Yanping Zheng
Future Link Prediction Without Memory or Aggregation
May 26, 2025Abstract:Future link prediction on temporal graphs is a fundamental task with wide applicability in real-world dynamic systems. These scenarios often involve both recurring (seen) and novel (unseen) interactions, requiring models to generalize effectively across both types of edges. However, existing methods typically rely on complex memory and aggregation modules, yet struggle to handle unseen edges. In this paper, we revisit the architecture of existing temporal graph models and identify two essential but overlooked modeling requirements for future link prediction: representing nodes with unique identifiers and performing target-aware matching between source and destination nodes. To this end, we propose Cross-Attention based Future Link Predictor on Temporal Graphs (CRAFT), a simple yet effective architecture that discards memory and aggregation modules and instead builds on two components: learnable node embeddings and cross-attention between the destination and the source's recent interactions. This design provides strong expressive power and enables target-aware modeling of the compatibility between candidate destinations and the source's interaction patterns. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets demonstrate that CRAFT consistently achieves superior performance with high efficiency, making it well-suited for large-scale real-world applications.
Rethinking Link Prediction for Directed Graphs
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:Link prediction for directed graphs is a crucial task with diverse real-world applications. Recent advances in embedding methods and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown promising improvements. However, these methods often lack a thorough analysis of embedding expressiveness and suffer from ineffective benchmarks for a fair evaluation. In this paper, we propose a unified framework to assess the expressiveness of existing methods, highlighting the impact of dual embeddings and decoder design on performance. To address limitations in current experimental setups, we introduce DirLinkBench, a robust new benchmark with comprehensive coverage and standardized evaluation. The results show that current methods struggle to achieve strong performance on the new benchmark, while DiGAE outperforms others overall. We further revisit DiGAE theoretically, showing its graph convolution aligns with GCN on an undirected bipartite graph. Inspired by these insights, we propose a novel spectral directed graph auto-encoder SDGAE that achieves SOTA results on DirLinkBench. Finally, we analyze key factors influencing directed link prediction and highlight open challenges.
TGB-Seq Benchmark: Challenging Temporal GNNs with Complex Sequential Dynamics
Feb 05, 2025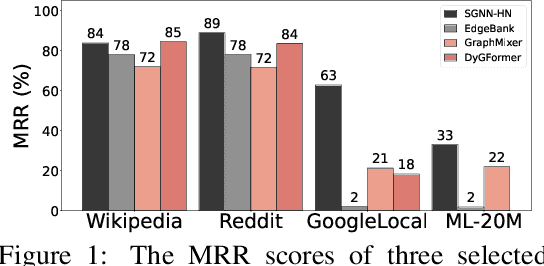
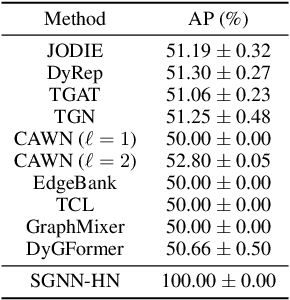
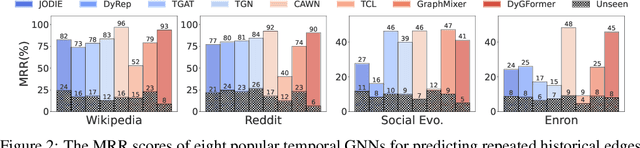

Abstract:Future link prediction is a fundamental challenge in various real-world dynamic systems. To address this, numerous temporal graph neural networks (temporal GNNs) and benchmark datasets have been developed. However, these datasets often feature excessive repeated edges and lack complex sequential dynamics, a key characteristic inherent in many real-world applications such as recommender systems and ``Who-To-Follow'' on social networks. This oversight has led existing methods to inadvertently downplay the importance of learning sequential dynamics, focusing primarily on predicting repeated edges. In this study, we demonstrate that existing methods, such as GraphMixer and DyGFormer, are inherently incapable of learning simple sequential dynamics, such as ``a user who has followed OpenAI and Anthropic is more likely to follow AI at Meta next.'' Motivated by this issue, we introduce the Temporal Graph Benchmark with Sequential Dynamics (TGB-Seq), a new benchmark carefully curated to minimize repeated edges, challenging models to learn sequential dynamics and generalize to unseen edges. TGB-Seq comprises large real-world datasets spanning diverse domains, including e-commerce interactions, movie ratings, business reviews, social networks, citation networks and web link networks. Benchmarking experiments reveal that current methods usually suffer significant performance degradation and incur substantial training costs on TGB-Seq, posing new challenges and opportunities for future research. TGB-Seq datasets, leaderboards, and example codes are available at https://tgb-seq.github.io/.
QAGCF: Graph Collaborative Filtering for Q&A Recommendation
Jun 07, 2024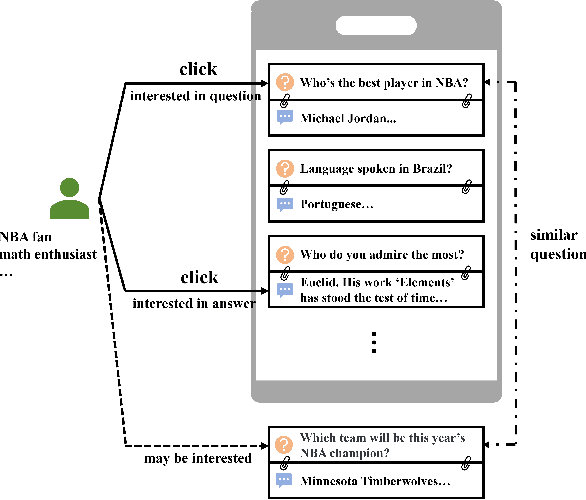
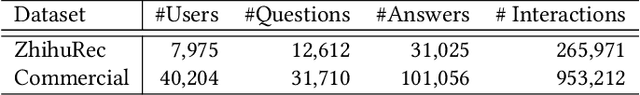
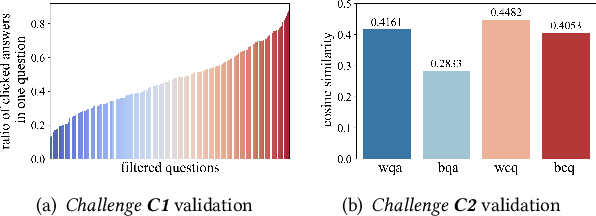
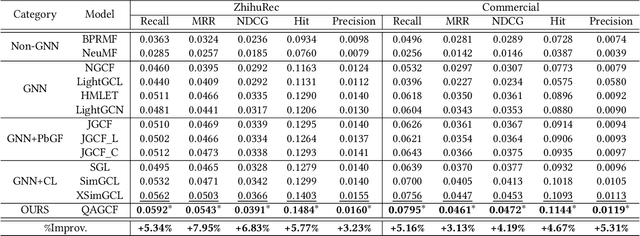
Abstract:Question and answer (Q&A) platforms usually recommend question-answer pairs to meet users' knowledge acquisition needs, unlike traditional recommendations that recommend only one item. This makes user behaviors more complex, and presents two challenges for Q&A recommendation, including: the collaborative information entanglement, which means user feedback is influenced by either the question or the answer; and the semantic information entanglement, where questions are correlated with their corresponding answers, and correlations also exist among different question-answer pairs. Traditional recommendation methods treat the question-answer pair as a whole or only consider the answer as a single item, which overlooks the two challenges and cannot effectively model user interests. To address these challenges, we introduce Question & Answer Graph Collaborative Filtering (QAGCF), a graph neural network model that creates separate graphs for collaborative and semantic views to disentangle the information in question-answer pairs. The collaborative view disentangles questions and answers to individually model collaborative information, while the semantic view captures the semantic information both within and between question-answer pairs. These views are further merged into a global graph to integrate the collaborative and semantic information. Polynomial-based graph filters are used to address the high heterophily issues of the global graph. Additionally, contrastive learning is utilized to obtain robust embeddings during training. Extensive experiments on industrial and public datasets demonstrate that QAGCF consistently outperforms baselines and achieves state-of-the-art results.
A survey of dynamic graph neural networks
Apr 28, 2024



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for effectively mining and learning from graph-structured data, with applications spanning numerous domains. However, most research focuses on static graphs, neglecting the dynamic nature of real-world networks where topologies and attributes evolve over time. By integrating sequence modeling modules into traditional GNN architectures, dynamic GNNs aim to bridge this gap, capturing the inherent temporal dependencies of dynamic graphs for a more authentic depiction of complex networks. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the fundamental concepts, key techniques, and state-of-the-art dynamic GNN models. We present the mainstream dynamic GNN models in detail and categorize models based on how temporal information is incorporated. We also discuss large-scale dynamic GNNs and pre-training techniques. Although dynamic GNNs have shown superior performance, challenges remain in scalability, handling heterogeneous information, and lack of diverse graph datasets. The paper also discusses possible future directions, such as adaptive and memory-enhanced models, inductive learning, and theoretical analysis.
GTP-ViT: Efficient Vision Transformers via Graph-based Token Propagation
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have revolutionized the field of computer vision, yet their deployments on resource-constrained devices remain challenging due to high computational demands. To expedite pre-trained ViTs, token pruning and token merging approaches have been developed, which aim at reducing the number of tokens involved in the computation. However, these methods still have some limitations, such as image information loss from pruned tokens and inefficiency in the token-matching process. In this paper, we introduce a novel Graph-based Token Propagation (GTP) method to resolve the challenge of balancing model efficiency and information preservation for efficient ViTs. Inspired by graph summarization algorithms, GTP meticulously propagates less significant tokens' information to spatially and semantically connected tokens that are of greater importance. Consequently, the remaining few tokens serve as a summarization of the entire token graph, allowing the method to reduce computational complexity while preserving essential information of eliminated tokens. Combined with an innovative token selection strategy, GTP can efficiently identify image tokens to be propagated. Extensive experiments have validated GTP's effectiveness, demonstrating both efficiency and performance improvements. Specifically, GTP decreases the computational complexity of both DeiT-S and DeiT-B by up to 26% with only a minimal 0.3% accuracy drop on ImageNet-1K without finetuning, and remarkably surpasses the state-of-the-art token merging method on various backbones at an even faster inference speed. The source code is available at https://github.com/Ackesnal/GTP-ViT.
Decoupled Graph Neural Networks for Large Dynamic Graphs
May 14, 2023



Abstract:Real-world graphs, such as social networks, financial transactions, and recommendation systems, often demonstrate dynamic behavior. This phenomenon, known as graph stream, involves the dynamic changes of nodes and the emergence and disappearance of edges. To effectively capture both the structural and temporal aspects of these dynamic graphs, dynamic graph neural networks have been developed. However, existing methods are usually tailored to process either continuous-time or discrete-time dynamic graphs, and cannot be generalized from one to the other. In this paper, we propose a decoupled graph neural network for large dynamic graphs, including a unified dynamic propagation that supports efficient computation for both continuous and discrete dynamic graphs. Since graph structure-related computations are only performed during the propagation process, the prediction process for the downstream task can be trained separately without expensive graph computations, and therefore any sequence model can be plugged-in and used. As a result, our algorithm achieves exceptional scalability and expressiveness. We evaluate our algorithm on seven real-world datasets of both continuous-time and discrete-time dynamic graphs. The experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance in both kinds of dynamic graphs. Most notably, the scalability of our algorithm is well illustrated by its successful application to large graphs with up to over a billion temporal edges and over a hundred million nodes.
Instant Graph Neural Networks for Dynamic Graphs
Jun 03, 2022
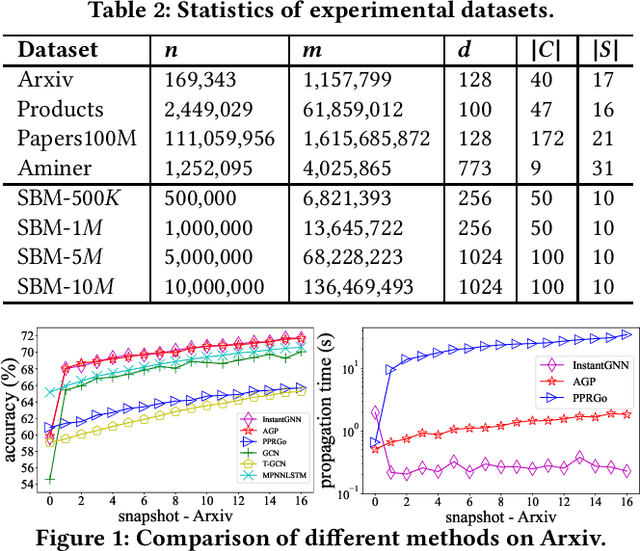
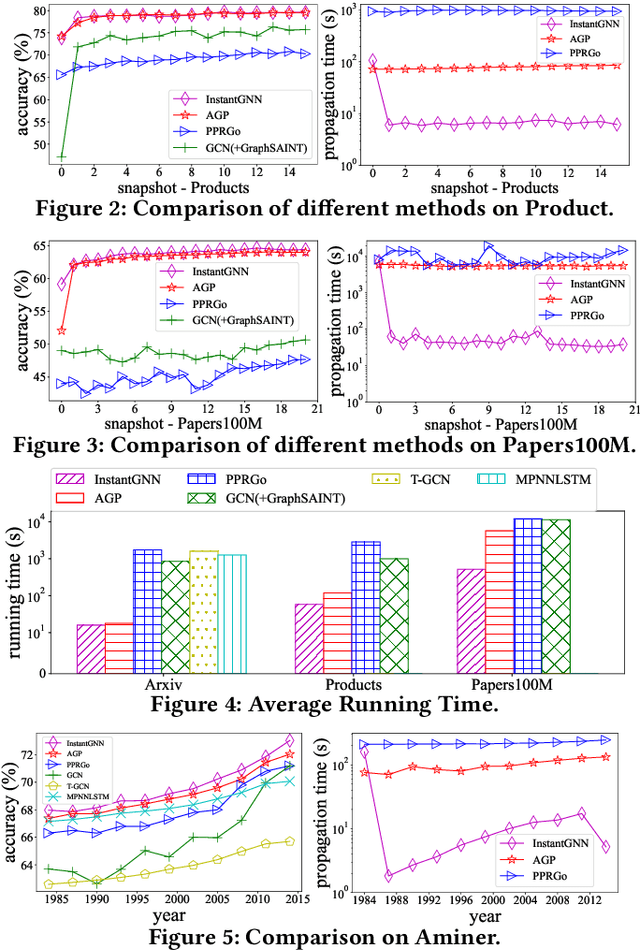
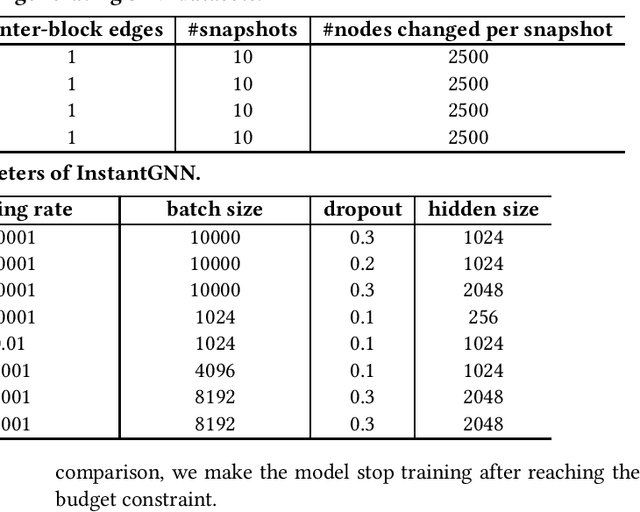
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been widely used for modeling graph-structured data. With the development of numerous GNN variants, recent years have witnessed groundbreaking results in improving the scalability of GNNs to work on static graphs with millions of nodes. However, how to instantly represent continuous changes of large-scale dynamic graphs with GNNs is still an open problem. Existing dynamic GNNs focus on modeling the periodic evolution of graphs, often on a snapshot basis. Such methods suffer from two drawbacks: first, there is a substantial delay for the changes in the graph to be reflected in the graph representations, resulting in losses on the model's accuracy; second, repeatedly calculating the representation matrix on the entire graph in each snapshot is predominantly time-consuming and severely limits the scalability. In this paper, we propose Instant Graph Neural Network (InstantGNN), an incremental computation approach for the graph representation matrix of dynamic graphs. Set to work with dynamic graphs with the edge-arrival model, our method avoids time-consuming, repetitive computations and allows instant updates on the representation and instant predictions. Graphs with dynamic structures and dynamic attributes are both supported. The upper bounds of time complexity of those updates are also provided. Furthermore, our method provides an adaptive training strategy, which guides the model to retrain at moments when it can make the greatest performance gains. We conduct extensive experiments on several real-world and synthetic datasets. Empirical results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while having orders-of-magnitude higher efficiency than existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge