Jinsong Zhang
Multimodal Mixture of Low-Rank Experts for Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Recognition
May 20, 2025Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) enables the efficient transfer of extra knowledge acquired from other tasks. The high correlation between multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) and multimodal emotion recognition (MER) supports their joint training. However, existing methods primarily employ hard parameter sharing, ignoring parameter conflicts caused by complex task correlations. In this paper, we present a novel MTL method for MSA and MER, termed Multimodal Mixture of Low-Rank Experts (MMoLRE). MMoLRE utilizes shared and task-specific experts to distinctly model common and unique task characteristics, thereby avoiding parameter conflicts. Additionally, inspired by low-rank structures in the Mixture of Experts (MoE) framework, we design low-rank expert networks to reduce parameter and computational overhead as the number of experts increases. Extensive experiments on the CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI benchmarks demonstrate that MMoLRE achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MSA task and competitive results on the MER task.
SpeechAct: Towards Generating Whole-body Motion from Speech
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of generating whole-body motion from speech. Despite great successes, prior methods still struggle to produce reasonable and diverse whole-body motions from speech. This is due to their reliance on suboptimal representations and a lack of strategies for generating diverse results. To address these challenges, we present a novel hybrid point representation to achieve accurate and continuous motion generation, e.g., avoiding foot skating, and this representation can be transformed into an easy-to-use representation, i.e., SMPL-X body mesh, for many applications. To generate whole-body motion from speech, for facial motion, closely tied to the audio signal, we introduce an encoder-decoder architecture to achieve deterministic outcomes. However, for the body and hands, which have weaker connections to the audio signal, we aim to generate diverse yet reasonable motions. To boost diversity in motion generation, we propose a contrastive motion learning method to encourage the model to produce more distinctive representations. Specifically, we design a robust VQ-VAE to learn a quantized motion codebook using our hybrid representation. Then, we regress the motion representation from the audio signal by a translation model employing our contrastive motion learning method. Experimental results validate the superior performance and the correctness of our model. The project page is available for research purposes at http://cic.tju.edu.cn/faculty/likun/projects/SpeechAct.
High-Quality Animatable Dynamic Garment Reconstruction from Monocular Videos
Nov 02, 2023
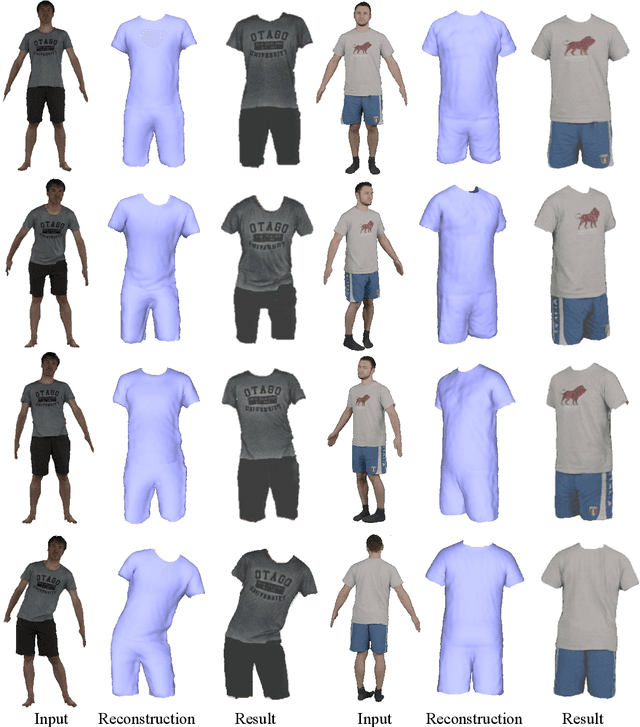
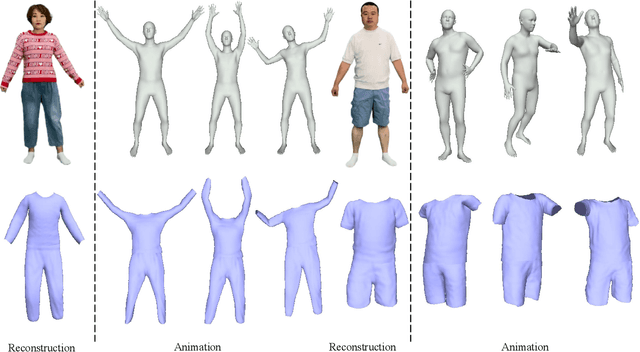

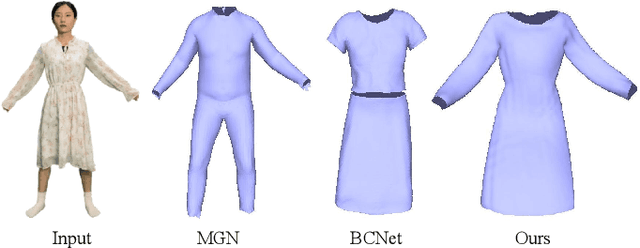
Abstract:Much progress has been made in reconstructing garments from an image or a video. However, none of existing works meet the expectations of digitizing high-quality animatable dynamic garments that can be adjusted to various unseen poses. In this paper, we propose the first method to recover high-quality animatable dynamic garments from monocular videos without depending on scanned data. To generate reasonable deformations for various unseen poses, we propose a learnable garment deformation network that formulates the garment reconstruction task as a pose-driven deformation problem. To alleviate the ambiguity estimating 3D garments from monocular videos, we design a multi-hypothesis deformation module that learns spatial representations of multiple plausible deformations. Experimental results on several public datasets demonstrate that our method can reconstruct high-quality dynamic garments with coherent surface details, which can be easily animated under unseen poses. The code will be provided for research purposes.
Towards Grouping in Large Scenes with Occlusion-aware Spatio-temporal Transformers
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Group detection, especially for large-scale scenes, has many potential applications for public safety and smart cities. Existing methods fail to cope with frequent occlusions in large-scale scenes with multiple people, and are difficult to effectively utilize spatio-temporal information. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end framework,GroupTransformer, for group detection in large-scale scenes. To deal with the frequent occlusions caused by multiple people, we design an occlusion encoder to detect and suppress severely occluded person crops. To explore the potential spatio-temporal relationship, we propose spatio-temporal transformers to simultaneously extract trajectory information and fuse inter-person features in a hierarchical manner. Experimental results on both large-scale and small-scale scenes demonstrate that our method achieves better performance compared with state-of-the-art methods. On large-scale scenes, our method significantly boosts the performance in terms of precision and F1 score by more than 10%. On small-scale scenes, our method still improves the performance of F1 score by more than 5%. The project page with code can be found at http://cic.tju.edu.cn/faculty/likun/projects/GroupTrans.
* 11 pages, 5 figures
Narrator: Towards Natural Control of Human-Scene Interaction Generation via Relationship Reasoning
Mar 16, 2023



Abstract:Naturally controllable human-scene interaction (HSI) generation has an important role in various fields, such as VR/AR content creation and human-centered AI. However, existing methods are unnatural and unintuitive in their controllability, which heavily limits their application in practice. Therefore, we focus on a challenging task of naturally and controllably generating realistic and diverse HSIs from textual descriptions. From human cognition, the ideal generative model should correctly reason about spatial relationships and interactive actions. To that end, we propose Narrator, a novel relationship reasoning-based generative approach using a conditional variation autoencoder for naturally controllable generation given a 3D scene and a textual description. Also, we model global and local spatial relationships in a 3D scene and a textual description respectively based on the scene graph, and introduce a partlevel action mechanism to represent interactions as atomic body part states. In particular, benefiting from our relationship reasoning, we further propose a simple yet effective multi-human generation strategy, which is the first exploration for controllable multi-human scene interaction generation. Our extensive experiments and perceptual studies show that Narrator can controllably generate diverse interactions and significantly outperform existing works. The code and dataset will be available for research purposes.
DiaASQ : A Benchmark of Conversational Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Analysis
Nov 20, 2022



Abstract:The rapid development of aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) within recent decades shows great potential for real-world society. The current ABSA works, however, are mostly limited to the scenario of a single text piece, leaving the study in dialogue contexts unexplored. In this work, we introduce a novel task of conversational aspect-based sentiment quadruple analysis, namely DiaASQ, aiming to detect the sentiment quadruple of \emph{target-aspect-opinion-sentiment} in a dialogue. DiaASQ bridges the gap between fine-grained sentiment analysis and conversational opinion mining. We manually construct a large-scale high-quality DiaASQ dataset in both Chinese and English languages. We deliberately develop a neural model to benchmark the task, which advances in effectively performing end-to-end quadruple prediction, and manages to incorporate rich dialogue-specific and discourse feature representations for better cross-utterance quadruple extraction. We finally point out several potential future works to facilitate the follow-up research of this new task.
Text-Aware End-to-end Mispronunciation Detection and Diagnosis
Jun 15, 2022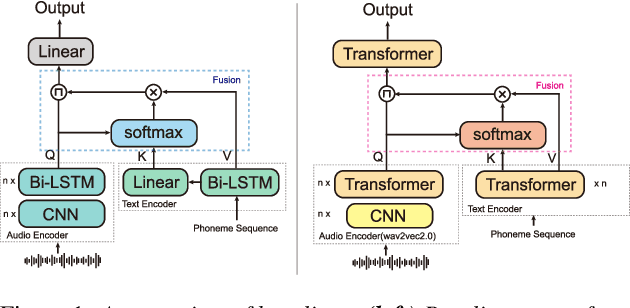
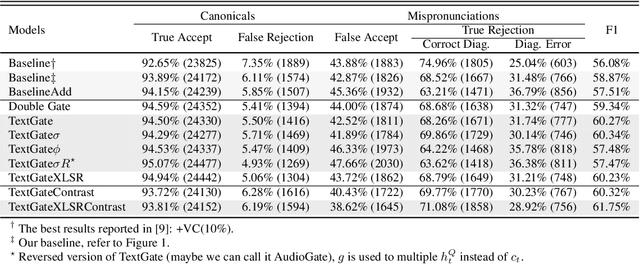
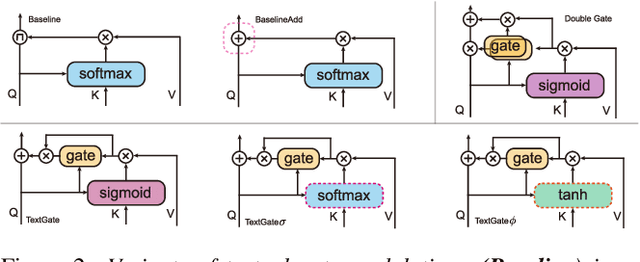
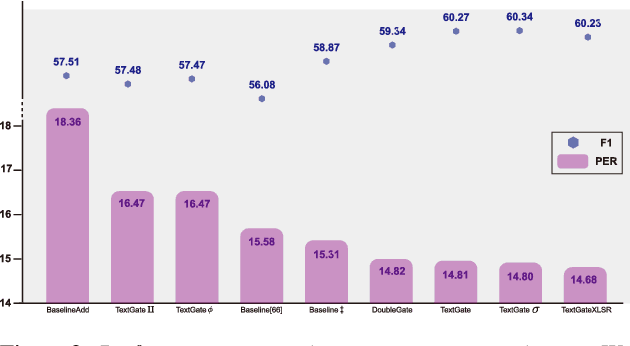
Abstract:Mispronunciation detection and diagnosis (MDD) technology is a key component of computer-assisted pronunciation training system (CAPT). In the field of assessing the pronunciation quality of constrained speech, the given transcriptions can play the role of a teacher. Conventional methods have fully utilized the prior texts for the model construction or improving the system performance, e.g. forced-alignment and extended recognition networks. Recently, some end-to-end based methods attempt to incorporate the prior texts into model training and preliminarily show the effectiveness. However, previous studies mostly consider applying raw attention mechanism to fuse audio representations with text representations, without taking possible text-pronunciation mismatch into account. In this paper, we present a gating strategy that assigns more importance to the relevant audio features while suppressing irrelevant text information. Moreover, given the transcriptions, we design an extra contrastive loss to reduce the gap between the learning objective of phoneme recognition and MDD. We conducted experiments using two publicly available datasets (TIMIT and L2-Arctic) and our best model improved the F1 score from $57.51\%$ to $61.75\%$ compared to the baselines. Besides, we provide a detailed analysis to shed light on the effectiveness of gating mechanism and contrastive learning on MDD.
Advancing CTC-CRF Based End-to-End Speech Recognition with Wordpieces and Conformers
Jul 08, 2021
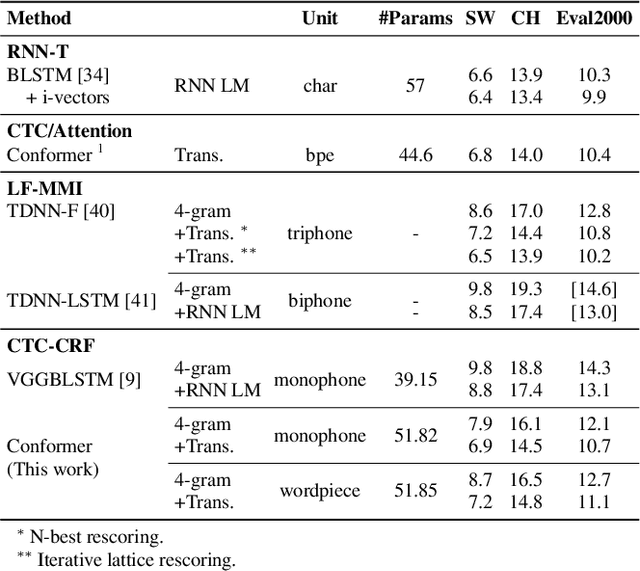

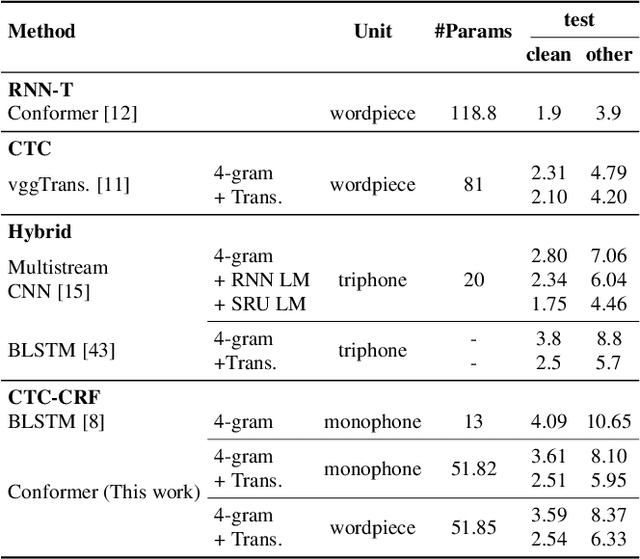
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition systems have been largely improved in the past few decades and current systems are mainly hybrid-based and end-to-end-based. The recently proposed CTC-CRF framework inherits the data-efficiency of the hybrid approach and the simplicity of the end-to-end approach. In this paper, we further advance CTC-CRF based ASR technique with explorations on modeling units and neural architectures. Specifically, we investigate techniques to enable the recently developed wordpiece modeling units and Conformer neural networks to be succesfully applied in CTC-CRFs. Experiments are conducted on two English datasets (Switchboard, Librispeech) and a German dataset from CommonVoice. Experimental results suggest that (i) Conformer can improve the recognition performance significantly; (ii) Wordpiece-based systems perform slightly worse compared with phone-based systems for the target language with a low degree of grapheme-phoneme correspondence (e.g. English), while the two systems can perform equally strong when such degree of correspondence is high for the target language (e.g. German).
Speech Enhancement using Separable Polling Attention and Global Layer Normalization followed with PReLU
May 06, 2021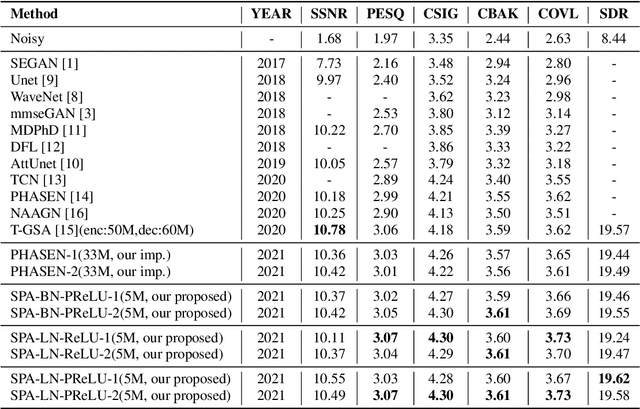
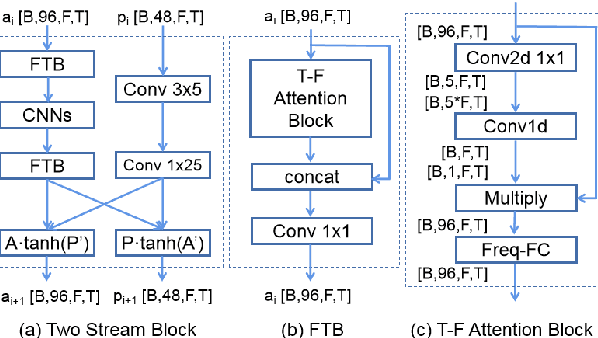

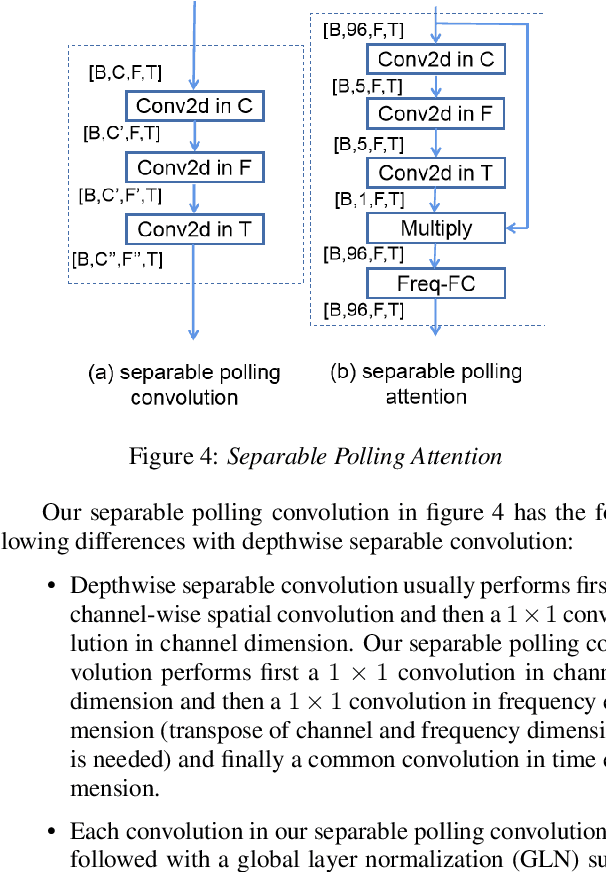
Abstract:Single channel speech enhancement is a challenging task in speech community. Recently, various neural networks based methods have been applied to speech enhancement. Among these models, PHASEN and T-GSA achieve state-of-the-art performances on the publicly opened VoiceBank+DEMAND corpus. Both of the models reach the COVL score of 3.62. PHASEN achieves the highest CSIG score of 4.21 while T-GSA gets the highest PESQ score of 3.06. However, both of these two models are very large. The contradiction between the model performance and the model size is hard to reconcile. In this paper, we introduce three kinds of techniques to shrink the PHASEN model and improve the performance. Firstly, seperable polling attention is proposed to replace the frequency transformation blocks in PHASEN. Secondly, global layer normalization followed with PReLU is used to replace batch normalization followed with ReLU. Finally, BLSTM in PHASEN is replaced with Conv2d operation and the phase stream is simplified. With all these modifications, the size of the PHASEN model is shrunk from 33M parameters to 5M parameters, while the performance on VoiceBank+DEMAND is improved to the CSIG score of 4.30, the PESQ score of 3.07 and the COVL score of 3.73.
A Full Text-Dependent End to End Mispronunciation Detection and Diagnosis with Easy Data Augmentation Techniques
Apr 17, 2021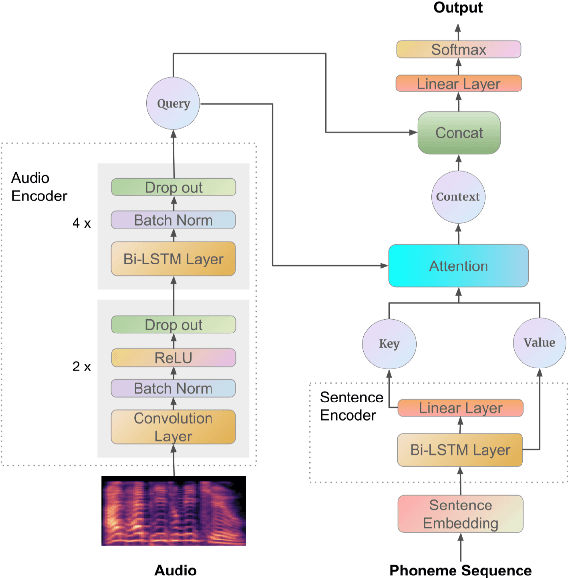
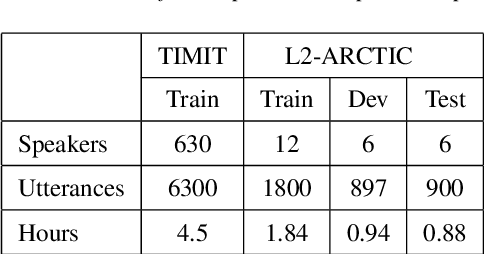
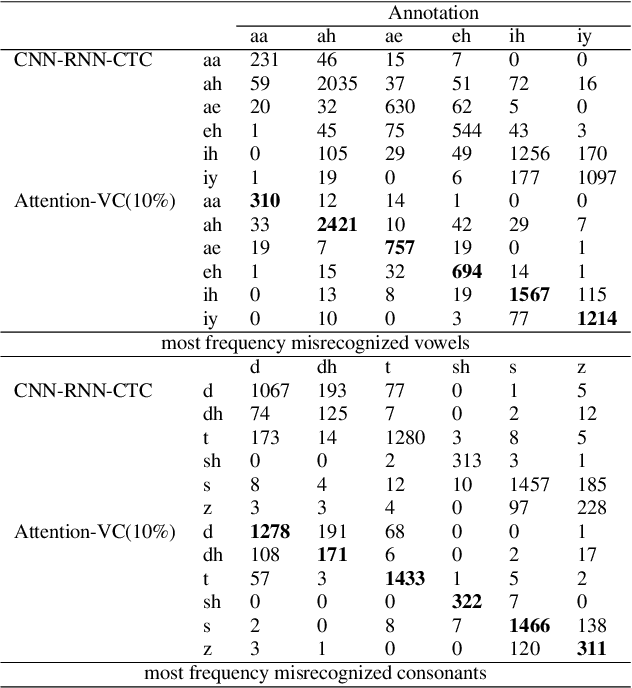
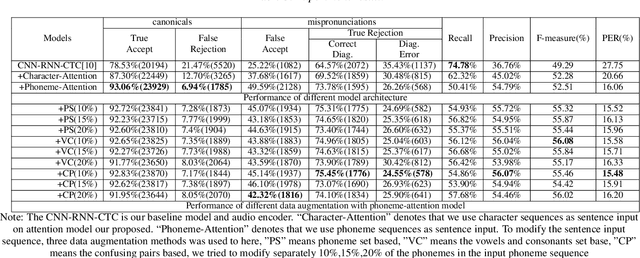
Abstract:Recently, end-to-end mispronunciation detection and diagnosis (MD&D) systems has become a popular alternative to greatly simplify the model-building process of conventional hybrid DNN-HMM systems by representing complicated modules with a single deep network architecture. In this paper, in order to utilize the prior text in the end-to-end structure, we present a novel text-dependent model which is difference with sed-mdd, the model achieves a fully end-to-end system by aligning the audio with the phoneme sequences of the prior text inside the model through the attention mechanism. Moreover, the prior text as input will be a problem of imbalance between positive and negative samples in the phoneme sequence. To alleviate this problem, we propose three simple data augmentation methods, which effectively improve the ability of model to capture mispronounced phonemes. We conduct experiments on L2-ARCTIC, and our best performance improved from 49.29% to 56.08% in F-measure metric compared to the CNN-RNN-CTC model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge