Stephen Ra
TwinWeaver: An LLM-Based Foundation Model Framework for Pan-Cancer Digital Twins
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Precision oncology requires forecasting clinical events and trajectories, yet modeling sparse, multi-modal clinical time series remains a critical challenge. We introduce TwinWeaver, an open-source framework that serializes longitudinal patient histories into text, enabling unified event prediction as well as forecasting with large language models, and use it to build Genie Digital Twin (GDT) on 93,054 patients across 20 cancer types. In benchmarks, GDT significantly reduces forecasting error, achieving a median Mean Absolute Scaled Error (MASE) of 0.87 compared to 0.97 for the strongest time-series baseline (p<0.001). Furthermore, GDT improves risk stratification, achieving an average concordance index (C-index) of 0.703 across survival, progression, and therapy switching tasks, surpassing the best baseline of 0.662. GDT also generalizes to out-of-distribution clinical trials, matching trained baselines at zero-shot and surpassing them with fine-tuning, achieving a median MASE of 0.75-0.88 and outperforming the strongest baseline in event prediction with an average C-index of 0.672 versus 0.648. Finally, TwinWeaver enables an interpretable clinical reasoning extension, providing a scalable and transparent foundation for longitudinal clinical modeling.
Supervised Contrastive Block Disentanglement
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Real-world datasets often combine data collected under different experimental conditions. This yields larger datasets, but also introduces spurious correlations that make it difficult to model the phenomena of interest. We address this by learning two embeddings to independently represent the phenomena of interest and the spurious correlations. The embedding representing the phenomena of interest is correlated with the target variable $y$, and is invariant to the environment variable $e$. In contrast, the embedding representing the spurious correlations is correlated with $e$. The invariance to $e$ is difficult to achieve on real-world datasets. Our primary contribution is an algorithm called Supervised Contrastive Block Disentanglement (SCBD) that effectively enforces this invariance. It is based purely on Supervised Contrastive Learning, and applies to real-world data better than existing approaches. We empirically validate SCBD on two challenging problems. The first problem is domain generalization, where we achieve strong performance on a synthetic dataset, as well as on Camelyon17-WILDS. We introduce a single hyperparameter $\alpha$ to control the degree of invariance to $e$. When we increase $\alpha$ to strengthen the degree of invariance, out-of-distribution performance improves at the expense of in-distribution performance. The second problem is batch correction, in which we apply SCBD to preserve biological signal and remove inter-well batch effects when modeling single-cell perturbations from 26 million Optical Pooled Screening images.
Blind Biological Sequence Denoising with Self-Supervised Set Learning
Sep 04, 2023Abstract:Biological sequence analysis relies on the ability to denoise the imprecise output of sequencing platforms. We consider a common setting where a short sequence is read out repeatedly using a high-throughput long-read platform to generate multiple subreads, or noisy observations of the same sequence. Denoising these subreads with alignment-based approaches often fails when too few subreads are available or error rates are too high. In this paper, we propose a novel method for blindly denoising sets of sequences without directly observing clean source sequence labels. Our method, Self-Supervised Set Learning (SSSL), gathers subreads together in an embedding space and estimates a single set embedding as the midpoint of the subreads in both the latent and sequence spaces. This set embedding represents the "average" of the subreads and can be decoded into a prediction of the clean sequence. In experiments on simulated long-read DNA data, SSSL methods denoise small reads of $\leq 6$ subreads with 17% fewer errors and large reads of $>6$ subreads with 8% fewer errors compared to the best baseline. On a real dataset of antibody sequences, SSSL improves over baselines on two self-supervised metrics, with a significant improvement on difficult small reads that comprise over 60% of the test set. By accurately denoising these reads, SSSL promises to better realize the potential of high-throughput DNA sequencing data for downstream scientific applications.
OpenProteinSet: Training data for structural biology at scale
Aug 10, 2023


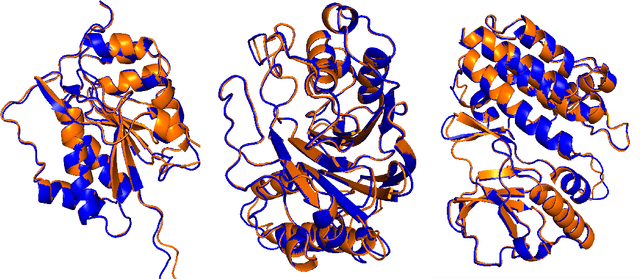
Abstract:Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) of proteins encode rich biological information and have been workhorses in bioinformatic methods for tasks like protein design and protein structure prediction for decades. Recent breakthroughs like AlphaFold2 that use transformers to attend directly over large quantities of raw MSAs have reaffirmed their importance. Generation of MSAs is highly computationally intensive, however, and no datasets comparable to those used to train AlphaFold2 have been made available to the research community, hindering progress in machine learning for proteins. To remedy this problem, we introduce OpenProteinSet, an open-source corpus of more than 16 million MSAs, associated structural homologs from the Protein Data Bank, and AlphaFold2 protein structure predictions. We have previously demonstrated the utility of OpenProteinSet by successfully retraining AlphaFold2 on it. We expect OpenProteinSet to be broadly useful as training and validation data for 1) diverse tasks focused on protein structure, function, and design and 2) large-scale multimodal machine learning research.
3D molecule generation by denoising voxel grids
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:We propose a new score-based approach to generate 3D molecules represented as atomic densities on regular grids. First, we train a denoising neural network that learns to map from a smooth distribution of noisy molecules to the distribution of real molecules. Then, we follow the neural empirical Bayes framework [Saremi and Hyvarinen, 2019] and generate molecules in two steps: (i) sample noisy density grids from a smooth distribution via underdamped Langevin Markov chain Monte Carlo, and (ii) recover the ``clean'' molecule by denoising the noisy grid with a single step. Our method, VoxMol, generates molecules in a fundamentally different way than the current state of the art (i.e., diffusion models applied to atom point clouds). It differs in terms of the data representation, the noise model, the network architecture and the generative modeling algorithm. VoxMol achieves comparable results to state of the art on unconditional 3D molecule generation while being simpler to train and faster to generate molecules.
Protein Discovery with Discrete Walk-Jump Sampling
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:We resolve difficulties in training and sampling from a discrete generative model by learning a smoothed energy function, sampling from the smoothed data manifold with Langevin Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), and projecting back to the true data manifold with one-step denoising. Our Discrete Walk-Jump Sampling formalism combines the maximum likelihood training of an energy-based model and improved sample quality of a score-based model, while simplifying training and sampling by requiring only a single noise level. We evaluate the robustness of our approach on generative modeling of antibody proteins and introduce the distributional conformity score to benchmark protein generative models. By optimizing and sampling from our models for the proposed distributional conformity score, 97-100% of generated samples are successfully expressed and purified and 35% of functional designs show equal or improved binding affinity compared to known functional antibodies on the first attempt in a single round of laboratory experiments. We also report the first demonstration of long-run fast-mixing MCMC chains where diverse antibody protein classes are visited in a single MCMC chain.
BOtied: Multi-objective Bayesian optimization with tied multivariate ranks
Jun 01, 2023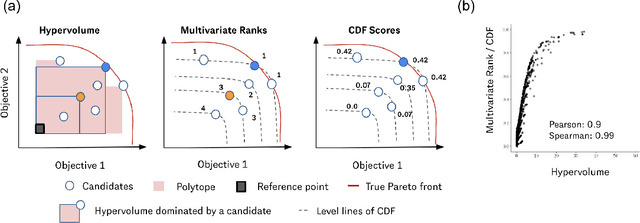
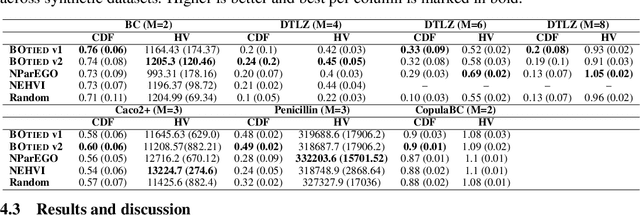
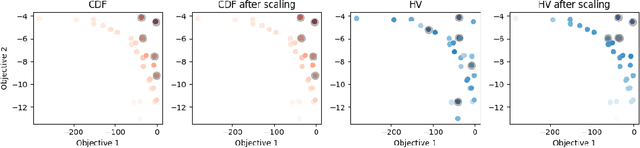
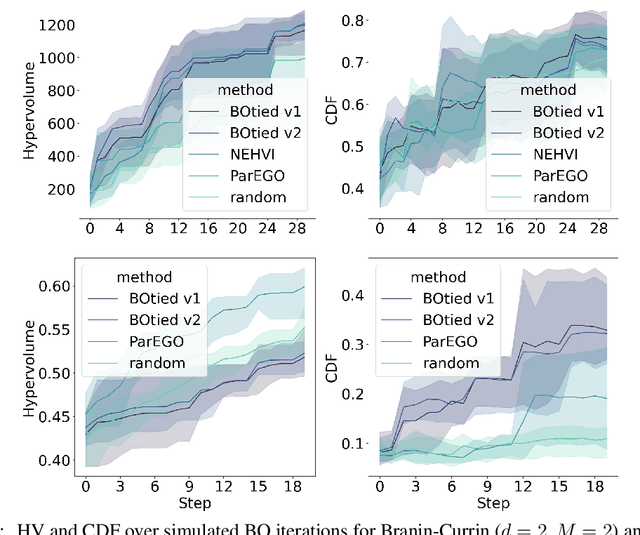
Abstract:Many scientific and industrial applications require joint optimization of multiple, potentially competing objectives. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization (MOBO) is a sample-efficient framework for identifying Pareto-optimal solutions. We show a natural connection between non-dominated solutions and the highest multivariate rank, which coincides with the outermost level line of the joint cumulative distribution function (CDF). We propose the CDF indicator, a Pareto-compliant metric for evaluating the quality of approximate Pareto sets that complements the popular hypervolume indicator. At the heart of MOBO is the acquisition function, which determines the next candidate to evaluate by navigating the best compromises among the objectives. Multi-objective acquisition functions that rely on box decomposition of the objective space, such as the expected hypervolume improvement (EHVI) and entropy search, scale poorly to a large number of objectives. We propose an acquisition function, called BOtied, based on the CDF indicator. BOtied can be implemented efficiently with copulas, a statistical tool for modeling complex, high-dimensional distributions. We benchmark BOtied against common acquisition functions, including EHVI and random scalarization (ParEGO), in a series of synthetic and real-data experiments. BOtied performs on par with the baselines across datasets and metrics while being computationally efficient.
Learning Causal Representations of Single Cells via Sparse Mechanism Shift Modeling
Nov 09, 2022



Abstract:Latent variable models such as the Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) have become a go-to tool for analyzing biological data, especially in the field of single-cell genomics. One remaining challenge is the interpretability of latent variables as biological processes that define a cell's identity. Outside of biological applications, this problem is commonly referred to as learning disentangled representations. Although several disentanglement-promoting variants of the VAE were introduced, and applied to single-cell genomics data, this task has been shown to be infeasible from independent and identically distributed measurements, without additional structure. Instead, recent methods propose to leverage non-stationary data, as well as the sparse mechanism shift assumption in order to learn disentangled representations with a causal semantic. Here, we extend the application of these methodological advances to the analysis of single-cell genomics data with genetic or chemical perturbations. More precisely, we propose a deep generative model of single-cell gene expression data for which each perturbation is treated as a stochastic intervention targeting an unknown, but sparse, subset of latent variables. We benchmark these methods on simulated single-cell data to evaluate their performance at latent units recovery, causal target identification and out-of-domain generalization. Finally, we apply those approaches to two real-world large-scale gene perturbation data sets and find that models that exploit the sparse mechanism shift hypothesis surpass contemporary methods on a transfer learning task. We implement our new model and benchmarks using the scvi-tools library, and release it as open-source software at https://github.com/Genentech/sVAE.
A Pareto-optimal compositional energy-based model for sampling and optimization of protein sequences
Oct 19, 2022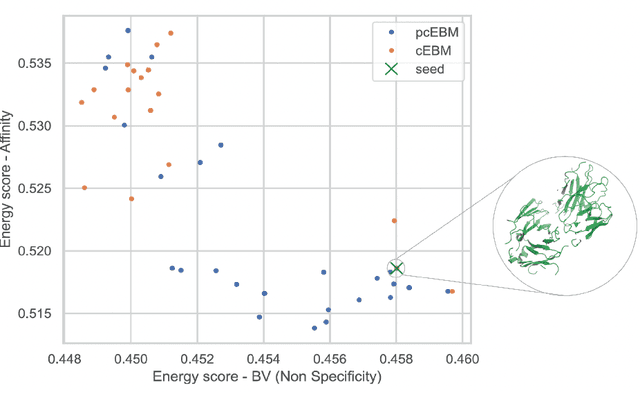
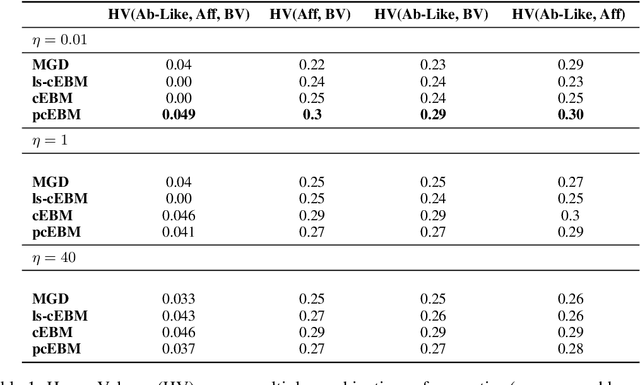
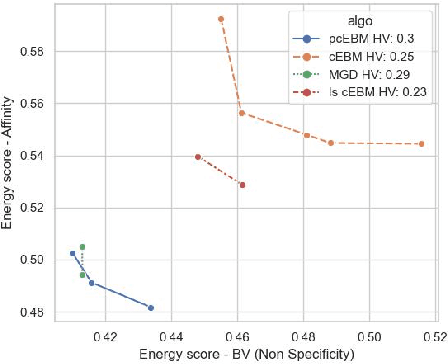
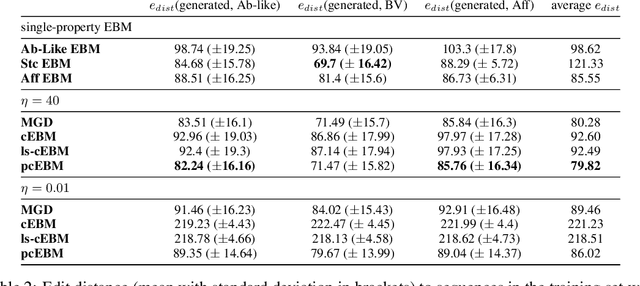
Abstract:Deep generative models have emerged as a popular machine learning-based approach for inverse design problems in the life sciences. However, these problems often require sampling new designs that satisfy multiple properties of interest in addition to learning the data distribution. This multi-objective optimization becomes more challenging when properties are independent or orthogonal to each other. In this work, we propose a Pareto-compositional energy-based model (pcEBM), a framework that uses multiple gradient descent for sampling new designs that adhere to various constraints in optimizing distinct properties. We demonstrate its ability to learn non-convex Pareto fronts and generate sequences that simultaneously satisfy multiple desired properties across a series of real-world antibody design tasks.
PropertyDAG: Multi-objective Bayesian optimization of partially ordered, mixed-variable properties for biological sequence design
Oct 08, 2022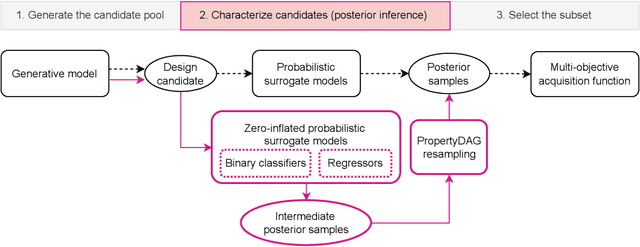
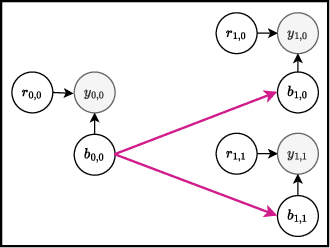
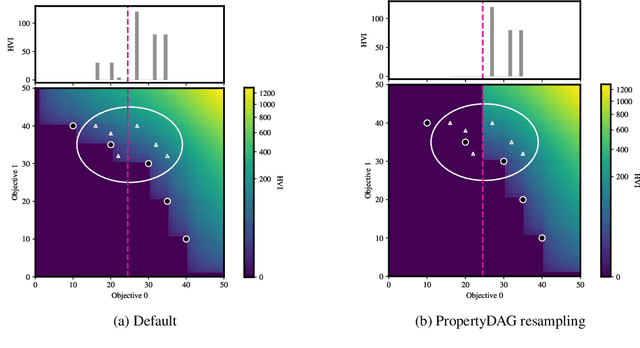
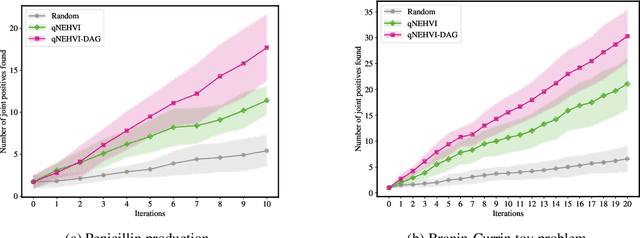
Abstract:Bayesian optimization offers a sample-efficient framework for navigating the exploration-exploitation trade-off in the vast design space of biological sequences. Whereas it is possible to optimize the various properties of interest jointly using a multi-objective acquisition function, such as the expected hypervolume improvement (EHVI), this approach does not account for objectives with a hierarchical dependency structure. We consider a common use case where some regions of the Pareto frontier are prioritized over others according to a specified $\textit{partial ordering}$ in the objectives. For instance, when designing antibodies, we would like to maximize the binding affinity to a target antigen only if it can be expressed in live cell culture -- modeling the experimental dependency in which affinity can only be measured for antibodies that can be expressed and thus produced in viable quantities. In general, we may want to confer a partial ordering to the properties such that each property is optimized conditioned on its parent properties satisfying some feasibility condition. To this end, we present PropertyDAG, a framework that operates on top of the traditional multi-objective BO to impose this desired ordering on the objectives, e.g. expression $\rightarrow$ affinity. We demonstrate its performance over multiple simulated active learning iterations on a penicillin production task, toy numerical problem, and a real-world antibody design task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge