Subrahmanyam Murala
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Image Super-Resolution ($\times$4): Methods and Results
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the NTIRE 2025 image super-resolution ($\times$4) challenge, one of the associated competitions of the 10th NTIRE Workshop at CVPR 2025. The challenge aims to recover high-resolution (HR) images from low-resolution (LR) counterparts generated through bicubic downsampling with a $\times$4 scaling factor. The objective is to develop effective network designs or solutions that achieve state-of-the-art SR performance. To reflect the dual objectives of image SR research, the challenge includes two sub-tracks: (1) a restoration track, emphasizes pixel-wise accuracy and ranks submissions based on PSNR; (2) a perceptual track, focuses on visual realism and ranks results by a perceptual score. A total of 286 participants registered for the competition, with 25 teams submitting valid entries. This report summarizes the challenge design, datasets, evaluation protocol, the main results, and methods of each team. The challenge serves as a benchmark to advance the state of the art and foster progress in image SR.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2025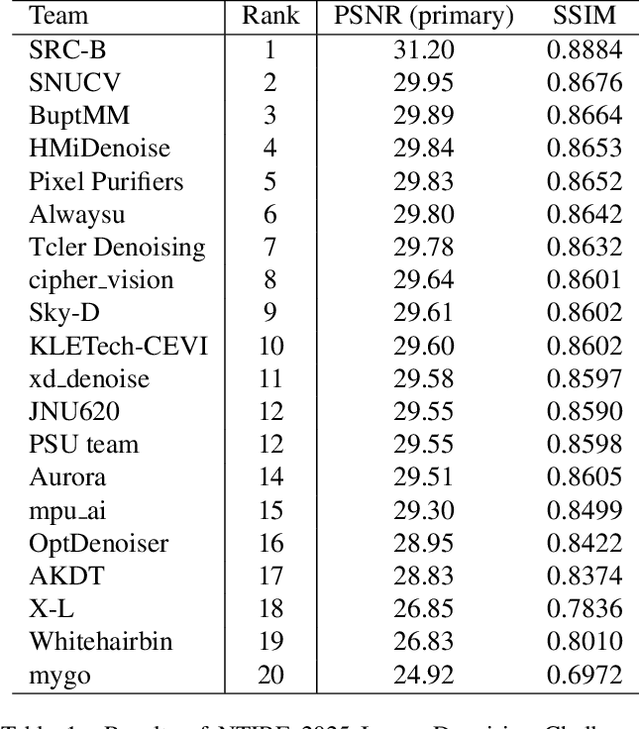

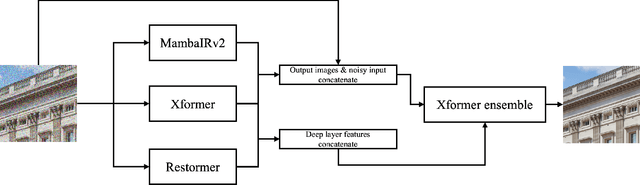

Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge ({\sigma} = 50), highlighting the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary objective is to develop a network architecture capable of achieving high-quality denoising performance, quantitatively evaluated using PSNR, without constraints on computational complexity or model size. The task assumes independent additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) with a fixed noise level of 50. A total of 290 participants registered for the challenge, with 20 teams successfully submitting valid results, providing insights into the current state-of-the-art in image denoising.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
Phaseformer: Phase-based Attention Mechanism for Underwater Image Restoration and Beyond
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Quality degradation is observed in underwater images due to the effects of light refraction and absorption by water, leading to issues like color cast, haziness, and limited visibility. This degradation negatively affects the performance of autonomous underwater vehicles used in marine applications. To address these challenges, we propose a lightweight phase-based transformer network with 1.77M parameters for underwater image restoration (UIR). Our approach focuses on effectively extracting non-contaminated features using a phase-based self-attention mechanism. We also introduce an optimized phase attention block to restore structural information by propagating prominent attentive features from the input. We evaluate our method on both synthetic (UIEB, UFO-120) and real-world (UIEB, U45, UCCS, SQUID) underwater image datasets. Additionally, we demonstrate its effectiveness for low-light image enhancement using the LOL dataset. Through extensive ablation studies and comparative analysis, it is clear that the proposed approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
MIPI 2024 Challenge on Nighttime Flare Removal: Methods and Results
Apr 30, 2024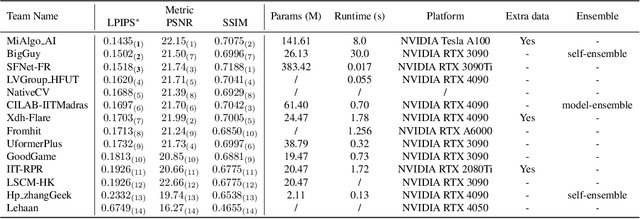
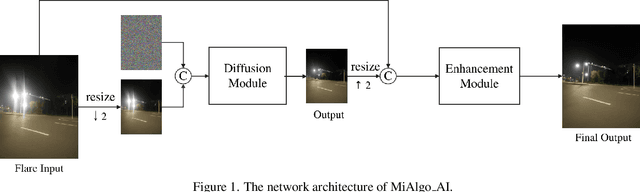
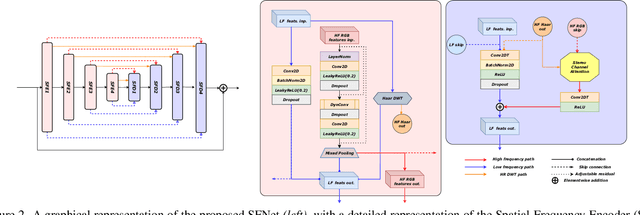
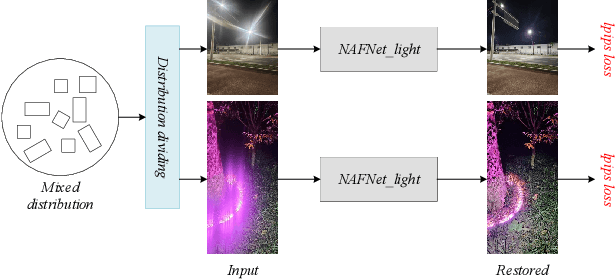
Abstract:The increasing demand for computational photography and imaging on mobile platforms has led to the widespread development and integration of advanced image sensors with novel algorithms in camera systems. However, the scarcity of high-quality data for research and the rare opportunity for in-depth exchange of views from industry and academia constrain the development of mobile intelligent photography and imaging (MIPI). Building on the achievements of the previous MIPI Workshops held at ECCV 2022 and CVPR 2023, we introduce our third MIPI challenge including three tracks focusing on novel image sensors and imaging algorithms. In this paper, we summarize and review the Nighttime Flare Removal track on MIPI 2024. In total, 170 participants were successfully registered, and 14 teams submitted results in the final testing phase. The developed solutions in this challenge achieved state-of-the-art performance on Nighttime Flare Removal. More details of this challenge and the link to the dataset can be found at https://mipi-challenge.org/MIPI2024/.
Gated Multi-Resolution Transfer Network for Burst Restoration and Enhancement
Apr 13, 2023Abstract:Burst image processing is becoming increasingly popular in recent years. However, it is a challenging task since individual burst images undergo multiple degradations and often have mutual misalignments resulting in ghosting and zipper artifacts. Existing burst restoration methods usually do not consider the mutual correlation and non-local contextual information among burst frames, which tends to limit these approaches in challenging cases. Another key challenge lies in the robust up-sampling of burst frames. The existing up-sampling methods cannot effectively utilize the advantages of single-stage and progressive up-sampling strategies with conventional and/or recent up-samplers at the same time. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Gated Multi-Resolution Transfer Network (GMTNet) to reconstruct a spatially precise high-quality image from a burst of low-quality raw images. GMTNet consists of three modules optimized for burst processing tasks: Multi-scale Burst Feature Alignment (MBFA) for feature denoising and alignment, Transposed-Attention Feature Merging (TAFM) for multi-frame feature aggregation, and Resolution Transfer Feature Up-sampler (RTFU) to up-scale merged features and construct a high-quality output image. Detailed experimental analysis on five datasets validates our approach and sets a state-of-the-art for burst super-resolution, burst denoising, and low-light burst enhancement.
Hyperrealistic Image Inpainting with Hypergraphs
Nov 05, 2020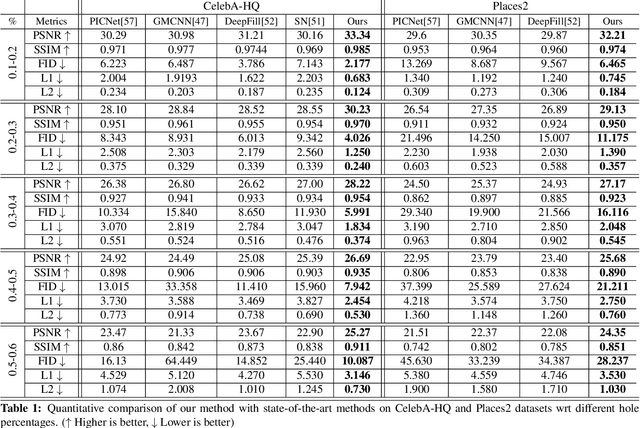

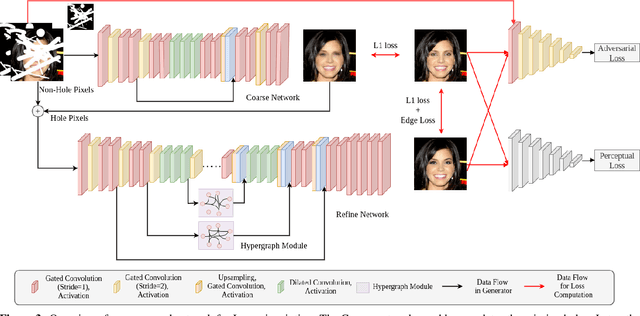

Abstract:Image inpainting is a non-trivial task in computer vision due to multiple possibilities for filling the missing data, which may be dependent on the global information of the image. Most of the existing approaches use the attention mechanism to learn the global context of the image. This attention mechanism produces semantically plausible but blurry results because of incapability to capture the global context. In this paper, we introduce hypergraph convolution on spatial features to learn the complex relationship among the data. We introduce a trainable mechanism to connect nodes using hyperedges for hypergraph convolution. To the best of our knowledge, hypergraph convolution have never been used on spatial features for any image-to-image tasks in computer vision. Further, we introduce gated convolution in the discriminator to enforce local consistency in the predicted image. The experiments on Places2, CelebA-HQ, Paris Street View, and Facades datasets, show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results.
LEARNet Dynamic Imaging Network for Micro Expression Recognition
Apr 20, 2019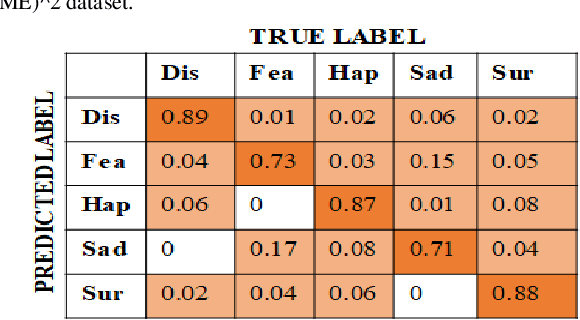
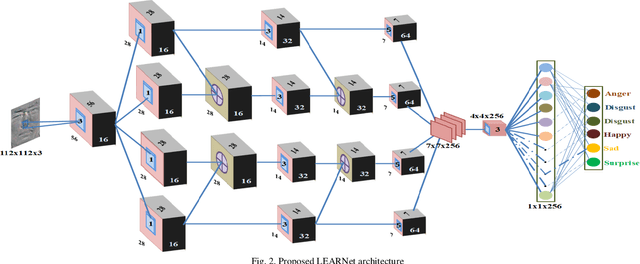
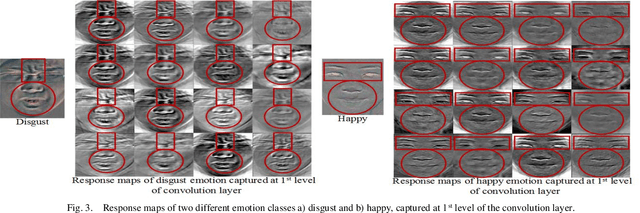
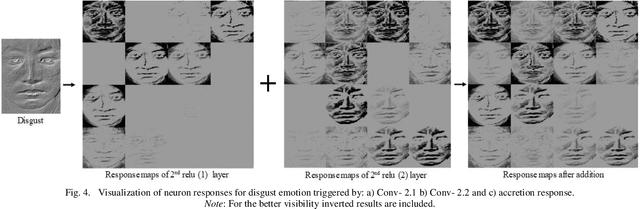
Abstract:Unlike prevalent facial expressions, micro expressions have subtle, involuntary muscle movements which are short-lived in nature. These minute muscle movements reflect true emotions of a person. Due to the short duration and low intensity, these micro-expressions are very difficult to perceive and interpret correctly. In this paper, we propose the dynamic representation of micro-expressions to preserve facial movement information of a video in a single frame. We also propose a Lateral Accretive Hybrid Network (LEARNet) to capture micro-level features of an expression in the facial region. The LEARNet refines the salient expression features in accretive manner by incorporating accretion layers (AL) in the network. The response of the AL holds the hybrid feature maps generated by prior laterally connected convolution layers. Moreover, LEARNet architecture incorporates the cross decoupled relationship between convolution layers which helps in preserving the tiny but influential facial muscle change information. The visual responses of the proposed LEARNet depict the effectiveness of the system by preserving both high- and micro-level edge features of facial expression. The effectiveness of the proposed LEARNet is evaluated on four benchmark datasets: CASME-I, CASME-II, CAS(ME)^2 and SMIC. The experimental results after investigation show a significant improvement of 4.03%, 1.90%, 1.79% and 2.82% as compared with ResNet on CASME-I, CASME-II, CAS(ME)^2 and SMIC datasets respectively.
Local Neighborhood Intensity Pattern: A new texture feature descriptor for image retrieval
Jul 02, 2018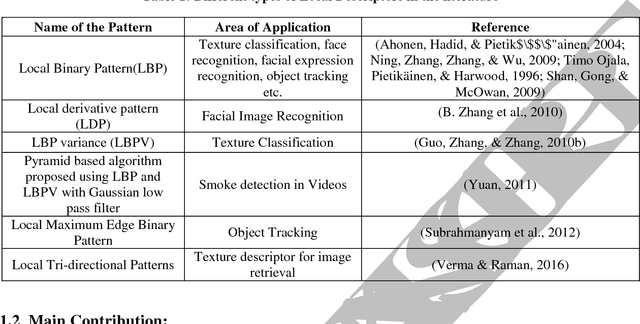
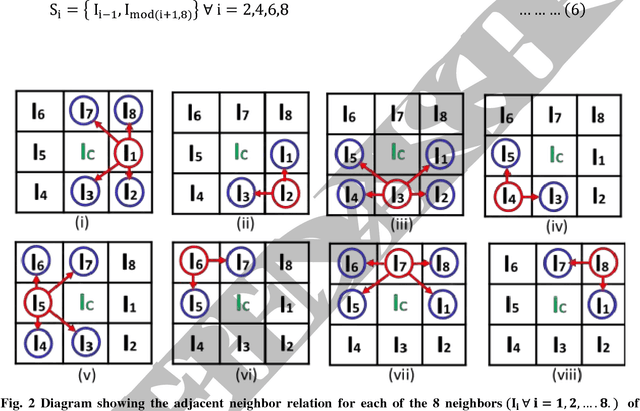
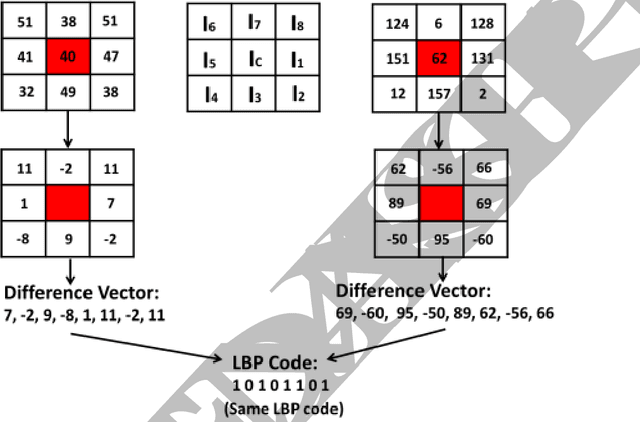
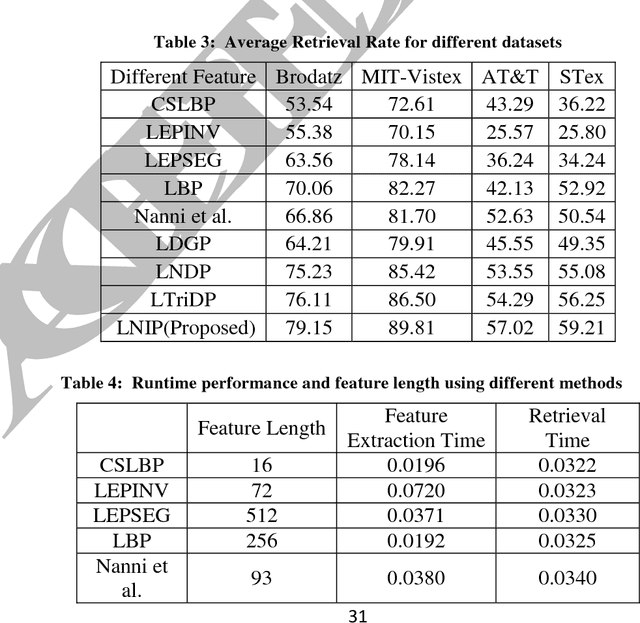
Abstract:In this paper, a new texture descriptor based on the local neighborhood intensity difference is proposed for content based image retrieval (CBIR). For computation of texture features like Local Binary Pattern (LBP), the center pixel in a 3*3 window of an image is compared with all the remaining neighbors, one pixel at a time to generate a binary bit pattern. It ignores the effect of the adjacent neighbors of a particular pixel for its binary encoding and also for texture description. The proposed method is based on the concept that neighbors of a particular pixel hold a significant amount of texture information that can be considered for efficient texture representation for CBIR. Taking this into account, we develop a new texture descriptor, named as Local Neighborhood Intensity Pattern (LNIP) which considers the relative intensity difference between a particular pixel and the center pixel by considering its adjacent neighbors and generate a sign and a magnitude pattern. Since sign and magnitude patterns hold complementary information to each other, these two patterns are concatenated into a single feature descriptor to generate a more concrete and useful feature descriptor. The proposed descriptor has been tested for image retrieval on four databases, including three texture image databases - Brodatz texture image database, MIT VisTex database and Salzburg texture database and one face database AT&T face database. The precision and recall values observed on these databases are compared with some state-of-art local patterns. The proposed method showed a significant improvement over many other existing methods.
Multichannel Distributed Local Pattern for Content Based Indexing and Retrieval
May 07, 2018



Abstract:A novel color feature descriptor, Multichannel Distributed Local Pattern (MDLP) is proposed in this manuscript. The MDLP combines the salient features of both local binary and local mesh patterns in the neighborhood. The multi-distance information computed by the MDLP aids in robust extraction of the texture arrangement. Further, MDLP features are extracted for each color channel of an image. The retrieval performance of the MDLP is evaluated on the three benchmark datasets for CBIR, namely Corel-5000, Corel-10000 and MIT-Color Vistex respectively. The proposed technique attains substantial improvement as compared to other state-of- the-art feature descriptors in terms of various evaluation parameters such as ARP and ARR on the respective databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge