Xinyu Tang
Rethinking Sample Polarity in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) are typically trained using reinforcement learning with verifiable reward (RLVR) to enhance their reasoning abilities. In this paradigm, policies are updated using both positive and negative self-generated rollouts, which correspond to distinct sample polarities. In this paper, we provide a systematic investigation into how these sample polarities affect RLVR training dynamics and behaviors. We find that positive samples sharpen existing correct reasoning patterns, while negative samples encourage exploration of new reasoning paths. We further explore how adjusting the advantage values of positive and negative samples at both the sample level and the token level affects RLVR training. Based on these insights, we propose an Adaptive and Asymmetric token-level Advantage shaping method for Policy Optimization, namely A3PO, that more precisely allocates advantage signals to key tokens across different polarities. Experiments across five reasoning benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model
Oct 21, 2025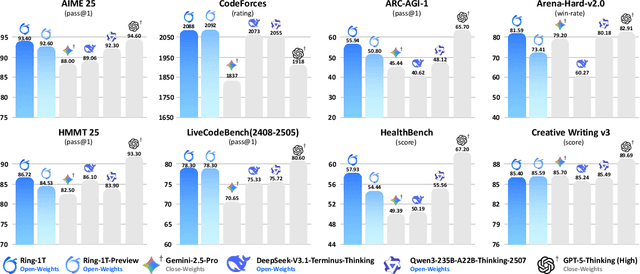
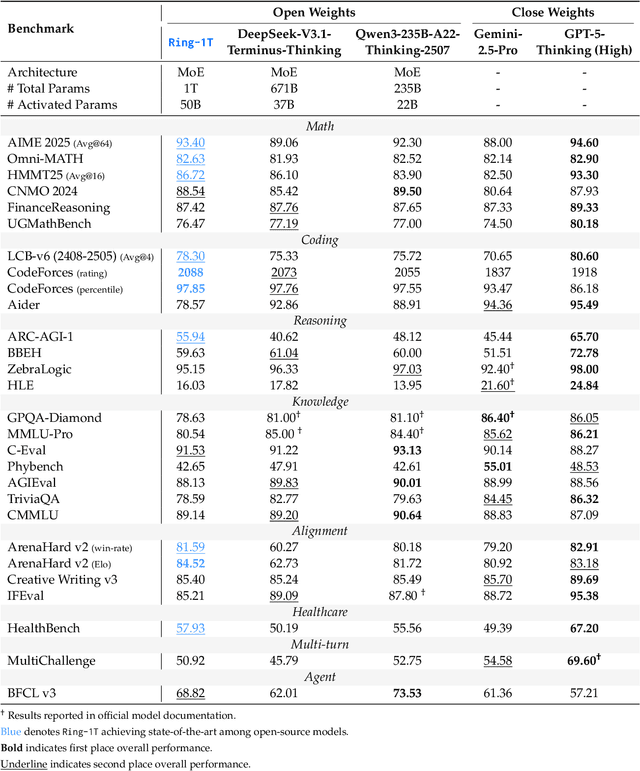
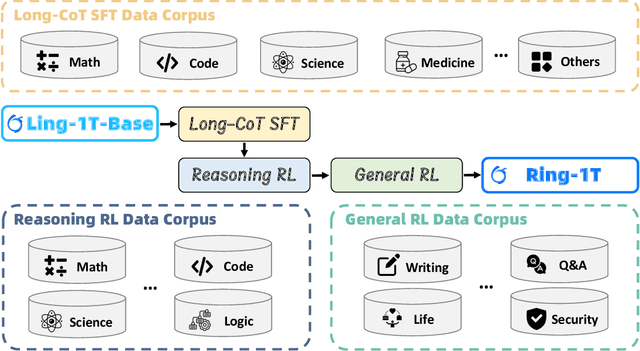
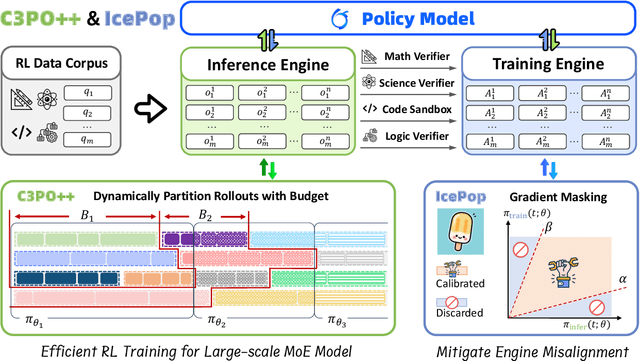
Abstract:We present Ring-1T, the first open-source, state-of-the-art thinking model with a trillion-scale parameter. It features 1 trillion total parameters and activates approximately 50 billion per token. Training such models at a trillion-parameter scale introduces unprecedented challenges, including train-inference misalignment, inefficiencies in rollout processing, and bottlenecks in the RL system. To address these, we pioneer three interconnected innovations: (1) IcePop stabilizes RL training via token-level discrepancy masking and clipping, resolving instability from training-inference mismatches; (2) C3PO++ improves resource utilization for long rollouts under a token budget by dynamically partitioning them, thereby obtaining high time efficiency; and (3) ASystem, a high-performance RL framework designed to overcome the systemic bottlenecks that impede trillion-parameter model training. Ring-1T delivers breakthrough results across critical benchmarks: 93.4 on AIME-2025, 86.72 on HMMT-2025, 2088 on CodeForces, and 55.94 on ARC-AGI-v1. Notably, it attains a silver medal-level result on the IMO-2025, underscoring its exceptional reasoning capabilities. By releasing the complete 1T parameter MoE model to the community, we provide the research community with direct access to cutting-edge reasoning capabilities. This contribution marks a significant milestone in democratizing large-scale reasoning intelligence and establishes a new baseline for open-source model performance.
Enhancing Cross-task Transfer of Large Language Models via Activation Steering
Jul 17, 2025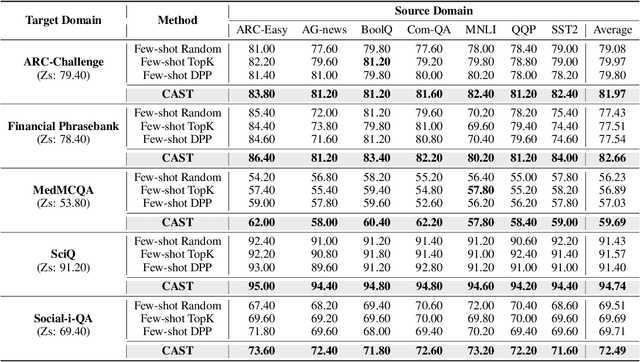

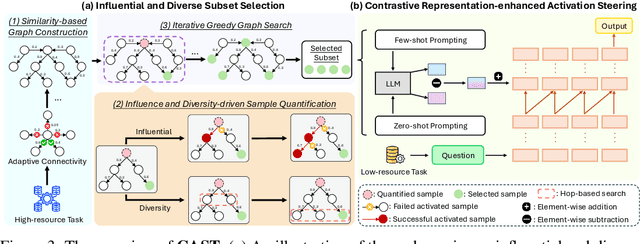
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive abilities in leveraging pretrained knowledge through prompting, but they often struggle with unseen tasks, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. While cross-task in-context learning offers a direct solution for transferring knowledge across tasks, it still faces critical challenges in terms of robustness, scalability, and efficiency. In this paper, we investigate whether cross-task transfer can be achieved via latent space steering without parameter updates or input expansion. Through an analysis of activation patterns in the latent space of LLMs, we observe that the enhanced activations induced by in-context examples have consistent patterns across different tasks. Inspired by these findings, we propose CAST, a novel Cross-task Activation Steering Transfer framework that enables effective transfer by manipulating the model's internal activation states. Our approach first selects influential and diverse samples from high-resource tasks, then utilizes their contrastive representation-enhanced activations to adapt LLMs to low-resource tasks. Extensive experiments across both cross-domain and cross-lingual transfer settings show that our method outperforms competitive baselines and demonstrates superior scalability and lower computational costs.
Incentivizing Dual Process Thinking for Efficient Large Language Model Reasoning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have demonstrated strong performance on complex reasoning tasks, but often suffer from overthinking, generating redundant content regardless of task difficulty. Inspired by the dual process theory in cognitive science, we propose Adaptive Cognition Policy Optimization (ACPO), a reinforcement learning framework that enables LRMs to achieve efficient reasoning through adaptive cognitive allocation and dynamic system switch. ACPO incorporates two key components: (1) introducing system-aware reasoning tokens to explicitly represent the thinking modes thereby making the model's cognitive process transparent, and (2) integrating online difficulty estimation and token length budget to guide adaptive system switch and reasoning during reinforcement learning. To this end, we propose a two-stage training strategy. The first stage begins with supervised fine-tuning to cold start the model, enabling it to generate reasoning paths with explicit thinking modes. In the second stage, we apply ACPO to further enhance adaptive system switch for difficulty-aware reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that ACPO effectively reduces redundant reasoning while adaptively adjusting cognitive allocation based on task complexity, achieving efficient hybrid reasoning.
Unlocking General Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Capabilities of Large Language Models via Representation Engineering
Mar 14, 2025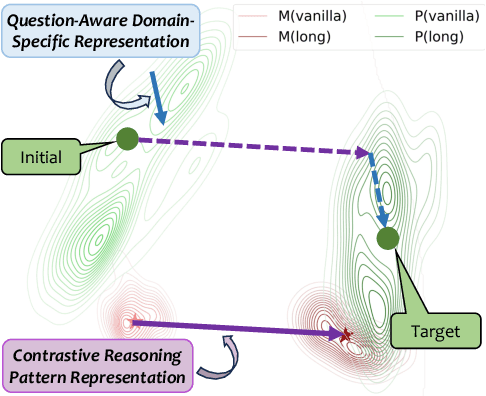



Abstract:Recent advancements in long chain-of-thoughts(long CoTs) have significantly improved the reasoning capabilities of large language models(LLMs). Existing work finds that the capability of long CoT reasoning can be efficiently elicited by tuning on only a few examples and can easily transfer to other tasks. This motivates us to investigate whether long CoT reasoning is a general capability for LLMs. In this work, we conduct an empirical analysis for this question from the perspective of representation. We find that LLMs do encode long CoT reasoning as a general capability, with a clear distinction from vanilla CoTs. Furthermore, domain-specific representations are also required for the effective transfer of long CoT reasoning. Inspired by these findings, we propose GLoRE, a novel representation engineering method to unleash the general long CoT reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of GLoRE in both in-domain and cross-domain scenarios.
Privacy Auditing of Large Language Models
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Current techniques for privacy auditing of large language models (LLMs) have limited efficacy -- they rely on basic approaches to generate canaries which leads to weak membership inference attacks that in turn give loose lower bounds on the empirical privacy leakage. We develop canaries that are far more effective than those used in prior work under threat models that cover a range of realistic settings. We demonstrate through extensive experiments on multiple families of fine-tuned LLMs that our approach sets a new standard for detection of privacy leakage. For measuring the memorization rate of non-privately trained LLMs, our designed canaries surpass prior approaches. For example, on the Qwen2.5-0.5B model, our designed canaries achieve $49.6\%$ TPR at $1\%$ FPR, vastly surpassing the prior approach's $4.2\%$ TPR at $1\%$ FPR. Our method can be used to provide a privacy audit of $\varepsilon \approx 1$ for a model trained with theoretical $\varepsilon$ of 4. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a privacy audit of LLM training has achieved nontrivial auditing success in the setting where the attacker cannot train shadow models, insert gradient canaries, or access the model at every iteration.
DAWN-ICL: Strategic Planning of Problem-solving Trajectories for Zero-Shot In-Context Learning
Oct 26, 2024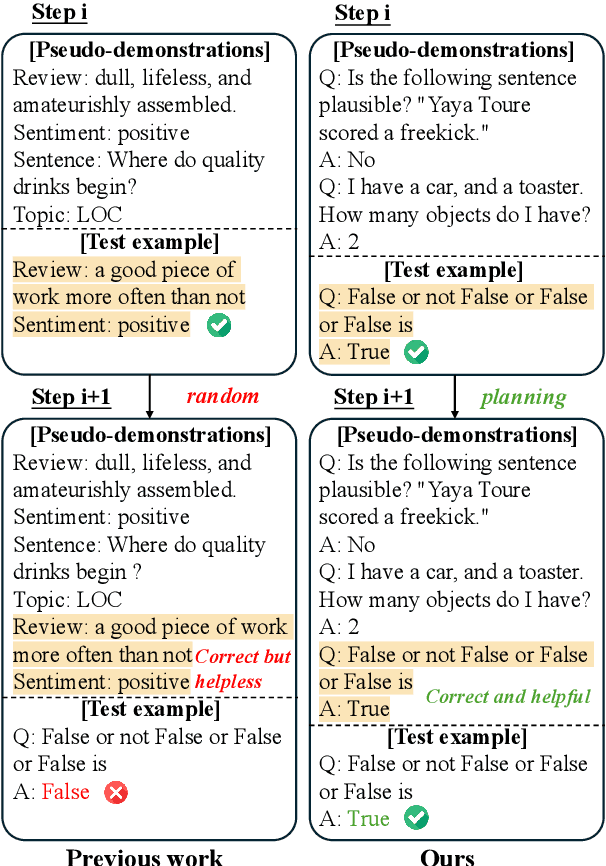
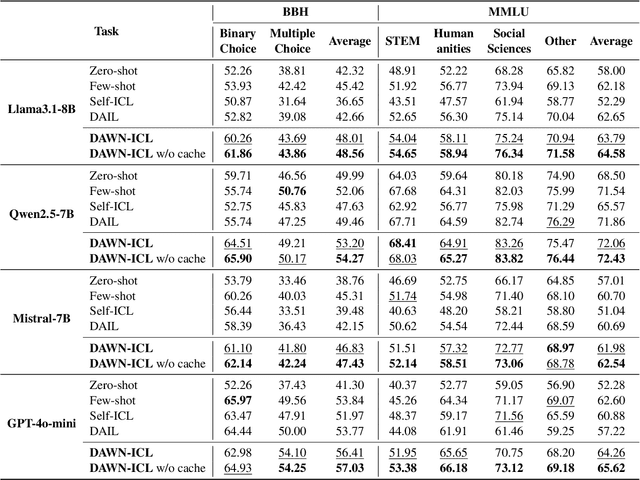
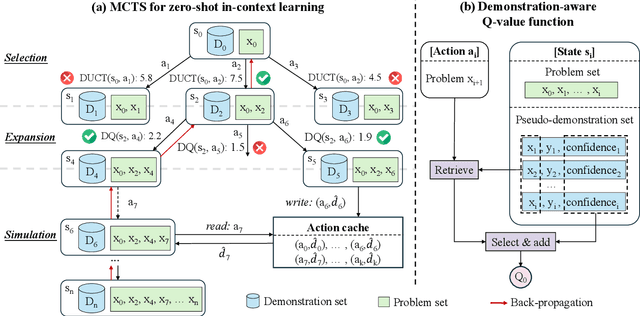
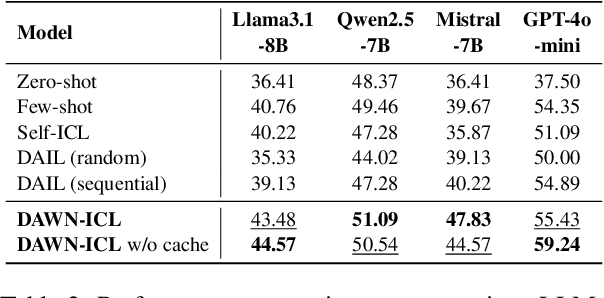
Abstract:Zero-shot in-context learning (ZS-ICL) aims to conduct in-context learning (ICL) without using human-annotated demonstrations. Most ZS-ICL methods use large language models (LLMs) to generate (input, label) pairs as pseudo-demonstrations and leverage historical pseudo-demonstrations to help solve the current problem. They assume that problems are from the same task and traverse them in a random order. However, in real-world scenarios, problems usually come from diverse tasks, and only a few belong to the same task. The random traversing order may generate unreliable pseudo-demonstrations and lead to error accumulation. To address this problem, we reformulate ZS-ICL as a planning problem and propose a Demonstration-aware Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) approach (DAWN-ICL), which leverages MCTS to strategically plan the problem-solving trajectories for ZS-ICL. In addition, to achieve effective and efficient Q value estimation, we propose a novel demonstration-aware Q-value function and use it to enhance the selection phase and accelerate the expansion and simulation phases in MCTS. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of DAWN-ICL on in-domain and cross-domain scenarios, and it even outperforms ICL using human-annotated labels. The code is available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/MCTS4ZSICL.
FedBChain: A Blockchain-enabled Federated Learning Framework for Improving DeepConvLSTM with Comparative Strategy Insights
Jul 31, 2024


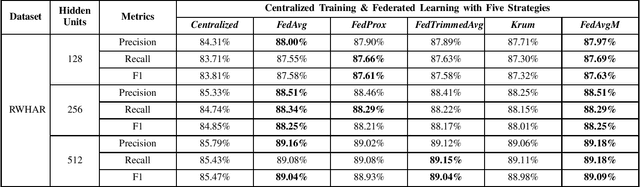
Abstract:Recent research in the field of Human Activity Recognition has shown that an improvement in prediction performance can be achieved by reducing the number of LSTM layers. However, this kind of enhancement is only significant on monolithic architectures, and when it runs on large-scale distributed training, data security and privacy issues will be reconsidered, and its prediction performance is unknown. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework: FedBChain, which integrates the federated learning paradigm based on a modified DeepConvLSTM architecture with a single LSTM layer. This framework performs comparative tests of prediction performance on three different real-world datasets based on three different hidden layer units (128, 256, and 512) combined with five different federated learning strategies, respectively. The results show that our architecture has significant improvements in Precision, Recall and F1-score compared to the centralized training approach on all datasets with all hidden layer units for all strategies: FedAvg strategy improves on average by 4.54%, FedProx improves on average by 4.57%, FedTrimmedAvg improves on average by 4.35%, Krum improves by 4.18% on average, and FedAvgM improves by 4.46% on average. Based on our results, it can be seen that FedBChain not only improves in performance, but also guarantees the security and privacy of user data compared to centralized training methods during the training process. The code for our experiments is publicly available (https://github.com/Glen909/FedBChain).
YuLan: An Open-source Large Language Model
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become the foundation of many applications, leveraging their extensive capabilities in processing and understanding natural language. While many open-source LLMs have been released with technical reports, the lack of training details hinders further research and development. This paper presents the development of YuLan, a series of open-source LLMs with $12$ billion parameters. The base model of YuLan is pre-trained on approximately $1.7$T tokens derived from a diverse corpus, including massive English, Chinese, and multilingual texts. We design a three-stage pre-training method to enhance YuLan's overall capabilities. Subsequent phases of training incorporate instruction-tuning and human alignment, employing a substantial volume of high-quality synthesized data. To facilitate the learning of complex and long-tail knowledge, we devise a curriculum-learning framework throughout across these stages, which helps LLMs learn knowledge in an easy-to-hard manner. YuLan's training is finished on Jan, 2024 and has achieved performance on par with state-of-the-art LLMs across various English and Chinese benchmarks. This paper outlines a comprehensive technical roadmap for developing LLMs from scratch. Our model and codes are available at https://github.com/RUC-GSAI/YuLan-Chat.
Investigating the Pre-Training Dynamics of In-Context Learning: Task Recognition vs. Task Learning
Jun 20, 2024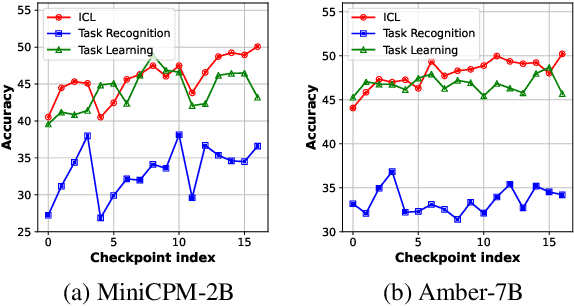
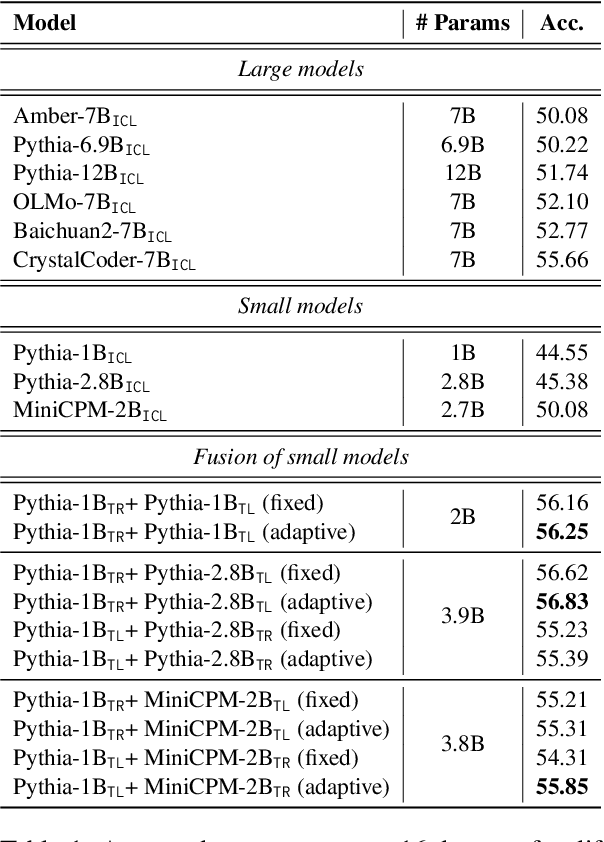
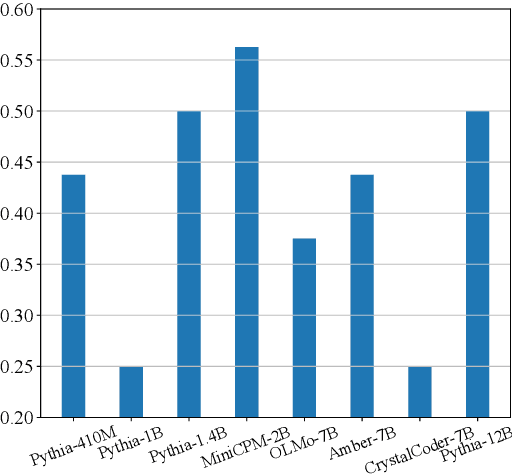
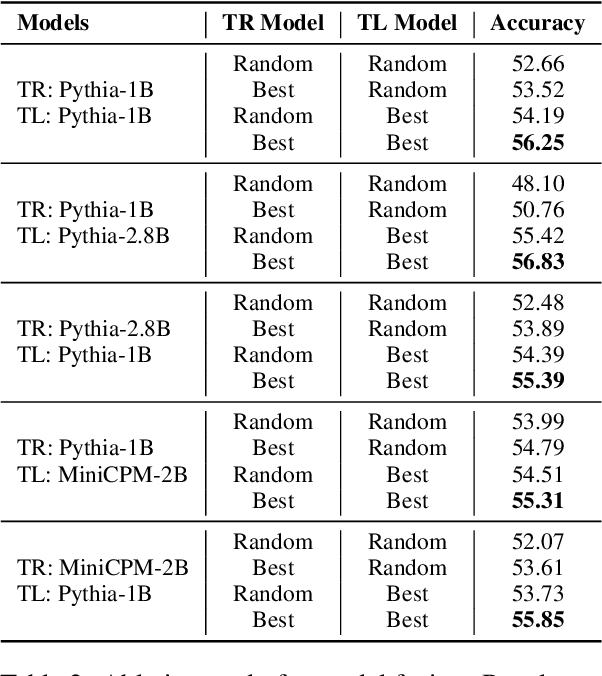
Abstract:The emergence of in-context learning (ICL) is potentially attributed to two major abilities: task recognition (TR) for recognizing the task from demonstrations and utilizing pre-trained priors, and task learning (TL) for learning from demonstrations. However, relationships between the two abilities and how such relationships affect the emergence of ICL is unclear. In this paper, we take the first step by examining the pre-training dynamics of the emergence of ICL. With carefully designed metrics, we find that these two abilities are, in fact, competitive during pre-training. Moreover, we observe a strong negative correlation between the competition and ICL performance. Further analysis of common pre-training factors (i.e., model size, dataset size, and data curriculum) demonstrates possible ways to manage the competition. Based on these insights, we propose a simple yet effective method to better integrate these two abilities for ICL at inference time. Through adaptive ensemble learning, the performance of ICL can be significantly boosted, enabling two small models to outperform a larger one with more than twice the parameters. The code is available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Competitive-ICL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge