Andrew M. Watkins
Disentangling multispecific antibody function with graph neural networks
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multispecific antibodies offer transformative therapeutic potential by engaging multiple epitopes simultaneously, yet their efficacy is an emergent property governed by complex molecular architectures. Rational design is often bottlenecked by the inability to predict how subtle changes in domain topology influence functional outcomes, a challenge exacerbated by the scarcity of comprehensive experimental data. Here, we introduce a computational framework to address part of this gap. First, we present a generative method for creating large-scale, realistic synthetic functional landscapes that capture non-linear interactions where biological activity depends on domain connectivity. Second, we propose a graph neural network architecture that explicitly encodes these topological constraints, distinguishing between format configurations that appear identical to sequence-only models. We demonstrate that this model, trained on synthetic landscapes, recapitulates complex functional properties and, via transfer learning, has the potential to achieve high predictive accuracy on limited biological datasets. We showcase the model's utility by optimizing trade-offs between efficacy and toxicity in trispecific T-cell engagers and retrieving optimal common light chains. This work provides a robust benchmarking environment for disentangling the combinatorial complexity of multispecifics, accelerating the design of next-generation therapeutics.
LLMs are Highly-Constrained Biophysical Sequence Optimizers
Oct 29, 2024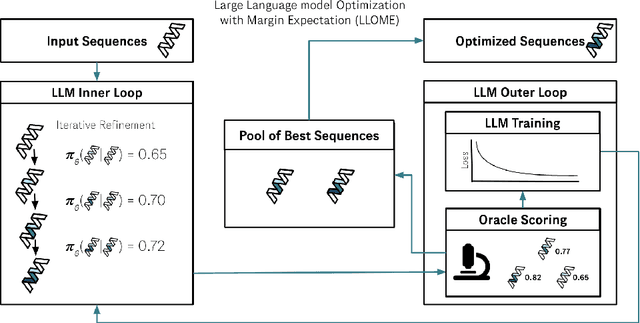
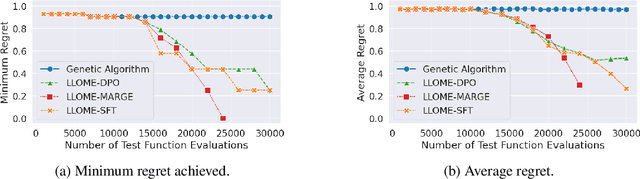
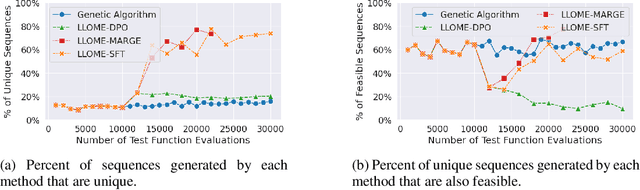
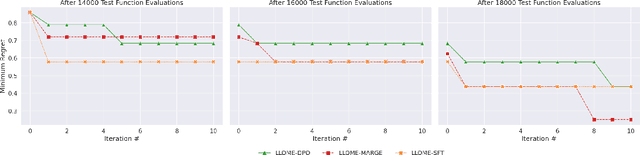
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently shown significant potential in various biological tasks such as protein engineering and molecule design. These tasks typically involve black-box discrete sequence optimization, where the challenge lies in generating sequences that are not only biologically feasible but also adhere to hard fine-grained constraints. However, LLMs often struggle with such constraints, especially in biological contexts where verifying candidate solutions is costly and time-consuming. In this study, we explore the possibility of employing LLMs as highly-constrained bilevel optimizers through a methodology we refer to as Language Model Optimization with Margin Expectation (LLOME). This approach combines both offline and online optimization, utilizing limited oracle evaluations to iteratively enhance the sequences generated by the LLM. We additionally propose a novel training objective -- Margin-Aligned Expectation (MargE) -- that trains the LLM to smoothly interpolate between the reward and reference distributions. Lastly, we introduce a synthetic test suite that bears strong geometric similarity to real biophysical problems and enables rapid evaluation of LLM optimizers without time-consuming lab validation. Our findings reveal that, in comparison to genetic algorithm baselines, LLMs achieve significantly lower regret solutions while requiring fewer test function evaluations. However, we also observe that LLMs exhibit moderate miscalibration, are susceptible to generator collapse, and have difficulty finding the optimal solution when no explicit ground truth rewards are available.
OpenProteinSet: Training data for structural biology at scale
Aug 10, 2023


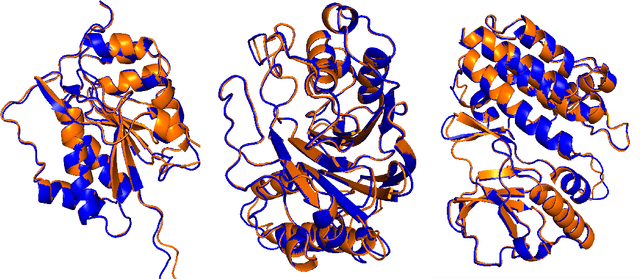
Abstract:Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) of proteins encode rich biological information and have been workhorses in bioinformatic methods for tasks like protein design and protein structure prediction for decades. Recent breakthroughs like AlphaFold2 that use transformers to attend directly over large quantities of raw MSAs have reaffirmed their importance. Generation of MSAs is highly computationally intensive, however, and no datasets comparable to those used to train AlphaFold2 have been made available to the research community, hindering progress in machine learning for proteins. To remedy this problem, we introduce OpenProteinSet, an open-source corpus of more than 16 million MSAs, associated structural homologs from the Protein Data Bank, and AlphaFold2 protein structure predictions. We have previously demonstrated the utility of OpenProteinSet by successfully retraining AlphaFold2 on it. We expect OpenProteinSet to be broadly useful as training and validation data for 1) diverse tasks focused on protein structure, function, and design and 2) large-scale multimodal machine learning research.
Predictive models of RNA degradation through dual crowdsourcing
Oct 14, 2021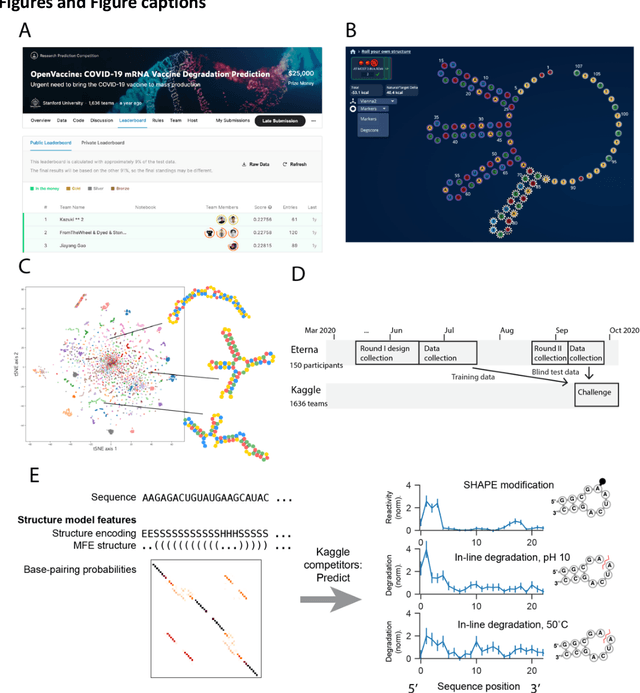
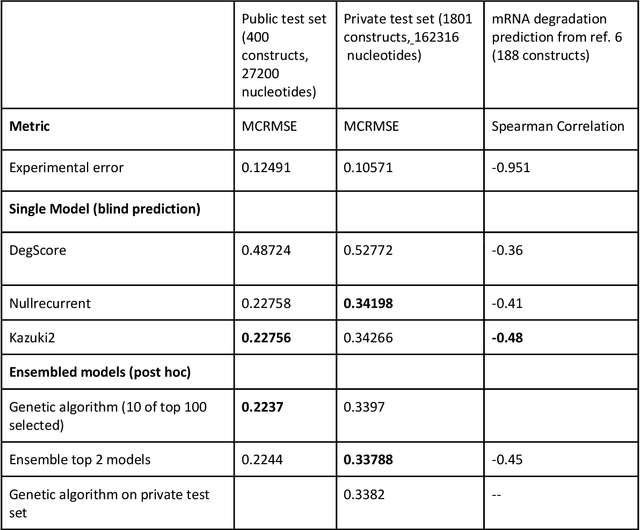
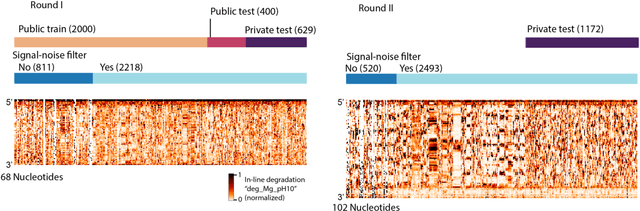
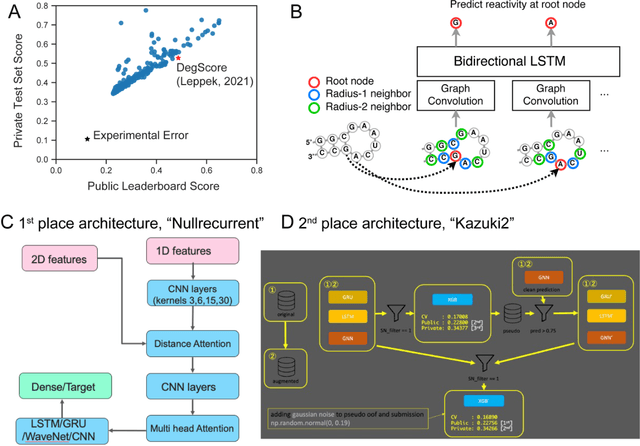
Abstract:Messenger RNA-based medicines hold immense potential, as evidenced by their rapid deployment as COVID-19 vaccines. However, worldwide distribution of mRNA molecules has been limited by their thermostability, which is fundamentally limited by the intrinsic instability of RNA molecules to a chemical degradation reaction called in-line hydrolysis. Predicting the degradation of an RNA molecule is a key task in designing more stable RNA-based therapeutics. Here, we describe a crowdsourced machine learning competition ("Stanford OpenVaccine") on Kaggle, involving single-nucleotide resolution measurements on 6043 102-130-nucleotide diverse RNA constructs that were themselves solicited through crowdsourcing on the RNA design platform Eterna. The entire experiment was completed in less than 6 months. Winning models demonstrated test set errors that were better by 50% than the previous state-of-the-art DegScore model. Furthermore, these models generalized to blindly predicting orthogonal degradation data on much longer mRNA molecules (504-1588 nucleotides) with improved accuracy over DegScore and other models. Top teams integrated natural language processing architectures and data augmentation techniques with predictions from previous dynamic programming models for RNA secondary structure. These results indicate that such models are capable of representing in-line hydrolysis with excellent accuracy, supporting their use for designing stabilized messenger RNAs. The integration of two crowdsourcing platforms, one for data set creation and another for machine learning, may be fruitful for other urgent problems that demand scientific discovery on rapid timescales.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge