Liang Hu
AppleVLM: End-to-end Autonomous Driving with Advanced Perception and Planning-Enhanced Vision-Language Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving has emerged as a promising paradigm integrating perception, decision-making, and control within a unified learning framework. Recently, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have gained significant attention for their potential to enhance the robustness and generalization of end-to-end driving models in diverse and unseen scenarios. However, existing VLM-based approaches still face challenges, including suboptimal lane perception, language understanding biases, and difficulties in handling corner cases. To address these issues, we propose AppleVLM, an advanced perception and planning-enhanced VLM model for robust end-to-end driving. AppleVLM introduces a novel vision encoder and a planning strategy encoder to improve perception and decision-making. Firstly, the vision encoder fuses spatial-temporal information from multi-view images across multiple timesteps using a deformable transformer mechanism, enhancing robustness to camera variations and facilitating scalable deployment across different vehicle platforms. Secondly, unlike traditional VLM-based approaches, AppleVLM introduces a dedicated planning modality that encodes explicit Bird's-Eye-View spatial information, mitigating language biases in navigation instructions. Finally, a VLM decoder fine-tuned by a hierarchical Chain-of-Thought integrates vision, language, and planning features to output robust driving waypoints. We evaluate AppleVLM in closed-loop experiments on two CARLA benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art driving performance. Furthermore, we deploy AppleVLM on an AGV platform and successfully showcase real-world end-to-end autonomous driving in complex outdoor environments.
FutureX-Pro: Extending Future Prediction to High-Value Vertical Domains
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Building upon FutureX, which established a live benchmark for general-purpose future prediction, this report introduces FutureX-Pro, including FutureX-Finance, FutureX-Retail, FutureX-PublicHealth, FutureX-NaturalDisaster, and FutureX-Search. These together form a specialized framework extending agentic future prediction to high-value vertical domains. While generalist agents demonstrate proficiency in open-domain search, their reliability in capital-intensive and safety-critical sectors remains under-explored. FutureX-Pro targets four economically and socially pivotal verticals: Finance, Retail, Public Health, and Natural Disaster. We benchmark agentic Large Language Models (LLMs) on entry-level yet foundational prediction tasks -- ranging from forecasting market indicators and supply chain demands to tracking epidemic trends and natural disasters. By adapting the contamination-free, live-evaluation pipeline of FutureX, we assess whether current State-of-the-Art (SOTA) agentic LLMs possess the domain grounding necessary for industrial deployment. Our findings reveal the performance gap between generalist reasoning and the precision required for high-value vertical applications.
AI for Mycetoma Diagnosis in Histopathological Images: The MICCAI 2024 Challenge
Dec 25, 2025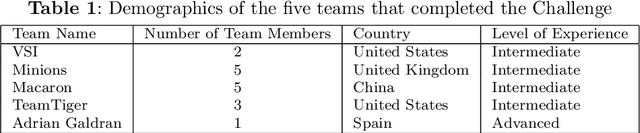
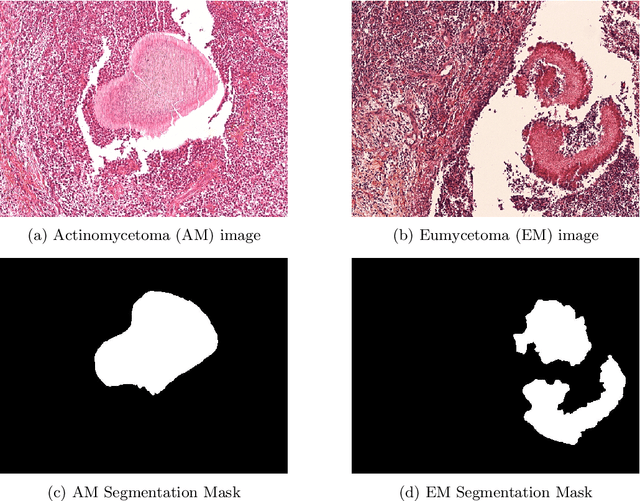

Abstract:Mycetoma is a neglected tropical disease caused by fungi or bacteria leading to severe tissue damage and disabilities. It affects poor and rural communities and presents medical challenges and socioeconomic burdens on patients and healthcare systems in endemic regions worldwide. Mycetoma diagnosis is a major challenge in mycetoma management, particularly in low-resource settings where expert pathologists are limited. To address this challenge, this paper presents an overview of the Mycetoma MicroImage: Detect and Classify Challenge (mAIcetoma) which was organized to advance mycetoma diagnosis through AI solutions. mAIcetoma focused on developing automated models for segmenting mycetoma grains and classifying mycetoma types from histopathological images. The challenge attracted the attention of several teams worldwide to participate and five finalist teams fulfilled the challenge objectives. The teams proposed various deep learning architectures for the ultimate goal of this challenge. Mycetoma database (MyData) was provided to participants as a standardized dataset to run the proposed models. Those models were evaluated using evaluation metrics. Results showed that all the models achieved high segmentation accuracy, emphasizing the necessitate of grain detection as a critical step in mycetoma diagnosis. In addition, the top-performing models show a significant performance in classifying mycetoma types.
DiscoX: Benchmarking Discourse-Level Translation task in Expert Domains
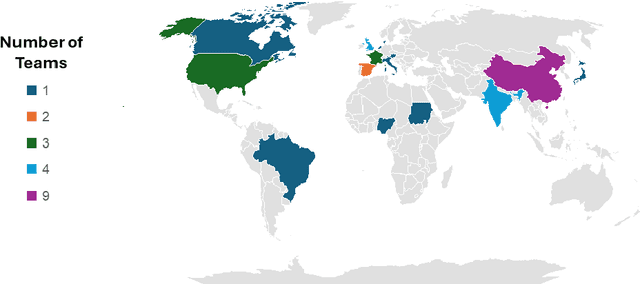
Nov 14, 2025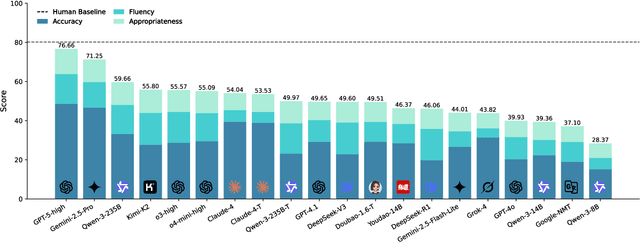
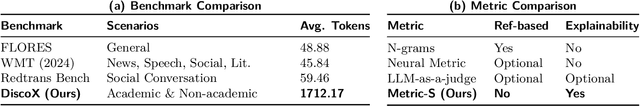
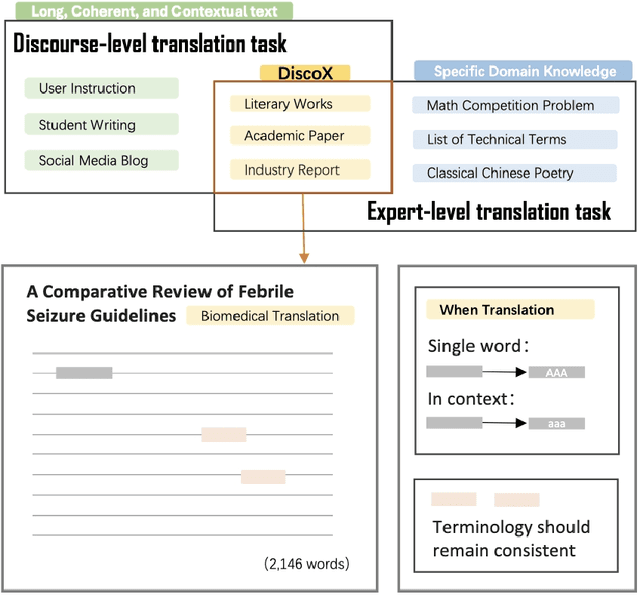
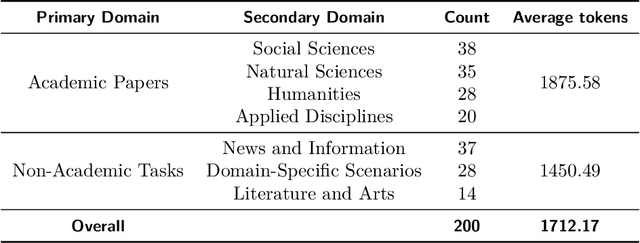
Abstract:The evaluation of discourse-level translation in expert domains remains inadequate, despite its centrality to knowledge dissemination and cross-lingual scholarly communication. While these translations demand discourse-level coherence and strict terminological precision, current evaluation methods predominantly focus on segment-level accuracy and fluency. To address this limitation, we introduce DiscoX, a new benchmark for discourse-level and expert-level Chinese-English translation. It comprises 200 professionally-curated texts from 7 domains, with an average length exceeding 1700 tokens. To evaluate performance on DiscoX, we also develop Metric-S, a reference-free system that provides fine-grained automatic assessments across accuracy, fluency, and appropriateness. Metric-S demonstrates strong consistency with human judgments, significantly outperforming existing metrics. Our experiments reveal a remarkable performance gap: even the most advanced LLMs still trail human experts on these tasks. This finding validates the difficulty of DiscoX and underscores the challenges that remain in achieving professional-grade machine translation. The proposed benchmark and evaluation system provide a robust framework for more rigorous evaluation, facilitating future advancements in LLM-based translation.
LPFQA: A Long-Tail Professional Forum-based Benchmark for LLM Evaluation
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in reasoning, question answering, and professional applications; however, their true capabilities remain difficult to evaluate using existing benchmarks. Current datasets often focus on simplified tasks or artificial scenarios, overlooking long-tail knowledge and the complexities of real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we propose LPFQA, a long-tail knowledge-based benchmark derived from authentic professional forums across 20 academic and industrial fields, covering 502 tasks grounded in practical expertise. LPFQA introduces four key innovations: fine-grained evaluation dimensions that target knowledge depth, reasoning, terminology comprehension, and contextual analysis; a hierarchical difficulty structure that ensures semantic clarity and unique answers; authentic professional scenario modeling with realistic user personas; and interdisciplinary knowledge integration across diverse domains. We evaluated 12 mainstream LLMs on LPFQA and observed significant performance disparities, especially in specialized reasoning tasks. LPFQA provides a robust, authentic, and discriminative benchmark for advancing LLM evaluation and guiding future model development.
GTR-Mamba: Geometry-to-Tangent Routing for Hyperbolic POI Recommendation
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation is a critical task in modern Location-Based Social Networks (LBSNs), aiming to model the complex decision-making process of human mobility to provide personalized recommendations for a user's next check-in location. Existing POI recommendation models, predominantly based on Graph Neural Networks and sequential models, have been extensively studied. However, these models face a fundamental limitation: they struggle to simultaneously capture the inherent hierarchical structure of spatial choices and the dynamics and irregular shifts of user-specific temporal contexts. To overcome this limitation, we propose GTR-Mamba, a novel framework for cross-manifold conditioning and routing. GTR-Mamba leverages the distinct advantages of different mathematical spaces for different tasks: it models the static, tree-like preference hierarchies in hyperbolic geometry, while routing the dynamic sequence updates to a novel Mamba layer in the computationally stable and efficient Euclidean tangent space. This process is coordinated by a cross-manifold channel that fuses spatio-temporal information to explicitly steer the State Space Model (SSM), enabling flexible adaptation to contextual changes. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that GTR-Mamba consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baseline models in next POI recommendation.
CUFG: Curriculum Unlearning Guided by the Forgetting Gradient
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:As privacy and security take center stage in AI, machine unlearning, the ability to erase specific knowledge from models, has garnered increasing attention. However, existing methods overly prioritize efficiency and aggressive forgetting, which introduces notable limitations. In particular, radical interventions like gradient ascent, influence functions, and random label noise can destabilize model weights, leading to collapse and reduced reliability. To address this, we propose CUFG (Curriculum Unlearning via Forgetting Gradients), a novel framework that enhances the stability of approximate unlearning through innovations in both forgetting mechanisms and data scheduling strategies. Specifically, CUFG integrates a new gradient corrector guided by forgetting gradients for fine-tuning-based unlearning and a curriculum unlearning paradigm that progressively forgets from easy to hard. These innovations narrow the gap with the gold-standard Retrain method by enabling more stable and progressive unlearning, thereby improving both effectiveness and reliability. Furthermore, we believe that the concept of curriculum unlearning has substantial research potential and offers forward-looking insights for the development of the MU field. Extensive experiments across various forgetting scenarios validate the rationale and effectiveness of our approach and CUFG. Codes are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CUFG-6375.
FinSearchComp: Towards a Realistic, Expert-Level Evaluation of Financial Search and Reasoning
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:Search has emerged as core infrastructure for LLM-based agents and is widely viewed as critical on the path toward more general intelligence. Finance is a particularly demanding proving ground: analysts routinely conduct complex, multi-step searches over time-sensitive, domain-specific data, making it ideal for assessing both search proficiency and knowledge-grounded reasoning. Yet no existing open financial datasets evaluate data searching capability of end-to-end agents, largely because constructing realistic, complicated tasks requires deep financial expertise and time-sensitive data is hard to evaluate. We present FinSearchComp, the first fully open-source agent benchmark for realistic, open-domain financial search and reasoning. FinSearchComp comprises three tasks -- Time-Sensitive Data Fetching, Simple Historical Lookup, and Complex Historical Investigation -- closely reproduce real-world financial analyst workflows. To ensure difficulty and reliability, we engage 70 professional financial experts for annotation and implement a rigorous multi-stage quality-assurance pipeline. The benchmark includes 635 questions spanning global and Greater China markets, and we evaluate 21 models (products) on it. Grok 4 (web) tops the global subset, approaching expert-level accuracy. DouBao (web) leads on the Greater China subset. Experimental analyses show that equipping agents with web search and financial plugins substantially improves results on FinSearchComp, and the country origin of models and tools impact performance significantly.By aligning with realistic analyst tasks and providing end-to-end evaluation, FinSearchComp offers a professional, high-difficulty testbed for complex financial search and reasoning.
Skywork UniPic 2.0: Building Kontext Model with Online RL for Unified Multimodal Model
Sep 04, 2025
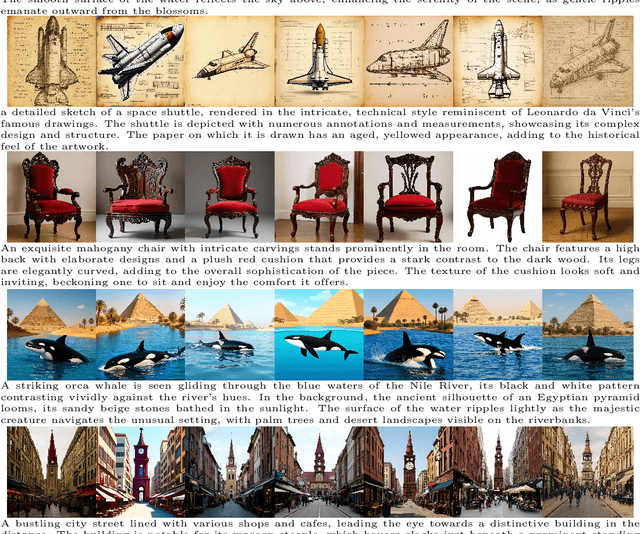
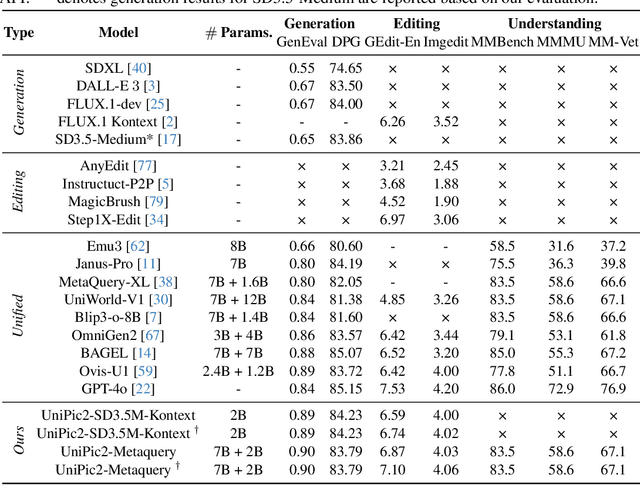
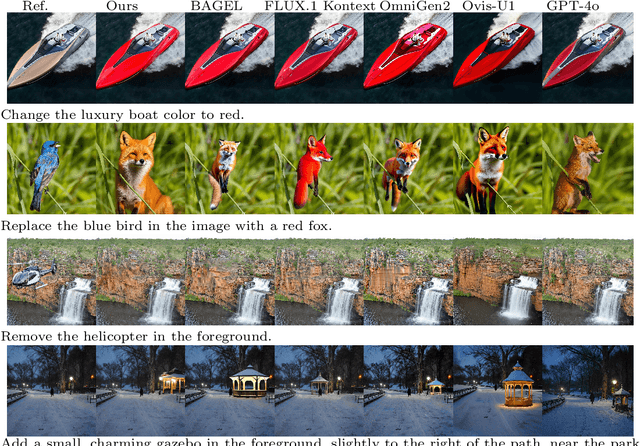
Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in unified image generation and editing. However, many prominent open-source models prioritize scaling model parameters over optimizing training strategies, limiting their efficiency and performance. In this work, we present UniPic2-SD3.5M-Kontext, a 2B-parameter DiT model based on SD3.5-Medium, which achieves state-of-the-art image generation and editing while extending seamlessly into a unified multimodal framework. Our approach begins with architectural modifications to SD3.5-Medium and large-scale pre-training on high-quality data, enabling joint text-to-image generation and editing capabilities. To enhance instruction following and editing consistency, we propose a novel Progressive Dual-Task Reinforcement strategy (PDTR), which effectively strengthens both tasks in a staged manner. We empirically validate that the reinforcement phases for different tasks are mutually beneficial and do not induce negative interference. After pre-training and reinforcement strategies, UniPic2-SD3.5M-Kontext demonstrates stronger image generation and editing capabilities than models with significantly larger generation parameters-including BAGEL (7B) and Flux-Kontext (12B). Furthermore, following the MetaQuery, we connect the UniPic2-SD3.5M-Kontext and Qwen2.5-VL-7B via a connector and perform joint training to launch a unified multimodal model UniPic2-Metaquery. UniPic2-Metaquery integrates understanding, generation, and editing, achieving top-tier performance across diverse tasks with a simple and scalable training paradigm. This consistently validates the effectiveness and generalizability of our proposed training paradigm, which we formalize as Skywork UniPic 2.0.
StructVRM: Aligning Multimodal Reasoning with Structured and Verifiable Reward Models
Aug 07, 2025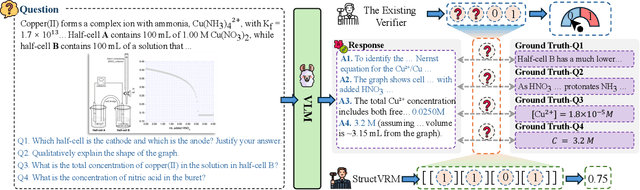

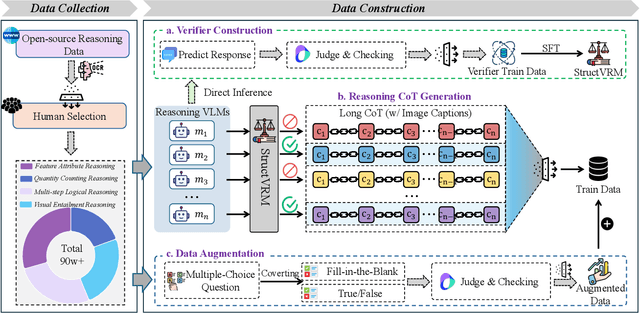
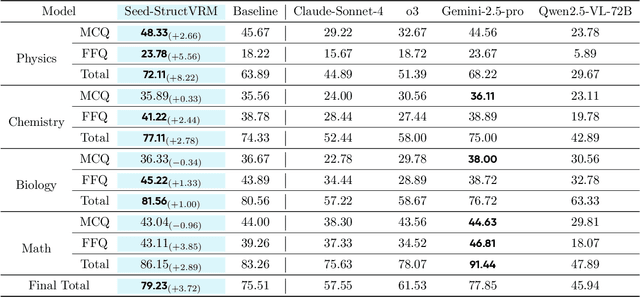
Abstract:Existing Vision-Language Models often struggle with complex, multi-question reasoning tasks where partial correctness is crucial for effective learning. Traditional reward mechanisms, which provide a single binary score for an entire response, are too coarse to guide models through intricate problems with multiple sub-parts. To address this, we introduce StructVRM, a method that aligns multimodal reasoning with Structured and Verifiable Reward Models. At its core is a model-based verifier trained to provide fine-grained, sub-question-level feedback, assessing semantic and mathematical equivalence rather than relying on rigid string matching. This allows for nuanced, partial credit scoring in previously intractable problem formats. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of StructVRM. Our trained model, Seed-StructVRM, achieves state-of-the-art performance on six out of twelve public multimodal benchmarks and our newly curated, high-difficulty STEM-Bench. The success of StructVRM validates that training with structured, verifiable rewards is a highly effective approach for advancing the capabilities of multimodal models in complex, real-world reasoning domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge