Arvind Rajpal
AbDiffuser: Full-Atom Generation of In-Vitro Functioning Antibodies
Jul 28, 2023



Abstract:We introduce AbDiffuser, an equivariant and physics-informed diffusion model for the joint generation of antibody 3D structures and sequences. AbDiffuser is built on top of a new representation of protein structure, relies on a novel architecture for aligned proteins, and utilizes strong diffusion priors to improve the denoising process. Our approach improves protein diffusion by taking advantage of domain knowledge and physics-based constraints; handles sequence-length changes; and reduces memory complexity by an order of magnitude enabling backbone and side chain generation. We validate AbDiffuser in silico and in vitro. Numerical experiments showcase the ability of AbDiffuser to generate antibodies that closely track the sequence and structural properties of a reference set. Laboratory experiments confirm that all 16 HER2 antibodies discovered were expressed at high levels and that 57.1% of selected designs were tight binders.
Protein Design with Guided Discrete Diffusion
May 31, 2023Abstract:A popular approach to protein design is to combine a generative model with a discriminative model for conditional sampling. The generative model samples plausible sequences while the discriminative model guides a search for sequences with high fitness. Given its broad success in conditional sampling, classifier-guided diffusion modeling is a promising foundation for protein design, leading many to develop guided diffusion models for structure with inverse folding to recover sequences. In this work, we propose diffusioN Optimized Sampling (NOS), a guidance method for discrete diffusion models that follows gradients in the hidden states of the denoising network. NOS makes it possible to perform design directly in sequence space, circumventing significant limitations of structure-based methods, including scarce data and challenging inverse design. Moreover, we use NOS to generalize LaMBO, a Bayesian optimization procedure for sequence design that facilitates multiple objectives and edit-based constraints. The resulting method, LaMBO-2, enables discrete diffusions and stronger performance with limited edits through a novel application of saliency maps. We apply LaMBO-2 to a real-world protein design task, optimizing antibodies for higher expression yield and binding affinity to a therapeutic target under locality and liability constraints, with 97% expression rate and 25% binding rate in exploratory in vitro experiments.
A Pareto-optimal compositional energy-based model for sampling and optimization of protein sequences
Oct 19, 2022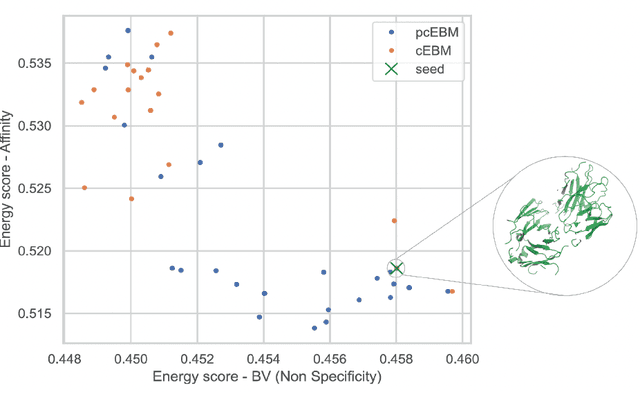
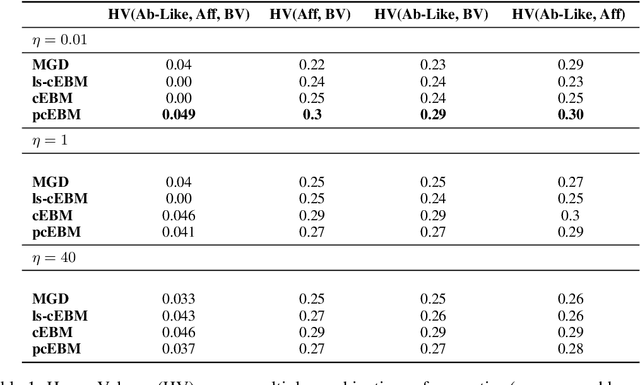
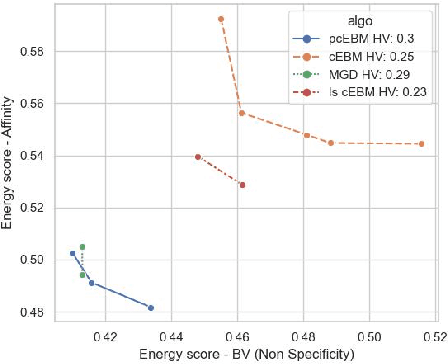
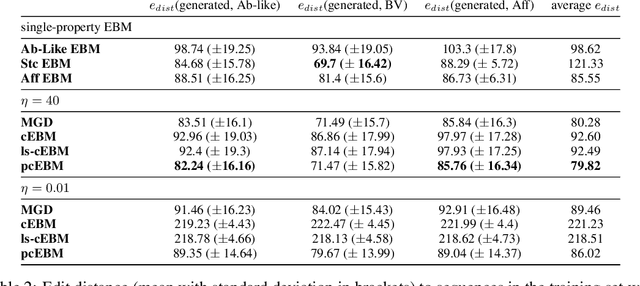
Abstract:Deep generative models have emerged as a popular machine learning-based approach for inverse design problems in the life sciences. However, these problems often require sampling new designs that satisfy multiple properties of interest in addition to learning the data distribution. This multi-objective optimization becomes more challenging when properties are independent or orthogonal to each other. In this work, we propose a Pareto-compositional energy-based model (pcEBM), a framework that uses multiple gradient descent for sampling new designs that adhere to various constraints in optimizing distinct properties. We demonstrate its ability to learn non-convex Pareto fronts and generate sequences that simultaneously satisfy multiple desired properties across a series of real-world antibody design tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge