Jiajun Liu
A multimodal vision foundation model for generalizable knee pathology
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Musculoskeletal disorders represent a leading cause of global disability, creating an urgent demand for precise interpretation of medical imaging. Current artificial intelligence (AI) approaches in orthopedics predominantly rely on task-specific, supervised learning paradigms. These methods are inherently fragmented, require extensive annotated datasets, and often lack generalizability across different modalities and clinical scenarios. The development of foundation models in this field has been constrained by the scarcity of large-scale, curated, and open-source musculoskeletal datasets. To address these challenges, we introduce OrthoFoundation, a multimodal vision foundation model optimized for musculoskeletal pathology. We constructed a pre-training dataset of 1.2 million unlabeled knee X-ray and MRI images from internal and public databases. Utilizing a Dinov3 backbone, the model was trained via self-supervised contrastive learning to capture robust radiological representations. OrthoFoundation achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across 14 downstream tasks. It attained superior accuracy in X-ray osteoarthritis diagnosis and ranked first in MRI structural injury detection. The model demonstrated remarkable label efficiency, matching supervised baselines using only 50% of labeled data. Furthermore, despite being pre-trained on knee images, OrthoFoundation exhibited exceptional cross-anatomy generalization to the hip, shoulder, and ankle. OrthoFoundation represents a significant advancement toward general-purpose AI for musculoskeletal imaging. By learning fundamental, joint-agnostic radiological semantics from large-scale multimodal data, it overcomes the limitations of conventional models, which provides a robust framework for reducing annotation burdens and enhancing diagnostic accuracy in clinical practice.
The Illusion of Clinical Reasoning: A Benchmark Reveals the Pervasive Gap in Vision-Language Models for Clinical Competency
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Background: The rapid integration of foundation models into clinical practice and public health necessitates a rigorous evaluation of their true clinical reasoning capabilities beyond narrow examination success. Current benchmarks, typically based on medical licensing exams or curated vignettes, fail to capture the integrated, multimodal reasoning essential for real-world patient care. Methods: We developed the Bones and Joints (B&J) Benchmark, a comprehensive evaluation framework comprising 1,245 questions derived from real-world patient cases in orthopedics and sports medicine. This benchmark assesses models across 7 tasks that mirror the clinical reasoning pathway, including knowledge recall, text and image interpretation, diagnosis generation, treatment planning, and rationale provision. We evaluated eleven vision-language models (VLMs) and six large language models (LLMs), comparing their performance against expert-derived ground truth. Results: Our results demonstrate a pronounced performance gap between task types. While state-of-the-art models achieved high accuracy, exceeding 90%, on structured multiple-choice questions, their performance markedly declined on open-ended tasks requiring multimodal integration, with accuracy scarcely reaching 60%. VLMs demonstrated substantial limitations in interpreting medical images and frequently exhibited severe text-driven hallucinations, often ignoring contradictory visual evidence. Notably, models specifically fine-tuned for medical applications showed no consistent advantage over general-purpose counterparts. Conclusions: Current artificial intelligence models are not yet clinically competent for complex, multimodal reasoning. Their safe deployment should currently be limited to supportive, text-based roles. Future advancement in core clinical tasks awaits fundamental breakthroughs in multimodal integration and visual understanding.
VLNVerse: A Benchmark for Vision-Language Navigation with Versatile, Embodied, Realistic Simulation and Evaluation
Dec 22, 2025
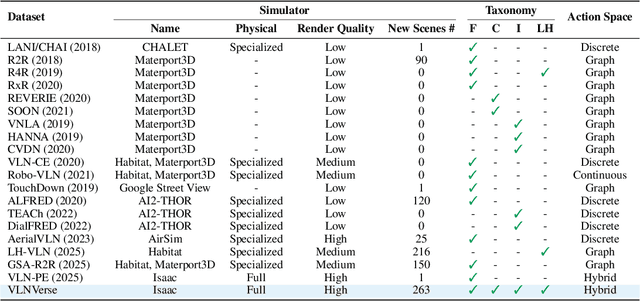
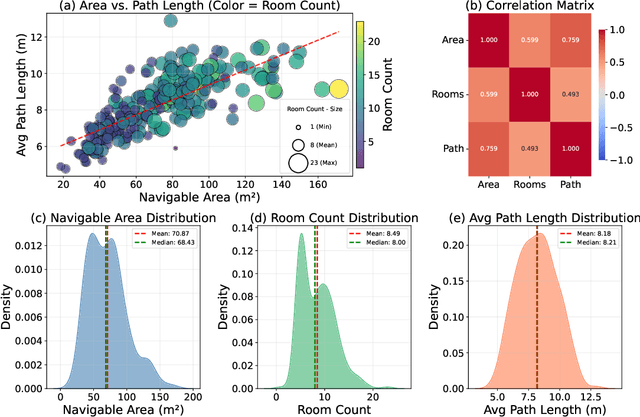
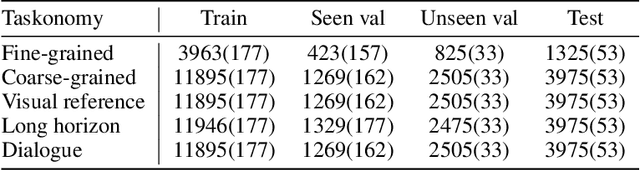
Abstract:Despite remarkable progress in Vision-Language Navigation (VLN), existing benchmarks remain confined to fixed, small-scale datasets with naive physical simulation. These shortcomings limit the insight that the benchmarks provide into sim-to-real generalization, and create a significant research gap. Furthermore, task fragmentation prevents unified/shared progress in the area, while limited data scales fail to meet the demands of modern LLM-based pretraining. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VLNVerse: a new large-scale, extensible benchmark designed for Versatile, Embodied, Realistic Simulation, and Evaluation. VLNVerse redefines VLN as a scalable, full-stack embodied AI problem. Its Versatile nature unifies previously fragmented tasks into a single framework and provides an extensible toolkit for researchers. Its Embodied design moves beyond intangible and teleporting "ghost" agents that support full-kinematics in a Realistic Simulation powered by a robust physics engine. We leverage the scale and diversity of VLNVerse to conduct a comprehensive Evaluation of existing methods, from classic models to MLLM-based agents. We also propose a novel unified multi-task model capable of addressing all tasks within the benchmark. VLNVerse aims to narrow the gap between simulated navigation and real-world generalization, providing the community with a vital tool to boost research towards scalable, general-purpose embodied locomotion agents.
A Class of Dual-Frame Passively-Tilting Fully-Actuated Hexacopter
Nov 19, 2025



Abstract:This paper proposed a novel fully-actuated hexacopter. It features a dual-frame passive tilting structure and achieves independent control of translational motion and attitude with minimal actuators. Compared to previous fully-actuated UAVs, it liminates internal force cancellation, resulting in higher flight efficiency and endurance under equivalent payload conditions. Based on the dynamic model of fully-actuated hexacopter, a full-actuation controller is designed to achieve efficient and stable control. Finally, simulation is conducted, validating the superior fully-actuated motion capability of fully-actuated hexacopter and the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy.
Estimating Pasture Biomass from Top-View Images: A Dataset for Precision Agriculture
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Accurate estimation of pasture biomass is important for decision-making in livestock production systems. Estimates of pasture biomass can be used to manage stocking rates to maximise pasture utilisation, while minimising the risk of overgrazing and promoting overall system health. We present a comprehensive dataset of 1,162 annotated top-view images of pastures collected across 19 locations in Australia. The images were taken across multiple seasons and include a range of temperate pasture species. Each image captures a 70cm * 30cm quadrat and is paired with on-ground measurements including biomass sorted by component (green, dead, and legume fraction), vegetation height, and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from Active Optical Sensors (AOS). The multidimensional nature of the data, which combines visual, spectral, and structural information, opens up new possibilities for advancing the use of precision grazing management. The dataset is released and hosted in a Kaggle competition that challenges the international Machine Learning community with the task of pasture biomass estimation. The dataset is available on the official Kaggle webpage: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/csiro-biomass
MARCO: A Cooperative Knowledge Transfer Framework for Personalized Cross-domain Recommendations
Oct 06, 2025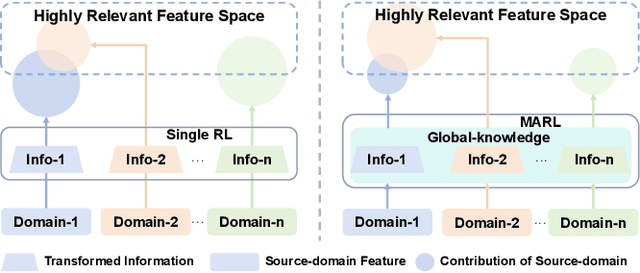
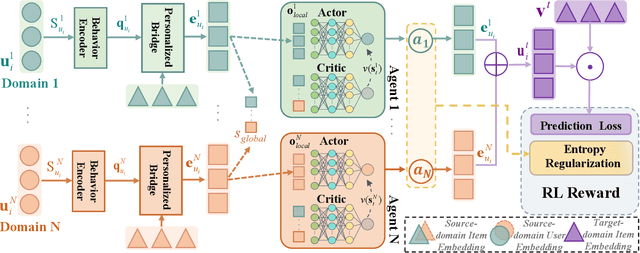
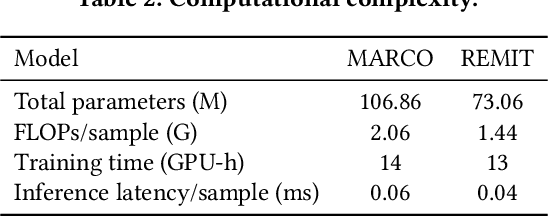
Abstract:Recommender systems frequently encounter data sparsity issues, particularly when addressing cold-start scenarios involving new users or items. Multi-source cross-domain recommendation (CDR) addresses these challenges by transferring valuable knowledge from multiple source domains to enhance recommendations in a target domain. However, existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based CDR methods typically rely on a single-agent framework, leading to negative transfer issues caused by inconsistent domain contributions and inherent distributional discrepancies among source domains. To overcome these limitations, MARCO, a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning-based Cross-Domain recommendation framework, is proposed. It leverages cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning, where each agent is dedicated to estimating the contribution from an individual source domain, effectively managing credit assignment and mitigating negative transfer. In addition, an entropy-based action diversity penalty is introduced to enhance policy expressiveness and stabilize training by encouraging diverse agents' joint actions. Extensive experiments across four benchmark datasets demonstrate MARCO's superior performance over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its robustness and strong generalization capabilities. The code is at https://github.com/xiewilliams/MARCO.
Unlearning of Knowledge Graph Embedding via Preference Optimization
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Existing knowledge graphs (KGs) inevitably contain outdated or erroneous knowledge that needs to be removed from knowledge graph embedding (KGE) models. To address this challenge, knowledge unlearning can be applied to eliminate specific information while preserving the integrity of the remaining knowledge in KGs. Existing unlearning methods can generally be categorized into exact unlearning and approximate unlearning. However, exact unlearning requires high training costs while approximate unlearning faces two issues when applied to KGs due to the inherent connectivity of triples: (1) It fails to fully remove targeted information, as forgetting triples can still be inferred from remaining ones. (2) It focuses on local data for specific removal, which weakens the remaining knowledge in the forgetting boundary. To address these issues, we propose GraphDPO, a novel approximate unlearning framework based on direct preference optimization (DPO). Firstly, to effectively remove forgetting triples, we reframe unlearning as a preference optimization problem, where the model is trained by DPO to prefer reconstructed alternatives over the original forgetting triples. This formulation penalizes reliance on forgettable knowledge, mitigating incomplete forgetting caused by KG connectivity. Moreover, we introduce an out-boundary sampling strategy to construct preference pairs with minimal semantic overlap, weakening the connection between forgetting and retained knowledge. Secondly, to preserve boundary knowledge, we introduce a boundary recall mechanism that replays and distills relevant information both within and across time steps. We construct eight unlearning datasets across four popular KGs with varying unlearning rates. Experiments show that GraphDPO outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by up to 10.1% in MRR_Avg and 14.0% in MRR_F1.
The Singapore Consensus on Global AI Safety Research Priorities
Jun 25, 2025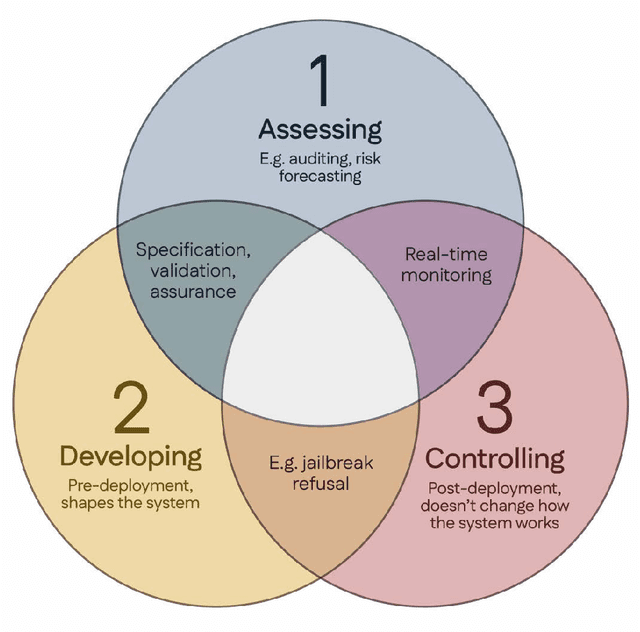
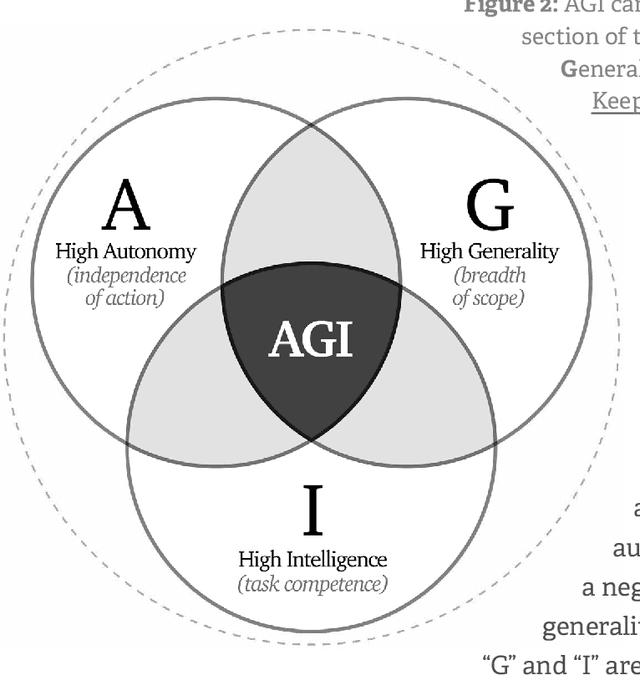
Abstract:Rapidly improving AI capabilities and autonomy hold significant promise of transformation, but are also driving vigorous debate on how to ensure that AI is safe, i.e., trustworthy, reliable, and secure. Building a trusted ecosystem is therefore essential -- it helps people embrace AI with confidence and gives maximal space for innovation while avoiding backlash. The "2025 Singapore Conference on AI (SCAI): International Scientific Exchange on AI Safety" aimed to support research in this space by bringing together AI scientists across geographies to identify and synthesise research priorities in AI safety. This resulting report builds on the International AI Safety Report chaired by Yoshua Bengio and backed by 33 governments. By adopting a defence-in-depth model, this report organises AI safety research domains into three types: challenges with creating trustworthy AI systems (Development), challenges with evaluating their risks (Assessment), and challenges with monitoring and intervening after deployment (Control).
OneEval: Benchmarking LLM Knowledge-intensive Reasoning over Diverse Knowledge Bases
Jun 14, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated substantial progress on reasoning tasks involving unstructured text, yet their capabilities significantly deteriorate when reasoning requires integrating structured external knowledge such as knowledge graphs, code snippets, or formal logic. This limitation is partly due to the absence of benchmarks capable of systematically evaluating LLM performance across diverse structured knowledge modalities. To address this gap, we introduce \textbf{\textsc{OneEval}}, a comprehensive benchmark explicitly designed to assess the knowledge-intensive reasoning capabilities of LLMs across four structured knowledge modalities, unstructured text, knowledge graphs, code, and formal logic, and five critical domains (general knowledge, government, science, law, and programming). \textsc{OneEval} comprises 4,019 carefully curated instances and includes a challenging subset, \textsc{OneEval}\textsubscript{Hard}, consisting of 1,285 particularly difficult cases. Through extensive evaluation of 18 state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary LLMs, we establish three core findings: a) \emph{persistent limitations in structured reasoning}, with even the strongest model achieving only 32.2\% accuracy on \textsc{OneEval}\textsubscript{Hard}; b) \emph{performance consistently declines as the structural complexity of the knowledge base increases}, with accuracy dropping sharply from 53\% (textual reasoning) to 25\% (formal logic); and c) \emph{diminishing returns from extended reasoning chains}, highlighting the critical need for models to adapt reasoning depth appropriately to task complexity. We release the \textsc{OneEval} datasets, evaluation scripts, and baseline results publicly, accompanied by a leaderboard to facilitate ongoing advancements in structured knowledge reasoning.
Chain-of-Action: Trajectory Autoregressive Modeling for Robotic Manipulation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:We present Chain-of-Action (CoA), a novel visuo-motor policy paradigm built upon Trajectory Autoregressive Modeling. Unlike conventional approaches that predict next step action(s) forward, CoA generates an entire trajectory by explicit backward reasoning with task-specific goals through an action-level Chain-of-Thought (CoT) process. This process is unified within a single autoregressive structure: (1) the first token corresponds to a stable keyframe action that encodes the task-specific goals; and (2) subsequent action tokens are generated autoregressively, conditioned on the initial keyframe and previously predicted actions. This backward action reasoning enforces a global-to-local structure, allowing each local action to be tightly constrained by the final goal. To further realize the action reasoning structure, CoA incorporates four complementary designs: continuous action token representation; dynamic stopping for variable-length trajectory generation; reverse temporal ensemble; and multi-token prediction to balance action chunk modeling with global structure. As a result, CoA gives strong spatial generalization capabilities while preserving the flexibility and simplicity of a visuo-motor policy. Empirically, we observe CoA achieves the state-of-the-art performance across 60 RLBench tasks and 8 real-world manipulation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge