Weijie Tu
Ranked from Within: Ranking Large Multimodal Models for Visual Question Answering Without Labels
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:As large multimodal models (LMMs) are increasingly deployed across diverse applications, the need for adaptable, real-world model ranking has become paramount. Traditional evaluation methods are largely dataset-centric, relying on fixed, labeled datasets and supervised metrics, which are resource-intensive and may lack generalizability to novel scenarios, highlighting the importance of unsupervised ranking. In this work, we explore unsupervised model ranking for LMMs by leveraging their uncertainty signals, such as softmax probabilities. We evaluate state-of-the-art LMMs (e.g., LLaVA) across visual question answering benchmarks, analyzing how uncertainty-based metrics can reflect model performance. Our findings show that uncertainty scores derived from softmax distributions provide a robust, consistent basis for ranking models across varied tasks. This finding enables the ranking of LMMs on real-world, unlabeled data for visual question answering, providing a practical approach for selecting models across diverse domains without requiring manual annotation.
Toward a Holistic Evaluation of Robustness in CLIP Models
Oct 02, 2024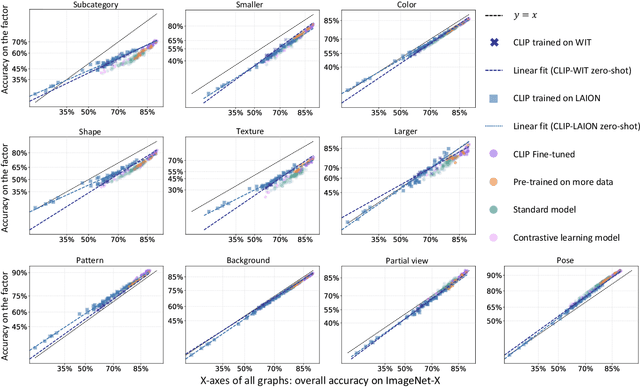
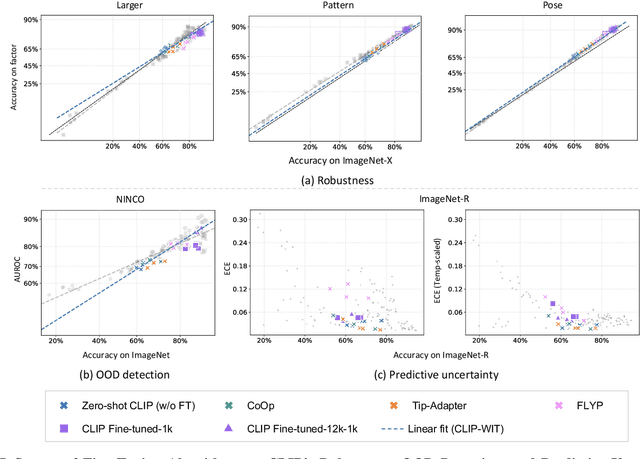


Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) models have shown significant potential, particularly in zero-shot classification across diverse distribution shifts. Building on existing evaluations of overall classification robustness, this work aims to provide a more comprehensive assessment of CLIP by introducing several new perspectives. First, we investigate their robustness to variations in specific visual factors. Second, we assess two critical safety objectives--confidence uncertainty and out-of-distribution detection--beyond mere classification accuracy. Third, we evaluate the finesse with which CLIP models bridge the image and text modalities. Fourth, we extend our examination to 3D awareness in CLIP models, moving beyond traditional 2D image understanding. Finally, we explore the interaction between vision and language encoders within modern large multimodal models (LMMs) that utilize CLIP as the visual backbone, focusing on how this interaction impacts classification robustness. In each aspect, we consider the impact of six factors on CLIP models: model architecture, training distribution, training set size, fine-tuning, contrastive loss, and test-time prompts. Our study uncovers several previously unknown insights into CLIP. For instance, the architecture of the visual encoder in CLIP plays a significant role in their robustness against 3D corruption. CLIP models tend to exhibit a bias towards shape when making predictions. Moreover, this bias tends to diminish after fine-tuning on ImageNet. Vision-language models like LLaVA, leveraging the CLIP vision encoder, could exhibit benefits in classification performance for challenging categories over CLIP alone. Our findings are poised to offer valuable guidance for enhancing the robustness and reliability of CLIP models.
What Does Softmax Probability Tell Us about Classifiers Ranking Across Diverse Test Conditions?
Jun 14, 2024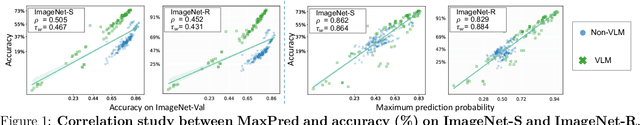

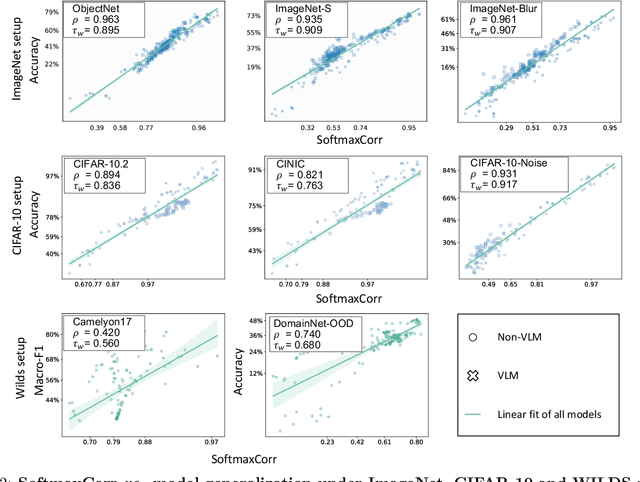
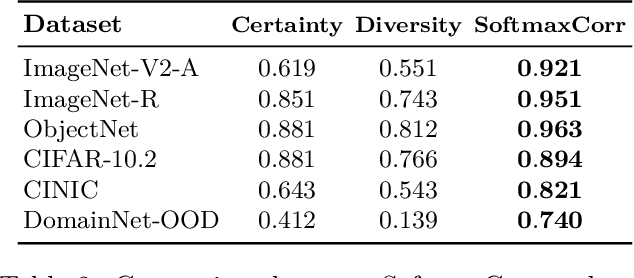
Abstract:This work aims to develop a measure that can accurately rank the performance of various classifiers when they are tested on unlabeled data from out-of-distribution (OOD) distributions. We commence by demonstrating that conventional uncertainty metrics, notably the maximum Softmax prediction probability, possess inherent utility in forecasting model generalization across certain OOD contexts. Building on this insight, we introduce a new measure called Softmax Correlation (SoftmaxCorr). It calculates the cosine similarity between a class-class correlation matrix, constructed from Softmax output vectors across an unlabeled test dataset, and a predefined reference matrix that embodies ideal class correlations. A high resemblance of predictions to the reference matrix signals that the model delivers confident and uniform predictions across all categories, reflecting minimal uncertainty and confusion. Through rigorous evaluation across a suite of datasets, including ImageNet, CIFAR-10, and WILDS, we affirm the predictive validity of SoftmaxCorr in accurately forecasting model performance within both in-distribution (ID) and OOD settings. Furthermore, we discuss the limitations of our proposed measure and suggest avenues for future research.
A Closer Look at the Robustness of Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training
Feb 12, 2024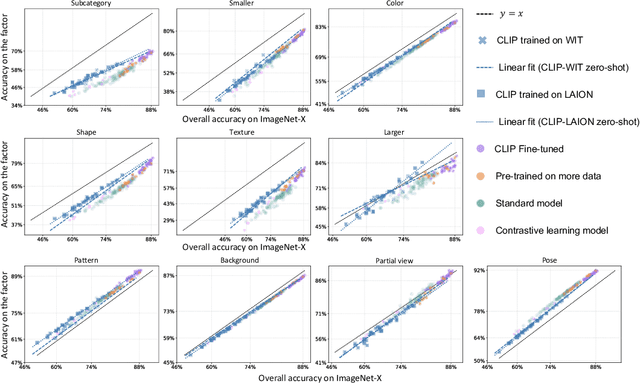
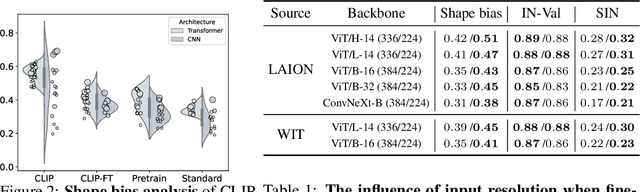
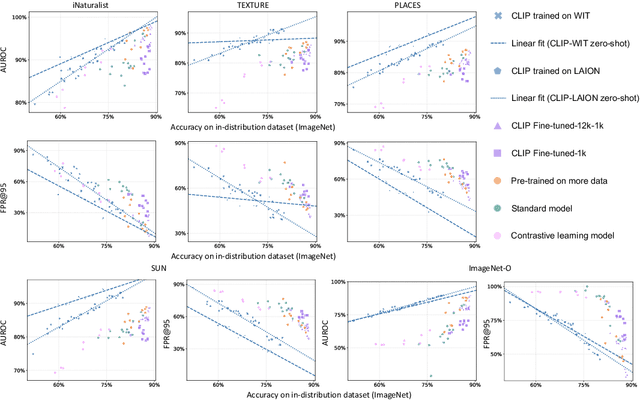

Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) models have demonstrated remarkable generalization capabilities across multiple challenging distribution shifts. However, there is still much to be explored in terms of their robustness to the variations of specific visual factors. In real-world applications, reliable and safe systems must consider other safety objectives beyond classification accuracy, such as predictive uncertainty. Yet, the effectiveness of CLIP models on such safety-related features is less-explored. Driven by the above, this work comprehensively investigates the safety objectives of CLIP models, specifically focusing on three key properties: resilience to visual factor variations, calibrated uncertainty estimations, and the ability to detect anomalous inputs. To this end, we study 83 CLIP models and 127 ImageNet classifiers. They are diverse in architecture, (pre)training distribution and training strategies. We consider 10 visual factors (e.g., shape and pattern), 5 types of out-of-distribution data, and 8 natural and challenging test conditions with different shift types, such as texture, style, and perturbation shifts. Our study has unveiled several previously unknown insights into CLIP models. For instance, they are not consistently more calibrated than other ImageNet models, which contradicts existing findings. Additionally, our analysis underscores the significance of training source design by showcasing its profound influence on the three safety-related properties. We believe our comprehensive study can shed light on and help guide the development of more robust and reliable CLIP models.
An Empirical Study Into What Matters for Calibrating Vision-Language Models
Feb 12, 2024
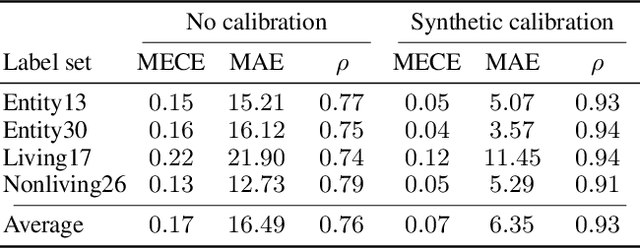

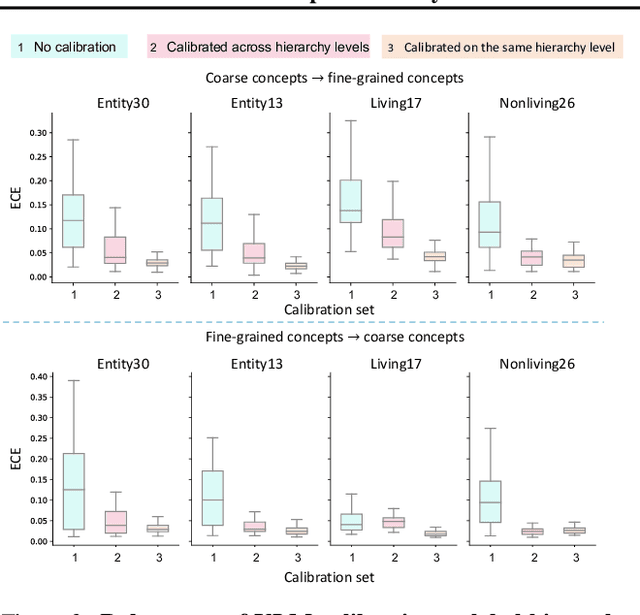
Abstract:Vision--Language Models (VLMs) have emerged as the dominant approach for zero-shot recognition, adept at handling diverse scenarios and significant distribution changes. However, their deployment in risk-sensitive areas requires a deeper understanding of their uncertainty estimation capabilities, a relatively uncharted area. In this study, we explore the calibration properties of VLMs across different architectures, datasets, and training strategies. In particular, we analyze the uncertainty estimation performance of VLMs when calibrated in one domain, label set or hierarchy level, and tested in a different one. Our findings reveal that while VLMs are not inherently calibrated for uncertainty, temperature scaling significantly and consistently improves calibration, even across shifts in distribution and changes in label set. Moreover, VLMs can be calibrated with a very small set of examples. Through detailed experimentation, we highlight the potential applications and importance of our insights, aiming for more reliable and effective use of VLMs in critical, real-world scenarios.
A Bag-of-Prototypes Representation for Dataset-Level Applications
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:This work investigates dataset vectorization for two dataset-level tasks: assessing training set suitability and test set difficulty. The former measures how suitable a training set is for a target domain, while the latter studies how challenging a test set is for a learned model. Central to the two tasks is measuring the underlying relationship between datasets. This needs a desirable dataset vectorization scheme, which should preserve as much discriminative dataset information as possible so that the distance between the resulting dataset vectors can reflect dataset-to-dataset similarity. To this end, we propose a bag-of-prototypes (BoP) dataset representation that extends the image-level bag consisting of patch descriptors to dataset-level bag consisting of semantic prototypes. Specifically, we develop a codebook consisting of K prototypes clustered from a reference dataset. Given a dataset to be encoded, we quantize each of its image features to a certain prototype in the codebook and obtain a K-dimensional histogram. Without assuming access to dataset labels, the BoP representation provides a rich characterization of the dataset semantic distribution. Furthermore, BoP representations cooperate well with Jensen-Shannon divergence for measuring dataset-to-dataset similarity. Although very simple, BoP consistently shows its advantage over existing representations on a series of benchmarks for two dataset-level tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge