Ritwik Sinha
Exploring Rewriting Approaches for Different Conversational Tasks
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Conversational assistants often require a question rewriting algorithm that leverages a subset of past interactions to provide a more meaningful (accurate) answer to the user's question or request. However, the exact rewriting approach may often depend on the use case and application-specific tasks supported by the conversational assistant, among other constraints. In this paper, we systematically investigate two different approaches, denoted as rewriting and fusion, on two fundamentally different generation tasks, including a text-to-text generation task and a multimodal generative task that takes as input text and generates a visualization or data table that answers the user's question. Our results indicate that the specific rewriting or fusion approach highly depends on the underlying use case and generative task. In particular, we find that for a conversational question-answering assistant, the query rewriting approach performs best, whereas for a data analysis assistant that generates visualizations and data tables based on the user's conversation with the assistant, the fusion approach works best. Notably, we explore two datasets for the data analysis assistant use case, for short and long conversations, and we find that query fusion always performs better, whereas for the conversational text-based question-answering, the query rewrite approach performs best.
BOTracle: A framework for Discriminating Bots and Humans
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Bots constitute a significant portion of Internet traffic and are a source of various issues across multiple domains. Modern bots often become indistinguishable from real users, as they employ similar methods to browse the web, including using real browsers. We address the challenge of bot detection in high-traffic scenarios by analyzing three distinct detection methods. The first method operates on heuristics, allowing for rapid detection. The second method utilizes, well known, technical features, such as IP address, window size, and user agent. It serves primarily for comparison with the third method. In the third method, we rely solely on browsing behavior, omitting all static features and focusing exclusively on how clients behave on a website. In contrast to related work, we evaluate our approaches using real-world e-commerce traffic data, comprising 40 million monthly page visits. We further compare our methods against another bot detection approach, Botcha, on the same dataset. Our performance metrics, including precision, recall, and AUC, reach 98 percent or higher, surpassing Botcha.
Diversify-verify-adapt: Efficient and Robust Retrieval-Augmented Ambiguous Question Answering
Sep 04, 2024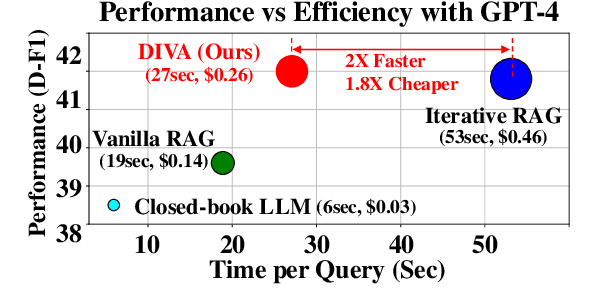
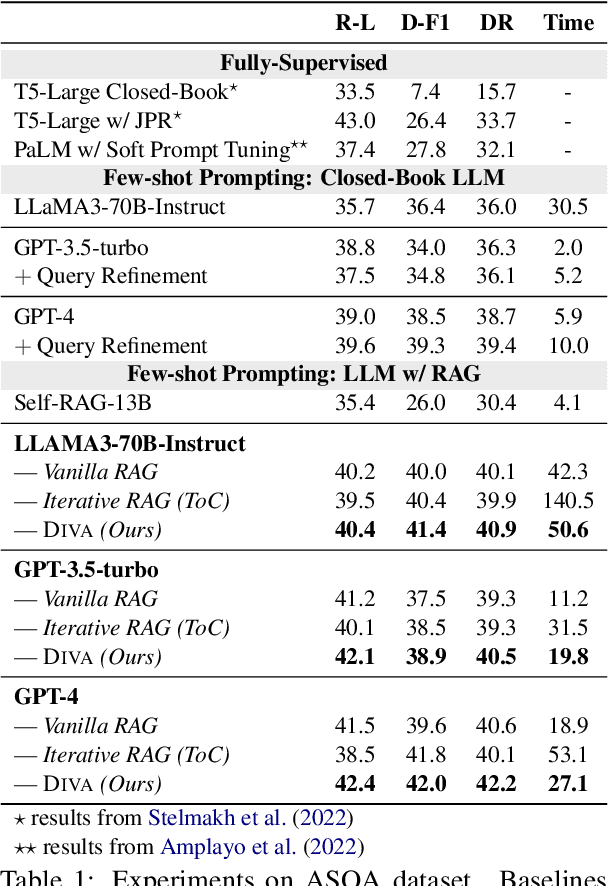
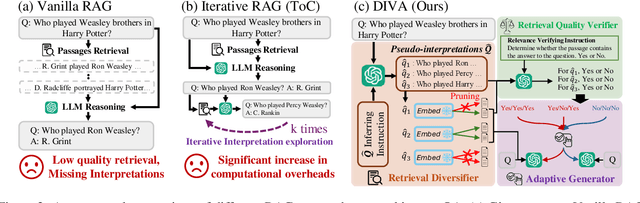
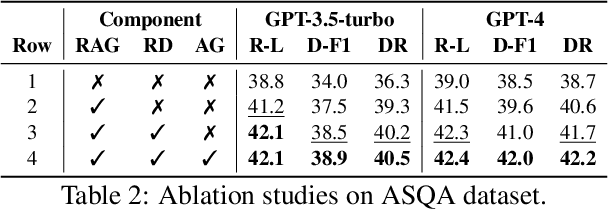
Abstract:The retrieval augmented generation (RAG) framework addresses an ambiguity in user queries in QA systems by retrieving passages that cover all plausible interpretations and generating comprehensive responses based on the passages. However, our preliminary studies reveal that a single retrieval process often suffers from low quality results, as the retrieved passages frequently fail to capture all plausible interpretations. Although the iterative RAG approach has been proposed to address this problem, it comes at the cost of significantly reduced efficiency. To address these issues, we propose the diversify-verify-adapt (DIVA) framework. DIVA first diversifies the retrieved passages to encompass diverse interpretations. Subsequently, DIVA verifies the quality of the passages and adapts the most suitable approach tailored to their quality. This approach improves the QA systems accuracy and robustness by handling low quality retrieval issue in ambiguous questions, while enhancing efficiency.
A/B testing under Interference with Partial Network Information
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:A/B tests are often required to be conducted on subjects that might have social connections. For e.g., experiments on social media, or medical and social interventions to control the spread of an epidemic. In such settings, the SUTVA assumption for randomized-controlled trials is violated due to network interference, or spill-over effects, as treatments to group A can potentially also affect the control group B. When the underlying social network is known exactly, prior works have demonstrated how to conduct A/B tests adequately to estimate the global average treatment effect (GATE). However, in practice, it is often impossible to obtain knowledge about the exact underlying network. In this paper, we present UNITE: a novel estimator that relax this assumption and can identify GATE while only relying on knowledge of the superset of neighbors for any subject in the graph. Through theoretical analysis and extensive experiments, we show that the proposed approach performs better in comparison to standard estimators.
Continuous Treatment Effects with Surrogate Outcomes
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:In many real-world causal inference applications, the primary outcomes (labels) are often partially missing, especially if they are expensive or difficult to collect. If the missingness depends on covariates (i.e., missingness is not completely at random), analyses based on fully-observed samples alone may be biased. Incorporating surrogates, which are fully observed post-treatment variables related to the primary outcome, can improve estimation in this case. In this paper, we study the role of surrogates in estimating continuous treatment effects and propose a doubly robust method to efficiently incorporate surrogates in the analysis, which uses both labeled and unlabeled data and does not suffer from the above selection bias problem. Importantly, we establish asymptotic normality of the proposed estimator and show possible improvements on the variance compared with methods that solely use labeled data. Extensive simulations show our methods enjoy appealing empirical performance.
Augment before You Try: Knowledge-Enhanced Table Question Answering via Table Expansion
Jan 28, 2024Abstract:Table question answering is a popular task that assesses a model's ability to understand and interact with structured data. However, the given table often does not contain sufficient information for answering the question, necessitating the integration of external knowledge. Existing methods either convert both the table and external knowledge into text, which neglects the structured nature of the table; or they embed queries for external sources in the interaction with the table, which complicates the process. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective method to integrate external information in a given table. Our method first constructs an augmenting table containing the missing information and then generates a SQL query over the two tables to answer the question. Experiments show that our method outperforms strong baselines on three table QA benchmarks. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/UCSB-NLP-Chang/Augment_tableQA.
SODA: Protecting Proprietary Information in On-Device Machine Learning Models
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:The growth of low-end hardware has led to a proliferation of machine learning-based services in edge applications. These applications gather contextual information about users and provide some services, such as personalized offers, through a machine learning (ML) model. A growing practice has been to deploy such ML models on the user's device to reduce latency, maintain user privacy, and minimize continuous reliance on a centralized source. However, deploying ML models on the user's edge device can leak proprietary information about the service provider. In this work, we investigate on-device ML models that are used to provide mobile services and demonstrate how simple attacks can leak proprietary information of the service provider. We show that different adversaries can easily exploit such models to maximize their profit and accomplish content theft. Motivated by the need to thwart such attacks, we present an end-to-end framework, SODA, for deploying and serving on edge devices while defending against adversarial usage. Our results demonstrate that SODA can detect adversarial usage with 89% accuracy in less than 50 queries with minimal impact on service performance, latency, and storage.
A Mathematical Abstraction for Balancing the Trade-off Between Creativity and Reality in Large Language Models
Jun 04, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models have become popular for their remarkable capabilities in human-oriented tasks and traditional natural language processing tasks. Its efficient functioning is attributed to the attention mechanism in the Transformer architecture, enabling it to concentrate on particular aspects of the input. LLMs are increasingly being used in domains such as generating prose, poetry or art, which require the model to be creative (e.g. Adobe firefly). LLMs possess advanced language generation abilities that enable them to generate distinctive and captivating content. This utilization of LLMs in generating narratives shows their flexibility and potential for use in domains that extend beyond conventional natural language processing duties. In different contexts, we may expect the LLM to generate factually correct answers, that match reality; e.g., question-answering systems or online assistants. In such situations, being correct is critical to LLMs being trusted in practice. The Bing Chatbot provides its users with the flexibility to select one of the three output modes: creative, balanced, and precise. Each mode emphasizes creativity and factual accuracy differently. In this work, we provide a mathematical abstraction to describe creativity and reality based on certain losses. A model trained on these losses balances the trade-off between the creativity and reality of the model.
VADER: Video Alignment Differencing and Retrieval
Mar 25, 2023



Abstract:We propose VADER, a spatio-temporal matching, alignment, and change summarization method to help fight misinformation spread via manipulated videos. VADER matches and coarsely aligns partial video fragments to candidate videos using a robust visual descriptor and scalable search over adaptively chunked video content. A transformer-based alignment module then refines the temporal localization of the query fragment within the matched video. A space-time comparator module identifies regions of manipulation between aligned content, invariant to any changes due to any residual temporal misalignments or artifacts arising from non-editorial changes of the content. Robustly matching video to a trusted source enables conclusions to be drawn on video provenance, enabling informed trust decisions on content encountered.
Privacy Aware Experiments without Cookies
Nov 03, 2022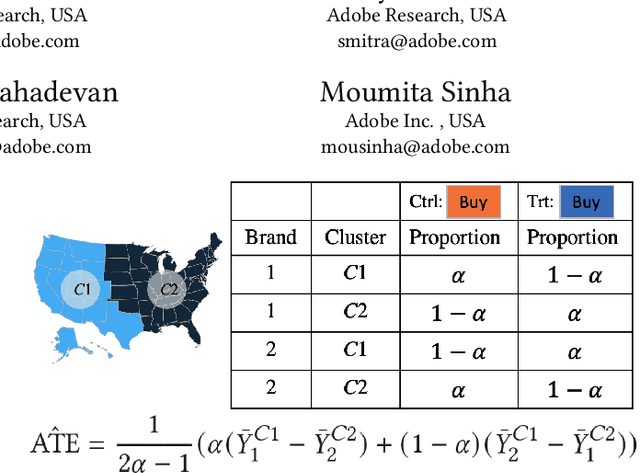
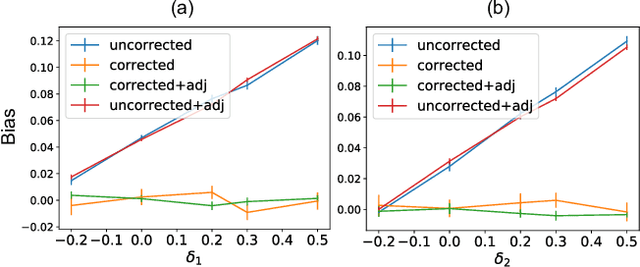
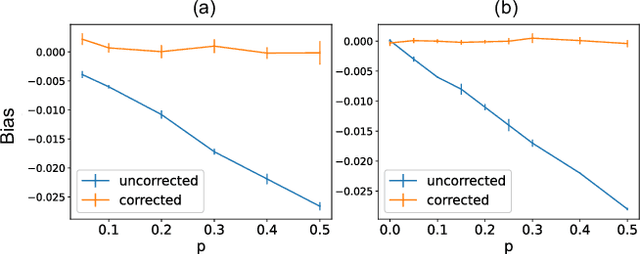
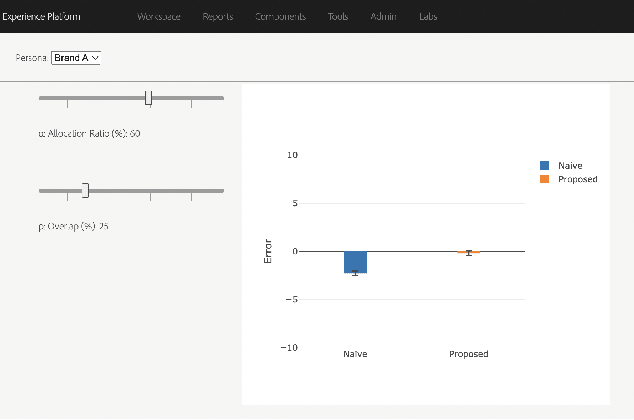
Abstract:Consider two brands that want to jointly test alternate web experiences for their customers with an A/B test. Such collaborative tests are today enabled using \textit{third-party cookies}, where each brand has information on the identity of visitors to another website. With the imminent elimination of third-party cookies, such A/B tests will become untenable. We propose a two-stage experimental design, where the two brands only need to agree on high-level aggregate parameters of the experiment to test the alternate experiences. Our design respects the privacy of customers. We propose an estimater of the Average Treatment Effect (ATE), show that it is unbiased and theoretically compute its variance. Our demonstration describes how a marketer for a brand can design such an experiment and analyze the results. On real and simulated data, we show that the approach provides valid estimate of the ATE with low variance and is robust to the proportion of visitors overlapping across the brands.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge