Samuel D. Stanton
Disentangling multispecific antibody function with graph neural networks
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multispecific antibodies offer transformative therapeutic potential by engaging multiple epitopes simultaneously, yet their efficacy is an emergent property governed by complex molecular architectures. Rational design is often bottlenecked by the inability to predict how subtle changes in domain topology influence functional outcomes, a challenge exacerbated by the scarcity of comprehensive experimental data. Here, we introduce a computational framework to address part of this gap. First, we present a generative method for creating large-scale, realistic synthetic functional landscapes that capture non-linear interactions where biological activity depends on domain connectivity. Second, we propose a graph neural network architecture that explicitly encodes these topological constraints, distinguishing between format configurations that appear identical to sequence-only models. We demonstrate that this model, trained on synthetic landscapes, recapitulates complex functional properties and, via transfer learning, has the potential to achieve high predictive accuracy on limited biological datasets. We showcase the model's utility by optimizing trade-offs between efficacy and toxicity in trispecific T-cell engagers and retrieving optimal common light chains. This work provides a robust benchmarking environment for disentangling the combinatorial complexity of multispecifics, accelerating the design of next-generation therapeutics.
LLMs are Highly-Constrained Biophysical Sequence Optimizers
Oct 29, 2024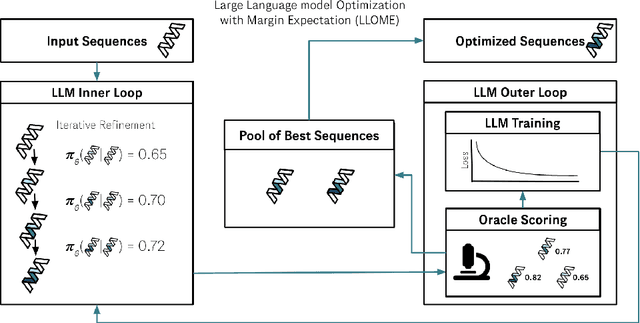
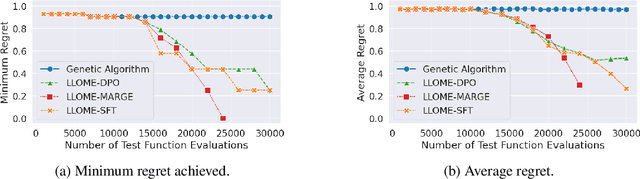
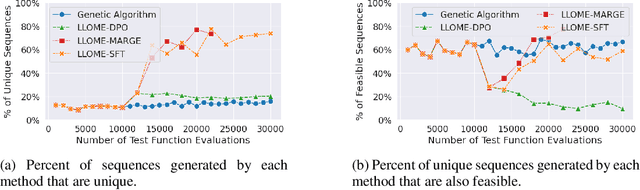
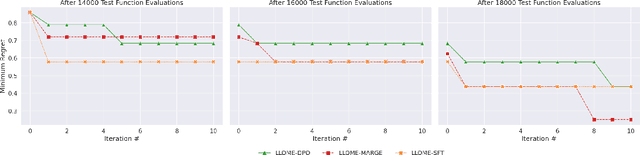
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently shown significant potential in various biological tasks such as protein engineering and molecule design. These tasks typically involve black-box discrete sequence optimization, where the challenge lies in generating sequences that are not only biologically feasible but also adhere to hard fine-grained constraints. However, LLMs often struggle with such constraints, especially in biological contexts where verifying candidate solutions is costly and time-consuming. In this study, we explore the possibility of employing LLMs as highly-constrained bilevel optimizers through a methodology we refer to as Language Model Optimization with Margin Expectation (LLOME). This approach combines both offline and online optimization, utilizing limited oracle evaluations to iteratively enhance the sequences generated by the LLM. We additionally propose a novel training objective -- Margin-Aligned Expectation (MargE) -- that trains the LLM to smoothly interpolate between the reward and reference distributions. Lastly, we introduce a synthetic test suite that bears strong geometric similarity to real biophysical problems and enables rapid evaluation of LLM optimizers without time-consuming lab validation. Our findings reveal that, in comparison to genetic algorithm baselines, LLMs achieve significantly lower regret solutions while requiring fewer test function evaluations. However, we also observe that LLMs exhibit moderate miscalibration, are susceptible to generator collapse, and have difficulty finding the optimal solution when no explicit ground truth rewards are available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge