Peter Zhang
Domain Gating Ensemble Networks for AI-Generated Text Detection
May 20, 2025Abstract:As state-of-the-art language models continue to improve, the need for robust detection of machine-generated text becomes increasingly critical. However, current state-of-the-art machine text detectors struggle to adapt to new unseen domains and generative models. In this paper we present DoGEN (Domain Gating Ensemble Networks), a technique that allows detectors to adapt to unseen domains by ensembling a set of domain expert detector models using weights from a domain classifier. We test DoGEN on a wide variety of domains from leading benchmarks and find that it achieves state-of-the-art performance on in-domain detection while outperforming models twice its size on out-of-domain detection. We release our code and trained models to assist in future research in domain-adaptive AI detection.
Visual and textual prompts for enhancing emotion recognition in video
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs) exhibit promising potential for multi-modal understanding, yet their application to video-based emotion recognition remains limited by insufficient spatial and contextual awareness. Traditional approaches, which prioritize isolated facial features, often neglect critical non-verbal cues such as body language, environmental context, and social interactions, leading to reduced robustness in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we propose Set-of-Vision-Text Prompting (SoVTP), a novel framework that enhances zero-shot emotion recognition by integrating spatial annotations (e.g., bounding boxes, facial landmarks), physiological signals (facial action units), and contextual cues (body posture, scene dynamics, others' emotions) into a unified prompting strategy. SoVTP preserves holistic scene information while enabling fine-grained analysis of facial muscle movements and interpersonal dynamics. Extensive experiments show that SoVTP achieves substantial improvements over existing visual prompting methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing VLLMs' video emotion recognition capabilities.
Optimal probabilistic feature shifts for reclassification in tree ensembles
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:In this paper we provide a novel mathematical optimization based methodology to perturb the features of a given observation to be re-classified, by a tree ensemble classification rule, to a certain desired class. The method is based on these facts: the most viable changes for an observation to reach the desired class do not always coincide with the closest distance point (in the feature space) of the target class; individuals put effort on a few number of features to reach the desired class; and each individual is endowed with a probability to change each of its features to a given value, which determines the overall probability of changing to the target class. Putting all together, we provide different methods to find the features where the individuals must exert effort to maximize the probability to reach the target class. Our method also allows us to rank the most important features in the tree-ensemble. The proposed methodology is tested on a real dataset, validating the proposal.
OpenDebateEvidence: A Massive-Scale Argument Mining and Summarization Dataset
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:We introduce OpenDebateEvidence, a comprehensive dataset for argument mining and summarization sourced from the American Competitive Debate community. This dataset includes over 3.5 million documents with rich metadata, making it one of the most extensive collections of debate evidence. OpenDebateEvidence captures the complexity of arguments in high school and college debates, providing valuable resources for training and evaluation. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models for argumentative abstractive summarization across various methods, models, and datasets. By providing this comprehensive resource, we aim to advance computational argumentation and support practical applications for debaters, educators, and researchers. OpenDebateEvidence is publicly available to support further research and innovation in computational argumentation. Access it here: https://huggingface.co/datasets/Yusuf5/OpenCaselist
Binary Noise for Binary Tasks: Masked Bernoulli Diffusion for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Mar 18, 2024

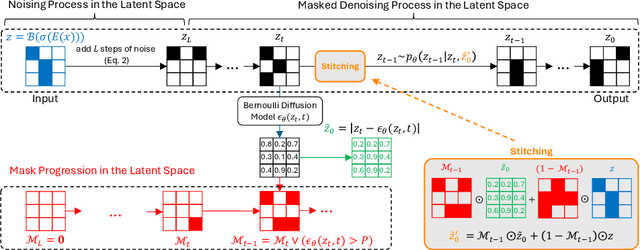

Abstract:The high performance of denoising diffusion models for image generation has paved the way for their application in unsupervised medical anomaly detection. As diffusion-based methods require a lot of GPU memory and have long sampling times, we present a novel and fast unsupervised anomaly detection approach based on latent Bernoulli diffusion models. We first apply an autoencoder to compress the input images into a binary latent representation. Next, a diffusion model that follows a Bernoulli noise schedule is employed to this latent space and trained to restore binary latent representations from perturbed ones. The binary nature of this diffusion model allows us to identify entries in the latent space that have a high probability of flipping their binary code during the denoising process, which indicates out-of-distribution data. We propose a masking algorithm based on these probabilities, which improves the anomaly detection scores. We achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to other diffusion-based unsupervised anomaly detection algorithms while significantly reducing sampling time and memory consumption. The code is available at https://github.com/JuliaWolleb/Anomaly_berdiff.
Goal Driven Discovery of Distributional Differences via Language Descriptions
Feb 28, 2023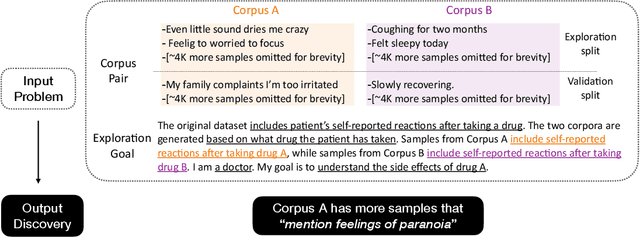
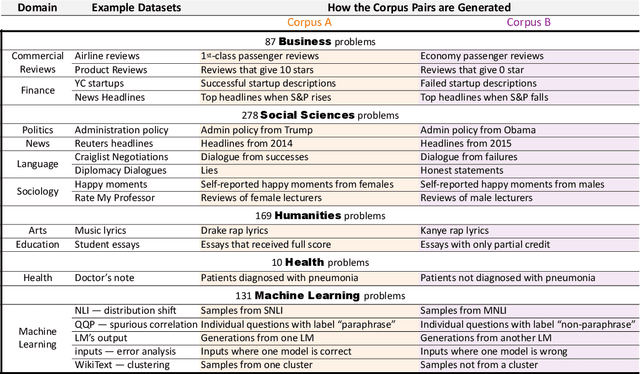


Abstract:Mining large corpora can generate useful discoveries but is time-consuming for humans. We formulate a new task, D5, that automatically discovers differences between two large corpora in a goal-driven way. The task input is a problem comprising a research goal "$\textit{comparing the side effects of drug A and drug B}$" and a corpus pair (two large collections of patients' self-reported reactions after taking each drug). The output is a language description (discovery) of how these corpora differ (patients taking drug A "$\textit{mention feelings of paranoia}$" more often). We build a D5 system, and to quantitatively measure its performance, we 1) contribute a meta-dataset, OpenD5, aggregating 675 open-ended problems ranging across business, social sciences, humanities, machine learning, and health, and 2) propose a set of unified evaluation metrics: validity, relevance, novelty, and significance. With the dataset and the unified metrics, we confirm that language models can use the goals to propose more relevant, novel, and significant candidate discoveries. Finally, our system produces discoveries previously unknown to the authors on a wide range of applications in OpenD5, including temporal and demographic differences in discussion topics, political stances and stereotypes in speech, insights in commercial reviews, and error patterns in NLP models.
A Mathematical Programming Approach to Optimal Classification Forests
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:In this paper we propose a novel mathematical optimization based methodology to construct classification forests. A given number of trees are simultaneously constructed, each of them providing a predicted class for each of the observations in the training dataset. An observation is then classified to its most frequently predicted class. We give a mixed integer linear programming formulation for the problem. We report the results of our computational experiments. Our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art tree-based classification methods on several standard datasets.
Model Mis-specification and Algorithmic Bias
May 31, 2021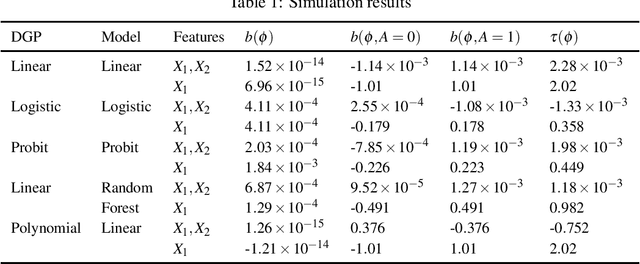
Abstract:Machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to inform critical decisions. There is a growing concern about bias, that algorithms may produce uneven outcomes for individuals in different demographic groups. In this work, we measure bias as the difference between mean prediction errors across groups. We show that even with unbiased input data, when a model is mis-specified: (1) population-level mean prediction error can still be negligible, but group-level mean prediction errors can be large; (2) such errors are not equal across groups; and (3) the difference between errors, i.e., bias, can take the worst-case realization. That is, when there are two groups of the same size, mean prediction errors for these two groups have the same magnitude but opposite signs. In closed form, we show such errors and bias are functions of the first and second moments of the joint distribution of features (for linear and probit regressions). We also conduct numerical experiments to show similar results in more general settings. Our work provides a first step for decoupling the impact of different causes of bias.
DEFT: Detection Embeddings for Tracking
Feb 03, 2021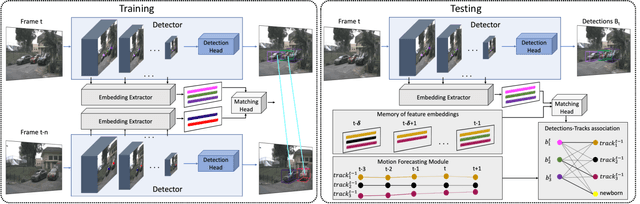
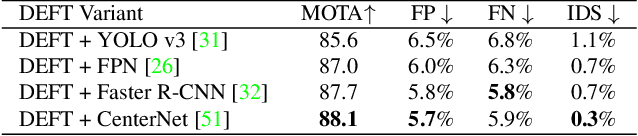
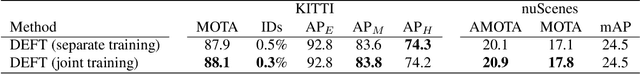
Abstract:Most modern multiple object tracking (MOT) systems follow the tracking-by-detection paradigm, consisting of a detector followed by a method for associating detections into tracks. There is a long history in tracking of combining motion and appearance features to provide robustness to occlusions and other challenges, but typically this comes with the trade-off of a more complex and slower implementation. Recent successes on popular 2D tracking benchmarks indicate that top-scores can be achieved using a state-of-the-art detector and relatively simple associations relying on single-frame spatial offsets -- notably outperforming contemporary methods that leverage learned appearance features to help re-identify lost tracks. In this paper, we propose an efficient joint detection and tracking model named DEFT, or "Detection Embeddings for Tracking." Our approach relies on an appearance-based object matching network jointly-learned with an underlying object detection network. An LSTM is also added to capture motion constraints. DEFT has comparable accuracy and speed to the top methods on 2D online tracking leaderboards while having significant advantages in robustness when applied to more challenging tracking data. DEFT raises the bar on the nuScenes monocular 3D tracking challenge, more than doubling the performance of the previous top method. Code is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge