Kexin Wang
Multi-context principal component analysis
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Principal component analysis (PCA) is a tool to capture factors that explain variation in data. Across domains, data are now collected across multiple contexts (for example, individuals with different diseases, cells of different types, or words across texts). While the factors explaining variation in data are undoubtedly shared across subsets of contexts, no tools currently exist to systematically recover such factors. We develop multi-context principal component analysis (MCPCA), a theoretical and algorithmic framework that decomposes data into factors shared across subsets of contexts. Applied to gene expression, MCPCA reveals axes of variation shared across subsets of cancer types and an axis whose variability in tumor cells, but not mean, is associated with lung cancer progression. Applied to contextualized word embeddings from language models, MCPCA maps stages of a debate on human nature, revealing a discussion between science and fiction over decades. These axes are not found by combining data across contexts or by restricting to individual contexts. MCPCA is a principled generalization of PCA to address the challenge of understanding factors underlying data across contexts.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
Physics-Constrained Diffusion Reconstruction with Posterior Correction for Quantitative and Fast PET Imaging
Aug 20, 2025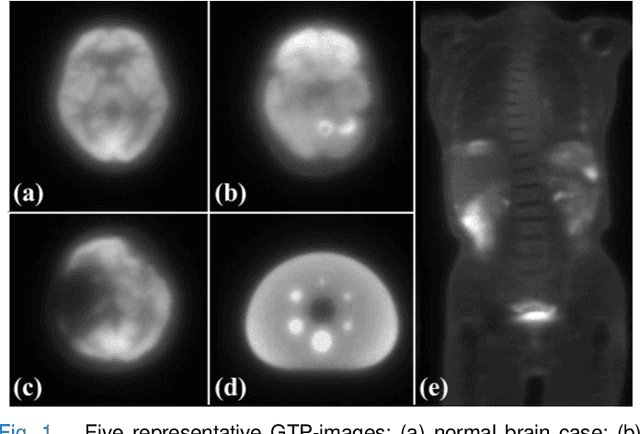
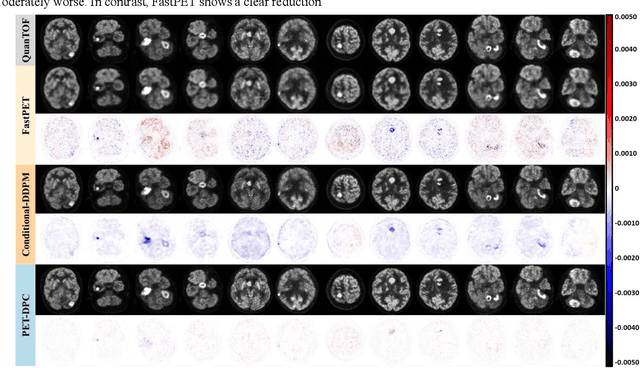
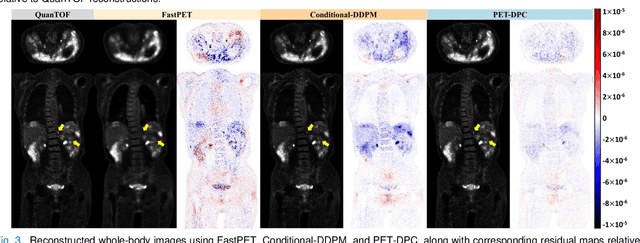
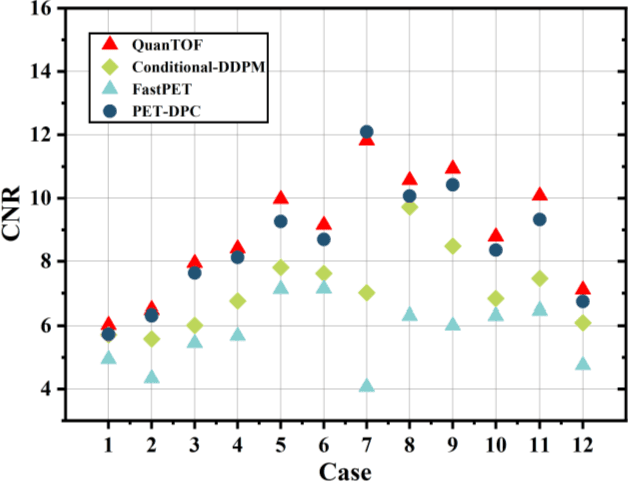
Abstract:Deep learning-based reconstruction of positron emission tomography(PET) data has gained increasing attention in recent years. While these methods achieve fast reconstruction,concerns remain regarding quantitative accuracy and the presence of artifacts,stemming from limited model interpretability,data driven dependence, and overfitting risks.These challenges have hindered clinical adoption.To address them,we propose a conditional diffusion model with posterior physical correction (PET-DPC) for PET image reconstruction. An innovative normalization procedure generates the input Geometric TOF Probabilistic Image (GTP-image),while physical information is incorporated during the diffusion sampling process to perform posterior scatter,attenuation,and random corrections. The model was trained and validated on 300 brain and 50 whole-body PET datasets,a physical phantom,and 20 simulated brain datasets. PET-DPC produced reconstructions closely aligned with fully corrected OSEM images,outperforming end-to-end deep learning models in quantitative metrics and,in some cases, surpassing traditional iterative methods. The model also generalized well to out-of-distribution(OOD) data. Compared to iterative methods,PET-DPC reduced reconstruction time by 50% for brain scans and 85% for whole-body scans. Ablation studies confirmed the critical role of posterior correction in implementing scatter and attenuation corrections,enhancing reconstruction accuracy. Experiments with physical phantoms further demonstrated PET-DPC's ability to preserve background uniformity and accurately reproduce tumor-to-background intensity ratios. Overall,these results highlight PET-DPC as a promising approach for rapid, quantitatively accurate PET reconstruction,with strong potential to improve clinical imaging workflows.
A Curriculum Learning Approach to Reinforcement Learning: Leveraging RAG for Multimodal Question Answering
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:This paper describes the solutions of the Dianping-Trust-Safety team for the META CRAG-MM challenge. The challenge requires building a comprehensive retrieval-augmented generation system capable for multi-modal multi-turn question answering. The competition consists of three tasks: (1) answering questions using structured data retrieved from an image-based mock knowledge graph, (2) synthesizing information from both knowledge graphs and web search results, and (3) handling multi-turn conversations that require context understanding and information aggregation from multiple sources. For Task 1, our solution is based on the vision large language model, enhanced by supervised fine-tuning with knowledge distilled from GPT-4.1. We further applied curriculum learning strategies to guide reinforcement learning, resulting in improved answer accuracy and reduced hallucination. For Task 2 and Task 3, we additionally leveraged web search APIs to incorporate external knowledge, enabling the system to better handle complex queries and multi-turn conversations. Our approach achieved 1st place in Task 1 with a significant lead of 52.38\%, and 3rd place in Task 3, demonstrating the effectiveness of the integration of curriculum learning with reinforcement learning in our training pipeline.
Dynamic Graph-Like Learning with Contrastive Clustering on Temporally-Factored Ship Motion Data for Imbalanced Sea State Estimation in Autonomous Vessel
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Accurate sea state estimation is crucial for the real-time control and future state prediction of autonomous vessels. However, traditional methods struggle with challenges such as data imbalance and feature redundancy in ship motion data, limiting their effectiveness. To address these challenges, we propose the Temporal-Graph Contrastive Clustering Sea State Estimator (TGC-SSE), a novel deep learning model that combines three key components: a time dimension factorization module to reduce data redundancy, a dynamic graph-like learning module to capture complex variable interactions, and a contrastive clustering loss function to effectively manage class imbalance. Our experiments demonstrate that TGC-SSE significantly outperforms existing methods across 14 public datasets, achieving the highest accuracy in 9 datasets, with a 20.79% improvement over EDI. Furthermore, in the field of sea state estimation, TGC-SSE surpasses five benchmark methods and seven deep learning models. Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of each module, demonstrating their respective roles in enhancing overall model performance. Overall, TGC-SSE not only improves the accuracy of sea state estimation but also exhibits strong generalization capabilities, providing reliable support for autonomous vessel operations.
MetaLA: Unified Optimal Linear Approximation to Softmax Attention Map
Nov 16, 2024



Abstract:Various linear complexity models, such as Linear Transformer (LinFormer), State Space Model (SSM), and Linear RNN (LinRNN), have been proposed to replace the conventional softmax attention in Transformer structures. However, the optimal design of these linear models is still an open question. In this work, we attempt to answer this question by finding the best linear approximation to softmax attention from a theoretical perspective. We start by unifying existing linear complexity models as the linear attention form and then identify three conditions for the optimal linear attention design: 1) Dynamic memory ability; 2) Static approximation ability; 3) Least parameter approximation. We find that none of the current linear models meet all three conditions, resulting in suboptimal performance. Instead, we propose Meta Linear Attention (MetaLA) as a solution that satisfies these conditions. Our experiments on Multi-Query Associative Recall (MQAR) task, language modeling, image classification, and Long-Range Arena (LRA) benchmark demonstrate that MetaLA is more effective than the existing linear models.
RegNLP in Action: Facilitating Compliance Through Automated Information Retrieval and Answer Generation
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:Regulatory documents, issued by governmental regulatory bodies, establish rules, guidelines, and standards that organizations must adhere to for legal compliance. These documents, characterized by their length, complexity and frequent updates, are challenging to interpret, requiring significant allocation of time and expertise on the part of organizations to ensure ongoing compliance.Regulatory Natural Language Processing (RegNLP) is a multidisciplinary subfield aimed at simplifying access to and interpretation of regulatory rules and obligations. We define an Automated Question-Passage Generation task for RegNLP, create the ObliQA dataset containing 27,869 questions derived from the Abu Dhabi Global Markets (ADGM) financial regulation document collection, design a baseline Regulatory Information Retrieval and Answer Generation system, and evaluate it with RePASs, a novel evaluation metric that tests whether generated answers accurately capture all relevant obligations and avoid contradictions.
Exploring Fungal Morphology Simulation and Dynamic Light Containment from a Graphics Generation Perspective
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:Fungal simulation and control are considered crucial techniques in Bio-Art creation. However, coding algorithms for reliable fungal simulations have posed significant challenges for artists. This study equates fungal morphology simulation to a two-dimensional graphic time-series generation problem. We propose a zero-coding, neural network-driven cellular automaton. Fungal spread patterns are learned through an image segmentation model and a time-series prediction model, which then supervise the training of neural network cells, enabling them to replicate real-world spreading behaviors. We further implemented dynamic containment of fungal boundaries with lasers. Synchronized with the automaton, the fungus successfully spreads into pre-designed complex shapes in reality.
Scalable Autoregressive Image Generation with Mamba
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:We introduce AiM, an autoregressive (AR) image generative model based on Mamba architecture. AiM employs Mamba, a novel state-space model characterized by its exceptional performance for long-sequence modeling with linear time complexity, to supplant the commonly utilized Transformers in AR image generation models, aiming to achieve both superior generation quality and enhanced inference speed. Unlike existing methods that adapt Mamba to handle two-dimensional signals via multi-directional scan, AiM directly utilizes the next-token prediction paradigm for autoregressive image generation. This approach circumvents the need for extensive modifications to enable Mamba to learn 2D spatial representations. By implementing straightforward yet strategically targeted modifications for visual generative tasks, we preserve Mamba's core structure, fully exploiting its efficient long-sequence modeling capabilities and scalability. We provide AiM models in various scales, with parameter counts ranging from 148M to 1.3B. On the ImageNet1K 256*256 benchmark, our best AiM model achieves a FID of 2.21, surpassing all existing AR models of comparable parameter counts and demonstrating significant competitiveness against diffusion models, with 2 to 10 times faster inference speed. Code is available at https://github.com/hp-l33/AiM
Modular Sentence Encoders: Separating Language Specialization from Cross-Lingual Alignment
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Multilingual sentence encoders are commonly obtained by training multilingual language models to map sentences from different languages into a shared semantic space. As such, they are subject to curse of multilinguality, a loss of monolingual representational accuracy due to parameter sharing. Another limitation of multilingual sentence encoders is the trade-off between monolingual and cross-lingual performance. Training for cross-lingual alignment of sentence embeddings distorts the optimal monolingual structure of semantic spaces of individual languages, harming the utility of sentence embeddings in monolingual tasks. In this work, we address both issues by modular training of sentence encoders, i.e., by separating monolingual specialization from cross-lingual alignment. We first efficiently train language-specific sentence encoders to avoid negative interference between languages (i.e., the curse). We then align all non-English monolingual encoders to the English encoder by training a cross-lingual alignment adapter on top of each, preventing interference with monolingual specialization from the first step. In both steps, we resort to contrastive learning on machine-translated paraphrase data. Monolingual and cross-lingual evaluations on semantic text similarity/relatedness and multiple-choice QA render our modular solution more effective than multilingual sentence encoders, especially benefiting low-resource languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge