Huseyin A. Inan
ACON: Optimizing Context Compression for Long-horizon LLM Agents
Oct 01, 2025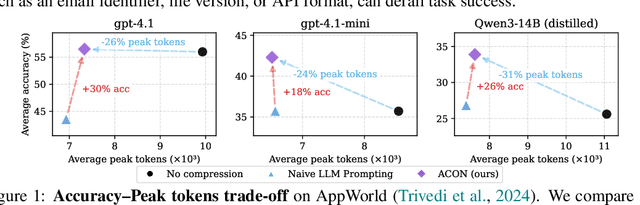
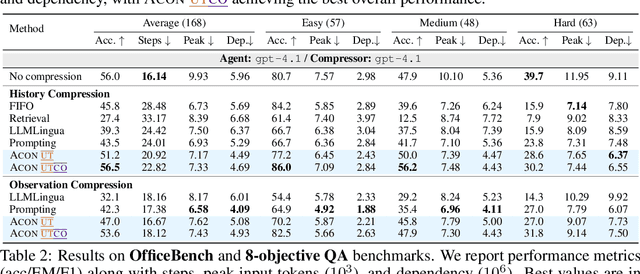
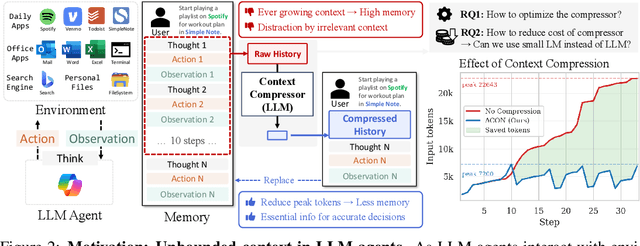
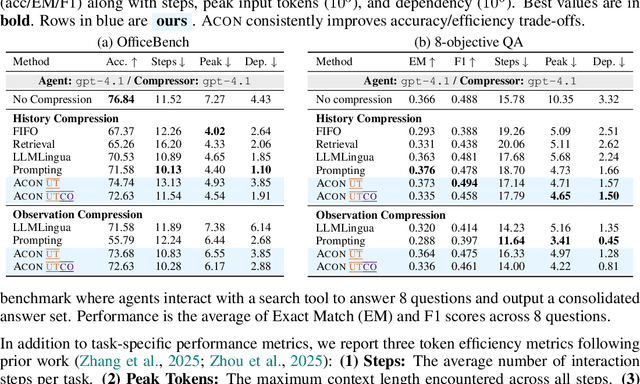
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as agents in dynamic, real-world environments, where success requires both reasoning and effective tool use. A central challenge for agentic tasks is the growing context length, as agents must accumulate long histories of actions and observations. This expansion raises costs and reduces efficiency in long-horizon tasks, yet prior work on context compression has mostly focused on single-step tasks or narrow applications. We introduce Agent Context Optimization (ACON), a unified framework that optimally compresses both environment observations and interaction histories into concise yet informative condensations. ACON leverages compression guideline optimization in natural language space: given paired trajectories where full context succeeds but compressed context fails, capable LLMs analyze the causes of failure, and the compression guideline is updated accordingly. Furthermore, we propose distilling the optimized LLM compressor into smaller models to reduce the overhead of the additional module. Experiments on AppWorld, OfficeBench, and Multi-objective QA show that ACON reduces memory usage by 26-54% (peak tokens) while largely preserving task performance, preserves over 95% of accuracy when distilled into smaller compressors, and enhances smaller LMs as long-horizon agents with up to 46% performance improvement.
On the Emergence of Thinking in LLMs I: Searching for the Right Intuition
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent AI advancements, such as OpenAI's new models, are transforming LLMs into LRMs (Large Reasoning Models) that perform reasoning during inference, taking extra time and compute for higher-quality outputs. We aim to uncover the algorithmic framework for training LRMs. Methods like self-consistency, PRM, and AlphaZero suggest reasoning as guided search. We ask: what is the simplest, most scalable way to enable search in LLMs? We propose a post-training framework called Reinforcement Learning via Self-Play (RLSP). RLSP involves three steps: (1) supervised fine-tuning with human or synthetic demonstrations of the reasoning process, (2) using an exploration reward signal to encourage diverse and efficient reasoning behaviors, and (3) RL training with an outcome verifier to ensure correctness while preventing reward hacking. Our key innovation is to decouple exploration and correctness signals during PPO training, carefully balancing them to improve performance and efficiency. Empirical studies in the math domain show that RLSP improves reasoning. On the Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct model, RLSP can boost performance by 23% in MATH-500 test set; On AIME 2024 math problems, Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct improved by 10% due to RLSP. However, a more important finding of this work is that the models trained using RLSP, even with the simplest exploration reward that encourages the model to take more intermediate steps, showed several emergent behaviors such as backtracking, exploration of ideas, and verification. These findings demonstrate that RLSP framework might be enough to enable emergence of complex reasoning abilities in LLMs when scaled. Lastly, we propose a theory as to why RLSP search strategy is more suitable for LLMs inspired by a remarkable result that says CoT provably increases computational power of LLMs, which grows as the number of steps in CoT \cite{li2024chain,merrill2023expresssive}.
Differentially Private Training of Mixture of Experts Models
Feb 11, 2024

Abstract:This position paper investigates the integration of Differential Privacy (DP) in the training of Mixture of Experts (MoE) models within the field of natural language processing. As Large Language Models (LLMs) scale to billions of parameters, leveraging expansive datasets, they exhibit enhanced linguistic capabilities and emergent abilities. However, this growth raises significant computational and privacy concerns. Our study addresses these issues by exploring the potential of MoE models, known for their computational efficiency, and the application of DP, a standard for privacy preservation. We present the first known attempt to train MoE models under the constraints of DP, addressing the unique challenges posed by their architecture and the complexities of DP integration. Our initial experimental studies demonstrate that MoE models can be effectively trained with DP, achieving performance that is competitive with their non-private counterparts. This initial study aims to provide valuable insights and ignite further research in the domain of privacy-preserving MoE models, softly laying the groundwork for prospective developments in this evolving field.
Privately Aligning Language Models with Reinforcement Learning
Oct 25, 2023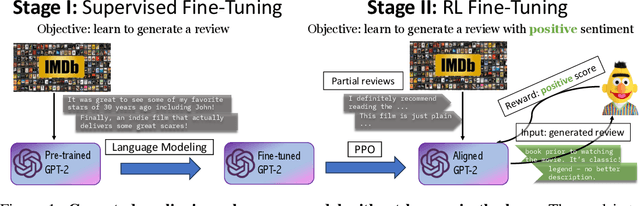
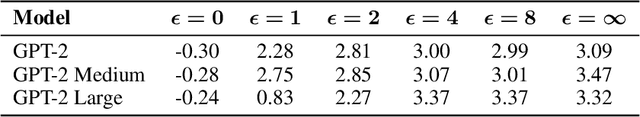

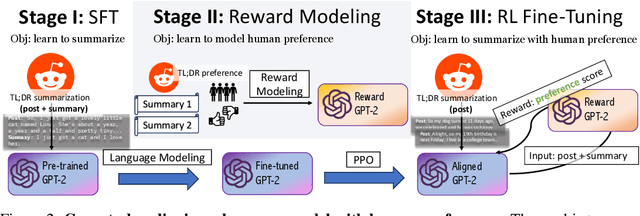
Abstract:Positioned between pre-training and user deployment, aligning large language models (LLMs) through reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a prevailing strategy for training instruction following-models such as ChatGPT. In this work, we initiate the study of privacy-preserving alignment of LLMs through Differential Privacy (DP) in conjunction with RL. Following the influential work of Ziegler et al. (2020), we study two dominant paradigms: (i) alignment via RL without human in the loop (e.g., positive review generation) and (ii) alignment via RL from human feedback (RLHF) (e.g., summarization in a human-preferred way). We give a new DP framework to achieve alignment via RL, and prove its correctness. Our experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, offering competitive utility while ensuring strong privacy protections.
Privacy-Preserving In-Context Learning with Differentially Private Few-Shot Generation
Sep 21, 2023



Abstract:We study the problem of in-context learning (ICL) with large language models (LLMs) on private datasets. This scenario poses privacy risks, as LLMs may leak or regurgitate the private examples demonstrated in the prompt. We propose a novel algorithm that generates synthetic few-shot demonstrations from the private dataset with formal differential privacy (DP) guarantees, and show empirically that it can achieve effective ICL. We conduct extensive experiments on standard benchmarks and compare our algorithm with non-private ICL and zero-shot solutions. Our results demonstrate that our algorithm can achieve competitive performance with strong privacy levels. These results open up new possibilities for ICL with privacy protection for a broad range of applications.
Planting and Mitigating Memorized Content in Predictive-Text Language Models
Dec 16, 2022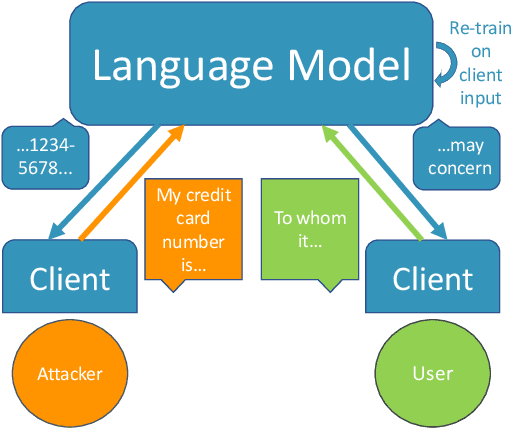
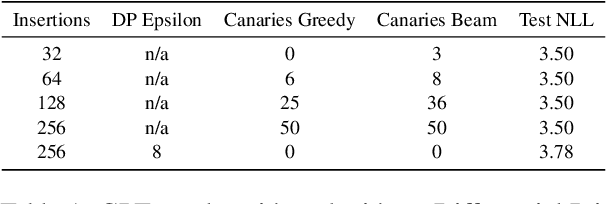
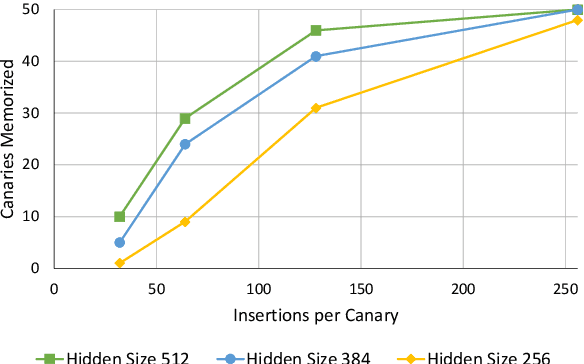
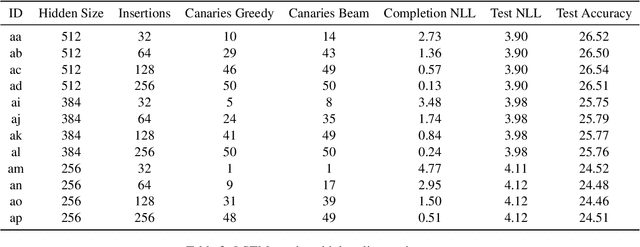
Abstract:Language models are widely deployed to provide automatic text completion services in user products. However, recent research has revealed that language models (especially large ones) bear considerable risk of memorizing private training data, which is then vulnerable to leakage and extraction by adversaries. In this study, we test the efficacy of a range of privacy-preserving techniques to mitigate unintended memorization of sensitive user text, while varying other factors such as model size and adversarial conditions. We test both "heuristic" mitigations (those without formal privacy guarantees) and Differentially Private training, which provides provable levels of privacy at the cost of some model performance. Our experiments show that (with the exception of L2 regularization), heuristic mitigations are largely ineffective in preventing memorization in our test suite, possibly because they make too strong of assumptions about the characteristics that define "sensitive" or "private" text. In contrast, Differential Privacy reliably prevents memorization in our experiments, despite its computational and model-performance costs.
Synthetic Text Generation with Differential Privacy: A Simple and Practical Recipe
Oct 25, 2022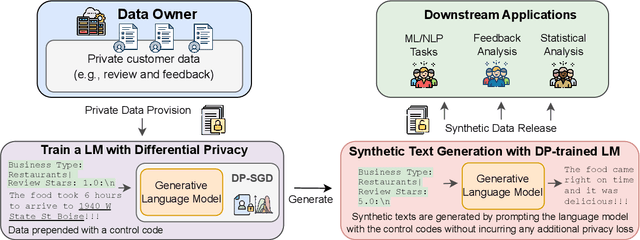
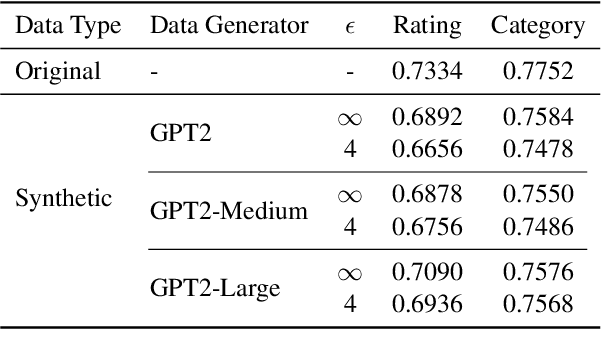
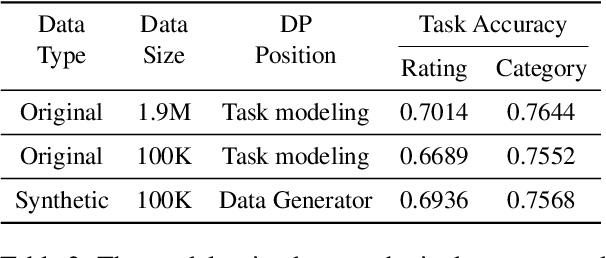
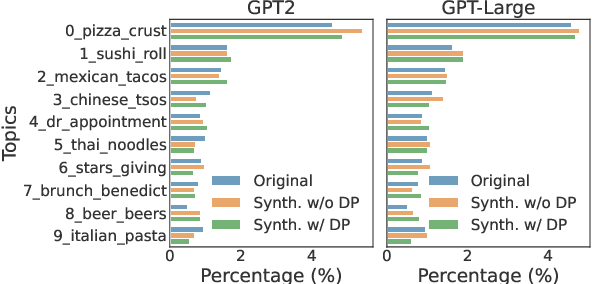
Abstract:Privacy concerns have attracted increasing attention in data-driven products and services. Existing legislation forbids arbitrary processing of personal data collected from individuals. Generating synthetic versions of such data with a formal privacy guarantee such as differential privacy (DP) is considered to be a solution to address privacy concerns. In this direction, we show a simple, practical, and effective recipe in the text domain: simply fine-tuning a generative language model with DP allows us to generate useful synthetic text while mitigating privacy concerns. Through extensive empirical analyses, we demonstrate that our method produces synthetic data that is competitive in terms of utility with its non-private counterpart and meanwhile provides strong protection against potential privacy leakages.
When Does Differentially Private Learning Not Suffer in High Dimensions?
Jul 09, 2022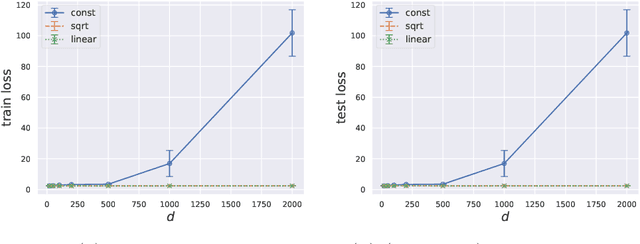
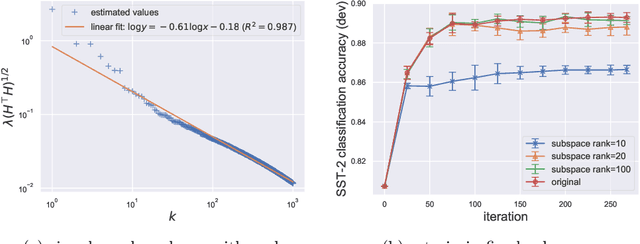
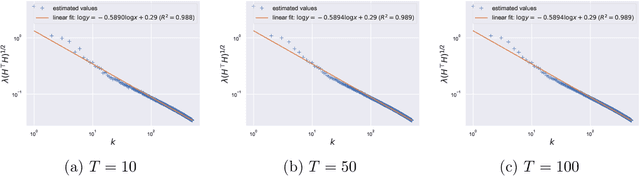
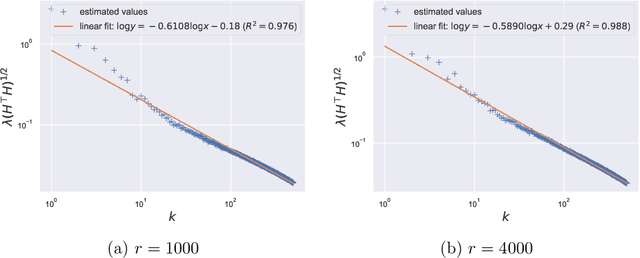
Abstract:Large pretrained models can be privately fine-tuned to achieve performance approaching that of non-private models. A common theme in these results is the surprising observation that high-dimensional models can achieve favorable privacy-utility trade-offs. This seemingly contradicts known results on the model-size dependence of differentially private convex learning and raises the following research question: When does the performance of differentially private learning not degrade with increasing model size? We identify that the magnitudes of gradients projected onto subspaces is a key factor that determines performance. To precisely characterize this for private convex learning, we introduce a condition on the objective that we term restricted Lipschitz continuity and derive improved bounds for the excess empirical and population risks that are dimension-independent under additional conditions. We empirically show that in private fine-tuning of large language models, gradients evaluated near a local optimum are mostly controlled by a few principal components. This behavior is similar to conditions under which we obtain dimension-independent bounds in convex settings. Our theoretical and empirical results together provide a possible explanation for recent successes in large-scale private fine-tuning.
Privacy Leakage in Text Classification: A Data Extraction Approach
Jun 09, 2022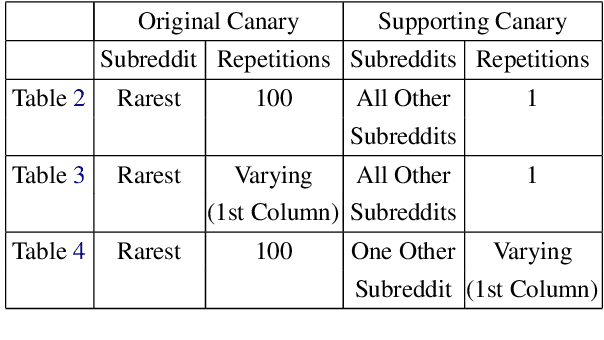
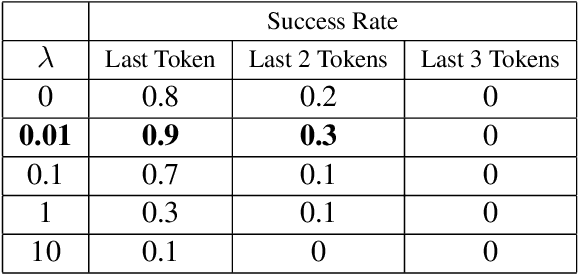
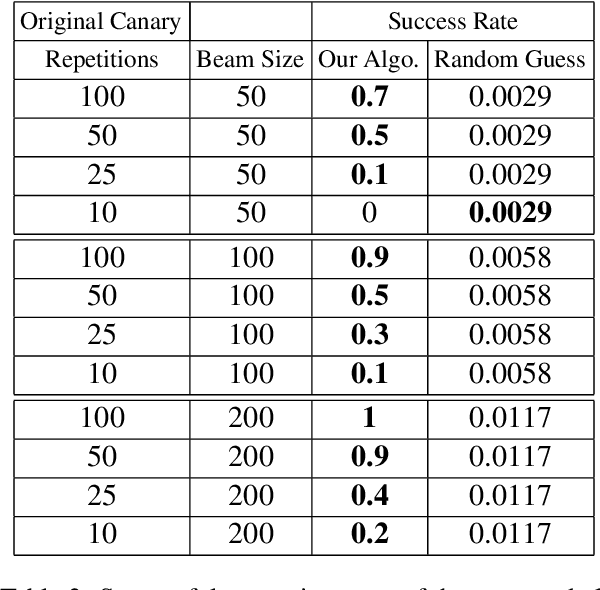
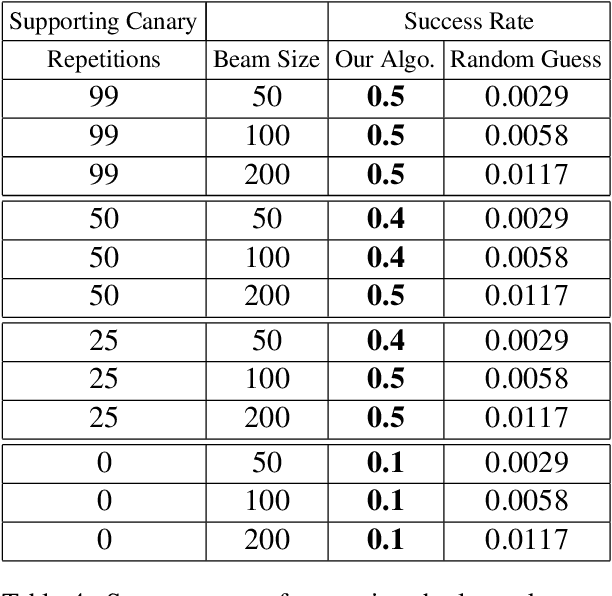
Abstract:Recent work has demonstrated the successful extraction of training data from generative language models. However, it is not evident whether such extraction is feasible in text classification models since the training objective is to predict the class label as opposed to next-word prediction. This poses an interesting challenge and raises an important question regarding the privacy of training data in text classification settings. Therefore, we study the potential privacy leakage in the text classification domain by investigating the problem of unintended memorization of training data that is not pertinent to the learning task. We propose an algorithm to extract missing tokens of a partial text by exploiting the likelihood of the class label provided by the model. We test the effectiveness of our algorithm by inserting canaries into the training set and attempting to extract tokens in these canaries post-training. In our experiments, we demonstrate that successful extraction is possible to some extent. This can also be used as an auditing strategy to assess any potential unauthorized use of personal data without consent.
Differentially Private Fine-tuning of Language Models
Oct 13, 2021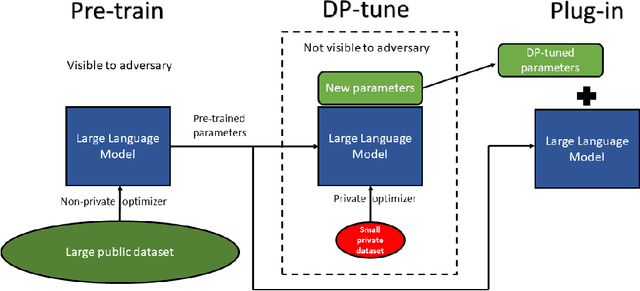
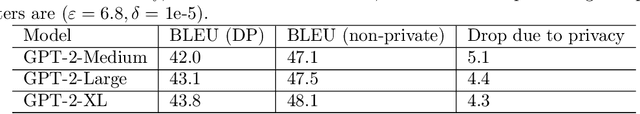

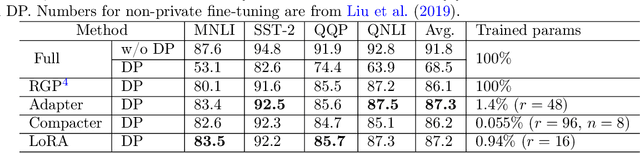
Abstract:We give simpler, sparser, and faster algorithms for differentially private fine-tuning of large-scale pre-trained language models, which achieve the state-of-the-art privacy versus utility tradeoffs on many standard NLP tasks. We propose a meta-framework for this problem, inspired by the recent success of highly parameter-efficient methods for fine-tuning. Our experiments show that differentially private adaptations of these approaches outperform previous private algorithms in three important dimensions: utility, privacy, and the computational and memory cost of private training. On many commonly studied datasets, the utility of private models approaches that of non-private models. For example, on the MNLI dataset we achieve an accuracy of $87.8\%$ using RoBERTa-Large and $83.5\%$ using RoBERTa-Base with a privacy budget of $\epsilon = 6.7$. In comparison, absent privacy constraints, RoBERTa-Large achieves an accuracy of $90.2\%$. Our findings are similar for natural language generation tasks. Privately fine-tuning with DART, GPT-2-Small, GPT-2-Medium, GPT-2-Large, and GPT-2-XL achieve BLEU scores of 38.5, 42.0, 43.1, and 43.8 respectively (privacy budget of $\epsilon = 6.8,\delta=$ 1e-5) whereas the non-private baseline is $48.1$. All our experiments suggest that larger models are better suited for private fine-tuning: while they are well known to achieve superior accuracy non-privately, we find that they also better maintain their accuracy when privacy is introduced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge