Jingru Fei
MedGNN: Towards Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Graph Learning for Medical Time Series Classification
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Medical time series has been playing a vital role in real-world healthcare systems as valuable information in monitoring health conditions of patients. Accurate classification for medical time series, e.g., Electrocardiography (ECG) signals, can help for early detection and diagnosis. Traditional methods towards medical time series classification rely on handcrafted feature extraction and statistical methods; with the recent advancement of artificial intelligence, the machine learning and deep learning methods have become more popular. However, existing methods often fail to fully model the complex spatial dynamics under different scales, which ignore the dynamic multi-resolution spatial and temporal joint inter-dependencies. Moreover, they are less likely to consider the special baseline wander problem as well as the multi-view characteristics of medical time series, which largely hinders their prediction performance. To address these limitations, we propose a Multi-resolution Spatiotemporal Graph Learning framework, MedGNN, for medical time series classification. Specifically, we first propose to construct multi-resolution adaptive graph structures to learn dynamic multi-scale embeddings. Then, to address the baseline wander problem, we propose Difference Attention Networks to operate self-attention mechanisms on the finite difference for temporal modeling. Moreover, to learn the multi-view characteristics, we utilize the Frequency Convolution Networks to capture complementary information of medical time series from the frequency domain. In addition, we introduce the Multi-resolution Graph Transformer architecture to model the dynamic dependencies and fuse the information from different resolutions. Finally, we have conducted extensive experiments on multiple medical real-world datasets that demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Our Code is available.
Amplifier: Bringing Attention to Neglected Low-Energy Components in Time Series Forecasting
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:We propose an energy amplification technique to address the issue that existing models easily overlook low-energy components in time series forecasting. This technique comprises an energy amplification block and an energy restoration block. The energy amplification block enhances the energy of low-energy components to improve the model's learning efficiency for these components, while the energy restoration block returns the energy to its original level. Moreover, considering that the energy-amplified data typically displays two distinct energy peaks in the frequency spectrum, we integrate the energy amplification technique with a seasonal-trend forecaster to model the temporal relationships of these two peaks independently, serving as the backbone for our proposed model, Amplifier. Additionally, we propose a semi-channel interaction temporal relationship enhancement block for Amplifier, which enhances the model's ability to capture temporal relationships from the perspective of the commonality and specificity of each channel in the data. Extensive experiments on eight time series forecasting benchmarks consistently demonstrate our model's superiority in both effectiveness and efficiency compared to state-of-the-art methods.
FilterNet: Harnessing Frequency Filters for Time Series Forecasting
Nov 05, 2024

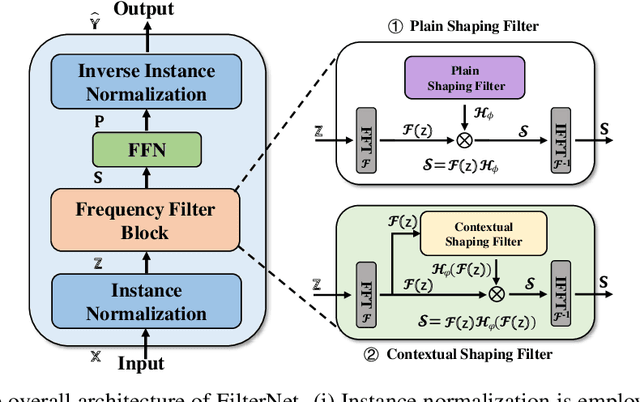

Abstract:While numerous forecasters have been proposed using different network architectures, the Transformer-based models have state-of-the-art performance in time series forecasting. However, forecasters based on Transformers are still suffering from vulnerability to high-frequency signals, efficiency in computation, and bottleneck in full-spectrum utilization, which essentially are the cornerstones for accurately predicting time series with thousands of points. In this paper, we explore a novel perspective of enlightening signal processing for deep time series forecasting. Inspired by the filtering process, we introduce one simple yet effective network, namely FilterNet, built upon our proposed learnable frequency filters to extract key informative temporal patterns by selectively passing or attenuating certain components of time series signals. Concretely, we propose two kinds of learnable filters in the FilterNet: (i) Plain shaping filter, that adopts a universal frequency kernel for signal filtering and temporal modeling; (ii) Contextual shaping filter, that utilizes filtered frequencies examined in terms of its compatibility with input signals for dependency learning. Equipped with the two filters, FilterNet can approximately surrogate the linear and attention mappings widely adopted in time series literature, while enjoying superb abilities in handling high-frequency noises and utilizing the whole frequency spectrum that is beneficial for forecasting. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on eight time series forecasting benchmarks, and experimental results have demonstrated our superior performance in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency compared with state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at this repository: https://github.com/aikunyi/FilterNet
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge