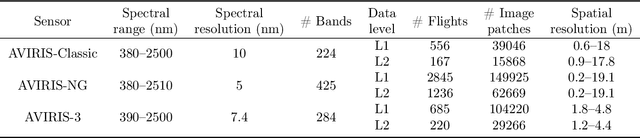
Abstract:Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) is a vital tool for fine-grained land-use and land-cover (LULC) mapping. However, the inherent heterogeneity of HSI data has long posed a major barrier to developing generalized models via joint training. Although HSI foundation models have shown promise for different downstream tasks, the existing approaches typically overlook the critical guiding role of sensor meta-attributes, and struggle with multi-sensor training, limiting their transferability. To address these challenges, we propose SpecAware, which is a novel hyperspectral spectral-content aware foundation model for unifying multi-sensor learning for HSI mapping. We also constructed the Hyper-400K dataset to facilitate this research, which is a new large-scale, high-quality benchmark dataset with over 400k image patches from diverse airborne AVIRIS sensors. The core of SpecAware is a two-step hypernetwork-driven encoding process for HSI data. Firstly, we designed a meta-content aware module to generate a unique conditional input for each HSI patch, tailored to each spectral band of every sample by fusing the sensor meta-attributes and its own image content. Secondly, we designed the HyperEmbedding module, where a sample-conditioned hypernetwork dynamically generates a pair of matrix factors for channel-wise encoding, consisting of adaptive spatial pattern extraction and latent semantic feature re-projection. Thus, SpecAware gains the ability to perceive and interpret spatial-spectral features across diverse scenes and sensors. This, in turn, allows SpecAware to adaptively process a variable number of spectral channels, establishing a unified framework for joint pre-training. Extensive experiments on six datasets demonstrate that SpecAware can learn superior feature representations, excelling in land-cover semantic segmentation classification, change detection, and scene classification.
Evontree: Ontology Rule-Guided Self-Evolution of Large Language Models
Oct 30, 2025
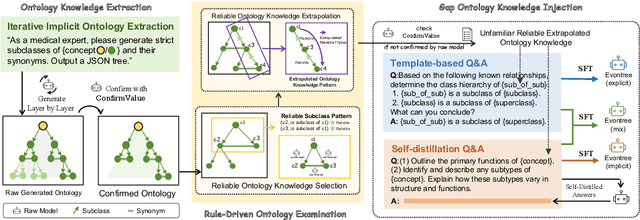
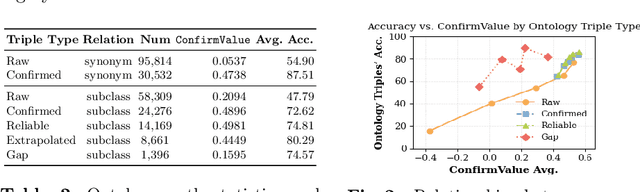
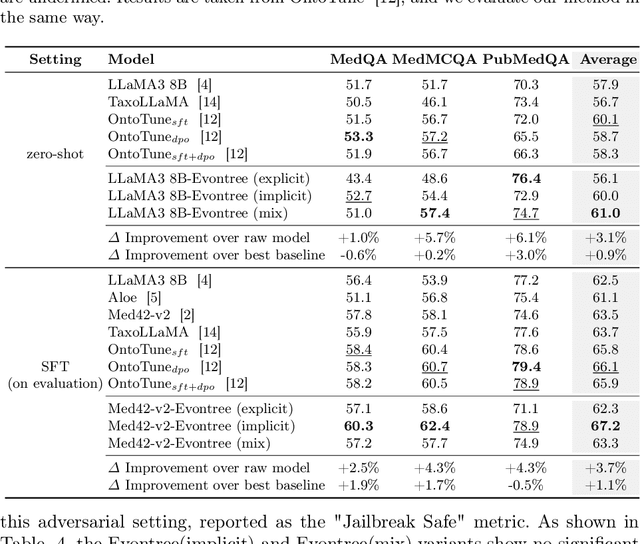
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities across multiple domains by leveraging massive pre-training and curated fine-tuning data. However, in data-sensitive fields such as healthcare, the lack of high-quality, domain-specific training corpus hinders LLMs' adaptation for specialized applications. Meanwhile, domain experts have distilled domain wisdom into ontology rules, which formalize relationships among concepts and ensure the integrity of knowledge management repositories. Viewing LLMs as implicit repositories of human knowledge, we propose Evontree, a novel framework that leverages a small set of high-quality ontology rules to systematically extract, validate, and enhance domain knowledge within LLMs, without requiring extensive external datasets. Specifically, Evontree extracts domain ontology from raw models, detects inconsistencies using two core ontology rules, and reinforces the refined knowledge via self-distilled fine-tuning. Extensive experiments on medical QA benchmarks with Llama3-8B-Instruct and Med42-v2 demonstrate consistent outperformance over both unmodified models and leading supervised baselines, achieving up to a 3.7% improvement in accuracy. These results confirm the effectiveness, efficiency, and robustness of our approach for low-resource domain adaptation of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge