Yan Tong
Simple Radiology VLLM Test-time Scaling with Thought Graph Traversal
Jun 13, 2025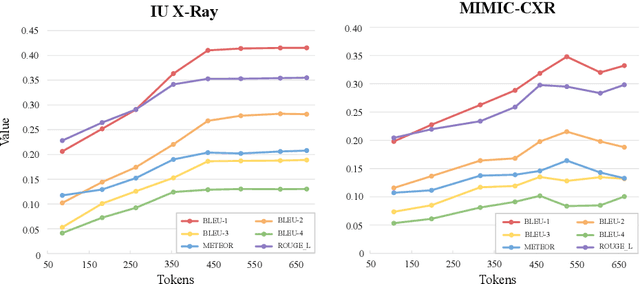
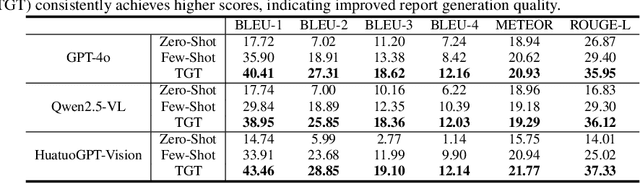
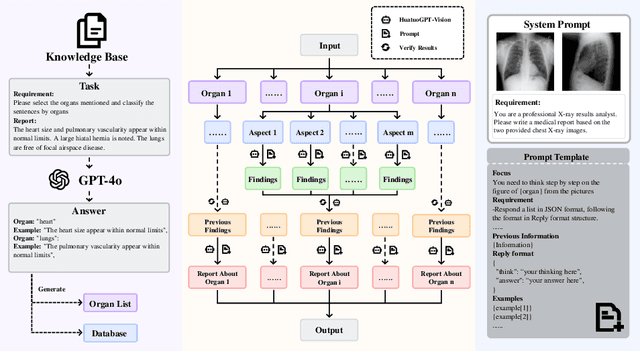
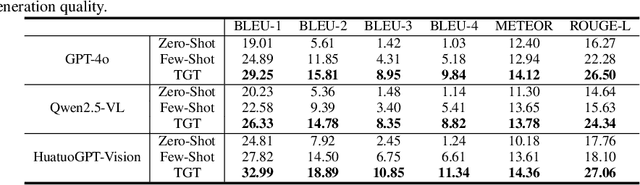
Abstract:Test-time scaling offers a promising way to improve the reasoning performance of vision-language large models (VLLMs) without additional training. In this paper, we explore a simple but effective approach for applying test-time scaling to radiology report generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Thought Graph Traversal (TGT) framework that guides the model to reason through organ-specific findings in a medically coherent order. This framework integrates structured medical priors into the prompt, enabling deeper and more logical analysis with no changes to the underlying model. To further enhance reasoning depth, we apply a reasoning budget forcing strategy that adjusts the model's inference depth at test time by dynamically extending its generation process. This simple yet powerful combination allows a frozen radiology VLLM to self-correct and generate more accurate, consistent chest X-ray reports. Our method outperforms baseline prompting approaches on standard benchmarks, and also reveals dataset biases through traceable reasoning paths. Code and prompts are open-sourced for reproducibility at https://github.com/glerium/Thought-Graph-Traversal.
LAMPER: LanguAge Model and Prompt EngineeRing for zero-shot time series classification
Mar 23, 2024



Abstract:This study constructs the LanguAge Model with Prompt EngineeRing (LAMPER) framework, designed to systematically evaluate the adaptability of pre-trained language models (PLMs) in accommodating diverse prompts and their integration in zero-shot time series (TS) classification. We deploy LAMPER in experimental assessments using 128 univariate TS datasets sourced from the UCR archive. Our findings indicate that the feature representation capacity of LAMPER is influenced by the maximum input token threshold imposed by PLMs.
Dual-Channel Reliable Breast Ultrasound Image Classification Based on Explainable Attribution and Uncertainty Quantification
Jan 08, 2024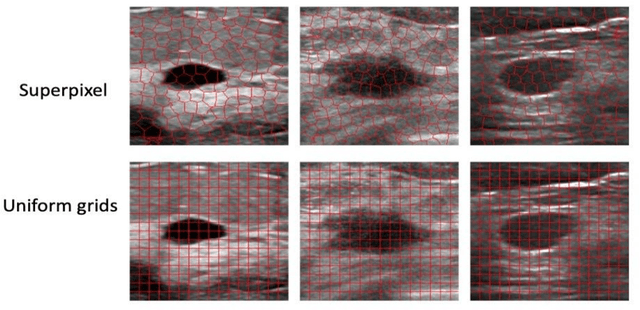
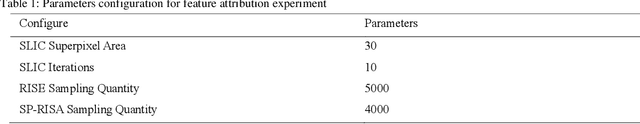
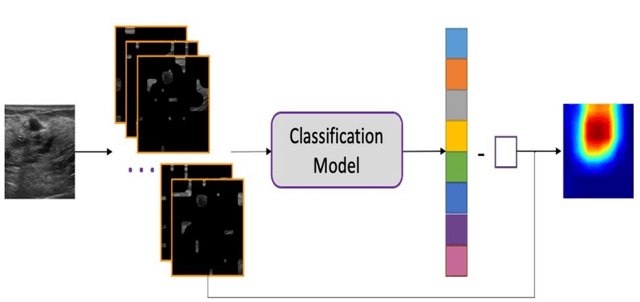

Abstract:This paper focuses on the classification task of breast ultrasound images and researches on the reliability measurement of classification results. We proposed a dual-channel evaluation framework based on the proposed inference reliability and predictive reliability scores. For the inference reliability evaluation, human-aligned and doctor-agreed inference rationales based on the improved feature attribution algorithm SP-RISA are gracefully applied. Uncertainty quantification is used to evaluate the predictive reliability via the Test Time Enhancement. The effectiveness of this reliability evaluation framework has been verified on our breast ultrasound clinical dataset YBUS, and its robustness is verified on the public dataset BUSI. The expected calibration errors on both datasets are significantly lower than traditional evaluation methods, which proves the effectiveness of our proposed reliability measurement.
Human-like Decision-making at Unsignalized Intersection using Social Value Orientation
Jun 30, 2023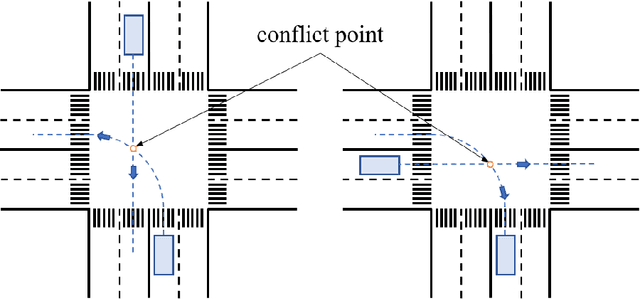
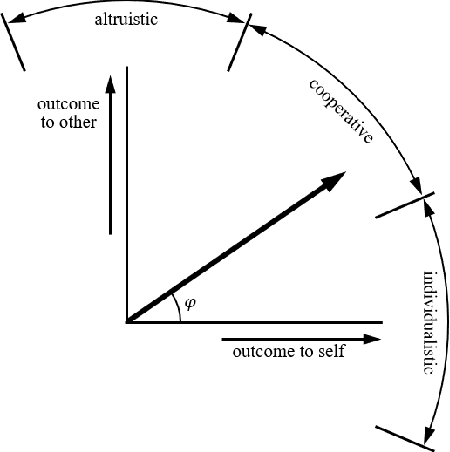
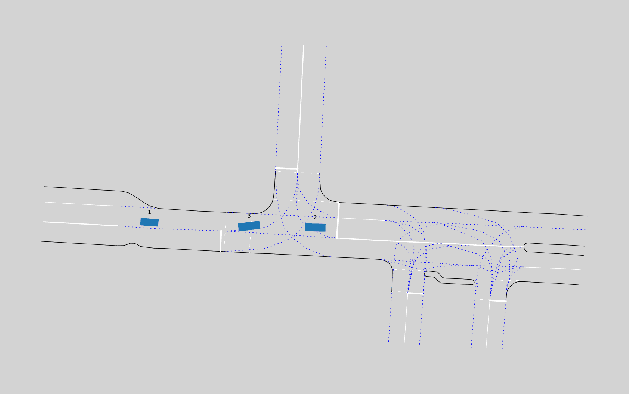
Abstract:With the commercial application of automated vehicles (AVs), the sharing of roads between AVs and human-driven vehicles (HVs) becomes a common occurrence in the future. While research has focused on improving the safety and reliability of autonomous driving, it's also crucial to consider collaboration between AVs and HVs. Human-like interaction is a required capability for AVs, especially at common unsignalized intersections, as human drivers of HVs expect to maintain their driving habits for inter-vehicle interactions. This paper uses the social value orientation (SVO) in the decision-making of vehicles to describe the social interaction among multiple vehicles. Specifically, we define the quantitative calculation of the conflict-involved SVO at unsignalized intersections to enhance decision-making based on the reinforcement learning method. We use naturalistic driving scenarios with highly interactive motions for performance evaluation of the proposed method. Experimental results show that SVO is more effective in characterizing inter-vehicle interactions than conventional motion state parameters like velocity, and the proposed method can accurately reproduce naturalistic driving trajectories compared to behavior cloning.
Feature-level and Model-level Audiovisual Fusion for Emotion Recognition in the Wild
Jun 06, 2019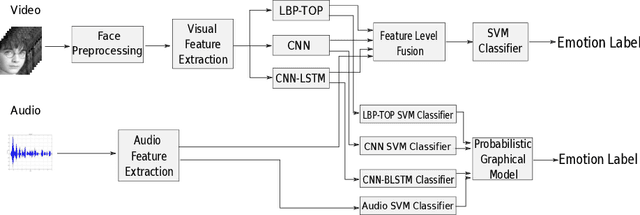
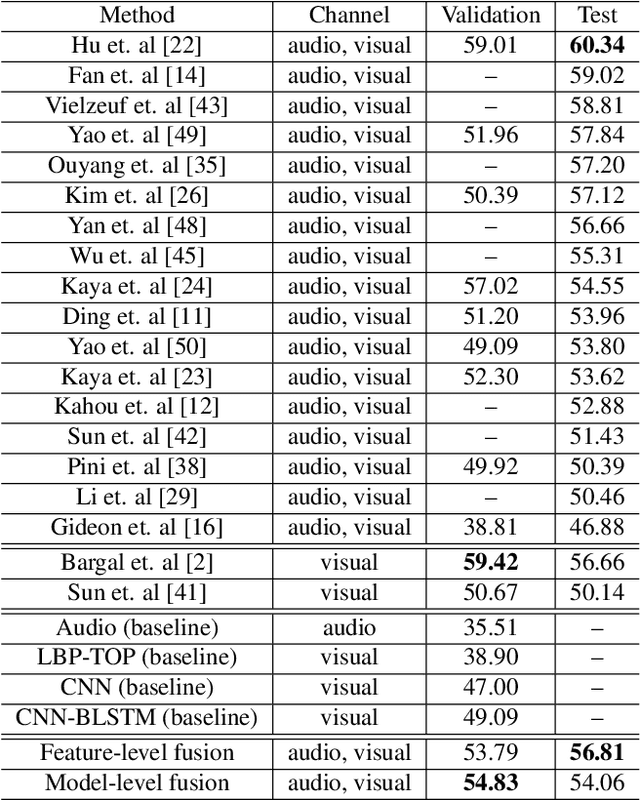
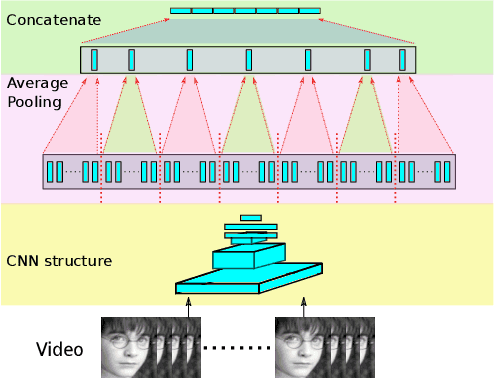
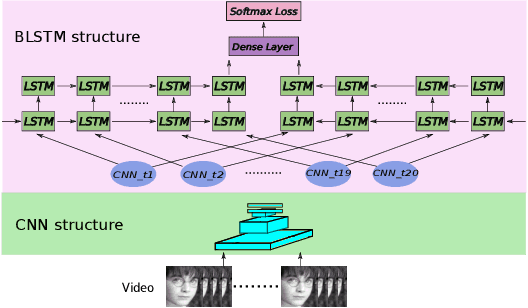
Abstract:Emotion recognition plays an important role in human-computer interaction (HCI) and has been extensively studied for decades. Although tremendous improvements have been achieved for posed expressions, recognizing human emotions in "close-to-real-world" environments remains a challenge. In this paper, we proposed two strategies to fuse information extracted from different modalities, i.e., audio and visual. Specifically, we utilized LBP-TOP, an ensemble of CNNs, and a bi-directional LSTM (BLSTM) to extract features from the visual channel, and the OpenSmile toolkit to extract features from the audio channel. Two kinds of fusion methods, i,e., feature-level fusion and model-level fusion, were developed to utilize the information extracted from the two channels. Experimental results on the EmotiW2018 AFEW dataset have shown that the proposed fusion methods outperform the baseline methods significantly and achieve better or at least comparable performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods, where the model-level fusion performs better when one of the channels totally fails.
Identity-Free Facial Expression Recognition using conditional Generative Adversarial Network
Mar 19, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we proposed a novel Identity-free conditional Generative Adversarial Network (IF-GAN) to explicitly reduce inter-subject variations for facial expression recognition. Specifically, for any given input face image, a conditional generative model was developed to transform an average neutral face, which is calculated from various subjects showing neutral expressions, to an average expressive face with the same expression as the input image. Since the transformed images have the same synthetic "average" identity, they differ from each other by only their expressions and thus, can be used for identity-free expression classification. In this work, an end-to-end system was developed to perform expression transformation and expression recognition in the IF-GAN framework. Experimental results on three facial expression datasets have demonstrated that the proposed IF-GAN outperforms the baseline CNN model and achieves comparable or better performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods for facial expression recognition.
Probabilistic Attribute Tree in Convolutional Neural Networks for Facial Expression Recognition
Dec 17, 2018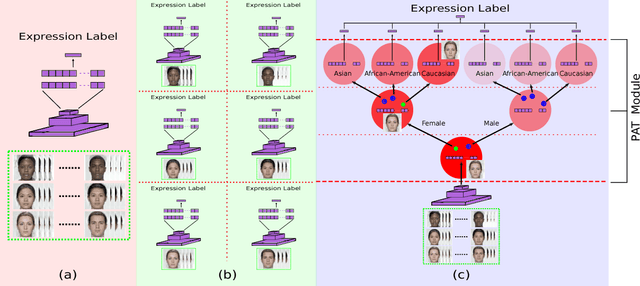
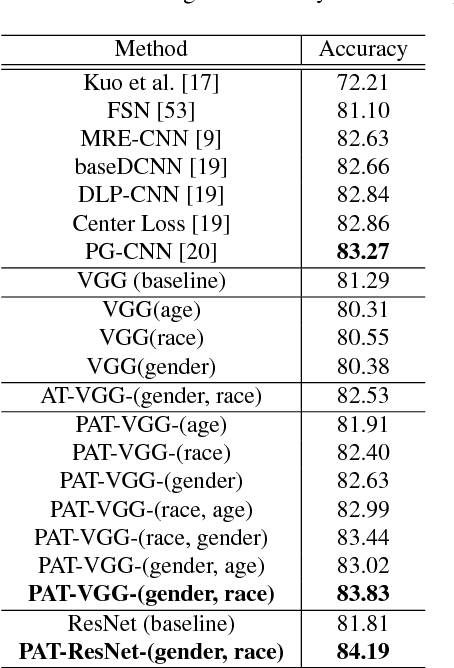
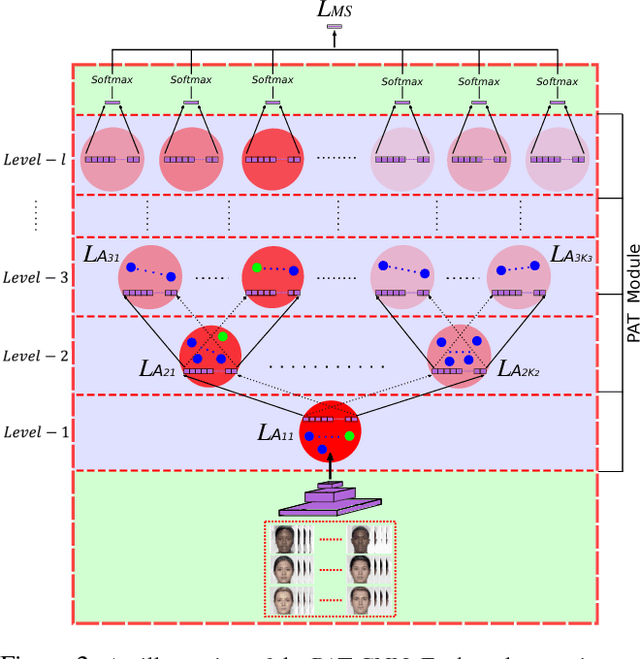
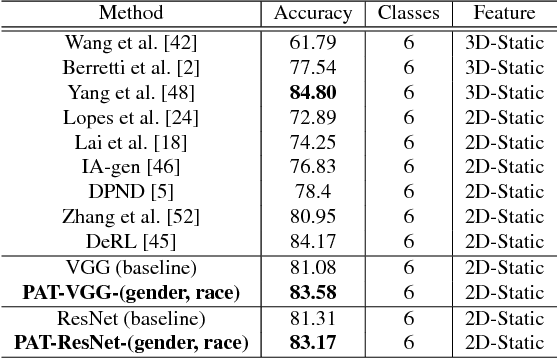
Abstract:In this paper, we proposed a novel Probabilistic Attribute Tree-CNN (PAT-CNN) to explicitly deal with the large intra-class variations caused by identity-related attributes, e.g., age, race, and gender. Specifically, a novel PAT module with an associated PAT loss was proposed to learn features in a hierarchical tree structure organized according to attributes, where the final features are less affected by the attributes. Then, expression-related features are extracted from leaf nodes. Samples are probabilistically assigned to tree nodes at different levels such that expression-related features can be learned from all samples weighted by probabilities. We further proposed a semi-supervised strategy to learn the PAT-CNN from limited attribute-annotated samples to make the best use of available data. Experimental results on five facial expression datasets have demonstrated that the proposed PAT-CNN outperforms the baseline models by explicitly modeling attributes. More impressively, the PAT-CNN using a single model achieves the best performance for faces in the wild on the SFEW dataset, compared with the state-of-the-art methods using an ensemble of hundreds of CNNs.
Optimizing Filter Size in Convolutional Neural Networks for Facial Action Unit Recognition
Nov 22, 2017



Abstract:Recognizing facial action units (AUs) during spontaneous facial displays is a challenging problem. Most recently, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown promise for facial AU recognition, where predefined and fixed convolution filter sizes are employed. In order to achieve the best performance, the optimal filter size is often empirically found by conducting extensive experimental validation. Such a training process suffers from expensive training cost, especially as the network becomes deeper. This paper proposes a novel Optimized Filter Size CNN (OFS-CNN), where the filter sizes and weights of all convolutional layers are learned simultaneously from the training data along with learning convolution filters. Specifically, the filter size is defined as a continuous variable, which is optimized by minimizing the training loss. Experimental results on two AU-coded spontaneous databases have shown that the proposed OFS-CNN is capable of estimating optimal filter size for varying image resolution and outperforms traditional CNNs with the best filter size obtained by exhaustive search. The OFS-CNN also beats the CNN using multiple filter sizes and more importantly, is much more efficient during testing with the proposed forward-backward propagation algorithm.
Island Loss for Learning Discriminative Features in Facial Expression Recognition
Oct 23, 2017



Abstract:Over the past few years, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown promise on facial expression recognition. However, the performance degrades dramatically under real-world settings due to variations introduced by subtle facial appearance changes, head pose variations, illumination changes, and occlusions. In this paper, a novel island loss is proposed to enhance the discriminative power of the deeply learned features. Specifically, the IL is designed to reduce the intra-class variations while enlarging the inter-class differences simultaneously. Experimental results on four benchmark expression databases have demonstrated that the CNN with the proposed island loss (IL-CNN) outperforms the baseline CNN models with either traditional softmax loss or the center loss and achieves comparable or better performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods for facial expression recognition.
Listen to Your Face: Inferring Facial Action Units from Audio Channel
Sep 19, 2017



Abstract:Extensive efforts have been devoted to recognizing facial action units (AUs). However, it is still challenging to recognize AUs from spontaneous facial displays especially when they are accompanied with speech. Different from all prior work that utilized visual observations for facial AU recognition, this paper presents a novel approach that recognizes speech-related AUs exclusively from audio signals based on the fact that facial activities are highly correlated with voice during speech. Specifically, dynamic and physiological relationships between AUs and phonemes are modeled through a continuous time Bayesian network (CTBN); then AU recognition is performed by probabilistic inference via the CTBN model. A pilot audiovisual AU-coded database has been constructed to evaluate the proposed audio-based AU recognition framework. The database consists of a "clean" subset with frontal and neutral faces and a challenging subset collected with large head movements and occlusions. Experimental results on this database show that the proposed CTBN model achieves promising recognition performance for 7 speech-related AUs and outperforms the state-of-the-art visual-based methods especially for those AUs that are activated at low intensities or "hardly visible" in the visual channel. Furthermore, the CTBN model yields more impressive recognition performance on the challenging subset, where the visual-based approaches suffer significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge