Louis Blankemeier
Comp2Comp: Open-Source Software with FDA-Cleared Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Computed Tomography Image Analysis
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Artificial intelligence allows automatic extraction of imaging biomarkers from already-acquired radiologic images. This paradigm of opportunistic imaging adds value to medical imaging without additional imaging costs or patient radiation exposure. However, many open-source image analysis solutions lack rigorous validation while commercial solutions lack transparency, leading to unexpected failures when deployed. Here, we report development and validation for two of the first fully open-sourced, FDA-510(k)-cleared deep learning pipelines to mitigate both challenges: Abdominal Aortic Quantification (AAQ) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD) estimation are both offered within the Comp2Comp package for opportunistic analysis of computed tomography scans. AAQ segments the abdominal aorta to assess aneurysm size; BMD segments vertebral bodies to estimate trabecular bone density and osteoporosis risk. AAQ-derived maximal aortic diameters were compared against radiologist ground-truth measurements on 258 patient scans enriched for abdominal aortic aneurysms from four external institutions. BMD binary classifications (low vs. normal bone density) were compared against concurrent DXA scan ground truths obtained on 371 patient scans from four external institutions. AAQ had an overall mean absolute error of 1.57 mm (95% CI 1.38-1.80 mm). BMD had a sensitivity of 81.0% (95% CI 74.0-86.8%) and specificity of 78.4% (95% CI 72.3-83.7%). Comp2Comp AAQ and BMD demonstrated sufficient accuracy for clinical use. Open-sourcing these algorithms improves transparency of typically opaque FDA clearance processes, allows hospitals to test the algorithms before cumbersome clinical pilots, and provides researchers with best-in-class methods.
MedVAE: Efficient Automated Interpretation of Medical Images with Large-Scale Generalizable Autoencoders
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Medical images are acquired at high resolutions with large fields of view in order to capture fine-grained features necessary for clinical decision-making. Consequently, training deep learning models on medical images can incur large computational costs. In this work, we address the challenge of downsizing medical images in order to improve downstream computational efficiency while preserving clinically-relevant features. We introduce MedVAE, a family of six large-scale 2D and 3D autoencoders capable of encoding medical images as downsized latent representations and decoding latent representations back to high-resolution images. We train MedVAE autoencoders using a novel two-stage training approach with 1,052,730 medical images. Across diverse tasks obtained from 20 medical image datasets, we demonstrate that (1) utilizing MedVAE latent representations in place of high-resolution images when training downstream models can lead to efficiency benefits (up to 70x improvement in throughput) while simultaneously preserving clinically-relevant features and (2) MedVAE can decode latent representations back to high-resolution images with high fidelity. Our work demonstrates that large-scale, generalizable autoencoders can help address critical efficiency challenges in the medical domain. Our code is available at https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/MedVAE.
Explaining 3D Computed Tomography Classifiers with Counterfactuals
Feb 11, 2025


Abstract:Counterfactual explanations in medical imaging are critical for understanding the predictions made by deep learning models. We extend the Latent Shift counterfactual generation method from 2D applications to 3D computed tomography (CT) scans. We address the challenges associated with 3D data, such as limited training samples and high memory demands, by implementing a slice-based approach. This method leverages a 2D encoder trained on CT slices, which are subsequently combined to maintain 3D context. We demonstrate this technique on two models for clinical phenotype prediction and lung segmentation. Our approach is both memory-efficient and effective for generating interpretable counterfactuals in high-resolution 3D medical imaging.
Foundation Models in Radiology: What, How, When, Why and Why Not
Nov 27, 2024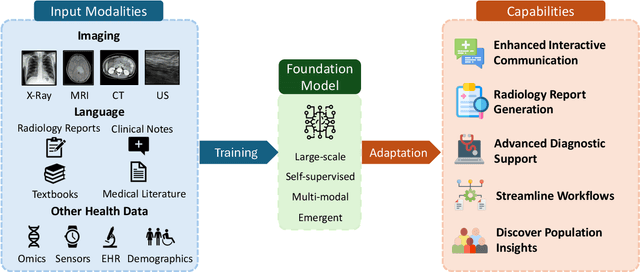
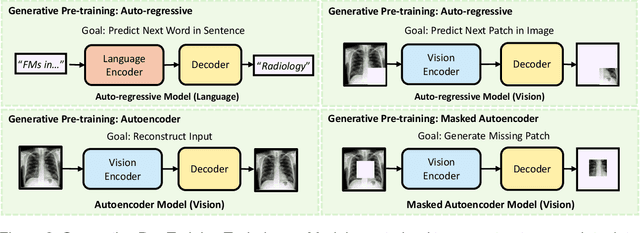
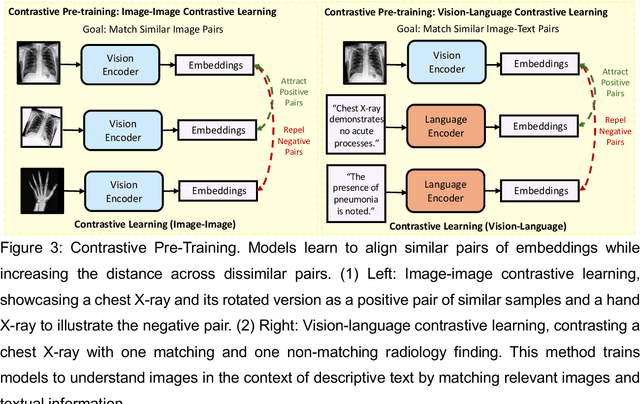
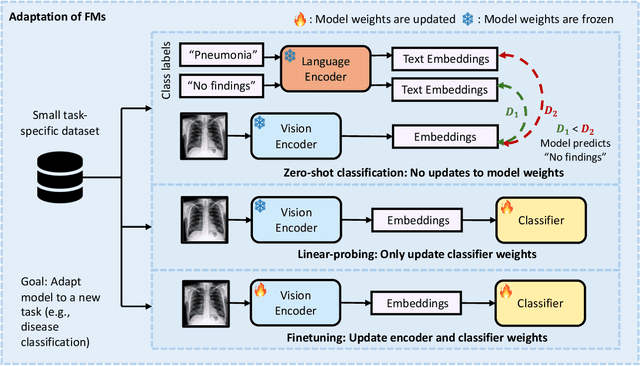
Abstract:Recent advances in artificial intelligence have witnessed the emergence of large-scale deep learning models capable of interpreting and generating both textual and imaging data. Such models, typically referred to as foundation models, are trained on extensive corpora of unlabeled data and demonstrate high performance across various tasks. Foundation models have recently received extensive attention from academic, industry, and regulatory bodies. Given the potentially transformative impact that foundation models can have on the field of radiology, this review aims to establish a standardized terminology concerning foundation models, with a specific focus on the requirements of training data, model training paradigms, model capabilities, and evaluation strategies. We further outline potential pathways to facilitate the training of radiology-specific foundation models, with a critical emphasis on elucidating both the benefits and challenges associated with such models. Overall, we envision that this review can unify technical advances and clinical needs in the training of foundation models for radiology in a safe and responsible manner, for ultimately benefiting patients, providers, and radiologists.
Time-to-Event Pretraining for 3D Medical Imaging
Nov 14, 2024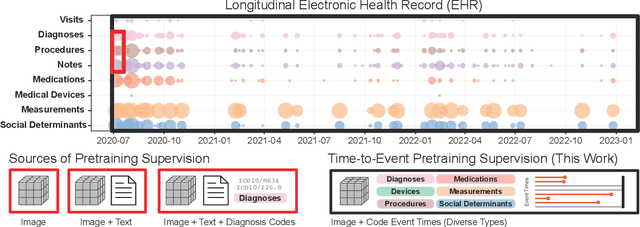
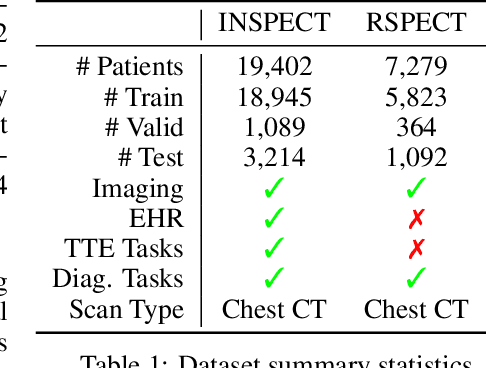
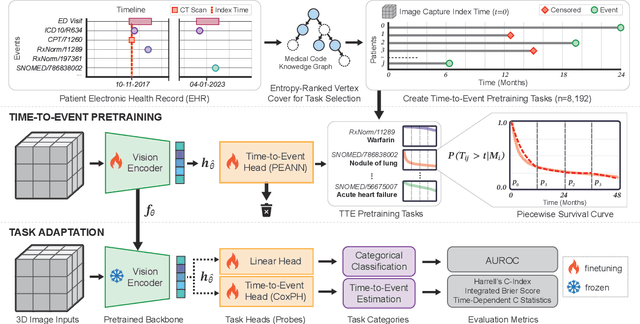
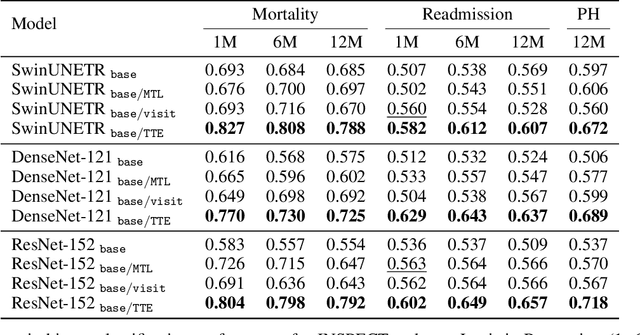
Abstract:With the rise of medical foundation models and the growing availability of imaging data, scalable pretraining techniques offer a promising way to identify imaging biomarkers predictive of future disease risk. While current self-supervised methods for 3D medical imaging models capture local structural features like organ morphology, they fail to link pixel biomarkers with long-term health outcomes due to a missing context problem. Current approaches lack the temporal context necessary to identify biomarkers correlated with disease progression, as they rely on supervision derived only from images and concurrent text descriptions. To address this, we introduce time-to-event pretraining, a pretraining framework for 3D medical imaging models that leverages large-scale temporal supervision from paired, longitudinal electronic health records (EHRs). Using a dataset of 18,945 CT scans (4.2 million 2D images) and time-to-event distributions across thousands of EHR-derived tasks, our method improves outcome prediction, achieving an average AUROC increase of 23.7% and a 29.4% gain in Harrell's C-index across 8 benchmark tasks. Importantly, these gains are achieved without sacrificing diagnostic classification performance. This study lays the foundation for integrating longitudinal EHR and 3D imaging data to advance clinical risk prediction.
Overview of the First Shared Task on Clinical Text Generation: RRG24 and "Discharge Me!"
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Recent developments in natural language generation have tremendous implications for healthcare. For instance, state-of-the-art systems could automate the generation of sections in clinical reports to alleviate physician workload and streamline hospital documentation. To explore these applications, we present a shared task consisting of two subtasks: (1) Radiology Report Generation (RRG24) and (2) Discharge Summary Generation ("Discharge Me!"). RRG24 involves generating the 'Findings' and 'Impression' sections of radiology reports given chest X-rays. "Discharge Me!" involves generating the 'Brief Hospital Course' and 'Discharge Instructions' sections of discharge summaries for patients admitted through the emergency department. "Discharge Me!" submissions were subsequently reviewed by a team of clinicians. Both tasks emphasize the goal of reducing clinician burnout and repetitive workloads by generating documentation. We received 201 submissions from across 8 teams for RRG24, and 211 submissions from across 16 teams for "Discharge Me!".
* ACL Proceedings. BioNLP workshop
Detecting Underdiagnosed Medical Conditions with Deep Learning-Based Opportunistic CT Imaging
Sep 18, 2024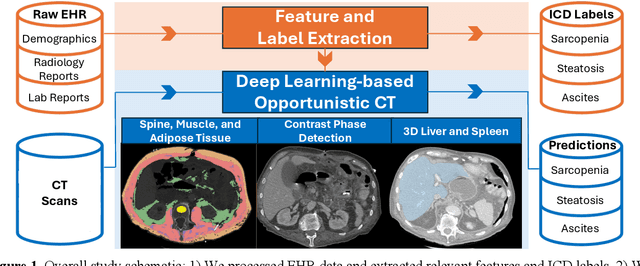
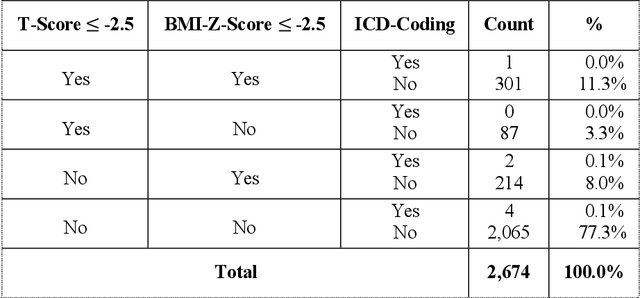
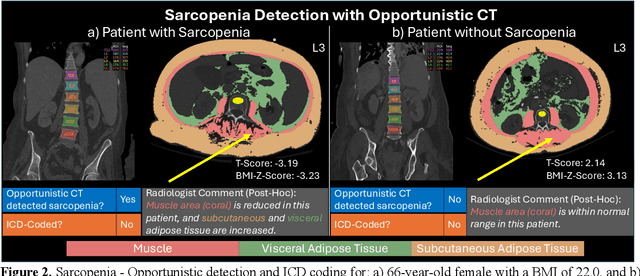
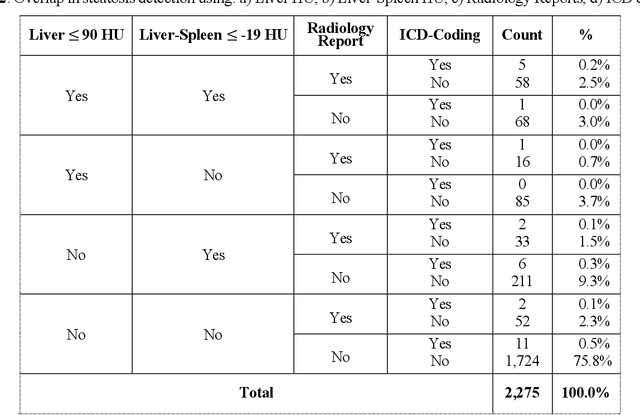
Abstract:Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scans are frequently performed in clinical settings. Opportunistic CT involves repurposing routine CT images to extract diagnostic information and is an emerging tool for detecting underdiagnosed conditions such as sarcopenia, hepatic steatosis, and ascites. This study utilizes deep learning methods to promote accurate diagnosis and clinical documentation. We analyze 2,674 inpatient CT scans to identify discrepancies between imaging phenotypes (characteristics derived from opportunistic CT scans) and their corresponding documentation in radiology reports and ICD coding. Through our analysis, we find that only 0.5%, 3.2%, and 30.7% of scans diagnosed with sarcopenia, hepatic steatosis, and ascites (respectively) through either opportunistic imaging or radiology reports were ICD-coded. Our findings demonstrate opportunistic CT's potential to enhance diagnostic precision and accuracy of risk adjustment models, offering advancements in precision medicine.
Merlin: A Vision Language Foundation Model for 3D Computed Tomography
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Over 85 million computed tomography (CT) scans are performed annually in the US, of which approximately one quarter focus on the abdomen. Given the current radiologist shortage, there is a large impetus to use artificial intelligence to alleviate the burden of interpreting these complex imaging studies. Prior state-of-the-art approaches for automated medical image interpretation leverage vision language models (VLMs). However, current medical VLMs are generally limited to 2D images and short reports, and do not leverage electronic health record (EHR) data for supervision. We introduce Merlin - a 3D VLM that we train using paired CT scans (6+ million images from 15,331 CTs), EHR diagnosis codes (1.8+ million codes), and radiology reports (6+ million tokens). We evaluate Merlin on 6 task types and 752 individual tasks. The non-adapted (off-the-shelf) tasks include zero-shot findings classification (31 findings), phenotype classification (692 phenotypes), and zero-shot cross-modal retrieval (image to findings and image to impressions), while model adapted tasks include 5-year disease prediction (6 diseases), radiology report generation, and 3D semantic segmentation (20 organs). We perform internal validation on a test set of 5,137 CTs, and external validation on 7,000 clinical CTs and on two public CT datasets (VerSe, TotalSegmentator). Beyond these clinically-relevant evaluations, we assess the efficacy of various network architectures and training strategies to depict that Merlin has favorable performance to existing task-specific baselines. We derive data scaling laws to empirically assess training data needs for requisite downstream task performance. Furthermore, unlike conventional VLMs that require hundreds of GPUs for training, we perform all training on a single GPU.
GREEN: Generative Radiology Report Evaluation and Error Notation
May 06, 2024
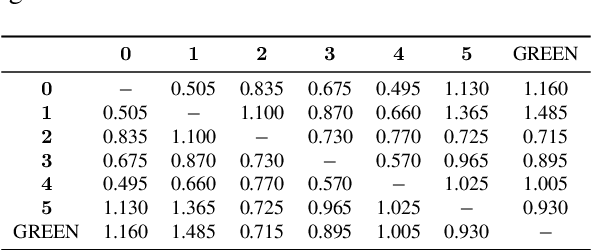

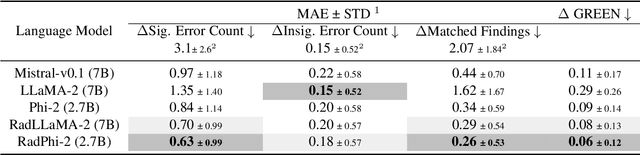
Abstract:Evaluating radiology reports is a challenging problem as factual correctness is extremely important due to the need for accurate medical communication about medical images. Existing automatic evaluation metrics either suffer from failing to consider factual correctness (e.g., BLEU and ROUGE) or are limited in their interpretability (e.g., F1CheXpert and F1RadGraph). In this paper, we introduce GREEN (Generative Radiology Report Evaluation and Error Notation), a radiology report generation metric that leverages the natural language understanding of language models to identify and explain clinically significant errors in candidate reports, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Compared to current metrics, GREEN offers: 1) a score aligned with expert preferences, 2) human interpretable explanations of clinically significant errors, enabling feedback loops with end-users, and 3) a lightweight open-source method that reaches the performance of commercial counterparts. We validate our GREEN metric by comparing it to GPT-4, as well as to error counts of 6 experts and preferences of 2 experts. Our method demonstrates not only higher correlation with expert error counts, but simultaneously higher alignment with expert preferences when compared to previous approaches."
HeAR -- Health Acoustic Representations
Mar 04, 2024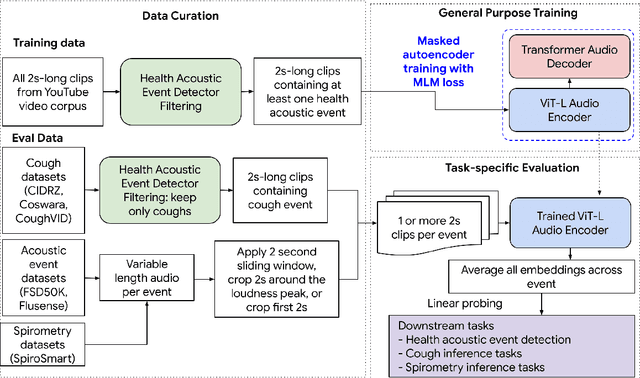
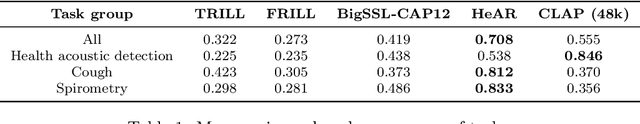
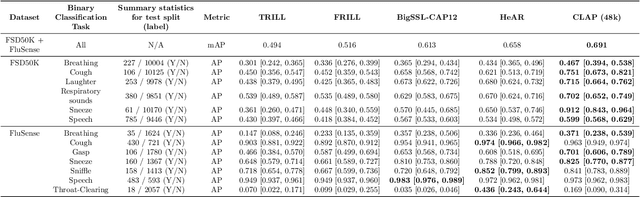
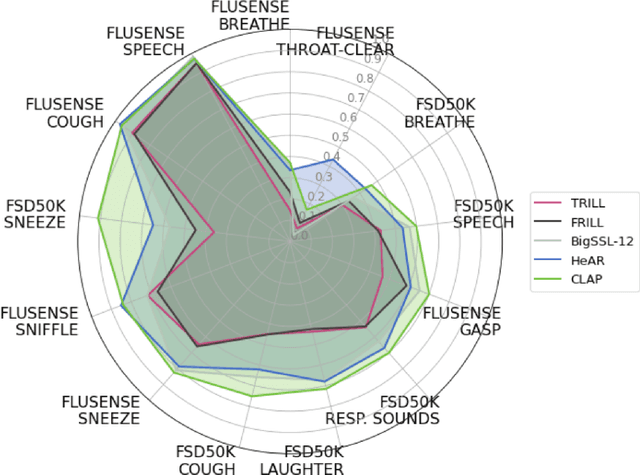
Abstract:Health acoustic sounds such as coughs and breaths are known to contain useful health signals with significant potential for monitoring health and disease, yet are underexplored in the medical machine learning community. The existing deep learning systems for health acoustics are often narrowly trained and evaluated on a single task, which is limited by data and may hinder generalization to other tasks. To mitigate these gaps, we develop HeAR, a scalable self-supervised learning-based deep learning system using masked autoencoders trained on a large dataset of 313 million two-second long audio clips. Through linear probes, we establish HeAR as a state-of-the-art health audio embedding model on a benchmark of 33 health acoustic tasks across 6 datasets. By introducing this work, we hope to enable and accelerate further health acoustics research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge