Jian Dai
FOR-Prompting: From Objection to Revision via an Asymmetric Prompting Protocol
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Reasoning protocols such as Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tree of Thought (ToT) organize internal deliberation but lack an explicit mechanism for external questioning that elicits self-revision. We present FOR-Prompting (From Objection to Revision Prompting), an asymmetric protocol where a Defender proposes an answer, an Objectioner raises question-style objections with no direct fixes, and a Host enforces consistency and closure. On GSM8K we observe about a 22% point gain over single-prompt and accuracy on par with CoT, with more than 10% higher ratings in reasoning and coherence from a uniform GPT 4.1 judge. FOR-Prompting also corrects mistakes without tools or human supervision on tricky queries, and improves performance for small-scale model (approx. 19% accuracy improved on Llama3.2:1b for GSM8K task), highlighting promise for small models and on personal device use. Beyond factual QA, qualitative analyses on open-ended tasks show enhanced exploration and refinement, with dialogue traces that make assumptions and trade-offs explicit. The protocol is model agnostic and operates purely at the prompt level through role-structured turns, so it works with hosted and local models of different sizes without retraining, and it supports large-scale study of objection-guided reasoning.
Efficient training for large-scale optical neural network using an evolutionary strategy and attention pruning
May 19, 2025Abstract:MZI-based block optical neural networks (BONNs), which can achieve large-scale network models, have increasingly drawn attentions. However, the robustness of the current training algorithm is not high enough. Moreover, large-scale BONNs usually contain numerous trainable parameters, resulting in expensive computation and power consumption. In this article, by pruning matrix blocks and directly optimizing the individuals in population, we propose an on-chip covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy and attention-based pruning (CAP) algorithm for large-scale BONNs. The calculated results demonstrate that the CAP algorithm can prune 60% and 80% of the parameters for MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets, respectively, while only degrades the performance by 3.289% and 4.693%. Considering the influence of dynamic noise in phase shifters, our proposed CAP algorithm (performance degradation of 22.327% for MNIST dataset and 24.019% for Fashion-MNIST dataset utilizing a poor fabricated chip and electrical control with a standard deviation of 0.5) exhibits strongest robustness compared with both our previously reported block adjoint training algorithm (43.963% and 41.074%) and the covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy (25.757% and 32.871%), respectively. Moreover, when 60% of the parameters are pruned, the CAP algorithm realizes 88.5% accuracy in experiment for the simplified MNIST dataset, which is similar to the simulation result without noise (92.1%). Additionally, we simulationally and experimentally demonstrate that using MZIs with only internal phase shifters to construct BONNs is an efficient way to reduce both the system area and the required trainable parameters. Notably, our proposed CAP algorithm show excellent potential for larger-scale network models and more complex tasks.
TPCH: Tensor-interacted Projection and Cooperative Hashing for Multi-view Clustering
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:In recent years, anchor and hash-based multi-view clustering methods have gained attention for their efficiency and simplicity in handling large-scale data. However, existing methods often overlook the interactions among multi-view data and higher-order cooperative relationships during projection, negatively impacting the quality of hash representation in low-dimensional spaces, clustering performance, and sensitivity to noise. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach named Tensor-Interacted Projection and Cooperative Hashing for Multi-View Clustering(TPCH). TPCH stacks multiple projection matrices into a tensor, taking into account the synergies and communications during the projection process. By capturing higher-order multi-view information through dual projection and Hamming space, TPCH employs an enhanced tensor nuclear norm to learn more compact and distinguishable hash representations, promoting communication within and between views. Experimental results demonstrate that this refined method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in clustering on five large-scale multi-view datasets. Moreover, in terms of CPU time, TPCH achieves substantial acceleration compared to the most advanced current methods. The code is available at \textcolor{red}{\url{https://github.com/jankin-wang/TPCH}}.
Dual-Channel Reliable Breast Ultrasound Image Classification Based on Explainable Attribution and Uncertainty Quantification
Jan 08, 2024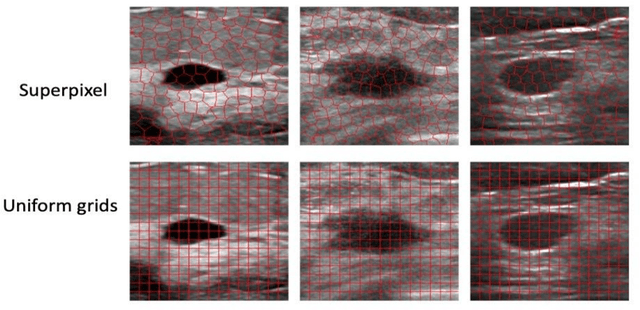
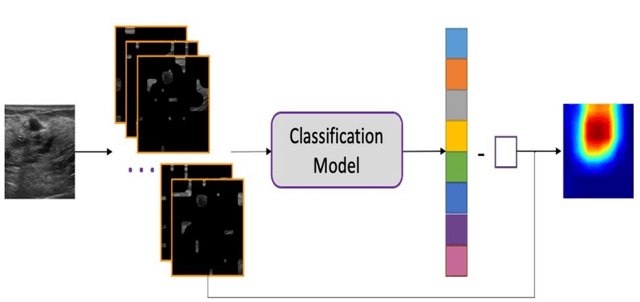

Abstract:This paper focuses on the classification task of breast ultrasound images and researches on the reliability measurement of classification results. We proposed a dual-channel evaluation framework based on the proposed inference reliability and predictive reliability scores. For the inference reliability evaluation, human-aligned and doctor-agreed inference rationales based on the improved feature attribution algorithm SP-RISA are gracefully applied. Uncertainty quantification is used to evaluate the predictive reliability via the Test Time Enhancement. The effectiveness of this reliability evaluation framework has been verified on our breast ultrasound clinical dataset YBUS, and its robustness is verified on the public dataset BUSI. The expected calibration errors on both datasets are significantly lower than traditional evaluation methods, which proves the effectiveness of our proposed reliability measurement.
Relational Learning with Gated and Attentive Neighbor Aggregator for Few-Shot Knowledge Graph Completion
Apr 27, 2021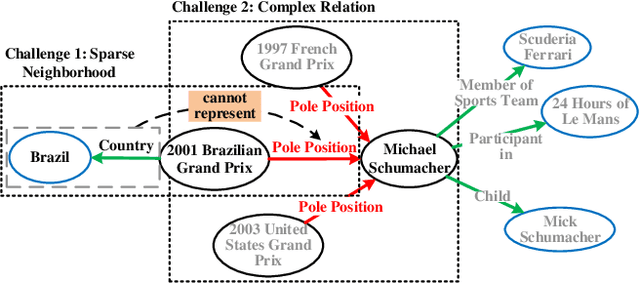
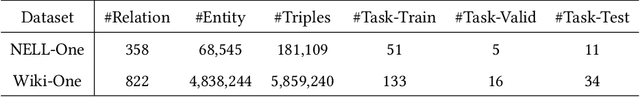
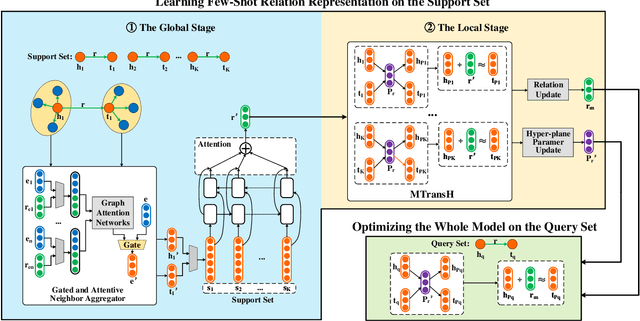
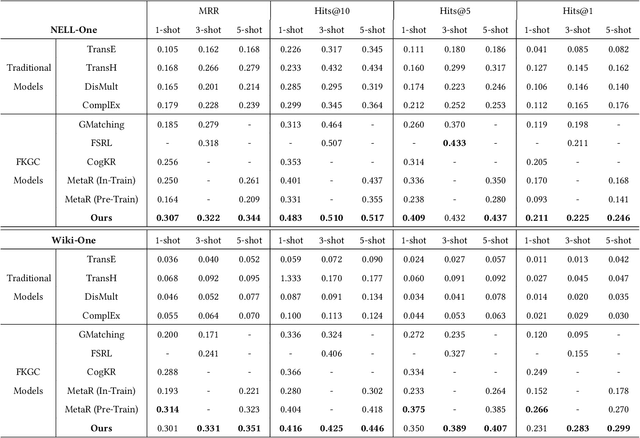
Abstract:Aiming at expanding few-shot relations' coverage in knowledge graphs (KGs), few-shot knowledge graph completion (FKGC) has recently gained more research interests. Some existing models employ a few-shot relation's multi-hop neighbor information to enhance its semantic representation. However, noise neighbor information might be amplified when the neighborhood is excessively sparse and no neighbor is available to represent the few-shot relation. Moreover, modeling and inferring complex relations of one-to-many (1-N), many-to-one (N-1), and many-to-many (N-N) by previous knowledge graph completion approaches requires high model complexity and a large amount of training instances. Thus, inferring complex relations in the few-shot scenario is difficult for FKGC models due to limited training instances. In this paper, we propose a few-shot relational learning with global-local framework to address the above issues. At the global stage, a novel gated and attentive neighbor aggregator is built for accurately integrating the semantics of a few-shot relation's neighborhood, which helps filtering the noise neighbors even if a KG contains extremely sparse neighborhoods. For the local stage, a meta-learning based TransH (MTransH) method is designed to model complex relations and train our model in a few-shot learning fashion. Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art FKGC approaches on the frequently-used benchmark datasets NELL-One and Wiki-One. Compared with the strong baseline model MetaR, our model achieves 5-shot FKGC performance improvements of 8.0% on NELL-One and 2.8% on Wiki-One by the metric Hits@10.
Knowledge AI: New Medical AI Solution for Medical image Diagnosis
Jan 08, 2021

Abstract:The implementation of medical AI has always been a problem. The effect of traditional perceptual AI algorithm in medical image processing needs to be improved. Here we propose a method of knowledge AI, which is a combination of perceptual AI and clinical knowledge and experience. Based on this method, the geometric information mining of medical images can represent the experience and information and evaluate the quality of medical images.
More Reliable AI Solution: Breast Ultrasound Diagnosis Using Multi-AI Combination
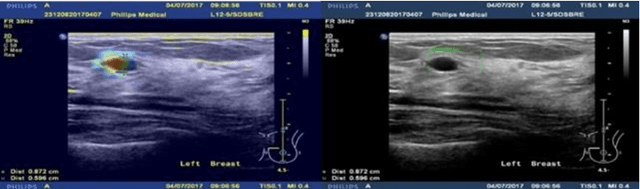
Jan 07, 2021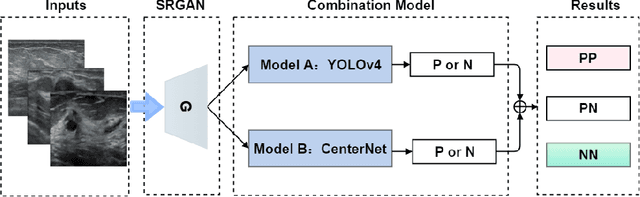
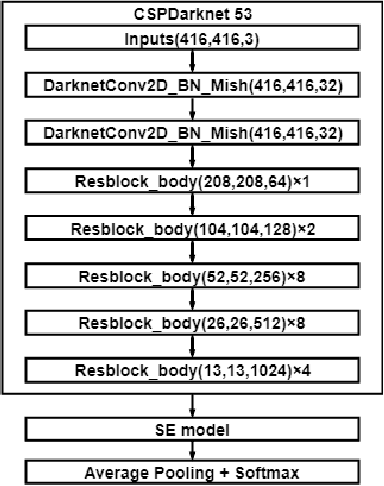
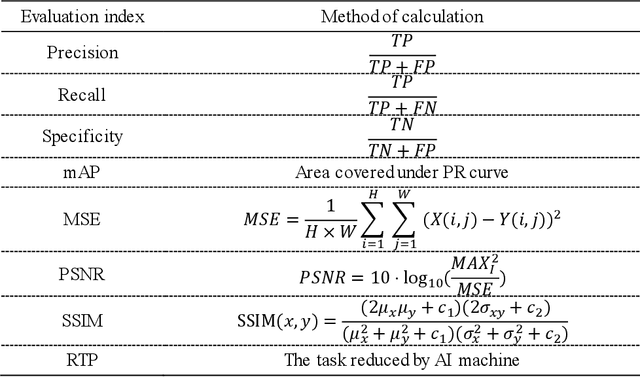
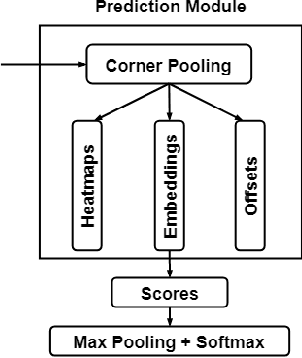
Abstract:Objective: Breast cancer screening is of great significance in contemporary women's health prevention. The existing machines embedded in the AI system do not reach the accuracy that clinicians hope. How to make intelligent systems more reliable is a common problem. Methods: 1) Ultrasound image super-resolution: the SRGAN super-resolution network reduces the unclearness of ultrasound images caused by the device itself and improves the accuracy and generalization of the detection model. 2) In response to the needs of medical images, we have improved the YOLOv4 and the CenterNet models. 3) Multi-AI model: based on the respective advantages of different AI models, we employ two AI models to determine clinical resuls cross validation. And we accept the same results and refuses others. Results: 1) With the help of the super-resolution model, the YOLOv4 model and the CenterNet model both increased the mAP score by 9.6% and 13.8%. 2) Two methods for transforming the target model into a classification model are proposed. And the unified output is in a specified format to facilitate the call of the molti-AI model. 3) In the classification evaluation experiment, concatenated by the YOLOv4 model (sensitivity 57.73%, specificity 90.08%) and the CenterNet model (sensitivity 62.64%, specificity 92.54%), the multi-AI model will refuse to make judgments on 23.55% of the input data. Correspondingly, the performance has been greatly improved to 95.91% for the sensitivity and 96.02% for the specificity. Conclusion: Our work makes the AI model more reliable in medical image diagnosis. Significance: 1) The proposed method makes the target detection model more suitable for diagnosing breast ultrasound images. 2) It provides a new idea for artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis, which can more conveniently introduce target detection models from other fields to serve medical lesion screening.
Knowledge Association with Hyperbolic Knowledge Graph Embeddings
Oct 05, 2020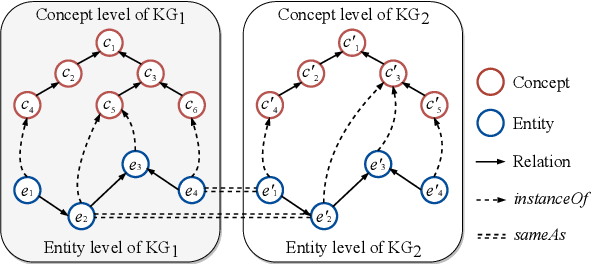
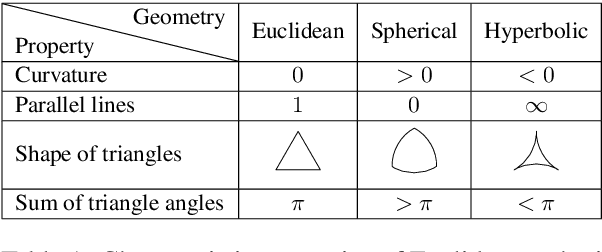
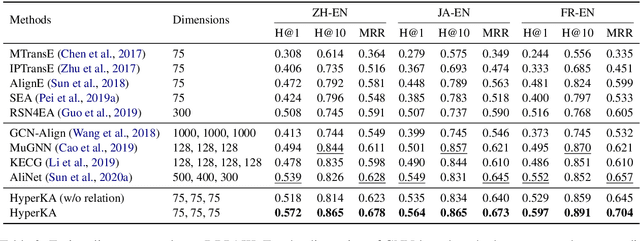
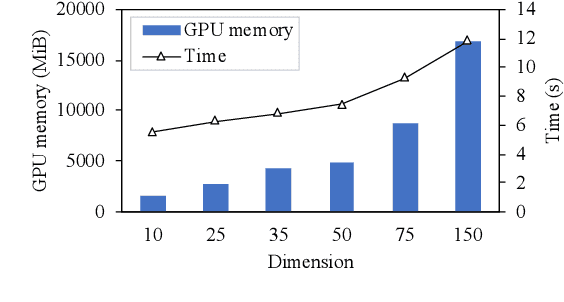
Abstract:Capturing associations for knowledge graphs (KGs) through entity alignment, entity type inference and other related tasks benefits NLP applications with comprehensive knowledge representations. Recent related methods built on Euclidean embeddings are challenged by the hierarchical structures and different scales of KGs. They also depend on high embedding dimensions to realize enough expressiveness. Differently, we explore with low-dimensional hyperbolic embeddings for knowledge association. We propose a hyperbolic relational graph neural network for KG embedding and capture knowledge associations with a hyperbolic transformation. Extensive experiments on entity alignment and type inference demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method.
Knowledge Graph Alignment Network with Gated Multi-hop Neighborhood Aggregation
Nov 20, 2019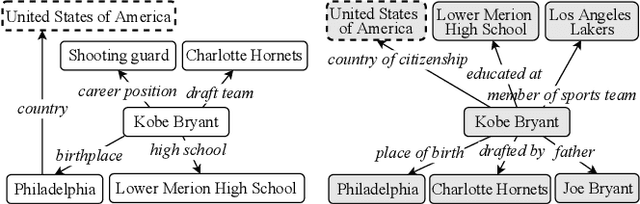
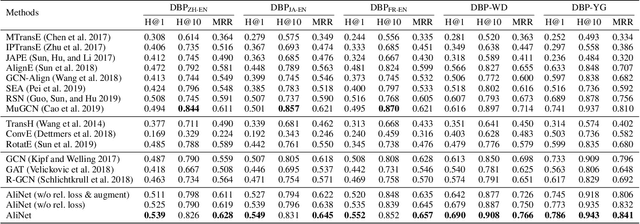
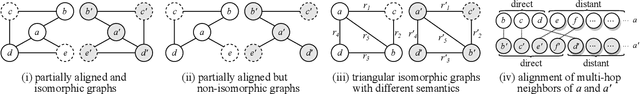
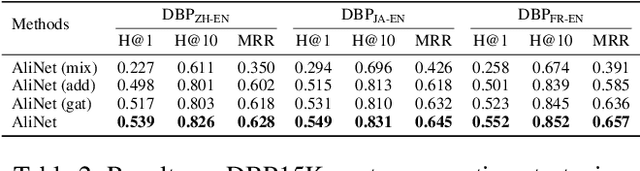
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for embedding-based entity alignment due to their capability of identifying isomorphic subgraphs. However, in real knowledge graphs (KGs), the counterpart entities usually have non-isomorphic neighborhood structures, which easily causes GNNs to yield different representations for them. To tackle this problem, we propose a new KG alignment network, namely AliNet, aiming at mitigating the non-isomorphism of neighborhood structures in an end-to-end manner. As the direct neighbors of counterpart entities are usually dissimilar due to the schema heterogeneity, AliNet introduces distant neighbors to expand the overlap between their neighborhood structures. It employs an attention mechanism to highlight helpful distant neighbors and reduce noises. Then, it controls the aggregation of both direct and distant neighborhood information using a gating mechanism. We further propose a relation loss to refine entity representations. We perform thorough experiments with detailed ablation studies and analyses on five entity alignment datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of AliNet.
Efficient training and design of photonic neural network through neuroevolution
Aug 04, 2019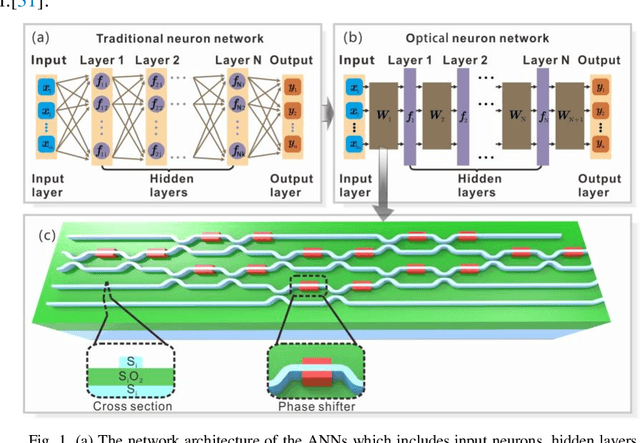
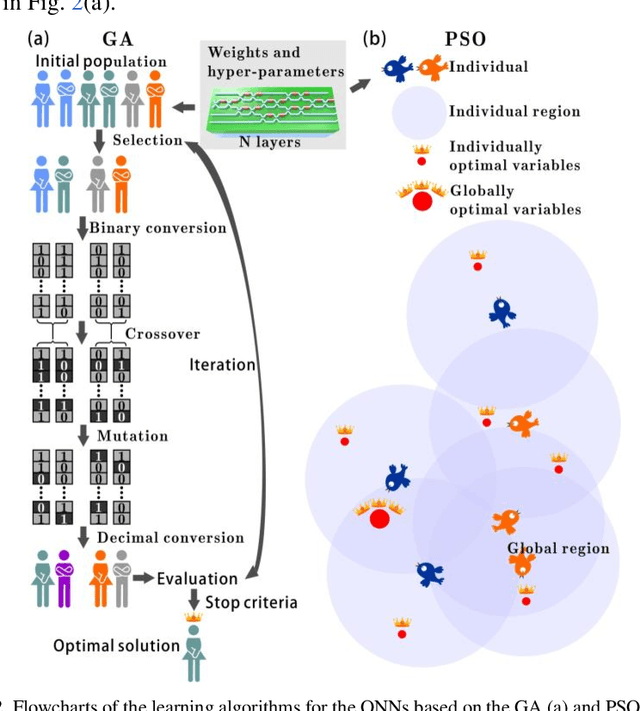
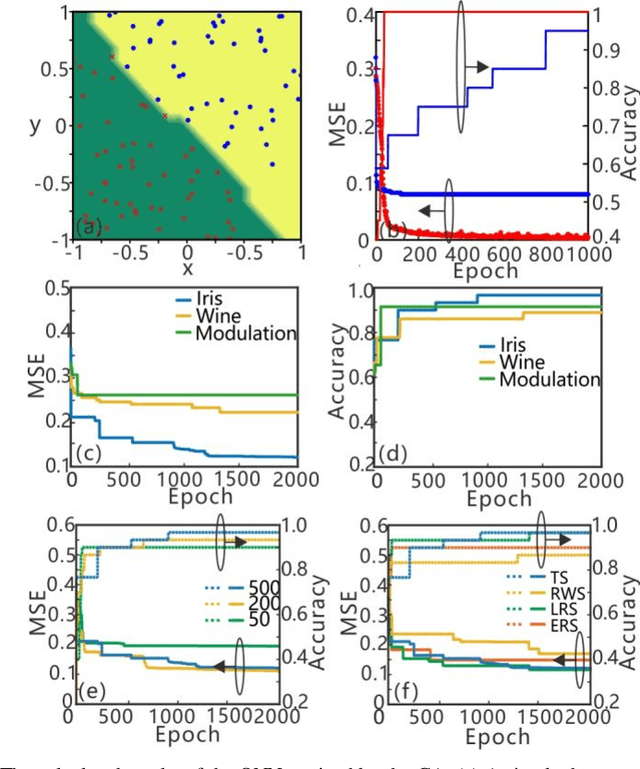
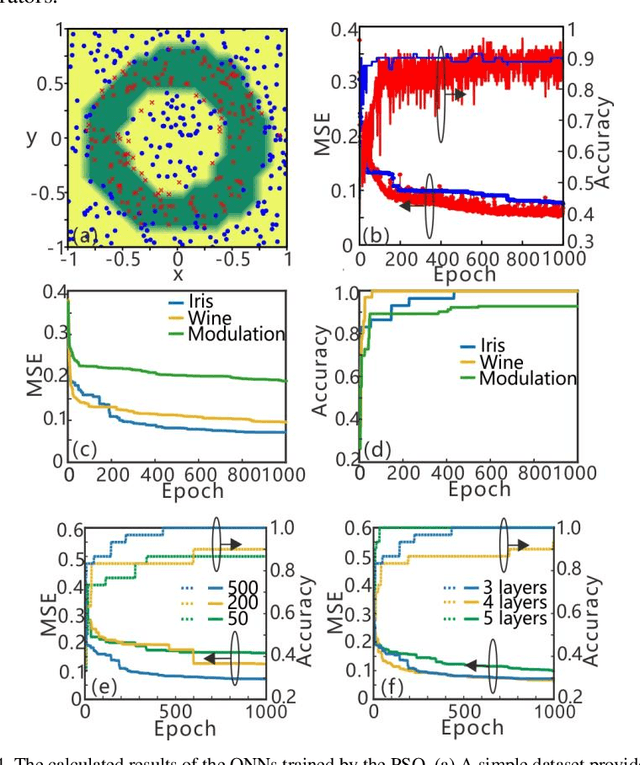
Abstract:Recently, optical neural networks (ONNs) integrated in photonic chips has received extensive attention because they are expected to implement the same pattern recognition tasks in the electronic platforms with high efficiency and low power consumption. However, the current lack of various learning algorithms to train the ONNs obstructs their further development. In this article, we propose a novel learning strategy based on neuroevolution to design and train the ONNs. Two typical neuroevolution algorithms are used to determine the hyper-parameters of the ONNs and to optimize the weights (phase shifters) in the connections. In order to demonstrate the effectiveness of the training algorithms, the trained ONNs are applied in the classification tasks for iris plants dataset, wine recognition dataset and modulation formats recognition. The calculated results exhibit that the training algorithms based on neuroevolution are competitive with other traditional learning algorithms on both accuracy and stability. Compared with previous works, we introduce an efficient training method for the ONNs and demonstrate their broad application prospects in pattern recognition, reinforcement learning and so on.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge