Xuwei Xu
RePaViT: Scalable Vision Transformer Acceleration via Structural Reparameterization on Feedforward Network Layers
May 28, 2025Abstract:We reveal that feedforward network (FFN) layers, rather than attention layers, are the primary contributors to Vision Transformer (ViT) inference latency, with their impact signifying as model size increases. This finding highlights a critical opportunity for optimizing the efficiency of large-scale ViTs by focusing on FFN layers. In this work, we propose a novel channel idle mechanism that facilitates post-training structural reparameterization for efficient FFN layers during testing. Specifically, a set of feature channels remains idle and bypasses the nonlinear activation function in each FFN layer, thereby forming a linear pathway that enables structural reparameterization during inference. This mechanism results in a family of ReParameterizable Vision Transformers (RePaViTs), which achieve remarkable latency reductions with acceptable sacrifices (sometimes gains) in accuracy across various ViTs. The benefits of our method scale consistently with model sizes, demonstrating greater speed improvements and progressively narrowing accuracy gaps or even higher accuracies on larger models. In particular, RePa-ViT-Large and RePa-ViT-Huge enjoy 66.8% and 68.7% speed-ups with +1.7% and +1.1% higher top-1 accuracies under the same training strategy, respectively. RePaViT is the first to employ structural reparameterization on FFN layers to expedite ViTs to our best knowledge, and we believe that it represents an auspicious direction for efficient ViTs. Source code is available at https://github.com/Ackesnal/RePaViT.
DARLR: Dual-Agent Offline Reinforcement Learning for Recommender Systems with Dynamic Reward
May 12, 2025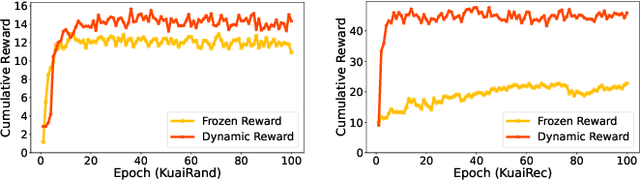
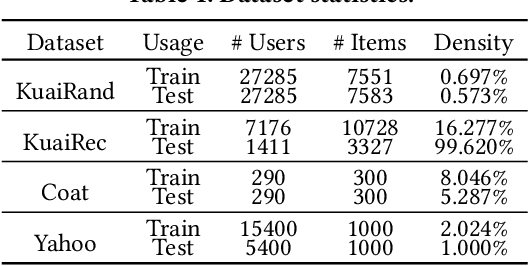
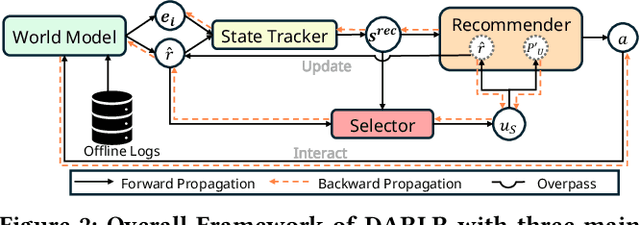
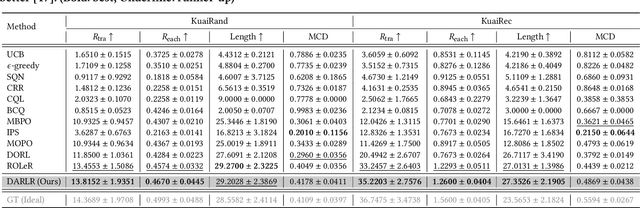
Abstract:Model-based offline reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising approach for recommender systems, enabling effective policy learning by interacting with frozen world models. However, the reward functions in these world models, trained on sparse offline logs, often suffer from inaccuracies. Specifically, existing methods face two major limitations in addressing this challenge: (1) deterministic use of reward functions as static look-up tables, which propagates inaccuracies during policy learning, and (2) static uncertainty designs that fail to effectively capture decision risks and mitigate the impact of these inaccuracies. In this work, a dual-agent framework, DARLR, is proposed to dynamically update world models to enhance recommendation policies. To achieve this, a \textbf{\textit{selector}} is introduced to identify reference users by balancing similarity and diversity so that the \textbf{\textit{recommender}} can aggregate information from these users and iteratively refine reward estimations for dynamic reward shaping. Further, the statistical features of the selected users guide the dynamic adaptation of an uncertainty penalty to better align with evolving recommendation requirements. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of DARLR, validating its effectiveness. The code is available at https://github.com/ArronDZhang/DARLR.
C2GM: Cascading Conditional Generation of Multi-scale Maps from Remote Sensing Images Constrained by Geographic Features
Feb 07, 2025
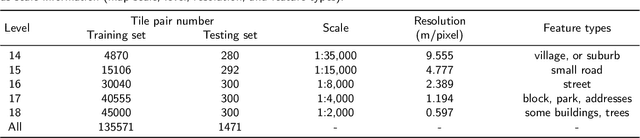

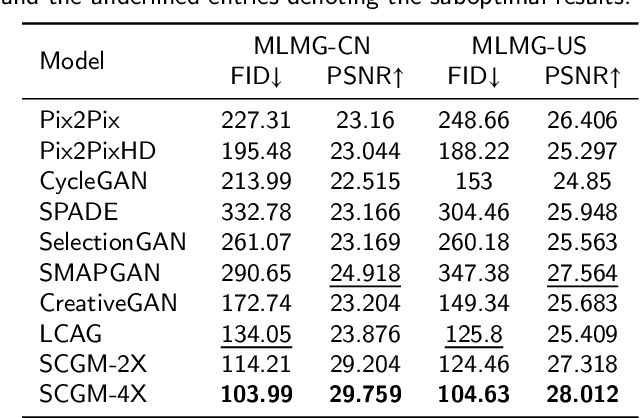
Abstract:Multi-scale maps are essential representations of surveying and cartographic results, serving as fundamental components of geographic services. Current image generation networks can quickly produce map tiles from remote-sensing images. However, generative models designed for natural images often focus on texture features, neglecting the unique characteristics of remote-sensing features and the scale attributes of tile maps. This limitation in generative models impairs the accurate representation of geographic information, and the quality of tile map generation still needs improvement. Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in various image generation tasks, highlighting their potential to address this challenge. This paper presents C2GM, a novel framework for generating multi-scale tile maps through conditional guided diffusion and multi-scale cascade generation. Specifically, we implement a conditional feature fusion encoder to extract object priors from remote sensing images and cascade reference double branch input, ensuring an accurate representation of complex features. Low-level generated tiles act as constraints for high-level map generation, enhancing visual continuity. Moreover, we incorporate map scale modality information using CLIP to simulate the relationship between map scale and cartographic generalization in tile maps. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that C2GM consistently achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on all metrics, facilitating the rapid and effective generation of multi-scale large-format maps for emergency response and remote mapping applications.
GTP-ViT: Efficient Vision Transformers via Graph-based Token Propagation
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have revolutionized the field of computer vision, yet their deployments on resource-constrained devices remain challenging due to high computational demands. To expedite pre-trained ViTs, token pruning and token merging approaches have been developed, which aim at reducing the number of tokens involved in the computation. However, these methods still have some limitations, such as image information loss from pruned tokens and inefficiency in the token-matching process. In this paper, we introduce a novel Graph-based Token Propagation (GTP) method to resolve the challenge of balancing model efficiency and information preservation for efficient ViTs. Inspired by graph summarization algorithms, GTP meticulously propagates less significant tokens' information to spatially and semantically connected tokens that are of greater importance. Consequently, the remaining few tokens serve as a summarization of the entire token graph, allowing the method to reduce computational complexity while preserving essential information of eliminated tokens. Combined with an innovative token selection strategy, GTP can efficiently identify image tokens to be propagated. Extensive experiments have validated GTP's effectiveness, demonstrating both efficiency and performance improvements. Specifically, GTP decreases the computational complexity of both DeiT-S and DeiT-B by up to 26% with only a minimal 0.3% accuracy drop on ImageNet-1K without finetuning, and remarkably surpasses the state-of-the-art token merging method on various backbones at an even faster inference speed. The source code is available at https://github.com/Ackesnal/GTP-ViT.
Understanding the Effects of Projectors in Knowledge Distillation
Oct 26, 2023



Abstract:Conventionally, during the knowledge distillation process (e.g. feature distillation), an additional projector is often required to perform feature transformation due to the dimension mismatch between the teacher and the student networks. Interestingly, we discovered that even if the student and the teacher have the same feature dimensions, adding a projector still helps to improve the distillation performance. In addition, projectors even improve logit distillation if we add them to the architecture too. Inspired by these surprising findings and the general lack of understanding of the projectors in the knowledge distillation process from existing literature, this paper investigates the implicit role that projectors play but so far have been overlooked. Our empirical study shows that the student with a projector (1) obtains a better trade-off between the training accuracy and the testing accuracy compared to the student without a projector when it has the same feature dimensions as the teacher, (2) better preserves its similarity to the teacher beyond shallow and numeric resemblance, from the view of Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA), and (3) avoids being over-confident as the teacher does at the testing phase. Motivated by the positive effects of projectors, we propose a projector ensemble-based feature distillation method to further improve distillation performance. Despite the simplicity of the proposed strategy, empirical results from the evaluation of classification tasks on benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior classification performance of our method on a broad range of teacher-student pairs and verify from the aspects of CKA and model calibration that the student's features are of improved quality with the projector ensemble design.
Plug n' Play: Channel Shuffle Module for Enhancing Tiny Vision Transformers
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in various computer vision tasks. However, the high computational complexity hinders ViTs' applicability on devices with limited memory and computing resources. Although certain investigations have delved into the fusion of convolutional layers with self-attention mechanisms to enhance the efficiency of ViTs, there remains a knowledge gap in constructing tiny yet effective ViTs solely based on the self-attention mechanism. Furthermore, the straightforward strategy of reducing the feature channels in a large but outperforming ViT often results in significant performance degradation despite improved efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose a novel channel shuffle module to improve tiny-size ViTs, showing the potential of pure self-attention models in environments with constrained computing resources. Inspired by the channel shuffle design in ShuffleNetV2 \cite{ma2018shufflenet}, our module expands the feature channels of a tiny ViT and partitions the channels into two groups: the \textit{Attended} and \textit{Idle} groups. Self-attention computations are exclusively employed on the designated \textit{Attended} group, followed by a channel shuffle operation that facilitates information exchange between the two groups. By incorporating our module into a tiny ViT, we can achieve superior performance while maintaining a comparable computational complexity to the vanilla model. Specifically, our proposed channel shuffle module consistently improves the top-1 accuracy on the ImageNet-1K dataset for various tiny ViT models by up to 2.8\%, with the changes in model complexity being less than 0.03 GMACs.
No Token Left Behind: Efficient Vision Transformer via Dynamic Token Idling
Oct 09, 2023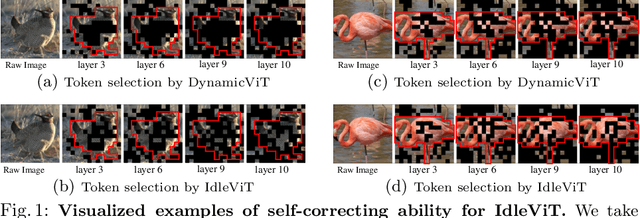
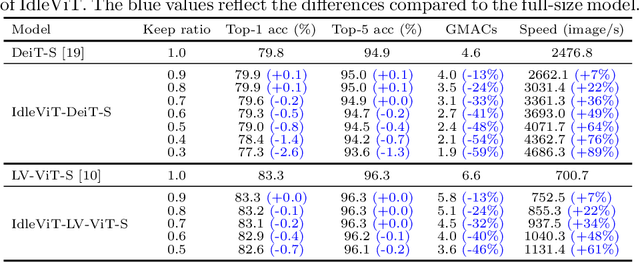
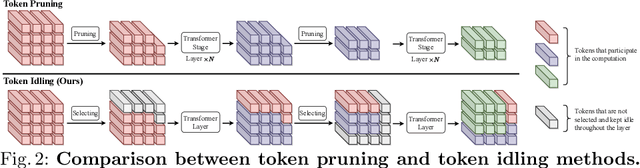

Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated outstanding performance in computer vision tasks, yet their high computational complexity prevents their deployment in computing resource-constrained environments. Various token pruning techniques have been introduced to alleviate the high computational burden of ViTs by dynamically dropping image tokens. However, some undesirable pruning at early stages may result in permanent loss of image information in subsequent layers, consequently hindering model performance. To address this problem, we propose IdleViT, a dynamic token-idle-based method that achieves an excellent trade-off between performance and efficiency. Specifically, in each layer, IdleViT selects a subset of the image tokens to participate in computations while keeping the rest of the tokens idle and directly passing them to this layer's output. By allowing the idle tokens to be re-selected in the following layers, IdleViT mitigates the negative impact of improper pruning in the early stages. Furthermore, inspired by the normalized graph cut, we devise a token cut loss on the attention map as regularization to improve IdleViT's token selection ability. Our method is simple yet effective and can be extended to pyramid ViTs since no token is completely dropped. Extensive experimental results on various ViT architectures have shown that IdleViT can diminish the complexity of pretrained ViTs by up to 33\% with no more than 0.2\% accuracy decrease on ImageNet, after finetuning for only 30 epochs. Notably, when the keep ratio is 0.5, IdleViT outperforms the state-of-the-art EViT on DeiT-S by 0.5\% higher accuracy and even faster inference speed. The source code is available in the supplementary material.
Improved Feature Distillation via Projector Ensemble
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:In knowledge distillation, previous feature distillation methods mainly focus on the design of loss functions and the selection of the distilled layers, while the effect of the feature projector between the student and the teacher remains under-explored. In this paper, we first discuss a plausible mechanism of the projector with empirical evidence and then propose a new feature distillation method based on a projector ensemble for further performance improvement. We observe that the student network benefits from a projector even if the feature dimensions of the student and the teacher are the same. Training a student backbone without a projector can be considered as a multi-task learning process, namely achieving discriminative feature extraction for classification and feature matching between the student and the teacher for distillation at the same time. We hypothesize and empirically verify that without a projector, the student network tends to overfit the teacher's feature distributions despite having different architecture and weights initialization. This leads to degradation on the quality of the student's deep features that are eventually used in classification. Adding a projector, on the other hand, disentangles the two learning tasks and helps the student network to focus better on the main feature extraction task while still being able to utilize teacher features as a guidance through the projector. Motivated by the positive effect of the projector in feature distillation, we propose an ensemble of projectors to further improve the quality of student features. Experimental results on different datasets with a series of teacher-student pairs illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge