Kun Yi
MTP: Exploring Multimodal Urban Traffic Profiling with Modality Augmentation and Spectrum Fusion
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:With rapid urbanization in the modern era, traffic signals from various sensors have been playing a significant role in monitoring the states of cities, which provides a strong foundation in ensuring safe travel, reducing traffic congestion and optimizing urban mobility. Most existing methods for traffic signal modeling often rely on the original data modality, i.e., numerical direct readings from the sensors in cities. However, this unimodal approach overlooks the semantic information existing in multimodal heterogeneous urban data in different perspectives, which hinders a comprehensive understanding of traffic signals and limits the accurate prediction of complex traffic dynamics. To address this problem, we propose a novel Multimodal framework, MTP, for urban Traffic Profiling, which learns multimodal features through numeric, visual, and textual perspectives. The three branches drive for a multimodal perspective of urban traffic signal learning in the frequency domain, while the frequency learning strategies delicately refine the information for extraction. Specifically, we first conduct the visual augmentation for the traffic signals, which transforms the original modality into frequency images and periodicity images for visual learning. Also, we augment descriptive texts for the traffic signals based on the specific topic, background information and item description for textual learning. To complement the numeric information, we utilize frequency multilayer perceptrons for learning on the original modality. We design a hierarchical contrastive learning on the three branches to fuse the spectrum of three modalities. Finally, extensive experiments on six real-world datasets demonstrate superior performance compared with the state-of-the-art approaches.
MedGNN: Towards Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Graph Learning for Medical Time Series Classification
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Medical time series has been playing a vital role in real-world healthcare systems as valuable information in monitoring health conditions of patients. Accurate classification for medical time series, e.g., Electrocardiography (ECG) signals, can help for early detection and diagnosis. Traditional methods towards medical time series classification rely on handcrafted feature extraction and statistical methods; with the recent advancement of artificial intelligence, the machine learning and deep learning methods have become more popular. However, existing methods often fail to fully model the complex spatial dynamics under different scales, which ignore the dynamic multi-resolution spatial and temporal joint inter-dependencies. Moreover, they are less likely to consider the special baseline wander problem as well as the multi-view characteristics of medical time series, which largely hinders their prediction performance. To address these limitations, we propose a Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Graph Learning framework, MedGNN, for medical time series classification. Specifically, we first propose to construct multi-resolution adaptive graph structures to learn dynamic multi-scale embeddings. Then, to address the baseline wander problem, we propose Difference Attention Networks to operate self-attention mechanisms on the finite difference for temporal modeling. Moreover, to learn the multi-view characteristics, we utilize the Frequency Convolution Networks to capture complementary information of medical time series from the frequency domain. In addition, we introduce the Multi-resolution Graph Transformer architecture to model the dynamic dependencies and fuse the information from different resolutions. Finally, we have conducted extensive experiments on multiple medical real-world datasets that demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Our Code is available.
Amplifier: Bringing Attention to Neglected Low-Energy Components in Time Series Forecasting
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:We propose an energy amplification technique to address the issue that existing models easily overlook low-energy components in time series forecasting. This technique comprises an energy amplification block and an energy restoration block. The energy amplification block enhances the energy of low-energy components to improve the model's learning efficiency for these components, while the energy restoration block returns the energy to its original level. Moreover, considering that the energy-amplified data typically displays two distinct energy peaks in the frequency spectrum, we integrate the energy amplification technique with a seasonal-trend forecaster to model the temporal relationships of these two peaks independently, serving as the backbone for our proposed model, Amplifier. Additionally, we propose a semi-channel interaction temporal relationship enhancement block for Amplifier, which enhances the model's ability to capture temporal relationships from the perspective of the commonality and specificity of each channel in the data. Extensive experiments on eight time series forecasting benchmarks consistently demonstrate our model's superiority in both effectiveness and efficiency compared to state-of-the-art methods.
FilterNet: Harnessing Frequency Filters for Time Series Forecasting
Nov 05, 2024

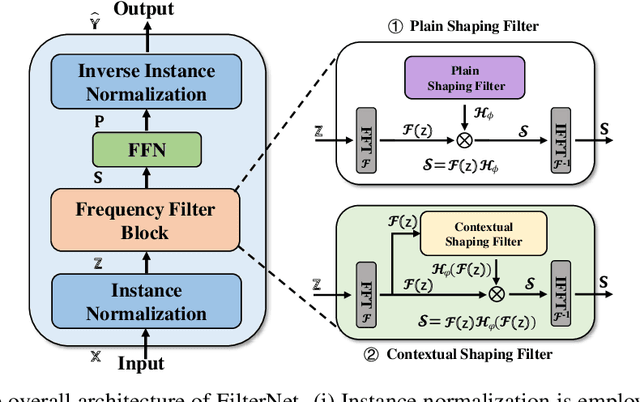

Abstract:While numerous forecasters have been proposed using different network architectures, the Transformer-based models have state-of-the-art performance in time series forecasting. However, forecasters based on Transformers are still suffering from vulnerability to high-frequency signals, efficiency in computation, and bottleneck in full-spectrum utilization, which essentially are the cornerstones for accurately predicting time series with thousands of points. In this paper, we explore a novel perspective of enlightening signal processing for deep time series forecasting. Inspired by the filtering process, we introduce one simple yet effective network, namely FilterNet, built upon our proposed learnable frequency filters to extract key informative temporal patterns by selectively passing or attenuating certain components of time series signals. Concretely, we propose two kinds of learnable filters in the FilterNet: (i) Plain shaping filter, that adopts a universal frequency kernel for signal filtering and temporal modeling; (ii) Contextual shaping filter, that utilizes filtered frequencies examined in terms of its compatibility with input signals for dependency learning. Equipped with the two filters, FilterNet can approximately surrogate the linear and attention mappings widely adopted in time series literature, while enjoying superb abilities in handling high-frequency noises and utilizing the whole frequency spectrum that is beneficial for forecasting. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on eight time series forecasting benchmarks, and experimental results have demonstrated our superior performance in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency compared with state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at this repository: https://github.com/aikunyi/FilterNet
Robust Multivariate Time Series Forecasting against Intra- and Inter-Series Transitional Shift
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:The non-stationary nature of real-world Multivariate Time Series (MTS) data presents forecasting models with a formidable challenge of the time-variant distribution of time series, referred to as distribution shift. Existing studies on the distribution shift mostly adhere to adaptive normalization techniques for alleviating temporal mean and covariance shifts or time-variant modeling for capturing temporal shifts. Despite improving model generalization, these normalization-based methods often assume a time-invariant transition between outputs and inputs but disregard specific intra-/inter-series correlations, while time-variant models overlook the intrinsic causes of the distribution shift. This limits model expressiveness and interpretability of tackling the distribution shift for MTS forecasting. To mitigate such a dilemma, we present a unified Probabilistic Graphical Model to Jointly capturing intra-/inter-series correlations and modeling the time-variant transitional distribution, and instantiate a neural framework called JointPGM for non-stationary MTS forecasting. Specifically, JointPGM first employs multiple Fourier basis functions to learn dynamic time factors and designs two distinct learners: intra-series and inter-series learners. The intra-series learner effectively captures temporal dynamics by utilizing temporal gates, while the inter-series learner explicitly models spatial dynamics through multi-hop propagation, incorporating Gumbel-softmax sampling. These two types of series dynamics are subsequently fused into a latent variable, which is inversely employed to infer time factors, generate final prediction, and perform reconstruction. We validate the effectiveness and efficiency of JointPGM through extensive experiments on six highly non-stationary MTS datasets, achieving state-of-the-art forecasting performance of MTS forecasting.
Deep Frequency Derivative Learning for Non-stationary Time Series Forecasting
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:While most time series are non-stationary, it is inevitable for models to face the distribution shift issue in time series forecasting. Existing solutions manipulate statistical measures (usually mean and std.) to adjust time series distribution. However, these operations can be theoretically seen as the transformation towards zero frequency component of the spectrum which cannot reveal full distribution information and would further lead to information utilization bottleneck in normalization, thus hindering forecasting performance. To address this problem, we propose to utilize the whole frequency spectrum to transform time series to make full use of data distribution from the frequency perspective. We present a deep frequency derivative learning framework, DERITS, for non-stationary time series forecasting. Specifically, DERITS is built upon a novel reversible transformation, namely Frequency Derivative Transformation (FDT) that makes signals derived in the frequency domain to acquire more stationary frequency representations. Then, we propose the Order-adaptive Fourier Convolution Network to conduct adaptive frequency filtering and learning. Furthermore, we organize DERITS as a parallel-stacked architecture for the multi-order derivation and fusion for forecasting. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on several datasets which show the consistent superiority in both time series forecasting and shift alleviation.
MLIP: Efficient Multi-Perspective Language-Image Pretraining with Exhaustive Data Utilization
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has achieved remarkable success, leading to rapid advancements in multimodal studies. However, CLIP faces a notable challenge in terms of inefficient data utilization. It relies on a single contrastive supervision for each image-text pair during representation learning, disregarding a substantial amount of valuable information that could offer richer supervision. Additionally, the retention of non-informative tokens leads to increased computational demands and time costs, particularly in CLIP's ViT image encoder. To address these issues, we propose Multi-Perspective Language-Image Pretraining (MLIP). In MLIP, we leverage the frequency transform's sensitivity to both high and low-frequency variations, which complements the spatial domain's sensitivity limited to low-frequency variations only. By incorporating frequency transforms and token-level alignment, we expand CILP's single supervision into multi-domain and multi-level supervision, enabling a more thorough exploration of informative image features. Additionally, we introduce a token merging method guided by comprehensive semantics from the frequency and spatial domains. This allows us to merge tokens to multi-granularity tokens with a controllable compression rate to accelerate CLIP. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our design.
SEED-X: Multimodal Models with Unified Multi-granularity Comprehension and Generation
Apr 22, 2024Abstract:The rapid evolution of multimodal foundation model has demonstrated significant progresses in vision-language understanding and generation, e.g., our previous work SEED-LLaMA. However, there remains a gap between its capability and the real-world applicability, primarily due to the model's limited capacity to effectively respond to various user instructions and interact with diverse visual data. In this work, we focus on bridging this gap through integrating two enhanced features: (1) comprehending images of arbitrary sizes and ratios, and (2) enabling multi-granularity image generation. We present a unified and versatile foundation model, namely, SEED-X, which is able to model multi-granularity visual semantics for comprehension and generation tasks. Besides the competitive results on public benchmarks, SEED-X demonstrates its effectiveness in handling real-world applications across various domains after instruction tuning. We hope that our work will inspire future research into what can be achieved by versatile multimodal foundation models in real-world applications. The models, codes, and datasets will be released in https://github.com/AILab-CVC/SEED-X.
Wills Aligner: A Robust Multi-Subject Brain Representation Learner
Apr 20, 2024



Abstract:Decoding visual information from human brain activity has seen remarkable advancements in recent research. However, due to the significant variability in cortical parcellation and cognition patterns across subjects, current approaches personalized deep models for each subject, constraining the practicality of this technology in real-world contexts. To tackle the challenges, we introduce Wills Aligner, a robust multi-subject brain representation learner. Our Wills Aligner initially aligns different subjects' brains at the anatomical level. Subsequently, it incorporates a mixture of brain experts to learn individual cognition patterns. Additionally, it decouples the multi-subject learning task into a two-stage training, propelling the deep model and its plugin network to learn inter-subject commonality knowledge and various cognition patterns, respectively. Wills Aligner enables us to overcome anatomical differences and to efficiently leverage a single model for multi-subject brain representation learning. We meticulously evaluate the performance of our approach across coarse-grained and fine-grained visual decoding tasks. The experimental results demonstrate that our Wills Aligner achieves state-of-the-art performance.
HyDiscGAN: A Hybrid Distributed cGAN for Audio-Visual Privacy Preservation in Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) aims to identify speakers' sentiment tendencies in multimodal video content, raising serious concerns about privacy risks associated with multimodal data, such as voiceprints and facial images. Recent distributed collaborative learning has been verified as an effective paradigm for privacy preservation in multimodal tasks. However, they often overlook the privacy distinctions among different modalities, struggling to strike a balance between performance and privacy preservation. Consequently, it poses an intriguing question of maximizing multimodal utilization to improve performance while simultaneously protecting necessary modalities. This paper forms the first attempt at modality-specified (i.e., audio and visual) privacy preservation in MSA tasks. We propose a novel Hybrid Distributed cross-modality cGAN framework (HyDiscGAN), which learns multimodality alignment to generate fake audio and visual features conditioned on shareable de-identified textual data. The objective is to leverage the fake features to approximate real audio and visual content to guarantee privacy preservation while effectively enhancing performance. Extensive experiments show that compared with the state-of-the-art MSA model, HyDiscGAN can achieve superior or competitive performance while preserving privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge