Chenxing Sun
Map Feature Perception Metric for Map Generation Quality Assessment and Loss Optimization
Mar 30, 2025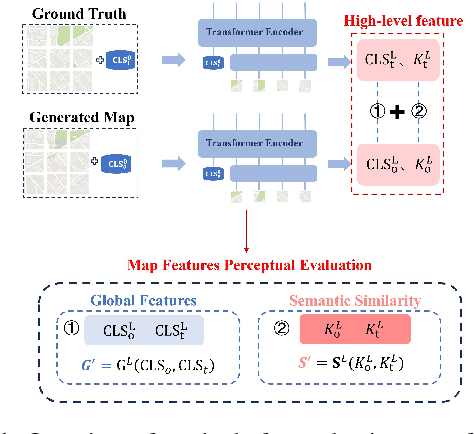
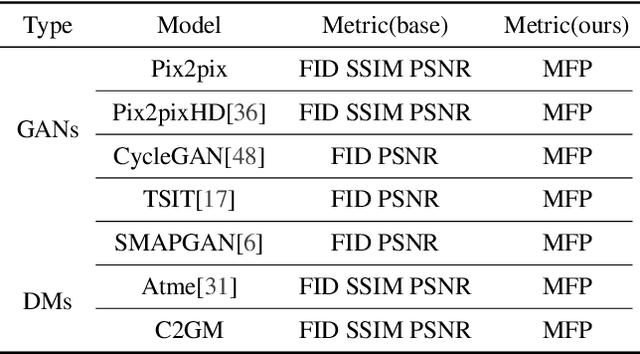
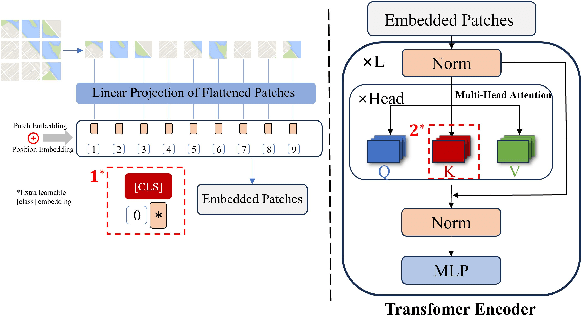
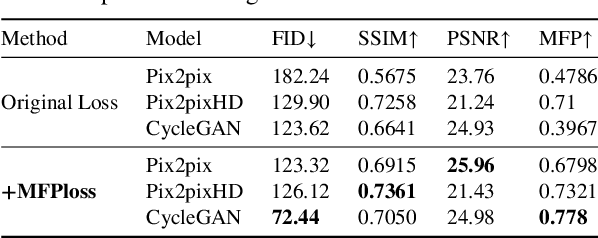
Abstract:In intelligent cartographic generation tasks empowered by generative models, the authenticity of synthesized maps constitutes a critical determinant. Concurrently, the selection of appropriate evaluation metrics to quantify map authenticity emerges as a pivotal research challenge. Current methodologies predominantly adopt computer vision-based image assessment metrics to compute discrepancies between generated and reference maps. However, conventional visual similarity metrics-including L1, L2, SSIM, and FID-primarily operate at pixel-level comparisons, inadequately capturing cartographic global features and spatial correlations, consequently inducing semantic-structural artifacts in generated outputs. This study introduces a novel Map Feature Perception Metric designed to evaluate global characteristics and spatial congruence between synthesized and target maps. Diverging from pixel-wise metrics, our approach extracts elemental-level deep features that comprehensively encode cartographic structural integrity and topological relationships. Experimental validation demonstrates MFP's superior capability in evaluating cartographic semantic features, with classification-enhanced implementations outperforming conventional loss functions across diverse generative frameworks. When employed as optimization objectives, our metric achieves performance gains ranging from 2% to 50% across multiple benchmarks compared to traditional L1, L2, and SSIM baselines. This investigation concludes that explicit consideration of cartographic global attributes and spatial coherence substantially enhances generative model optimization, thereby significantly improving the geographical plausibility of synthesized maps.
C2GM: Cascading Conditional Generation of Multi-scale Maps from Remote Sensing Images Constrained by Geographic Features
Feb 07, 2025
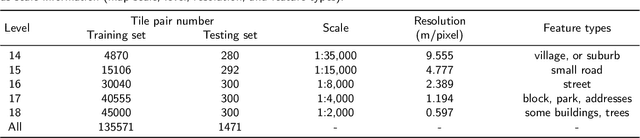

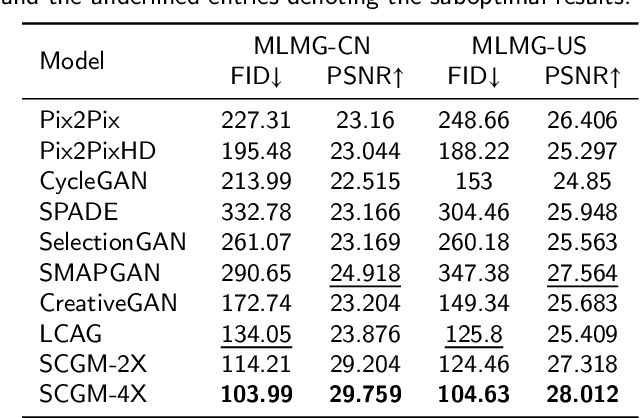
Abstract:Multi-scale maps are essential representations of surveying and cartographic results, serving as fundamental components of geographic services. Current image generation networks can quickly produce map tiles from remote-sensing images. However, generative models designed for natural images often focus on texture features, neglecting the unique characteristics of remote-sensing features and the scale attributes of tile maps. This limitation in generative models impairs the accurate representation of geographic information, and the quality of tile map generation still needs improvement. Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in various image generation tasks, highlighting their potential to address this challenge. This paper presents C2GM, a novel framework for generating multi-scale tile maps through conditional guided diffusion and multi-scale cascade generation. Specifically, we implement a conditional feature fusion encoder to extract object priors from remote sensing images and cascade reference double branch input, ensuring an accurate representation of complex features. Low-level generated tiles act as constraints for high-level map generation, enhancing visual continuity. Moreover, we incorporate map scale modality information using CLIP to simulate the relationship between map scale and cartographic generalization in tile maps. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that C2GM consistently achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on all metrics, facilitating the rapid and effective generation of multi-scale large-format maps for emergency response and remote mapping applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge