Mathias Fischer
BOTracle: A framework for Discriminating Bots and Humans
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Bots constitute a significant portion of Internet traffic and are a source of various issues across multiple domains. Modern bots often become indistinguishable from real users, as they employ similar methods to browse the web, including using real browsers. We address the challenge of bot detection in high-traffic scenarios by analyzing three distinct detection methods. The first method operates on heuristics, allowing for rapid detection. The second method utilizes, well known, technical features, such as IP address, window size, and user agent. It serves primarily for comparison with the third method. In the third method, we rely solely on browsing behavior, omitting all static features and focusing exclusively on how clients behave on a website. In contrast to related work, we evaluate our approaches using real-world e-commerce traffic data, comprising 40 million monthly page visits. We further compare our methods against another bot detection approach, Botcha, on the same dataset. Our performance metrics, including precision, recall, and AUC, reach 98 percent or higher, surpassing Botcha.
SoK: Towards Security and Safety of Edge AI
Oct 07, 2024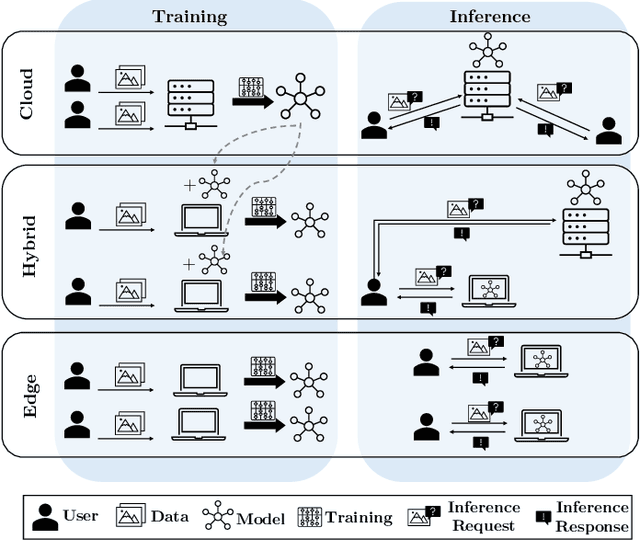
Abstract:Advanced AI applications have become increasingly available to a broad audience, e.g., as centrally managed large language models (LLMs). Such centralization is both a risk and a performance bottleneck - Edge AI promises to be a solution to these problems. However, its decentralized approach raises additional challenges regarding security and safety. In this paper, we argue that both of these aspects are critical for Edge AI, and even more so, their integration. Concretely, we survey security and safety threats, summarize existing countermeasures, and collect open challenges as a call for more research in this area.
Towards Synthesizing Datasets for IEEE 802.1 Time-sensitive Networking
Aug 20, 2023
Abstract:IEEE 802.1 Time-sensitive Networking (TSN) protocols have recently been proposed to replace legacy networking technologies across different mission-critical systems (MCSs). Design, configuration, and maintenance of TSN within MCSs require advanced methods to tackle the highly complex and interconnected nature of those systems. Accordingly, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are the most prominent enablers to develop such methods. However, they usually require a significant amount of data for model training, which is not easily accessible. This short paper aims to recapitulate the need for TSN datasets to flourish research on AI/ML-based techniques for TSN systems. Moreover, it analyzes the main requirements and alternative designs to build a TSN platform to synthesize realistic datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge