Tom Gedeon
Bob
Bipartite Mode Matching for Vision Training Set Search from a Hierarchical Data Server
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We explore a situation in which the target domain is accessible, but real-time data annotation is not feasible. Instead, we would like to construct an alternative training set from a large-scale data server so that a competitive model can be obtained. For this problem, because the target domain usually exhibits distinct modes (i.e., semantic clusters representing data distribution), if the training set does not contain these target modes, the model performance would be compromised. While prior existing works improve algorithms iteratively, our research explores the often-overlooked potential of optimizing the structure of the data server. Inspired by the hierarchical nature of web search engines, we introduce a hierarchical data server, together with a bipartite mode matching algorithm (BMM) to align source and target modes. For each target mode, we look in the server data tree for the best mode match, which might be large or small in size. Through bipartite matching, we aim for all target modes to be optimally matched with source modes in a one-on-one fashion. Compared with existing training set search algorithms, we show that the matched server modes constitute training sets that have consistently smaller domain gaps with the target domain across object re-identification (re-ID) and detection tasks. Consequently, models trained on our searched training sets have higher accuracy than those trained otherwise. BMM allows data-centric unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) orthogonal to existing model-centric UDA methods. By combining the BMM with existing UDA methods like pseudo-labeling, further improvement is observed.
CSGaze: Context-aware Social Gaze Prediction
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:A person's gaze offers valuable insights into their focus of attention, level of social engagement, and confidence. In this work, we investigate how contextual cues combined with visual scene and facial information can be effectively utilized to predict and interpret social gaze patterns during conversational interactions. We introduce CSGaze, a context aware multimodal approach that leverages facial, scene information as complementary inputs to enhance social gaze pattern prediction from multi-person images. The model also incorporates a fine-grained attention mechanism centered on the principal speaker, which helps in better modeling social gaze dynamics. Experimental results show that CSGaze performs competitively with state-of-the-art methods on GP-Static, UCO-LAEO and AVA-LAEO. Our findings highlight the role of contextual cues in improving social gaze prediction. Additionally, we provide initial explainability through generated attention scores, offering insights into the model's decision-making process. We also demonstrate our model's generalizability by testing our model on open set datasets that demonstrating its robustness across diverse scenarios.
Gems: Group Emotion Profiling Through Multimodal Situational Understanding
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Understanding individual, group and event level emotions along with contextual information is crucial for analyzing a multi-person social situation. To achieve this, we frame emotion comprehension as the task of predicting fine-grained individual emotion to coarse grained group and event level emotion. We introduce GEMS that leverages a multimodal swin-transformer and S3Attention based architecture, which processes an input scene, group members, and context information to generate joint predictions. Existing multi-person emotion related benchmarks mainly focus on atomic interactions primarily based on emotion perception over time and group level. To this end, we extend and propose VGAF-GEMS to provide more fine grained and holistic analysis on top of existing group level annotation of VGAF dataset. GEMS aims to predict basic discrete and continuous emotions (including valence and arousal) as well as individual, group and event level perceived emotions. Our benchmarking effort links individual, group and situational emotional responses holistically. The quantitative and qualitative comparisons with adapted state-of-the-art models demonstrate the effectiveness of GEMS framework on VGAF-GEMS benchmarking. We believe that it will pave the way of further research. The code and data is available at: https://github.com/katariaak579/GEMS
AV-Deepfake1M++: A Large-Scale Audio-Visual Deepfake Benchmark with Real-World Perturbations
Jul 28, 2025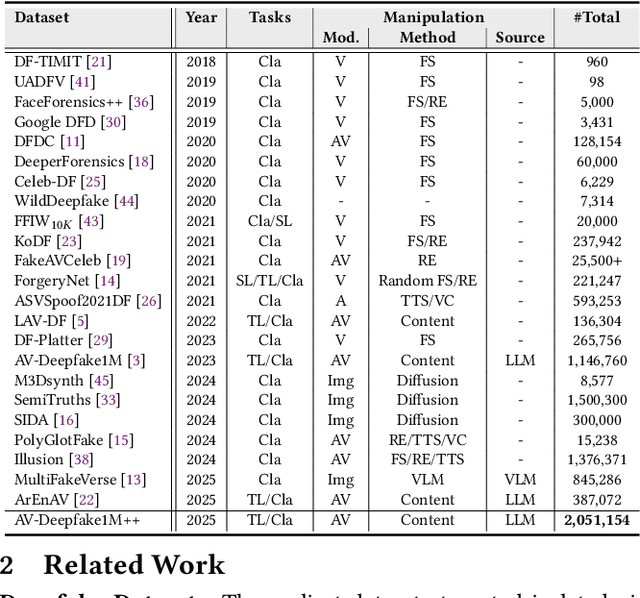
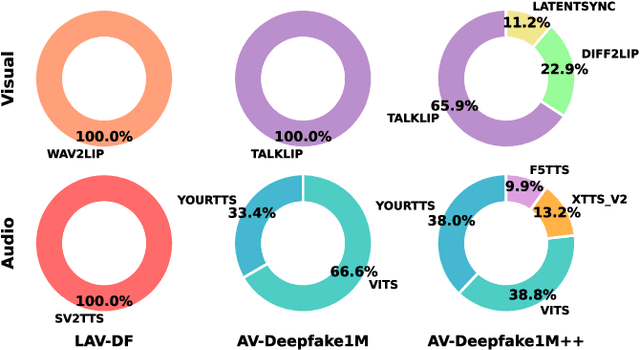
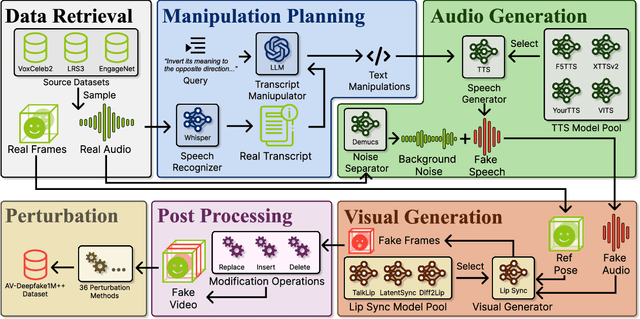
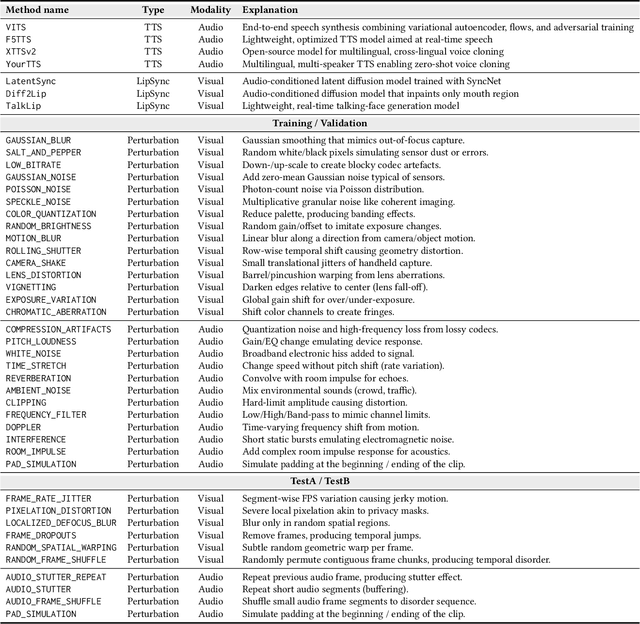
Abstract:The rapid surge of text-to-speech and face-voice reenactment models makes video fabrication easier and highly realistic. To encounter this problem, we require datasets that rich in type of generation methods and perturbation strategy which is usually common for online videos. To this end, we propose AV-Deepfake1M++, an extension of the AV-Deepfake1M having 2 million video clips with diversified manipulation strategy and audio-visual perturbation. This paper includes the description of data generation strategies along with benchmarking of AV-Deepfake1M++ using state-of-the-art methods. We believe that this dataset will play a pivotal role in facilitating research in Deepfake domain. Based on this dataset, we host the 2025 1M-Deepfakes Detection Challenge. The challenge details, dataset and evaluation scripts are available online under a research-only license at https://deepfakes1m.github.io/2025.
Simple Radiology VLLM Test-time Scaling with Thought Graph Traversal
Jun 13, 2025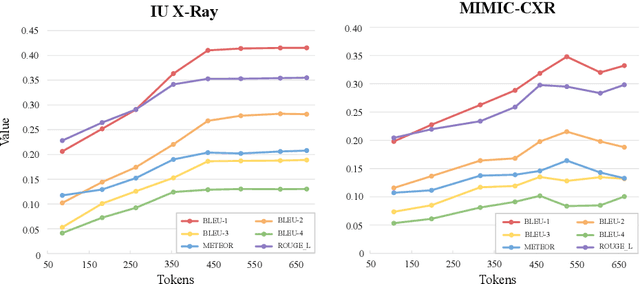
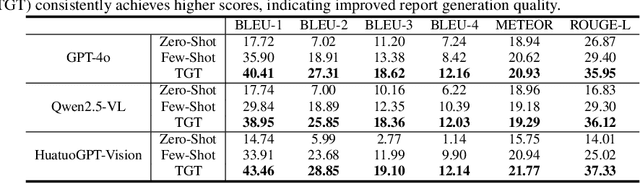
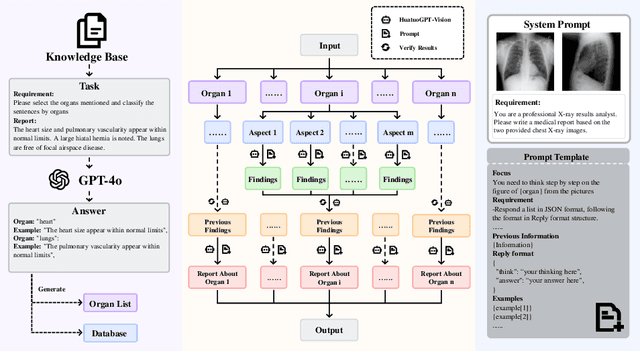
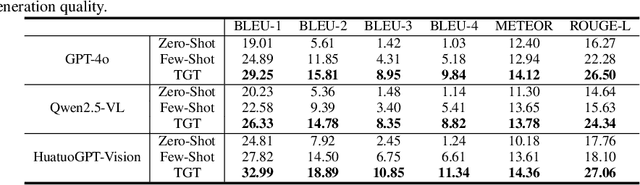
Abstract:Test-time scaling offers a promising way to improve the reasoning performance of vision-language large models (VLLMs) without additional training. In this paper, we explore a simple but effective approach for applying test-time scaling to radiology report generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Thought Graph Traversal (TGT) framework that guides the model to reason through organ-specific findings in a medically coherent order. This framework integrates structured medical priors into the prompt, enabling deeper and more logical analysis with no changes to the underlying model. To further enhance reasoning depth, we apply a reasoning budget forcing strategy that adjusts the model's inference depth at test time by dynamically extending its generation process. This simple yet powerful combination allows a frozen radiology VLLM to self-correct and generate more accurate, consistent chest X-ray reports. Our method outperforms baseline prompting approaches on standard benchmarks, and also reveals dataset biases through traceable reasoning paths. Code and prompts are open-sourced for reproducibility at https://github.com/glerium/Thought-Graph-Traversal.
Visual and textual prompts for enhancing emotion recognition in video
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs) exhibit promising potential for multi-modal understanding, yet their application to video-based emotion recognition remains limited by insufficient spatial and contextual awareness. Traditional approaches, which prioritize isolated facial features, often neglect critical non-verbal cues such as body language, environmental context, and social interactions, leading to reduced robustness in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we propose Set-of-Vision-Text Prompting (SoVTP), a novel framework that enhances zero-shot emotion recognition by integrating spatial annotations (e.g., bounding boxes, facial landmarks), physiological signals (facial action units), and contextual cues (body posture, scene dynamics, others' emotions) into a unified prompting strategy. SoVTP preserves holistic scene information while enabling fine-grained analysis of facial muscle movements and interpersonal dynamics. Extensive experiments show that SoVTP achieves substantial improvements over existing visual prompting methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing VLLMs' video emotion recognition capabilities.
Tabular foundation model to detect empathy from visual cues
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Detecting empathy from video interactions is an emerging area of research. Video datasets, however, are often released as extracted features (i.e., tabular data) rather than raw footage due to privacy and ethical concerns. Prior research on such tabular datasets established tree-based classical machine learning approaches as the best-performing models. Motivated by the recent success of textual foundation models (i.e., large language models), we explore the use of tabular foundation models in empathy detection from tabular visual features. We experiment with two recent tabular foundation models $-$ TabPFN v2 and TabICL $-$ through in-context learning and fine-tuning setups. Our experiments on a public human-robot interaction benchmark demonstrate a significant boost in cross-subject empathy detection accuracy over several strong baselines (accuracy: $0.590 \rightarrow 0.730$; AUC: $0.564 \rightarrow 0.669$). In addition to performance improvement, we contribute novel insights and an evaluation setup to ensure generalisation on unseen subjects in this public benchmark. As the practice of releasing video features as tabular datasets is likely to persist due to privacy constraints, our findings will be widely applicable to future empathy detection video datasets as well.
Unsupervised Search for Ethnic Minorities' Medical Segmentation Training Set
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:This article investigates the critical issue of dataset bias in medical imaging, with a particular emphasis on racial disparities caused by uneven population distribution in dataset collection. Our analysis reveals that medical segmentation datasets are significantly biased, primarily influenced by the demographic composition of their collection sites. For instance, Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (SLO) fundus datasets collected in the United States predominantly feature images of White individuals, with minority racial groups underrepresented. This imbalance can result in biased model performance and inequitable clinical outcomes, particularly for minority populations. To address this challenge, we propose a novel training set search strategy aimed at reducing these biases by focusing on underrepresented racial groups. Our approach utilizes existing datasets and employs a simple greedy algorithm to identify source images that closely match the target domain distribution. By selecting training data that aligns more closely with the characteristics of minority populations, our strategy improves the accuracy of medical segmentation models on specific minorities, i.e., Black. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in mitigating bias. We also discuss the broader societal implications, highlighting how addressing these disparities can contribute to more equitable healthcare outcomes.
Labels Generated by Large Language Model Helps Measuring People's Empathy in Vitro
Jan 01, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionised numerous fields, with LLM-as-a-service (LLMSaaS) having a strong generalisation ability that offers accessible solutions directly without the need for costly training. In contrast to the widely studied prompt engineering for task solving directly (in vivo), this paper explores its potential in in-vitro applications. These involve using LLM to generate labels to help the supervised training of mainstream models by (1) noisy label correction and (2) training data augmentation with LLM-generated labels. In this paper, we evaluate this approach in the emerging field of empathy computing -- automating the prediction of psychological questionnaire outcomes from inputs like text sequences. Specifically, crowdsourced datasets in this domain often suffer from noisy labels that misrepresent underlying empathy. By leveraging LLM-generated labels to train pre-trained language models (PLMs) like RoBERTa, we achieve statistically significant accuracy improvements over baselines, achieving a state-of-the-art Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.648 on NewsEmp benchmarks. In addition, we bring insightful discussions, including current challenges in empathy computing, data biases in training data and evaluation metric selection. Code and LLM-generated data are available at https://github.com/hasan-rakibul/LLMPathy (available once the paper is accepted).
Ranked from Within: Ranking Large Multimodal Models for Visual Question Answering Without Labels
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:As large multimodal models (LMMs) are increasingly deployed across diverse applications, the need for adaptable, real-world model ranking has become paramount. Traditional evaluation methods are largely dataset-centric, relying on fixed, labeled datasets and supervised metrics, which are resource-intensive and may lack generalizability to novel scenarios, highlighting the importance of unsupervised ranking. In this work, we explore unsupervised model ranking for LMMs by leveraging their uncertainty signals, such as softmax probabilities. We evaluate state-of-the-art LMMs (e.g., LLaVA) across visual question answering benchmarks, analyzing how uncertainty-based metrics can reflect model performance. Our findings show that uncertainty scores derived from softmax distributions provide a robust, consistent basis for ranking models across varied tasks. This finding enables the ranking of LMMs on real-world, unlabeled data for visual question answering, providing a practical approach for selecting models across diverse domains without requiring manual annotation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge